spring状态机深度解析:从入门到生产实战
spring state machine是spring生态系统中一个强大的状态机框架,它让复杂的状态流转变得优雅而简单。本文将带你从基础概念出发,逐步深入理解并掌握spring状态机在实际生产环境中的应用。
一、状态机是什么?为什么要用它?
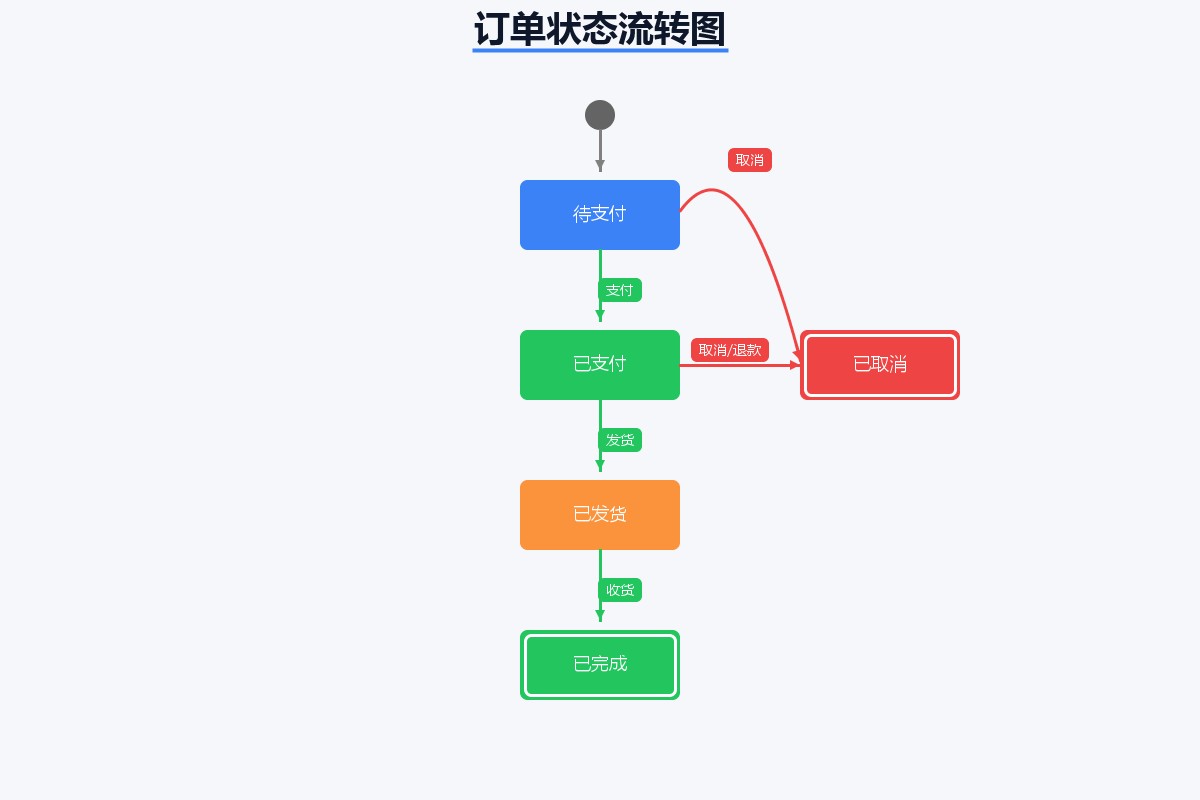
想象一下订单系统:用户下单后,订单会经历"待支付→已支付→待发货→已发货→已完成"等一系列状态变化。如果在代码里用if-else来处理这些状态流转,很快就会变成一团乱麻。
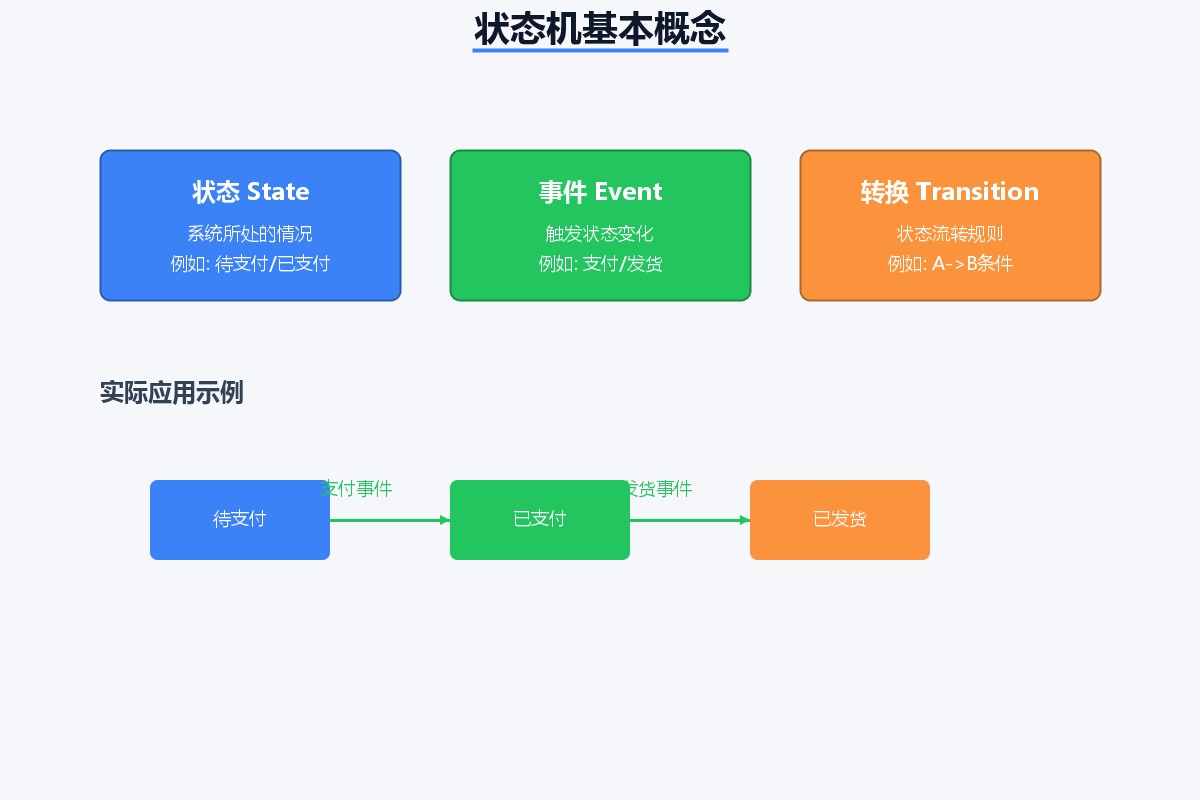
状态机(state machine)就是解决这类问题的利器!它明确定义了:
- 状态(state):系统可能处于的状态
- 事件(event):触发状态变化的动作
- 转换(transition):状态之间的流转规则
二、spring状态机核心概念
2.1 三大核心组件
// 1. 定义状态枚举
public enum orderstatus {
wait_payment, // 待支付
paid, // 已支付
wait_deliver, // 待发货
delivered, // 已发货
completed, // 已完成
cancelled // 已取消
}
// 2. 定义事件枚举
public enum orderevent {
pay, // 支付
deliver, // 发货
receive, // 收货
cancel // 取消
}
// 3. 配置状态机
@configuration
@enablestatemachine
public class orderstatemachineconfig
extends statemachineconfigureradapter<orderstatus, orderevent> {
@override
public void configure(statemachinestateconfigurer<orderstatus, orderevent> states)
throws exception {
states.withstates()
.initial(orderstatus.wait_payment)
.states(enumset.allof(orderstatus.class));
}
@override
public void configure(statemachinetransitionconfigurer<orderstatus, orderevent> transitions)
throws exception {
