应用场景
在搜索应用中,我们一般会提供一个搜索框,输入关健字,点击查询按钮以获取结果数据。大部分情况我们会提供模糊查询的形式以在一个或多个字段进行搜索以获取结果。这样可以简化用户的操作,扩大搜索范围,为提高精度而提供基础范围数据。因此按汉字拼音搜索,即可以进一步简化输入,又可以进一步扩大搜索范围。
举例
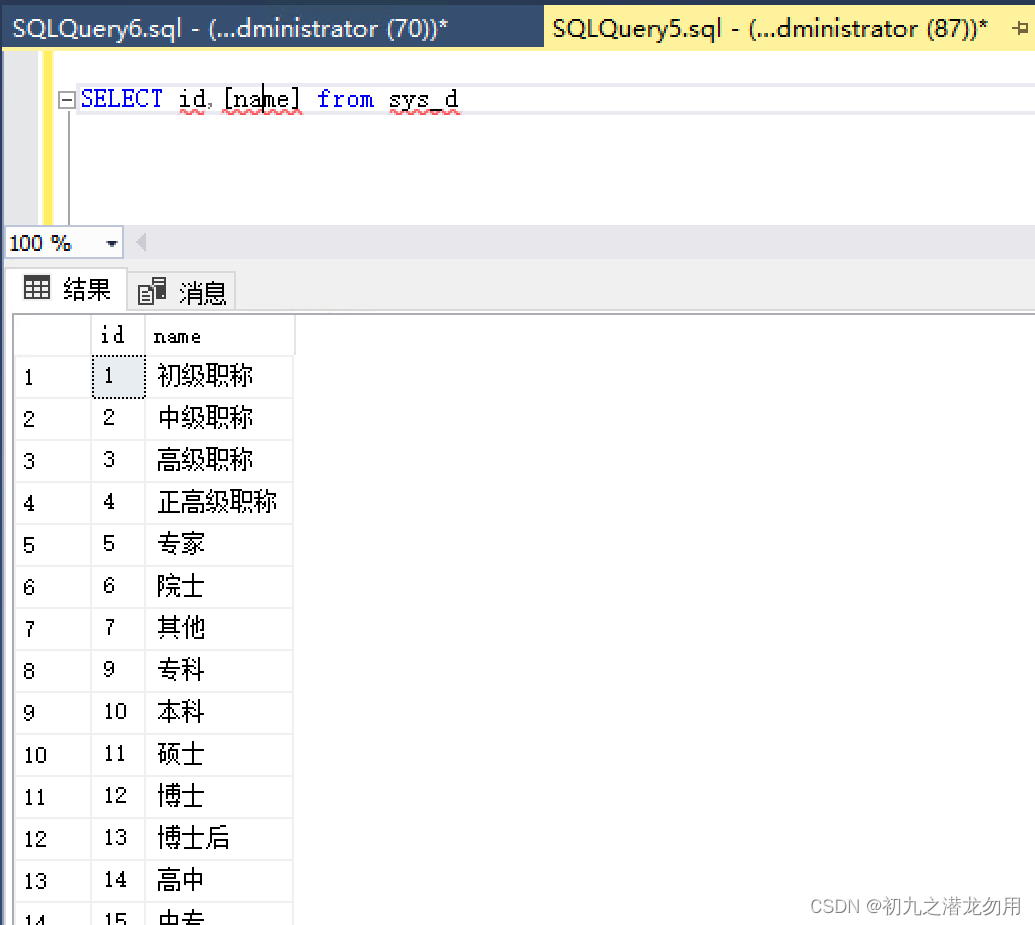
假设有字典表,表名 sys_d,包括 id 和 name 字段,我们要对 name 字段进行搜索,如下图:
对于模糊搜索,我们可以通过 like 来实现,比如我们想得到name字段中包含“职称”的记录,如下图执行:

用拼音简码的形式,可以更加进一步的增加搜索范围,并可以简化切换输入法的操作,比如输入 zc,即可以找到字典表中的数据。 因此我们可以编写汉字转拼音的函数 getpy 进行进一步操作,如下图:
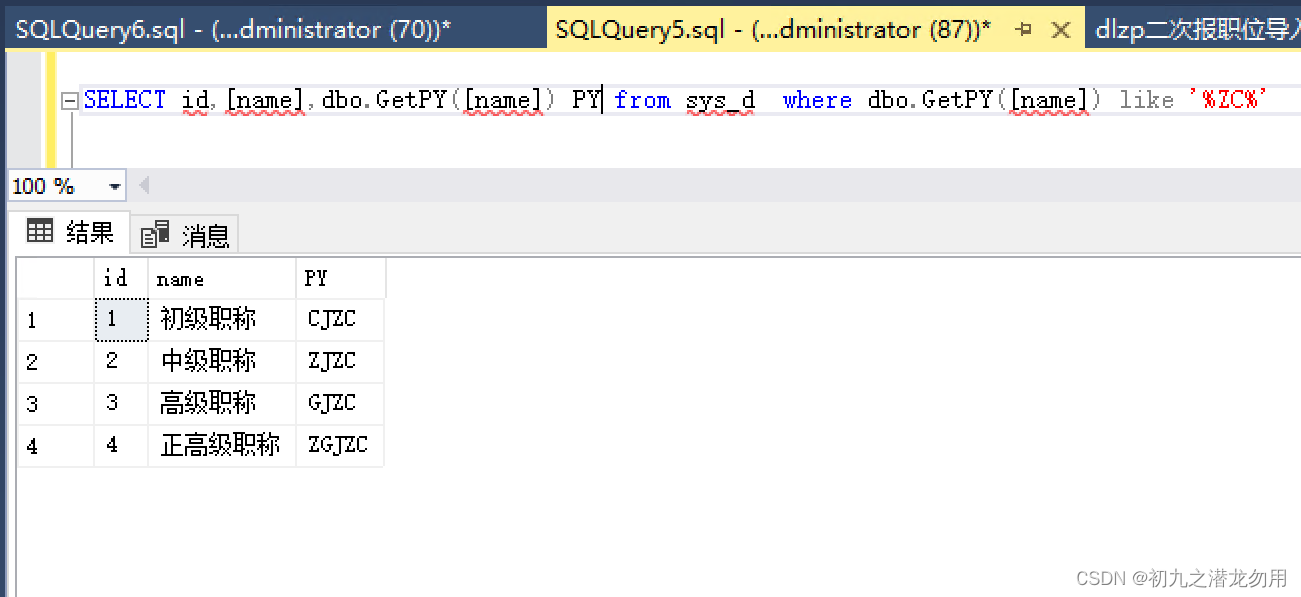
在搜索时,我们通过该函数进行了一次转化,以得到预期结果,另外通过在查询字段列表里进行转化验证,可以看到 py 字段对应 name 的拼音简写转化。
函数实现
打开sql server 查询分析器,执行如下代码:
create function [dbo].[getpy](@str varchar(500))
returns varchar(500)
as
begin
declare @cyc int,@length int,@str1 varchar(100),@charcate varbinary(20)
set @cyc=1--从第几个字开始取
set @length=len(@str)--输入汉字的长度
set @str1=''--用于存放返回值
while @cyc<=@length
begin
select @charcate=cast(substring(@str,@cyc,1) as varbinary)--每次取出一个字并将其转变成二进制,便于与gbk编码表进行比较
if @charcate>=0xb0a1 and @charcate<=0xb0c4
set @str1=@str1+'a'--说明此汉字的首字母为a,以下同上
else if @charcate>=0xb0c5 and @charcate<=0xb2c0
set @str1=@str1+'b'
else if @charcate>=0xb2c1 and @charcate<=0xb4ed
set @str1=@str1+'c'
else if @charcate>=0xb4ee and @charcate<=0xb6e9
set @str1=@str1+'d'
else if @charcate>=0xb6ea and @charcate<=0xb7a1
set @str1=@str1+'e'
else if @charcate>=0xb7a2 and @charcate<=0xb8c0
set @str1=@str1+'f'
else if @charcate>=0xb8c1 and @charcate<=0xb9fd
set @str1=@str1+'g'
else if @charcate>=0xb9fe and @charcate<=0xbbf6
set @str1=@str1+'h'
