1、math
- math是一个内置对象,它拥有一些数学常数属性和数学函数方法,math不是一个函数对象
——————引用自官网
2、描述
- 与其他全局对象不同的是,math 不是一个构造器。math 的所有属性与方法都是静态的。引用圆周率的写法是 math.pi,调用正余弦函数的写法是 math.sin(x),x 是要传入的参数。math 的常量是使用 javascript 中的全精度浮点数来定义的。
——————引用自官网
3、方法
(1)获取随机数
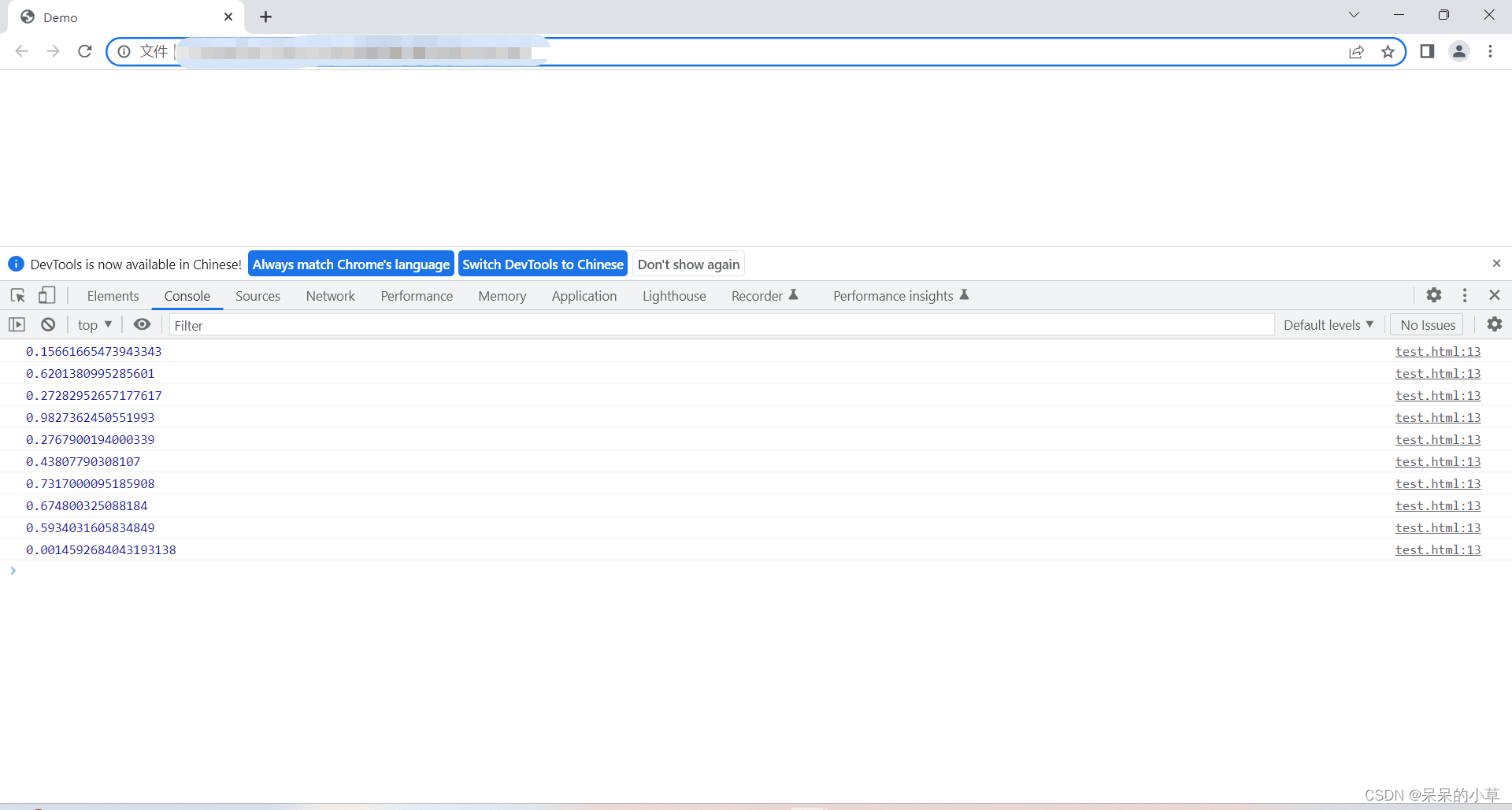
- 随机数默认返回0~1之间的数
① 语法格式:
math.random();
② 示例:
//这里为了方便展示效果,用for循环输出10次随机数
<script>
let num;
for (i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