transitions
.withexternal()
.source(orderstatus.wait_payment)
.target(orderstatus.paid)
.event(orderevent.pay)
.and()
.withexternal()
.source(orderstatus.paid)
.target(orderstatus.wait_deliver)
.event(orderevent.deliver)
.and()
.withexternal()
.source(orderstatus.wait_deliver)
.target(orderstatus.delivered)
.event(orderevent.receive)
.and()
.withexternal()
.source(orderstatus.delivered)
.target(orderstatus.completed)
.event(orderevent.receive);
}
}

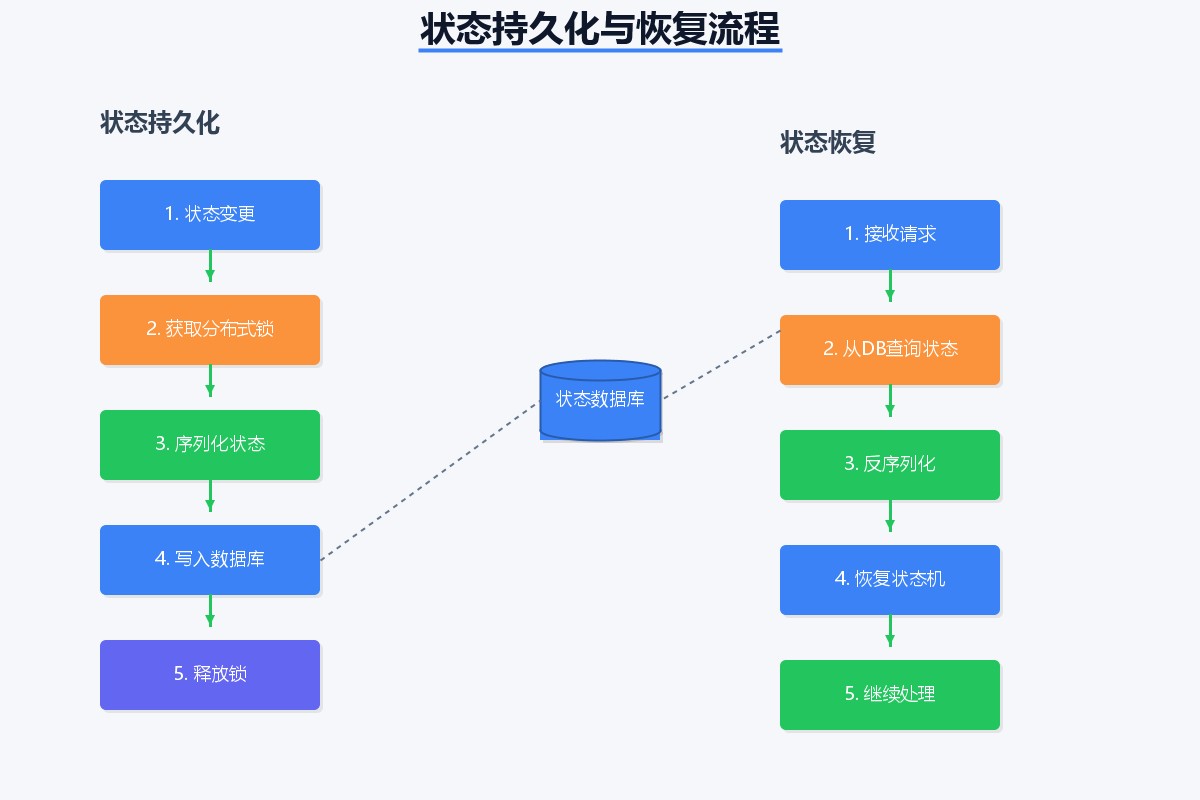
2.2 状态持久化
生产环境中,状态必须持久化。spring状态机支持多种持久化方式:
@service
@requiredargsconstructor
public class orderservice {
private final statemachinefactory<orderstatus, orderevent> factory;
private final statemachinepersist<orderstatus, orderevent, string> persist;
public boolean pay(string orderid) {
statemachine<orderstatus, orderevent> sm = restorestatemachine(orderid);
boolean result = sm.sendevent(orderevent.pay);
if (result) {
persiststatemachine(orderid, sm);
// 发送支付成功消息
publishpaymentsuccessevent(orderid);
}
return result;
}
private statemachine<orderstatus, orderevent> restorestatemachine(string orderid) {
try {
return persist.restore(factory.getstatemachine(), orderid);
