通配符模式
概述
通配符模式是一种灵活的消息传递模式,可以根据消息的路由键(routing key)和绑定(binding)模式来实现精确的消息过滤和匹配。在rabbitmq中,路由键由生产者定义,用于标识消息的目的地;而绑定则由消费者定义,用于指定消息的接收规则。

路由模式的升级版, 在routingkey的基础上,增加了通配符的功能, 使之更加灵活.
topics和routing的基本原理相同,即:⽣产者将消息发给交换机,交换机根据routingkey将消息转发给与routingkey匹配的队列. 类似于正则表达式的⽅式来定义routingkey的模式.
不同之处是:routingkey的匹配⽅式不同,routing模式是相等匹配,topics模式是通配符匹配.
应用场景
rabbitmq的通配符模式在需要根据消息的特定属性进行路由和过滤的场景中非常有用。例如,在一个日志系统中,可以使用通配符模式来将不同级别的日志消息路由到不同的队列中,以便进行不同的处理和分析。
优势
通配符模式的优势在于它可以灵活地匹配消息,使得消息可以根据不同的条件进行过滤和选择。通过合理地定义绑定和路由键,可以实现复杂的消息过滤和路由策略,提高系统的灵活性和性能。
代码案例
引入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.rabbitmq/amqp-client -->
<dependency>
<groupid>com.rabbitmq</groupid>
<artifactid>amqp-client</artifactid>
<version>5.21.0</version>
</dependency>常量类
public class constants {
public static final string host = "47.98.109.138";
public static final int port = 5672;
public static final string user_name = "study";
public static final string password = "study";
public static final string virtual_host = "aaa";
//通配符模式
public static final string topic_exchange = "topic.exchange";
public static final string topic_queue1 = "topic_queue1";
public static final string topic_queue2 = "topic_queue2";
}编写生产者代码
import com.rabbitmq.client.builtinexchangetype;
import com.rabbitmq.client.channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.connectionfactory;
import rabbitmq.constant.constants;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.concurrent.timeoutexception;
/**
* 通配符模式生产者
*/
public class producer {
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception, timeoutexception {
//1. 建立连接
connectionfactory connectionfactory = new connectionfactory();
connectionfactory.sethost(constants.host);
connectionfactory.setport(constants.port); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionfactory.setusername(constants.user_name);//账号
connectionfactory.setpassword(constants.password); //密码
connectionfactory.setvirtualhost(constants.virtual_host); //虚拟主机
connection connection = connectionfactory.newconnection();
//2. 开启信道
channel channel = connection.createchannel();
//3. 声明交换机
channel.exchangedeclare(constants.topic_exchange, builtinexchangetype.topic, true);
//4. 声明队列
channel.queuedeclare(constants.topic_queue1, true, false, false, null);
channel.queuedeclare(constants.topic_queue2, true, false, false, null);
//5. 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queuebind(constants.topic_queue1, constants.topic_exchange, "*.a.*");
channel.queuebind(constants.topic_queue2, constants.topic_exchange, "*.*.b");
channel.queuebind(constants.topic_queue2, constants.topic_exchange, "c.#");
//6. 发送消息
string msg = "hello topic, my routingkey is ae.a.f....";
channel.basicpublish(constants.topic_exchange,"ae.a.f", null, msg.getbytes()); //转发到q1
string msg_b = "hello topic, my routingkey is ef.a.b....";
channel.basicpublish(constants.topic_exchange,"ef.a.b", null, msg_b.getbytes()); //转发到q1和q2