num = math.random();
console.log(num);
}
</script>
③ 运行效果
(2)获取整数随机数
方法1(取整)
- parseint(math.random()*(最大值-最小值+1))+最小值
方法2(向下取整)
- math.floor(math.random()*(最大值-最小值+1))+最小值
① 语法格式:
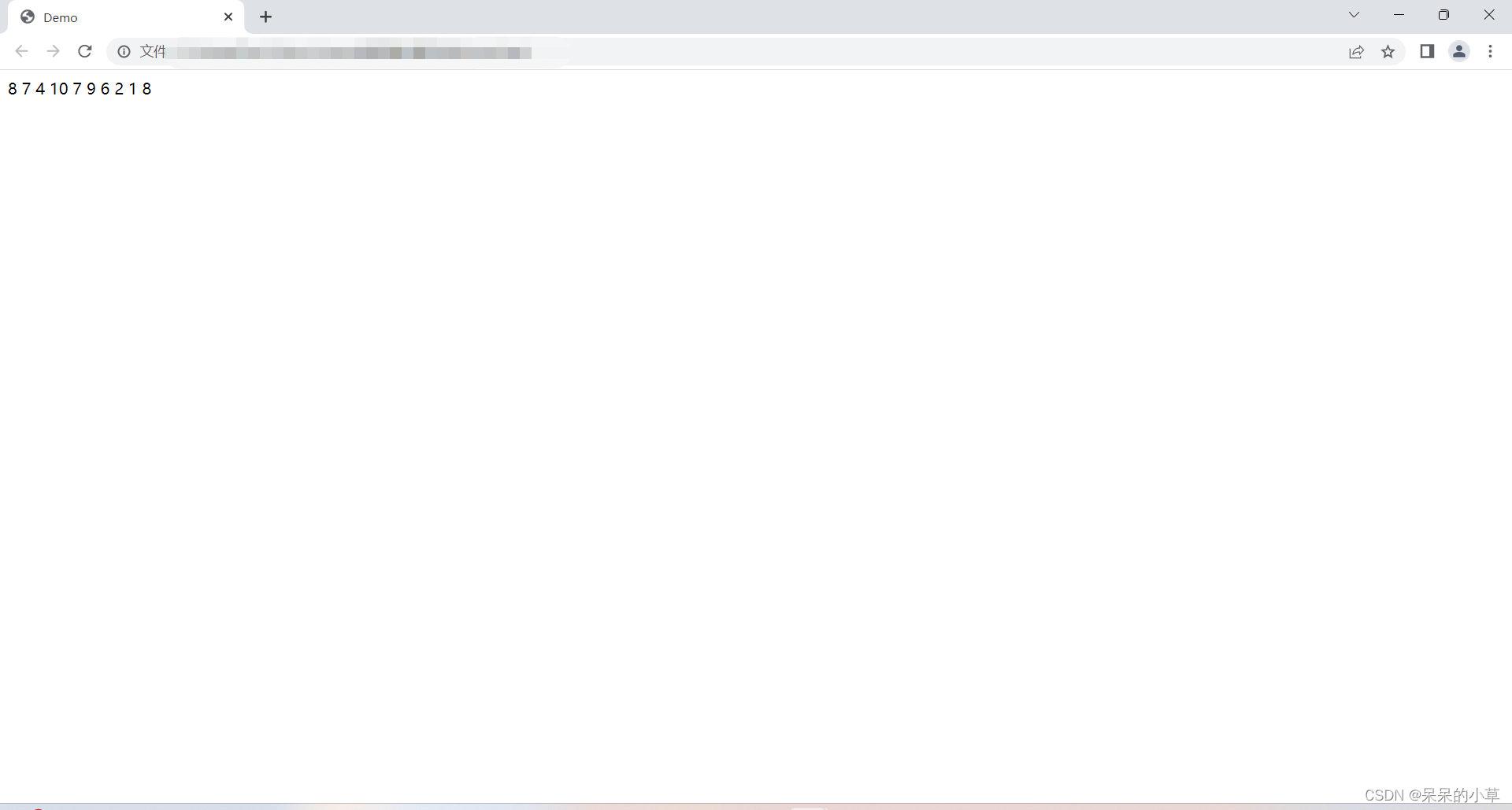
- 获取1~10的随机数
//取整 parseint(math.random() * (最大值 - 最小值 + 1 )) + 最小值; //向下取整 math.floor(math.random() * (最大值 - 最小值 + 1)) + 最小值;
② 示例:
//取整,用for循环取10次随机数
<script>
let num;
for (i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