} catch (exception e) {
throw new runtimeexception("恢复状态机失败", e);
}
}
private void persiststatemachine(string orderid, statemachine<orderstatus, orderevent> sm) {
try {
persist.persist(sm, orderid);
} catch (exception e) {
throw new runtimeexception("保存状态机失败", e);
}
}
}
三、生产实战:工作流引擎
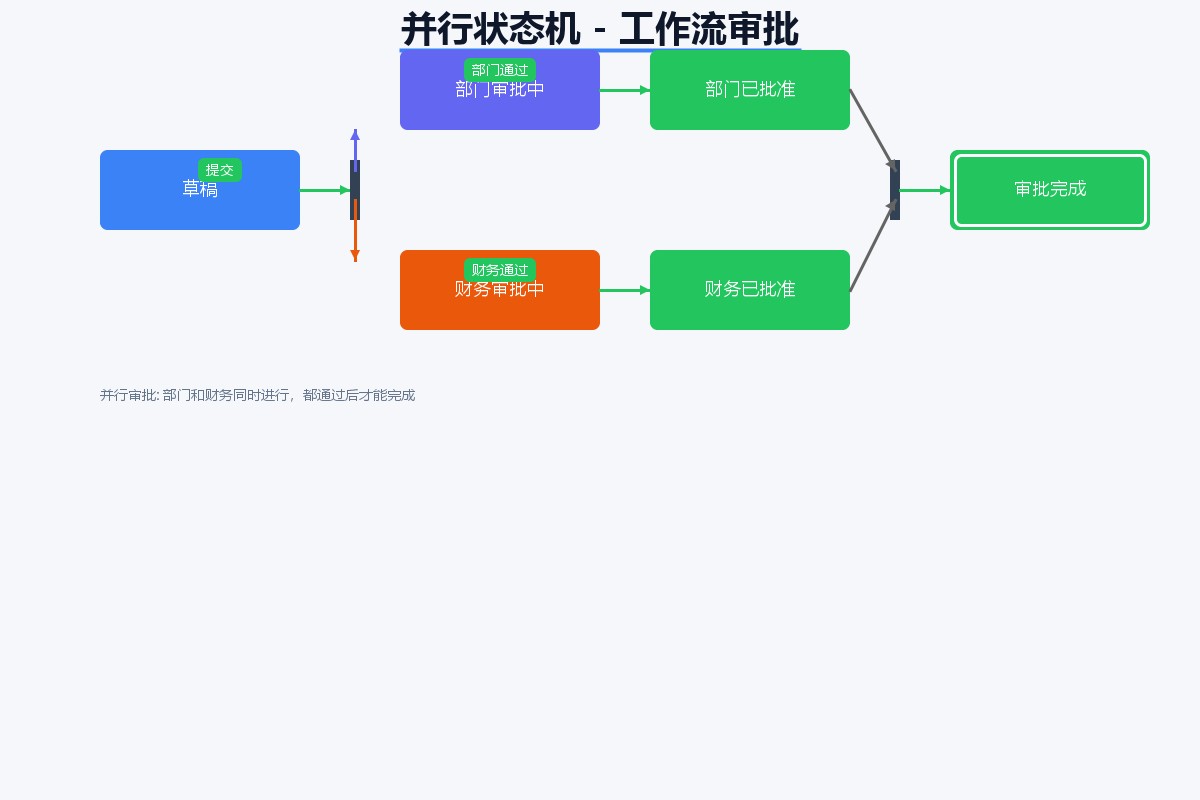
让我们看一个更复杂的例子——审批工作流系统:
// 支持并行审批的复杂状态机
@configuration
@enablestatemachine(name = "workflowstatemachine")
public class workflowstatemachineconfig
extends enumstatemachineconfigureradapter<workflowstate, workflowevent> {
@override
public void configure(statemachinestateconfigurer<workflowstate, workflowevent> states)
throws exception {
states
.withstates()
.initial(workflowstate.draft)
.fork(workflowstate.fork)
.join(workflowstate.join)
.state(workflowstate.finished)
.and()
.withstates()
.parent(workflowstate.fork)
.initial(workflowstate.dept_approval)
.state(workflowstate.dept_approved)
.and()
.withstates()
.parent(workflowstate.fork)
.initial(workflowstate.finance_approval)
.state(workflowstate.finance_approved);
}
@override
public void configure(statemachinetransitionconfigurer<workflowstate, workflowevent> transitions)
throws exception {
