springboot aop切面execution表达式
aspectj切入点语法定义在使用spring框架配置aop的时候,不管是通过xml配置文件还是注解的方式都需要定pointcut"切入点"
例如:
定义切入点表达式 execution (* com.nandao.demo.controller.*.*.*(..))
/**
* 监控controller层的接口
*/
@pointcut("execution(* com.nandao.demo.controller.*.*.*(..))")
private void pointcut(){}execution()是最常用的切点函数,其语法如下所示:
整个表达式可以分为五个部分
1、execution(): 表达式主体,可以扫描控制层的接口、某个注解、或者其他需要扫描的类。
2、第一个*号:表示返回类型,*号表示所有的类型,比如public,protect,private等。
3、包名:表示需要拦截的包名,后面的两个句点表示当前包和当前包的所有子包,com.demo.service.impl包、子孙包下所有类的方法。
4、第二个*号:表示子包名,*号表示所有子包。
5、第三个*号:表示类名,*号表示所有子包下的类。
6、*(..):最后这个星号表示方法名,*号表示所有的方法,后面括弧里面表示方法的参数,两个句点表示任何参数。
springboot aop自定义切面编程
本文结合springboot,实现切面编程。
- @before 前置通知:在某连接点(joinpoint)之前执行的通知, 但这个通知不能阻止连接点前的执行。
- @after 后通知:当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知 (不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。
- @afterreturning 返回后通知 :在某连接点正常完成后执行的通知, 不包括抛出异常的情况。
- @around 环绕通知 :包围一个连接点的通知,类似web中servlet ,规范中的filter的dofilter方法。可以在方法的调用前后完成 自定义的行为,也可以选择不执行。
- @afterthrowing 抛出异常后通知:在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。
1.首先pom文件引入aop依赖
<!-- spring-boot的aop切面服务 -->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactid>
</dependency>2.新建两个类
- 一个实现切面的处理类
- 一个定义注解
首先是定义注解:
@documented
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@target(elementtype.method)
public @interface testannotation {
}然后是:切面处理类
@order(2)
@aspect //定义一个切面
@configuration
public class testaspect {
// 定义切点pointcut
//第一个注解:表示扫描的包或类, 第一个*可以写具体的类,第二个*是方法,括号里是传参
//第二个注解表示定义的注解, 哪个方法需要切面,就在方法上加上 @testannotation
@pointcut("execution(public * com.example.demo.controller.*.*(..)) && @annotation(com.example.demo.aop.annotation.testannotation)")
public void executeservice() {
}
//执行方法之前,进入切面
@before(value = "executeservice()")
public void dobeforeadvice(joinpoint joinpoint) {
}
//在进去方法的同时,进入切面
@around("executeservice()")
public object doaroundadvice(proceedingjoinpoint pjp) throws throwable {
requestattributes ra = requestcontextholder.getrequestattributes();
servletrequestattributes sra = (servletrequestattributes) ra;
httpservletresponse response = sra.getresponse();
httpservletrequest request = sra.getrequest();
string uri = request.getrequesturi();
object result = pjp.proceed();
return result;
}
//在执行完方法后,进入切面,并返回方法的结果值,returning定义的参数必须和object后的形参一致
@afterreturning(value = "executeservice()", returning = "result")
public void doafteradvice(joinpoint joinpoint, object result) throws throwable {
requestattributes ra = requestcontextholder.getrequestattributes();
servletrequestattributes sra = (servletrequestattributes) ra;
httpservletresponse response = sra.getresponse();
if (response.getstatus() == 200) {
httpservletrequest request = sra.getrequest();
string uri = request.getrequesturi();
httpsession session = request.getsession(true);
gson gson = new gson();
jsonobject jsonobject = json.parseobject(gson.tojson(result));
}
}
}具体方法 的注解已经放到代码中,
gson 的pom依赖:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.google.code.gson/gson -->
<dependency>
<groupid>com.google.code.gson</groupid>
<artifactid>gson</artifactid>
<version>2.8.5</version>
</dependency>注意:
假如定义了一个切面: 即一个方法只被一个aspect类拦截,aspect类内部的 advice 将按照以下的顺序进行执行:
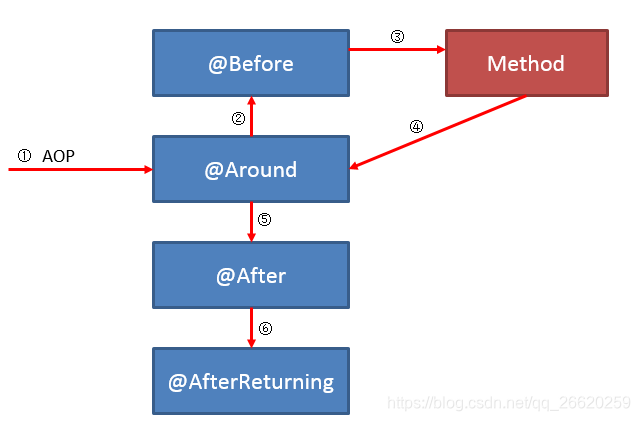
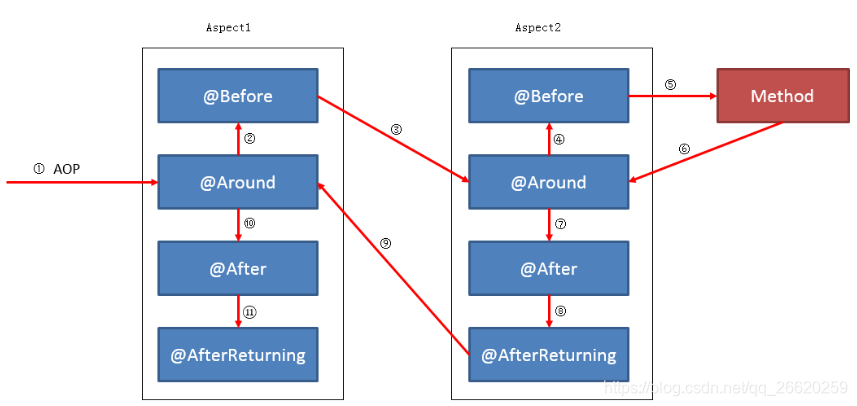
若同一个方法被多个aspect类拦截,执行顺序是不一定的。
想要有一定的顺序,可以在处理类中加入@order 注解;
执行顺序如下:
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。




发表评论