在编程中,尤其是在网络通信、文件读写等场景下,经常需要将基本数据类型(如int、long、double等)转换为字节数组(byte array),或者从字节数组中恢复基本数据类型。本文将详细介绍java中如何实现这些转换。
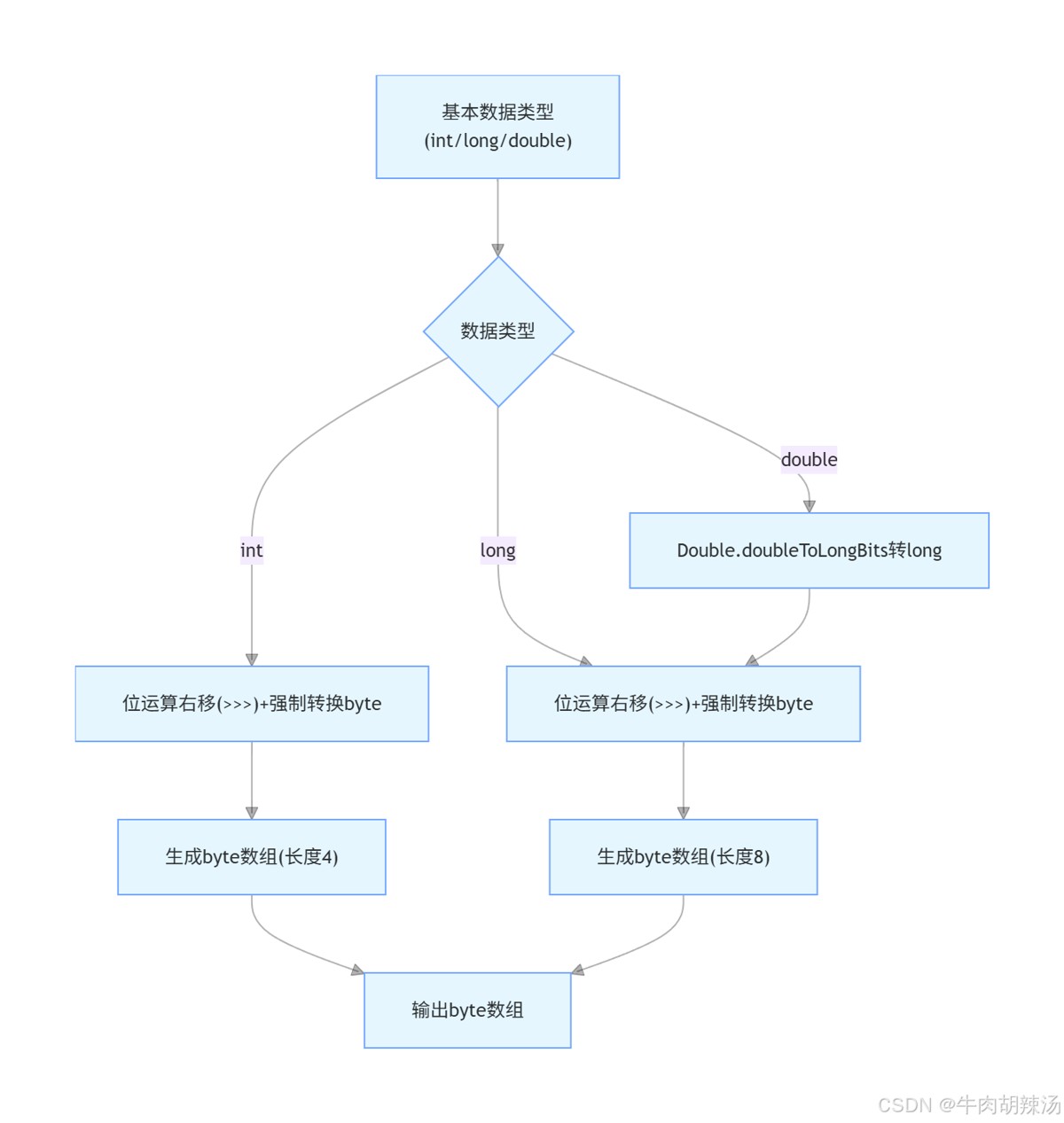
1. 基本数据类型转byte数组
1.1 int转byte数组
将一个int类型的值转换为byte数组,可以使用位运算来实现:
public static byte[] inttobytes(int value) {
return new byte[]{
(byte) (value >>> 24),
(byte) (value >>> 16),
(byte) (value >>> 8),
(byte) value
};
}1.2 long转byte数组
将一个long类型的值转换为byte数组,同样可以使用位运算:
public static byte[] longtobytes(long value) {
return new byte[]{
(byte) (value >>> 56),
(byte) (value >>> 48),
(byte) (value >>> 40),
(byte) (value >>> 32),
(byte) (value >>> 24),
(byte) (value >>> 16),
(byte) (value >>> 8),
(byte) value
};
}1.3 double转byte数组
将一个double类型的值转换为byte数组,可以先将其转换为long,然后再使用上述方法:
public static byte[] doubletobytes(double value) {
long longvalue = double.doubletolongbits(value);
return longtobytes(longvalue);
}2. byte数组转基本数据类型
2.1 byte数组转int
将一个byte数组转换为int类型的值,可以使用位运算和移位操作:
public static int bytestoint(byte[] bytes) {
return (bytes[0] << 24) |
(bytes[1] << 16) |
(bytes[2] << 8) |
(bytes[3]);
}2.2 byte数组转long
将一个byte数组转换为long类型的值,同样可以使用位运算和移位操作:
public static long bytestolong(byte[] bytes) {
return ((long) bytes[0] << 56) |
((long) bytes[1] << 48) |
((long) bytes[2] << 40) |
((long) bytes[3] << 32) |
((long) bytes[4] << 24) |
((long) bytes[5] << 16) |
((long) bytes[6] << 8) |
((long) bytes[7]);
}2.3 byte数组转double
将一个byte数组转换为double类型的值,可以先将其转换为long,然后再使用double.longbitstodouble方法:
public static double bytestodouble(byte[] bytes) {
long longvalue = bytestolong(bytes);
return double.longbitstodouble(longvalue);
}3. 示例代码
以下是一个完整的示例代码,展示了如何使用上述方法进行基本数据类型和byte数组之间的转换:
public class datatypeconversion {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// int to byte array
int intvalue = 123456;
byte[] intbytes = inttobytes(intvalue);
system.out.println("int to byte array: " + bytestohex(intbytes));
// byte array to int
int intvaluefrombytes = bytestoint(intbytes);
system.out.println("byte array to int: " + intvaluefrombytes);
// long to byte array