transitions
// 提交到并行审批
.withexternal()
.source(workflowstate.draft)
.target(workflowstate.fork)
.event(workflowevent.submit)
// 部门审批分支
.and()
.withexternal()
.source(workflowstate.dept_approval)
.target(workflowstate.dept_approved)
.event(workflowevent.dept_approve)
// 财务审批分支
.and()
.withexternal()
.source(workflowstate.finance_approval)
.target(workflowstate.finance_approved)
.event(workflowevent.finance_approve)
// 合并后完成
.and()
.withexternal()
.source(workflowstate.join)
.target(workflowstate.finished)
.event(workflowevent.complete);
}
}
四、状态监听器:记录每一次变化
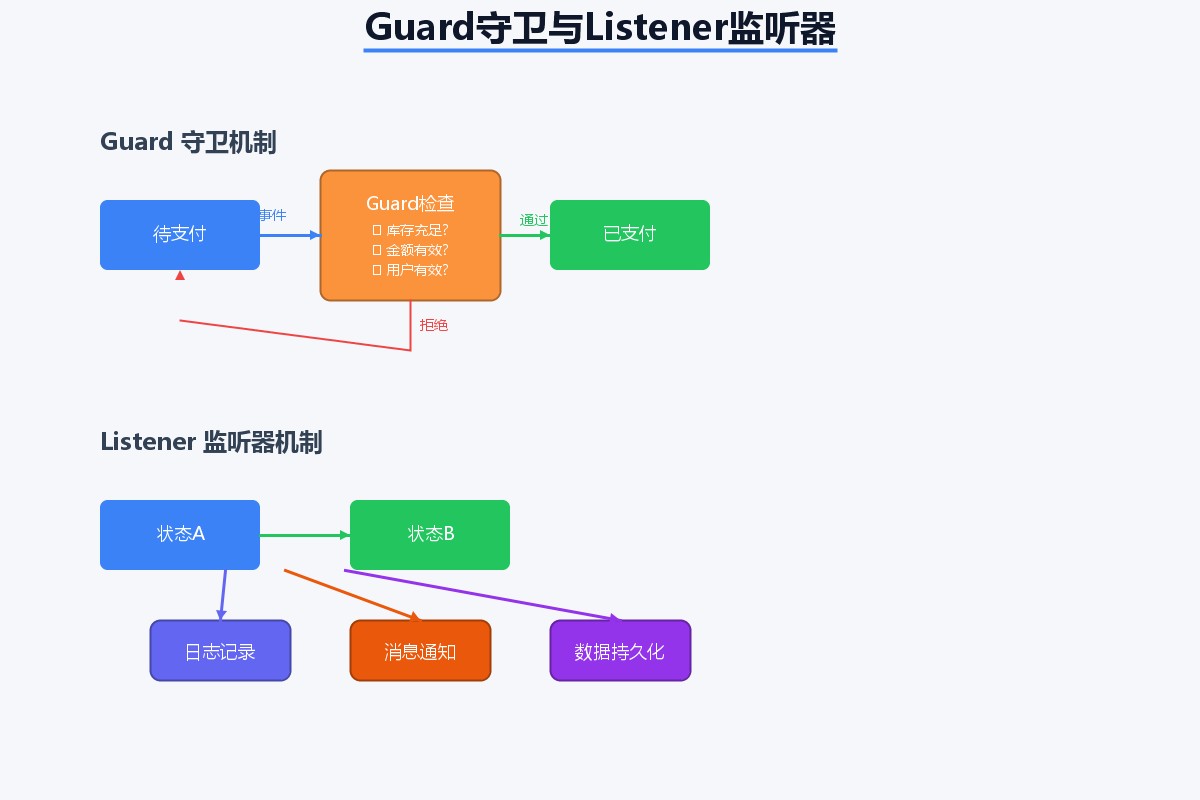
@withstatemachine
public class orderstatelistener {
private static final logger log = loggerfactory.getlogger(orderstatelistener.class);
@ontransition(target = "paid")
public void onpay(message<orderevent> message) {
string orderid = getheader(message, "orderid");
log.info("订单{}支付成功,状态流转到已支付", orderid);
// 触发后续业务逻辑
paymentsuccesshandler.handle(orderid);
}
@ontransition(target = "delivered")
public void ondeliver(message<orderevent> message) {
string orderid = getheader(message, "orderid");
log.info("订单{}已发货,状态流转到已发货", orderid);
// 发送短信通知
smsservice.senddeliverysms(orderid);