//公式:parseint(math.random() * (最大值 - 最小值 + 1)) + 最小值
num = parseint(math.random() * (10 - 1 + 1)) + 1;
//最小值为1的时候可以简写:num = parseint(math.random() * 10) + 1
document.write(num + ' ');
}
</script>
运行效果
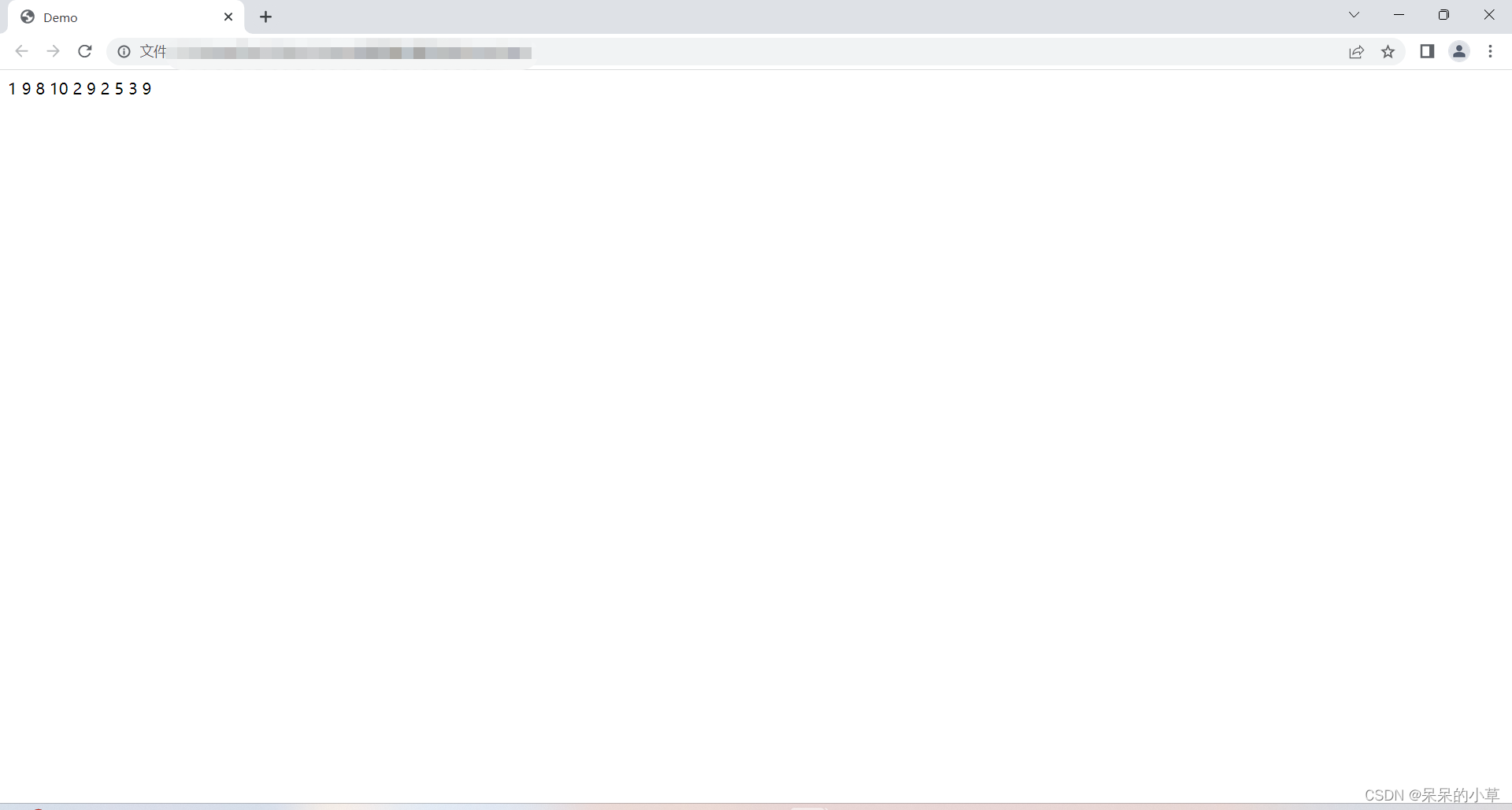
//向下取整,用for循环取10次随机数
<script>
let num;
for (i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
//公式:math.floor(math.random() * (最大值 - 最小值 + 1)) + 最小值;