long longvalue = 1234567890123456789l;
byte[] longbytes = longtobytes(longvalue);
system.out.println("long to byte array: " + bytestohex(longbytes));
// byte array to long
long longvaluefrombytes = bytestolong(longbytes);
system.out.println("byte array to long: " + longvaluefrombytes);
// double to byte array
double doublevalue = 123.456;
byte[] doublebytes = doubletobytes(doublevalue);
system.out.println("double to byte array: " + bytestohex(doublebytes));
// byte array to double
double doublevaluefrombytes = bytestodouble(doublebytes);
system.out.println("byte array to double: " + doublevaluefrombytes);
}
public static byte[] inttobytes(int value) {
return new byte[]{
(byte) (value >>> 24),
(byte) (value >>> 16),
(byte) (value >>> 8),
(byte) value
};
}
public static byte[] longtobytes(long value) {
return new byte[]{
(byte) (value >>> 56),
(byte) (value >>> 48),
(byte) (value >>> 40),
(byte) (value >>> 32),
(byte) (value >>> 24),
(byte) (value >>> 16),
(byte) (value >>> 8),
(byte) value
};
}
public static byte[] doubletobytes(double value) {
long longvalue = double.doubletolongbits(value);
return longtobytes(longvalue);
}
public static int bytestoint(byte[] bytes) {
return (bytes[0] << 24) |
(bytes[1] << 16) |
(bytes[2] << 8) |
(bytes[3]);
}
public static long bytestolong(byte[] bytes) {
return ((long) bytes[0] << 56) |
((long) bytes[1] << 48) |
((long) bytes[2] << 40) |
((long) bytes[3] << 32) |
((long) bytes[4] << 24) |
((long) bytes[5] << 16) |
((long) bytes[6] << 8) |
((long) bytes[7]);
}
public static double bytestodouble(byte[] bytes) {
long longvalue = bytestolong(bytes);
return double.longbitstodouble(longvalue);
}
public static string bytestohex(byte[] bytes) {
stringbuilder hexstring = new stringbuilder();
for (byte b : bytes) {
string hex = integer.tohexstring(0xff & b);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
hexstring.append('0');
}
hexstring.append(hex);
}
return hexstring.tostring();
}
}以上是关于基本数据类型与byte数组相互转化的技术博客文章。希望对你有所帮助!