}
@ontransitionend
public void ontransitionend(statecontext<orderstatus, orderevent> context) {
log.info("状态转换完成:{} -> {}, 事件:{}",
context.getsource().getid(),
context.gettarget().getid(),
context.getevent()
);
// 持久化状态转换记录
transitionlogservice.log(context);
}
private string getheader(message<orderevent> message, string headername) {
return message.getheaders().get(headername, string.class);
}
}
五、guards:智能的状态转换守卫
@component
public class orderguard {
@bean
public guard<orderstatus, orderevent> payguard() {
return context -> {
string orderid = context.getmessageheader("orderid");
bigdecimal amount = orderservice.getorderamount(orderid);
// 检查订单金额
if (amount.compareto(bigdecimal.zero) <= 0) {
log.warn("订单{}支付失败:金额为0", orderid);
return false;
}
// 检查库存
boolean hasstock = inventoryservice.checkstock(orderid);
if (!hasstock) {
log.warn("订单{}支付失败:库存不足", orderid);
return false;
}
return true;
};
}
}
// 在状态机配置中使用guard
@override
public void configure(statemachinetransitionconfigurer<orderstatus, orderevent> transitions)
throws exception {
transitions
.withexternal()
.source(orderstatus.wait_payment)
.target(orderstatus.paid)
.event(orderevent.pay)