num = math.floor(math.random() * (10 - 1 + 1)) + 1;
//最小值为1的时候可以简写:num = parseint(math.random() * 10) + 1
document.write(num + ' ');
}
</script>
运行效果
(3)四舍五入
① 语法格式:
math.round();
② 示例:
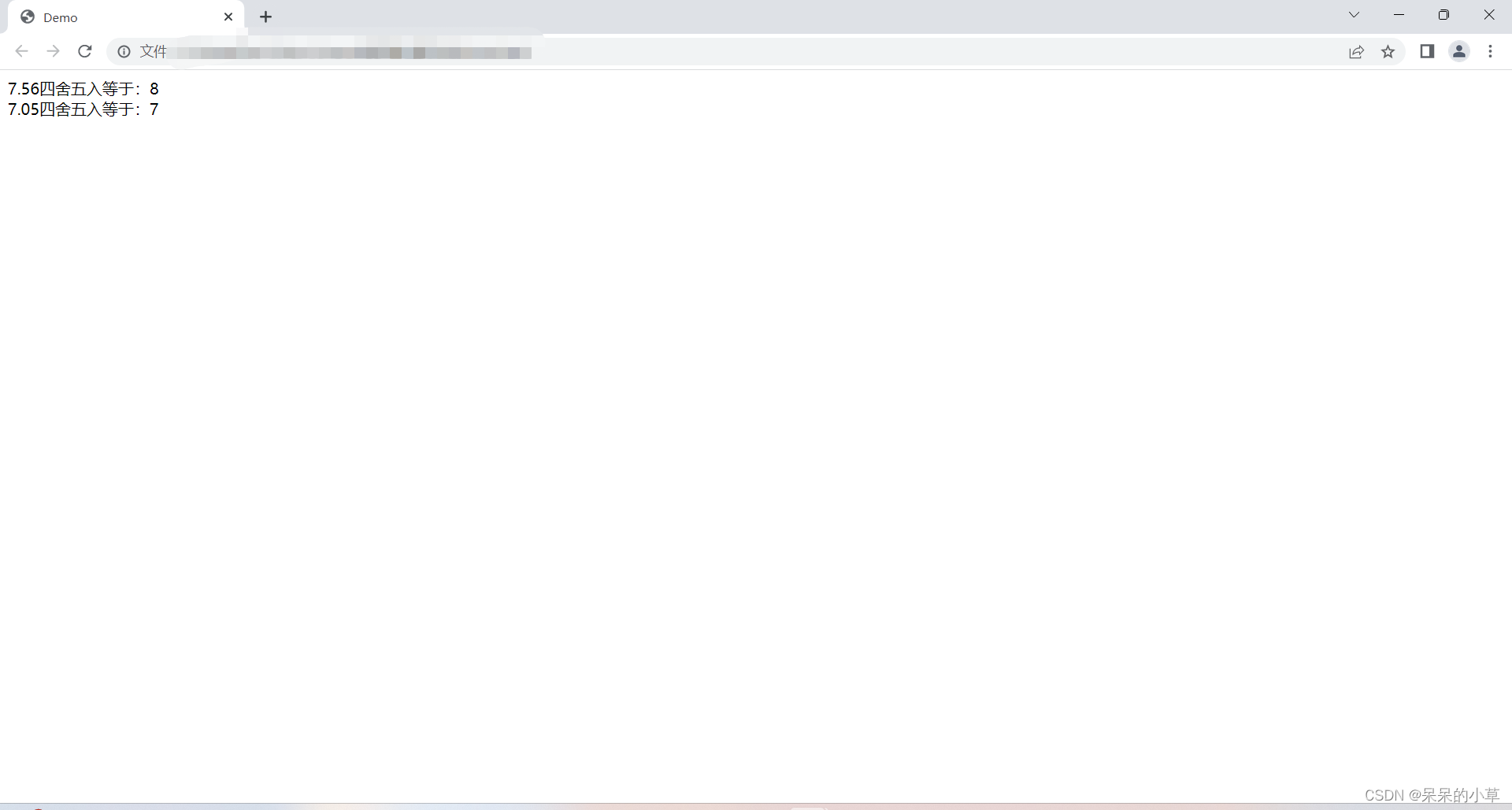
<script>
let numone = math.round(7.56);
let numtwo = math.round(7.05);
document.write(`
7.56四舍五入等于:${numone} <br />
7.05四舍五入等于:${numtwo}
`);
// <br />:换行
</script>
③ 运行效果
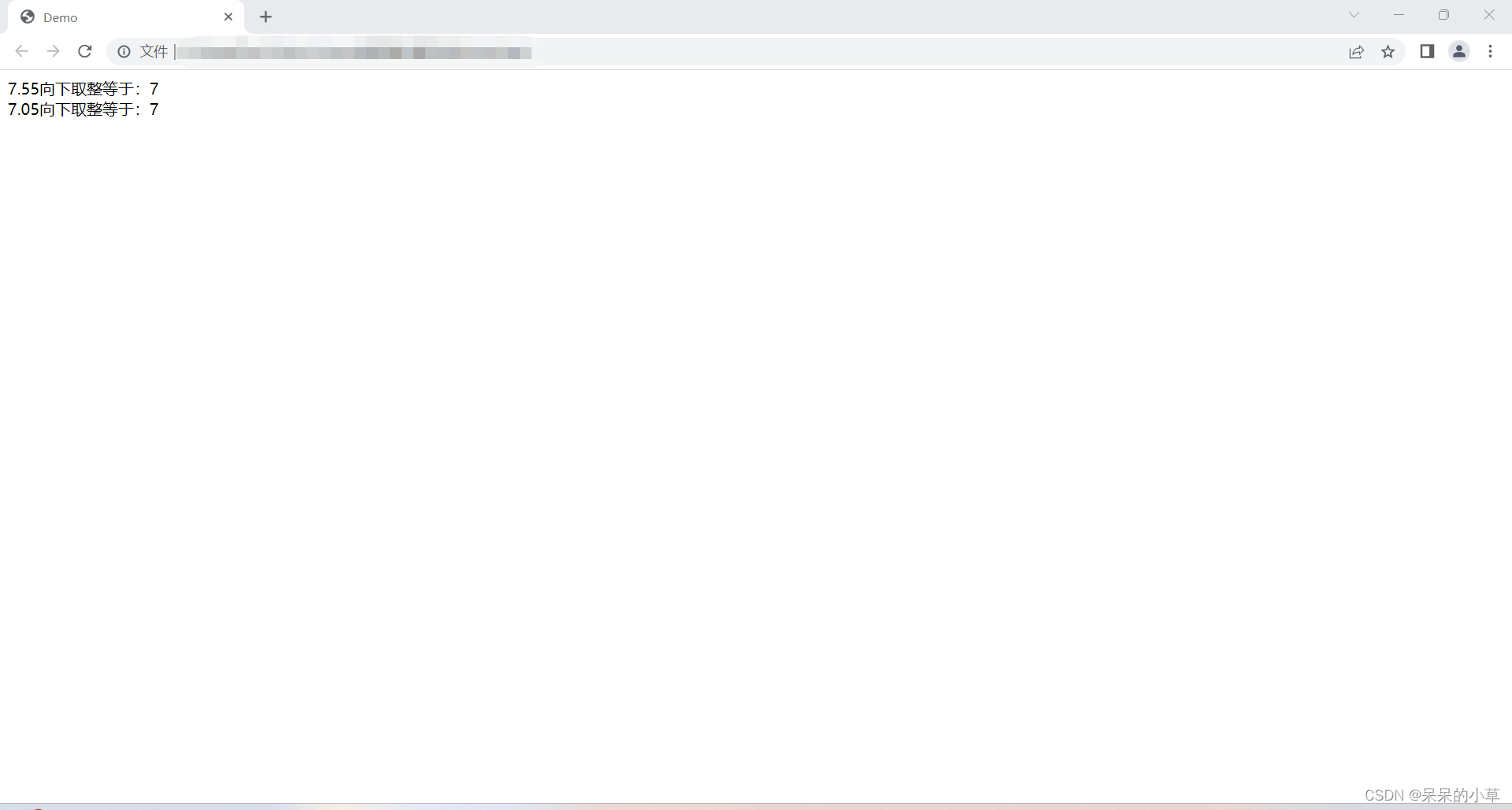
(4)向下取整
① 语法格式:
