一.array.prototype.sort()
1.默认排序 sort()
sort() 方法就地对数组的元素进行排序,并返回对相同数组的引用。默认排序是将元素转换为字符串,然后按照它们的 utf-16 码元值升序排序。
由于它取决于具体实现,因此无法保证排序的时间和空间复杂度。
如果想要不改变原数组的排序方法,可以使用 tosorted()。
说明:两个重点。1、会改变原数组。2、默认按将元素转换为字符串排序。
const months = ['march', 'jan', 'feb', 'dec']; months.sort(); console.log(months); // expected output: array ["dec", "feb", "jan", "march"] const array1 = [1, 30, 4, 21, 100000]; array1.sort(); console.log(array1); // expected output: array [1, 100000, 21, 30, 4]
2.比较函数 sort(comparefn)
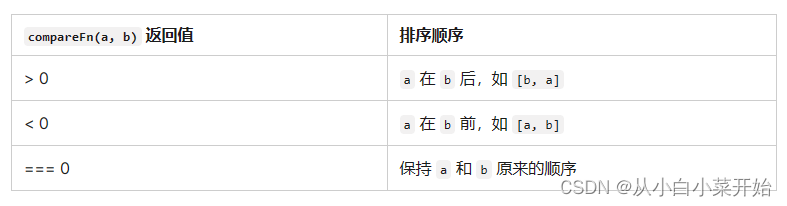
定义排序顺序的函数。返回值应该是一个数字,其符号表示两个元素的相对顺序:如果 a 小于 b,返回值为负数,如果 a 大于 b,返回值为正数,如果两个元素相等,返回值为 0。nan 被视为 0。
说明:自定义比较函数返回一个数值。一般为1,-1,0.
function comparefn(a, b) {
if (根据排序标准,a 小于 b) {
return -1;
}
if (根据排序标准,a 大于 b) {
return 1;
}
// a 一定等于 b
return 0;
}
const stringarray = ["blue", "humpback", "beluga"];
const numberarray = [40, 1, 5, 200];
const numericstringarray = ["80", "9", "700"];
const mixednumericarray = ["80", "9", "700", 40, 1, 5, 200];
function comparenumbers(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
stringarray.sort(); // ['beluga', 'blue', 'humpback']
numberarray.sort(comparenumbers); // [1, 5, 40, 200]
numericstringarray.sort(); // ['700', '80', '9']
numericstringarray.sort(comparenumbers); // ['9', '80', '700']
mixednumericarray.sort(comparenumbers); // [1, 5, '9', 40, '80', 200, '700']
二.对象数组
let arr = [
{ name: 'zhang', age: 25, score: 85 },
{ name: 'li', age: 20, score: 90 },
{ name: 'wang', age: 22, score: 80 },
{ name: 'zhao', age: 22, score: 92 }
];
// 按 age 升序排序,如果 age 相同则按 score 降序排序
arr.sort((a, b) => {
if (a.age !== b.age) {
return a.age - b.age; // 按 age 升序排序
} else {
return b.score - a.score; // 如果 age 相同,按 score 降序排序
}
});
console.log(arr);[
{ name: 'li', age: 20, score: 90 },
{ name: 'wang', age: 22, score: 80 },
{ name: 'zhao', age: 22, score: 92 },
{ name: 'zhang', age: 25, score: 85 }
]三.通用方法
1.指定单一对象元素属性
function sortobjectsbyproperty(array, property) {
return array.sort(function(a, b) {
if (a[property] < b[property]) {
return -1;
} else if (a[property] > b[property]) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
});
}
var objects = [
{ name: 'apple', price: 15 },
{ name: 'banana', price: 10 },
{ name: 'cherry', price: 20 }
];
var sortedobjects = sortobjectsbyproperty(objects, 'price');
console.log(sortedobjects);
输出:
[
{ name: 'banana', price: 10 },
{ name: 'apple', price: 15 },
{ name: 'cherry', price: 20 }
]2.指定对象元素多属性
function sortobjectsbyproperties(array, ...properties) {
return array.sort((a, b) => {
for (const property of properties) {
if (a[property] < b[property]) {
return -1;
} else if (a[property] > b[property]) {
return 1;
}
// 如果属性相等,则继续比较下一个属性
}
// 所有属性都相等
return 0;
});
}
// 示例对象数组
const employees = [
{ name: 'alice', age: 30, salary: 50000 },
{ name: 'bob', age: 25, salary: 60000 },
{ name: 'charlie', age: 35, salary: 55000 },
];
// 使用剩余参数传入多个属性进行排序
const sortedemployees = sortobjectsbyproperties(employees, 'age', 'salary');
console.log(sortedemployees);输出:
[
{ name: 'bob', age: 25, salary: 60000 }, // 年龄最小
{ name: 'alice', age: 30, salary: 50000 }, // 年龄次小,但薪水低于charlie
{ name: 'charlie', age: 35, salary: 55000 } // 年龄最大,薪水也最高(在同龄人中)
]四. 对象数组汉字按拼音排序
1.使用stringobject.localecompare(target)
const chinesepeople = [
{ name: '张三', age: 30 },
{ name: '李四', age: 25 },
{ name: '王五', age: 35 },
{ name: '赵六', age: 40 },
];
// 使用 localecompare 对名字属性进行排序
chinesepeople.sort((a, b) => a.name.localecompare(b.name, 'zh-cn'));
console.log(chinesepeople);输出:
[
{ name: '李四', age: 25 },
{ name: '王五', age: 35 },
{ name: '张三', age: 30 },
{ name: '赵六', age: 40 }
]2.使用第三方库
如果你想要根据汉字拼音对对象数组进行排序,你需要先将汉字转换为拼音,然后根据拼音进行排序。这通常需要使用到第三方库来实现汉字到拼音的转换,比如 pinyin 库。
npm install pinyin
const pinyin = require('pinyin');
function sortobjectsbychinesepinyin(array, propertyname) {
return array.sort((a, b) => {
const apinyin = pinyin(a[propertyname], { style: pinyin.style_normal, heteronym: false }).join('');
const bpinyin = pinyin(b[propertyname], { style: pinyin.style_normal, heteronym: false }).join('');
return apinyin.localecompare(bpinyin);
});
}
// 示例对象数组
const chinesenames = [
{ name: '张三', age: 30 },
{ name: '李四', age: 25 },
{ name: '王五', age: 35 },
];
// 使用汉字拼音对名字进行排序
const sortedchinesenames = sortobjectsbychinesepinyin(chinesenames, 'name');
console.log(sortedchinesenames);输出:
[
{ name: '李四', age: 25 }, // 'lǐ sì'
{ name: '王五', age: 35 }, // 'wáng wǔ'
{ name: '张三', age: 30 } // 'zhāng sān'
]强调:如果用vs调试,别忘记了在luanch.jsion文件中添加 "console": "integratedterminal",这句话,不然会报错。还看不到运行结果。
总结
到此这篇关于js对象数组排序方法测试的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关js对象数组排序方法内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论