.guard(payguard()); // 添加守卫条件
}
六、实战技巧与最佳实践
6.1 状态机可视化
@requestmapping("/state-machine")
public class statemachinevisualcontroller {
@getmapping("/diagram/{orderid}")
public responseentity<string> getstatediagram(@pathvariable string orderid) {
// 获取当前状态
orderstatus currentstatus = orderservice.getorderstatus(orderid);
// 生成plantuml格式的状态图
string diagram = generateplantumldiagram(currentstatus);
return responseentity.ok()
.contenttype(mediatype.text_plain)
.body(diagram);
}
private string generateplantumldiagram(orderstatus currentstatus) {
stringbuilder sb = new stringbuilder();
sb.append("@startuml\n");
sb.append("[*] --> wait_payment\n");
sb.append("wait_payment --> paid : pay\n");
sb.append("paid --> wait_deliver : deliver\n");
sb.append("wait_deliver --> delivered : receive\n");
sb.append("delivered --> completed : receive\n");
// 高亮当前状态
sb.append("skinparam state {\n");
sb.append(" backgroundcolor<<current>> lightblue\n");
sb.append("}\n");
sb.append("state ").append(currentstatus).append(" <<current>>\n");
sb.append("@enduml\n");
return sb.tostring();
}
}
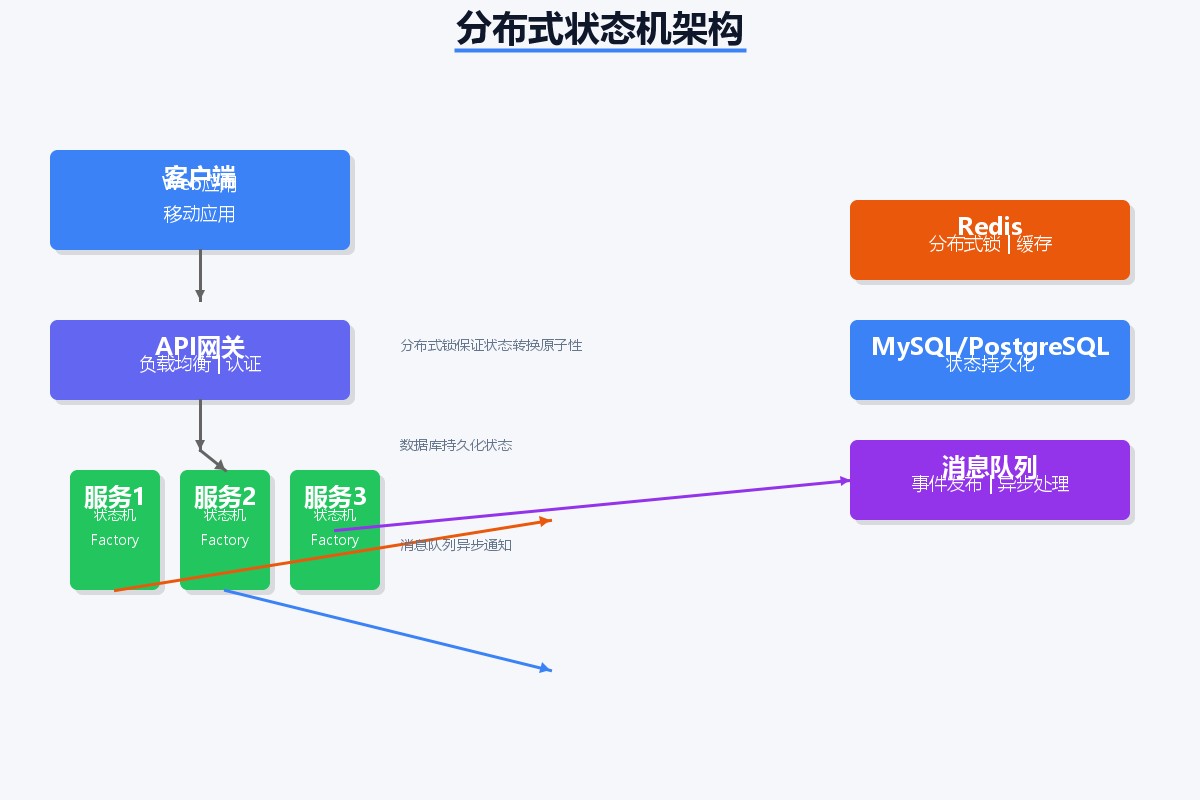
6.2 分布式状态一致性

// 使用分布式锁确保状态转换的原子性
@service