math.floor();
② 示例:
<script>
let numone = math.floor(7.55);
let numtwo = math.floor(7.05);
document.write(`
7.55向下取整等于:${numone} <br />
7.05向下取整等于:${numtwo}
`);
// <br />:换行
</script>
③ 运行效果
(5)向上取整
① 语法格式:
math.ceil();
② 示例:
<script>
let numone = math.ceil(7.55);
let numtwo = math.ceil(7.05);
document.write(`
7.55向上取整等于:${numone} <br />
7.05向上取整等于:${numtwo}
`);
// <br />:换行
</script>
③ 运行效果
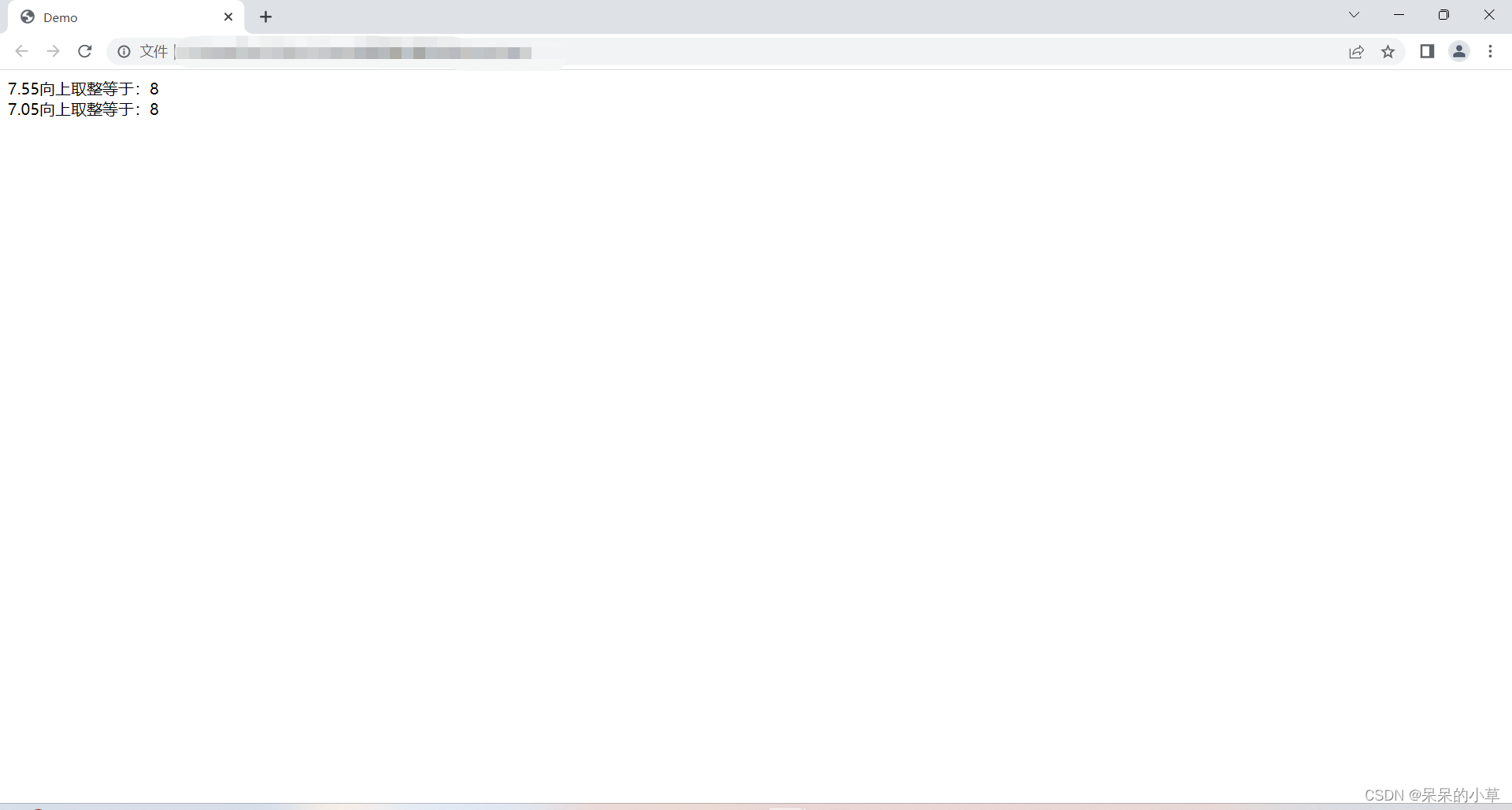