string msg_c = "hello topic, my routingkey is c.ef.d....";
channel.basicpublish(constants.topic_exchange,"c.ef.d", null, msg_c.getbytes());//转发q2
system.out.println("消息发送成功");
//7. 释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}编写消费者1代码
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import rabbitmq.constant.constants;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.concurrent.timeoutexception;
public class consumer1 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception, timeoutexception {
//1. 建立连接
connectionfactory connectionfactory = new connectionfactory();
connectionfactory.sethost(constants.host);
connectionfactory.setport(constants.port); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionfactory.setusername(constants.user_name);//账号
connectionfactory.setpassword(constants.password); //密码
connectionfactory.setvirtualhost(constants.virtual_host); //虚拟主机
connection connection = connectionfactory.newconnection();
//2. 开启信道
channel channel = connection.createchannel();
//3. 声明队列
channel.queuedeclare(constants.topic_queue1,true,false,false,null);
//4. 消费消息
defaultconsumer consumer = new defaultconsumer(channel){
//从队列中收到消息, 就会执行的方法
@override
public void handledelivery(string consumertag, envelope envelope, amqp.basicproperties properties, byte[] body) throws ioexception {
system.out.println("接收到消息:"+ new string(body));
}
};
channel.basicconsume(constants.topic_queue1, true, consumer);
}
}编写消费者2代码
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import rabbitmq.constant.constants;
import java.io.ioexception;
import java.util.concurrent.timeoutexception;
public class consumer2 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception, timeoutexception {
//1. 建立连接
connectionfactory connectionfactory = new connectionfactory();
connectionfactory.sethost(constants.host);
connectionfactory.setport(constants.port); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionfactory.setusername(constants.user_name);//账号
connectionfactory.setpassword(constants.password); //密码
connectionfactory.setvirtualhost(constants.virtual_host); //虚拟主机
connection connection = connectionfactory.newconnection();
//2. 开启信道
channel channel = connection.createchannel();
//3. 声明队列
channel.queuedeclare(constants.topic_queue2,true,false,false,null);
//4. 消费消息
defaultconsumer consumer = new defaultconsumer(channel){
//从队列中收到消息, 就会执行的方法
@override
public void handledelivery(string consumertag, envelope envelope, amqp.basicproperties properties, byte[] body) throws ioexception {
system.out.println("接收到消息:"+ new string(body));
}
};
channel.basicconsume(constants.topic_queue2, true, consumer);
}
}运行代码
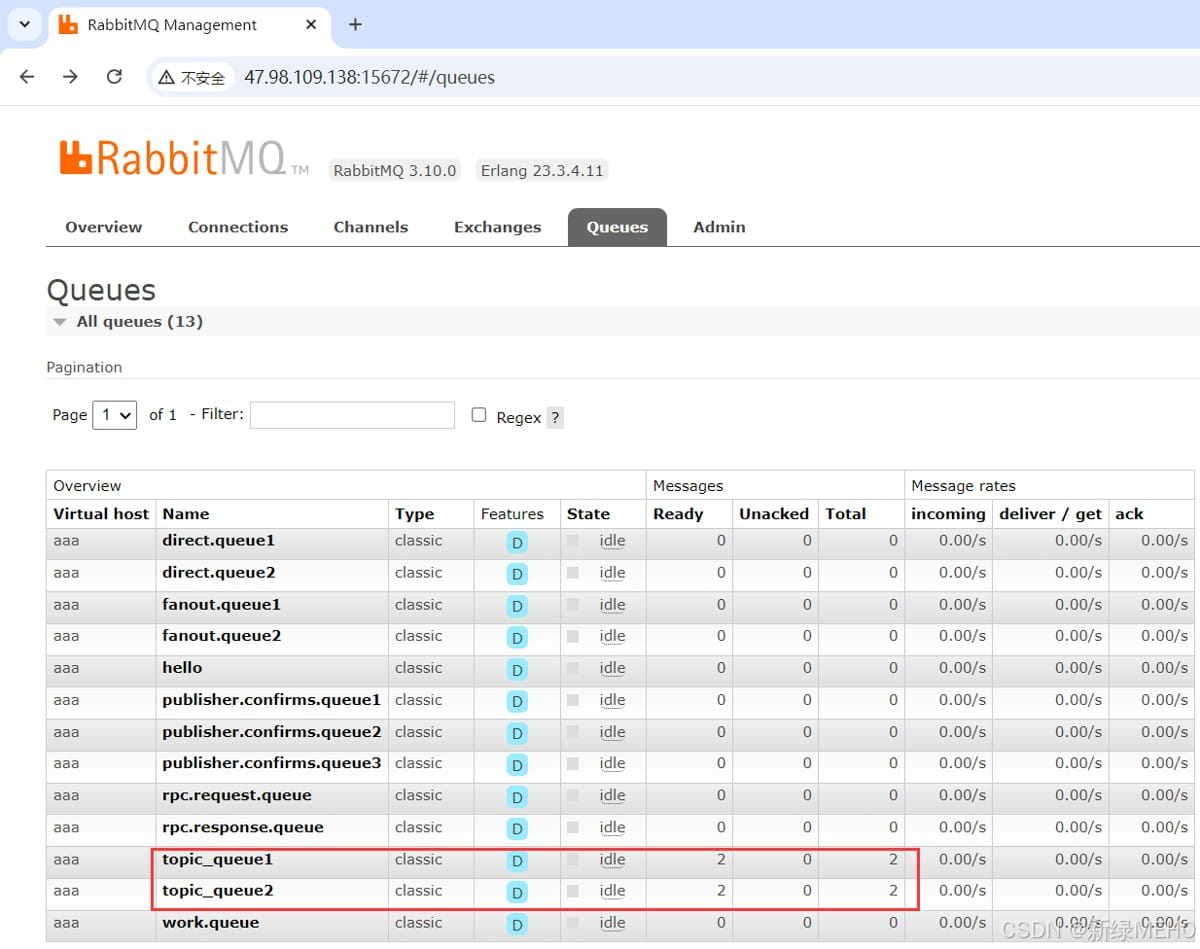
观察管理界面可以看到两个队列都各自收到了2条消息,与预期符合。

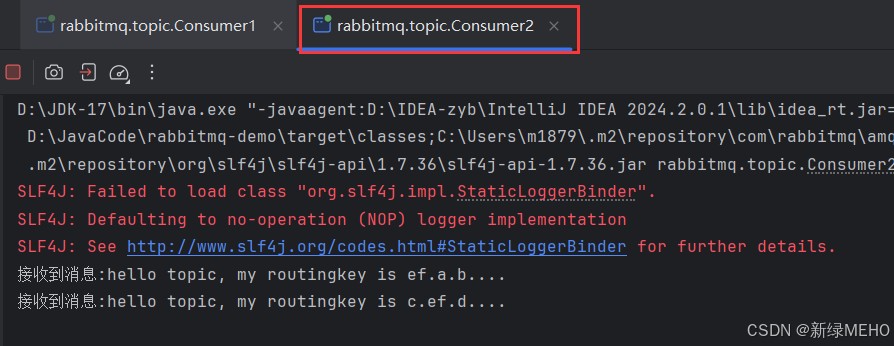
两个消费者都各自从两个不同的队列中取出并消费了2条消息,与预期符合。
到此这篇关于rabbitmq工作模式之通配符模式详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关rabbitmq通配符模式内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论