else if @charcate>=0xbbf7 and @charcate<=0xbfa5
set @str1=@str1+'j'
else if @charcate>=0xbfa6 and @charcate<=0xc0ab
set @str1=@str1+'k'
else if @charcate>=0xc0ac and @charcate<=0xc2e7
set @str1=@str1+'l'
else if @charcate>=0xc2e8 and @charcate<=0xc4c2
set @str1=@str1+'m'
else if @charcate>=0xc4c3 and @charcate<=0xc5b5
set @str1=@str1+'n'
else if @charcate>=0xc5b6 and @charcate<=0xc5bd
set @str1=@str1+'o'
else if @charcate>=0xc5be and @charcate<=0xc6d9
set @str1=@str1+'p'
else if @charcate>=0xc6da and @charcate<=0xc8ba
set @str1=@str1+'q'
else if @charcate>=0xc8bb and @charcate<=0xc8f5
set @str1=@str1+'r'
else if @charcate>=0xc8f6 and @charcate<=0xcbf9
set @str1=@str1+'s'
else if @charcate>=0xcbfa and @charcate<=0xcdd9
set @str1=@str1+'t'
else if @charcate>=0xcdda and @charcate<=0xcef3
set @str1=@str1+'w'
else if @charcate>=0xcef4 and @charcate<=0xd1b8
set @str1=@str1+'x'
else if @charcate>=0xd1b9 and @charcate<=0xd4d0
set @str1=@str1+'y'
else if @charcate>=0xd4d1 and @charcate<=0xd7f9
set @str1=@str1+'z'
else
set @str1 =@str1 + substring(@str,@cyc,1)
set @str1= ltrim(rtrim(@str1 ))
set @cyc=@cyc+1--取出输入汉字的下一个字
end
return @str1--返回输入汉字的首字母
end
go
getpy函数需要传递 类型为varchar(500) 的字符串参数。
小结
以上代码基于 microsoft sql server 2016 编写与实现。 实际的应用中,还要结合原始输入进行查询,可以使用或条件,拼音码做为辅助查询条件。另外,对于大数据量的表,可以采用空间换时间的做法,增加字段,存储拼音简写值。可以通过在业务程序时,录入或修改功能实现,也可以通过触发器来实现。
以上就是基于microsoft sql server实现编写汉字转拼音函数的详细内容,更多关于sql server汉字转拼音的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!


发表评论