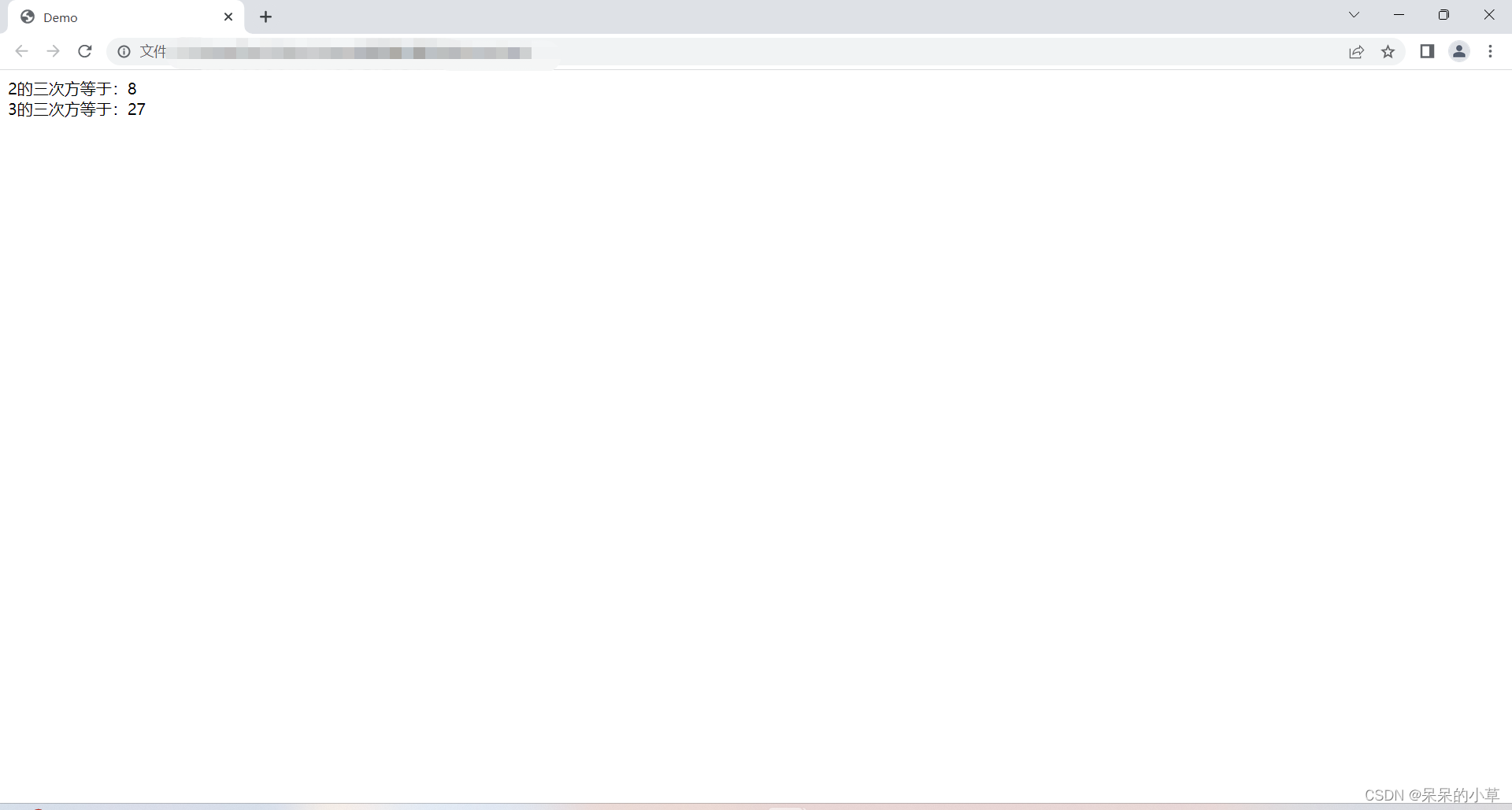
(6)次方
① 语法格式:
math.pow(底数,指数/幂);
② 示例:
<script>
//计算2的三次方
let numone = math.pow(2,3);
//计算3的三次方
let numtwo = math.pow(3,3);
document.write(`
2的三次方等于:${numone} <br />
3的三次方等于:${numtwo}
`)
</script>
③ 运行效果
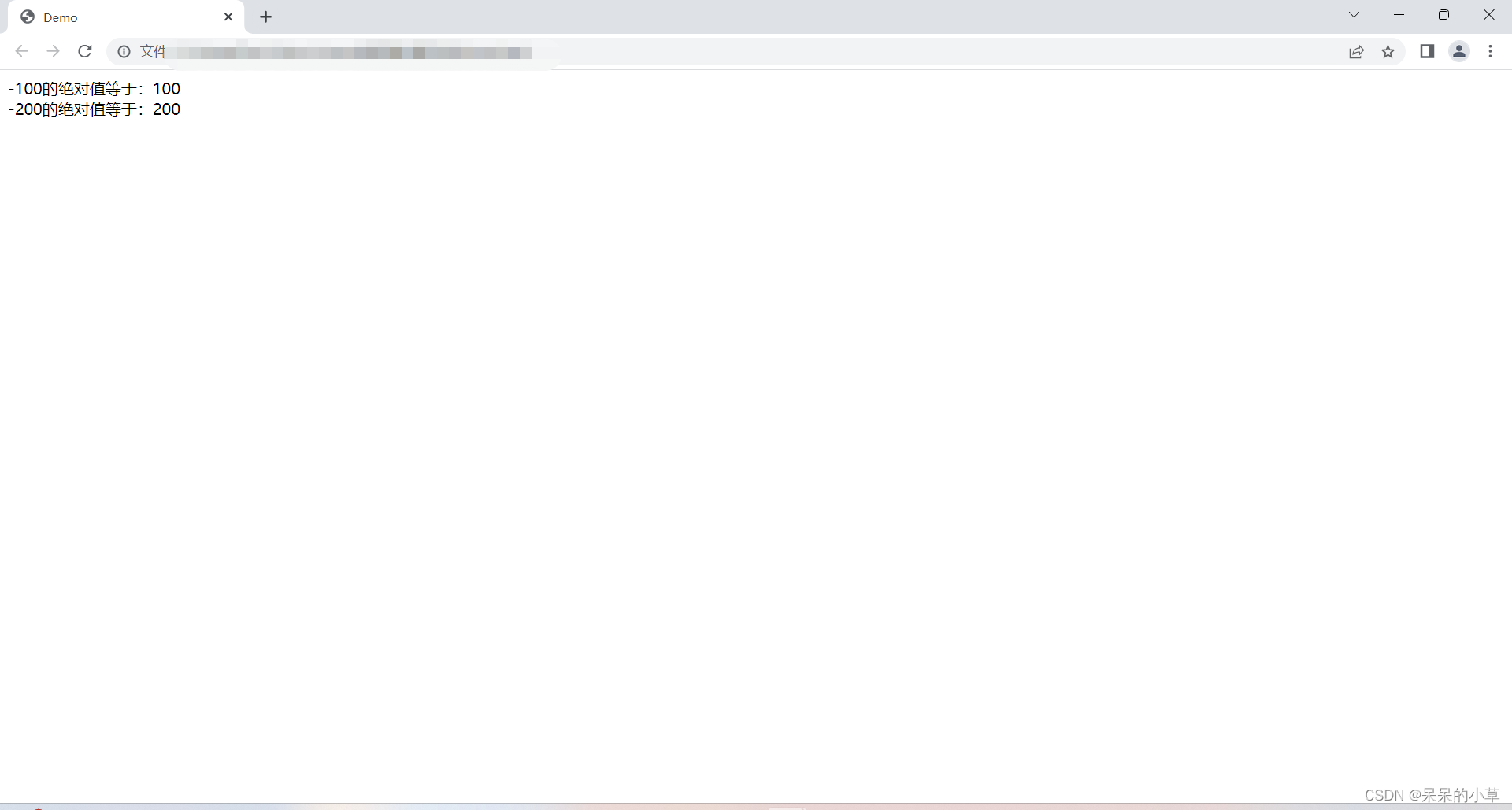
(7)绝对值
① 语法格式:
math.abs();
② 示例:
<script>
let numone = math.abs(-100);
let numtwo = math.abs(-200);
document.write(`
-100的绝对值等于:${numone} <br />