public class distributedorderservice {
private final redissonclient redisson;
private final statemachinefactory<orderstatus, orderevent> factory;
public boolean transition(string orderid, orderevent event) {
rlock lock = redisson.getlock("order:state:" + orderid);
try {
// 最多等待3秒,持锁10秒
if (lock.trylock(3, 10, timeunit.seconds)) {
// 恢复状态机
statemachine<orderstatus, orderevent> sm = restorestatemachine(orderid);
// 发送事件并处理结果
boolean result = sm.sendevent(event);
if (result) {
// 持久化新状态
persiststatemachine(orderid, sm);
// 发布领域事件
publishdomainevent(orderid, event, sm.getstate().getid());
}
return result;
}
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
thread.currentthread().interrupt();
throw new runtimeexception("状态转换被中断", e);
} finally {
if (lock.isheldbycurrentthread()) {
lock.unlock();
}
}
return false;
}
}
七、性能优化建议
- 状态机缓存:频繁使用的状态机实例可以缓存,避免重复创建
- 异步事件处理:使用spring的事件驱动模型异步处理状态变化
- 批量持久化:多个状态变化可以合并为一次数据库操作
- 读写分离:状态查询走从库,状态更新走主库
八、总结
spring状态机的优势在于:
- 代码清晰:将复杂的状态流转从业务代码中分离
- 易于维护:状态转换规则集中管理
- 可测试性强:可以单独测试状态机逻辑
- 生产就绪:支持持久化、监听、分布式等高级特性
当你的业务涉及复杂的状态流转时,spring状态机绝对是你的得力助手。它让状态管理变得优雅,让代码更容易理解和维护。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。






发表评论