-200的绝对值等于:${numtwo}
`)
</script>
③ 运行效果
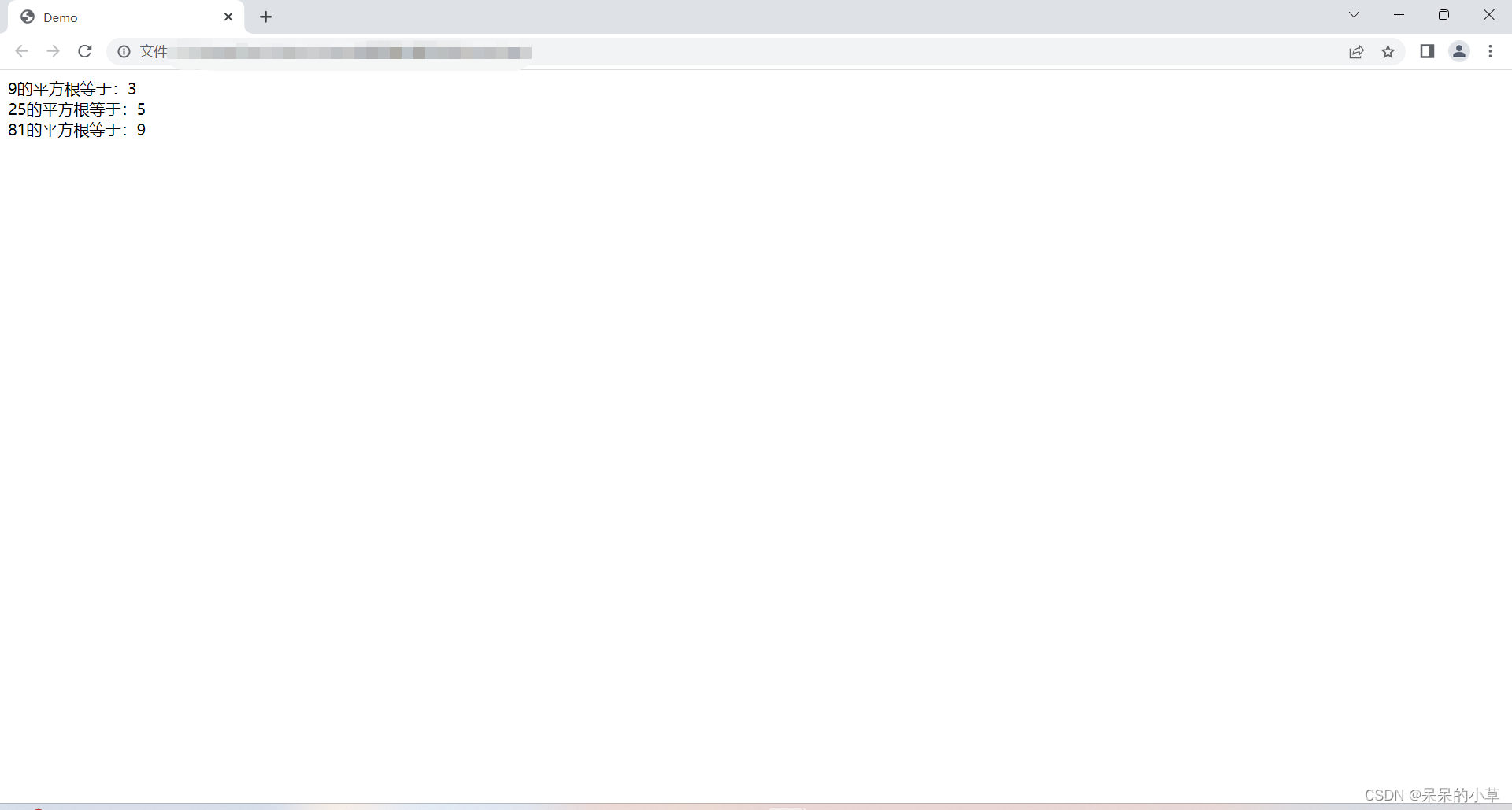
(8)平方根
① 语法格式:
math.sqrt();
② 示例:
<script>
let numone = math.sqrt(9);
let numtwo = math.sqrt(25);
let numthr = math.sqrt(81);
document.write(`
9的平方根等于:${numone} <br />
25的平方根等于:${numtwo} <br />
81的平方根等于:${numthr}
`)
</script>
③ 运行效果
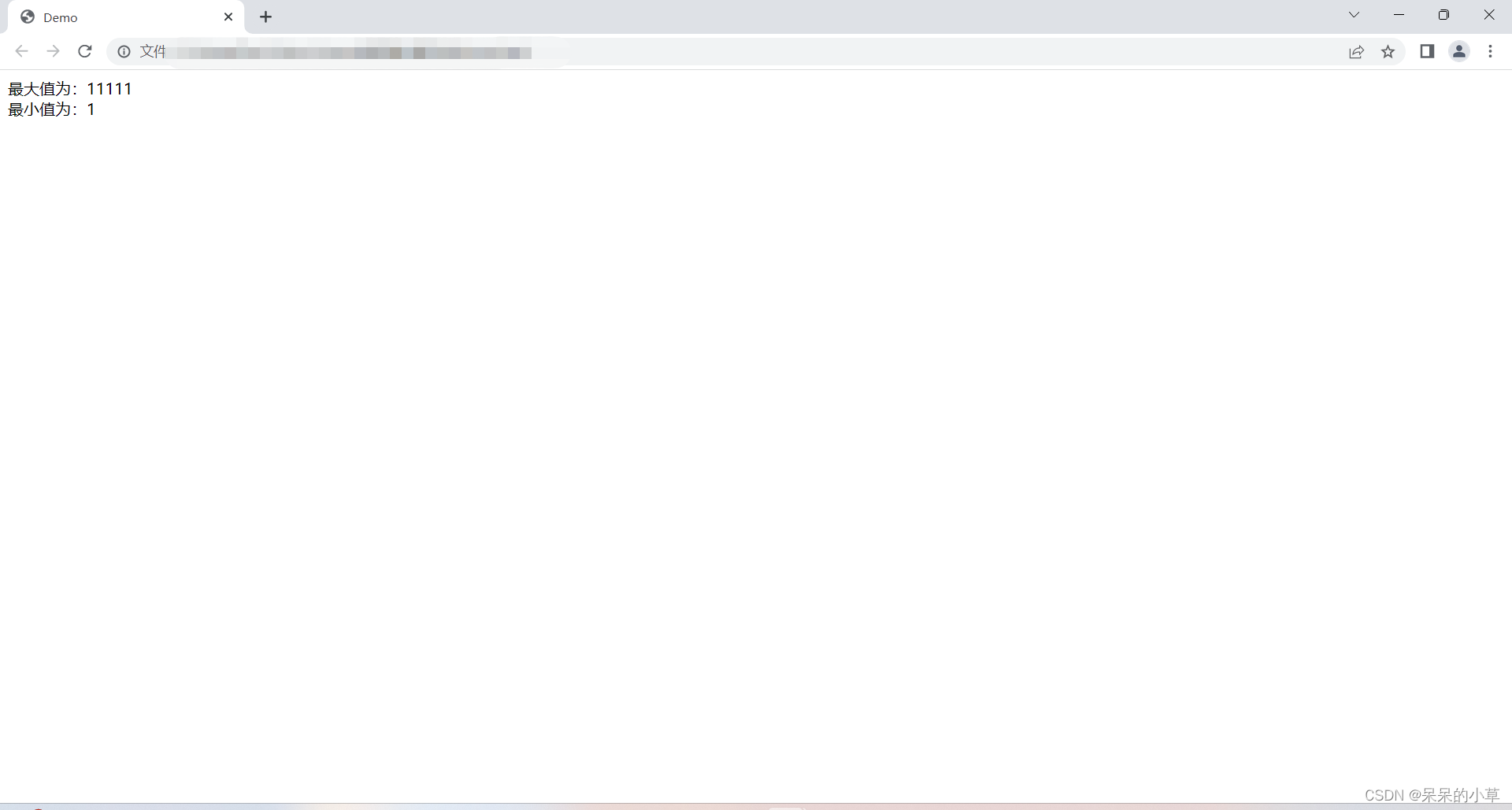
(9)最大值 / 最小值
① 语法格式:
//最大值 math.max(); //最小值 math.min();
② 示例:
<script>
let nummax = math.max(1,11,111,1111,11111);
let nummin = math.min(1,11,111,1111,11111);
document.write(`
最大值为:${nummax} <br />
最小值为:${nummin}
`)
</script>
③ 运行效果
更多数学对象学习,请参考官方文档
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-cn/docs/web/javascript/reference/global_objects/math
总结
到此这篇关于javascript数学对象(math)方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关js数学对象math内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论