4.方法补充
在java中,基本数据类型(如int、float、double等)和byte数组之间的转换是常见的需求,尤其是在网络通信、文件读写等场景中。下面我将分别给出几个示例,展示如何将基本数据类型转换为byte数组,以及如何从byte数组恢复基本数据类型。
1. int 和 byte[] 的转换
int 转换为 byte[]
public class inttobytearray {
public static void main(string[] args) {
int number = 123456789;
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
// 将int转换为byte数组
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
bytes[i] = (byte) ((number >> (i * 8)) & 0xff);
}
system.out.println("byte array: " + arrays.tostring(bytes));
}
}byte[] 转换为 int
public class bytearraytoint {
public static void main(string[] args) {
byte[] bytes = { -86, 46, -42, 77 }; // 这个数组是从上面的例子得到的
int number = 0;
// 将byte数组转换为int
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
number |= (bytes[i] & 0xff) << (i * 8);
}
system.out.println("number: " + number);
}
}2. float 和 byte[] 的转换
float 转换为 byte[]
public class floattobytearray {
public static void main(string[] args) {
float number = 3.14f;
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
// 将float转换为byte数组
bytebuffer buffer = bytebuffer.allocate(4);
buffer.putfloat(number);
buffer.flip(); // 翻转缓冲区
buffer.get(bytes);
system.out.println("byte array: " + arrays.tostring(bytes));
}
}byte[] 转换为 float
public class bytearraytofloat {
public static void main(string[] args) {
byte[] bytes = { 64, 9, 21, 115 }; // 这个数组是从上面的例子得到的
float number = 0.0f;
// 将byte数组转换为float
bytebuffer buffer = bytebuffer.wrap(bytes);
number = buffer.getfloat();
system.out.println("number: " + number);
}
}3. double 和 byte[] 的转换
double 转换为 byte[]
public class doubletobytearray {
public static void main(string[] args) {
double number = 3.141592653589793;
byte[] bytes = new byte[8];
// 将double转换为byte数组
bytebuffer buffer = bytebuffer.allocate(8);
buffer.putdouble(number);
buffer.flip(); // 翻转缓冲区
buffer.get(bytes);
system.out.println("byte array: " + arrays.tostring(bytes));
}
}byte[] 转换为 double
public class bytearraytodouble {
public static void main(string[] args) {
byte[] bytes = { 64, 9, 21, 115, -31, -11, -10, -21 }; // 这个数组是从上面的例子得到的
double number = 0.0;
// 将byte数组转换为double
bytebuffer buffer = bytebuffer.wrap(bytes);
number = buffer.getdouble();
system.out.println("number: " + number);
}
}在java中,基本数据类型(如int, double, char, boolean等)和byte[]之间的转换是一个常见的需求,尤其是在处理网络通信、文件读写或加密解密时。下面将详细介绍如何在java中实现这些转换。
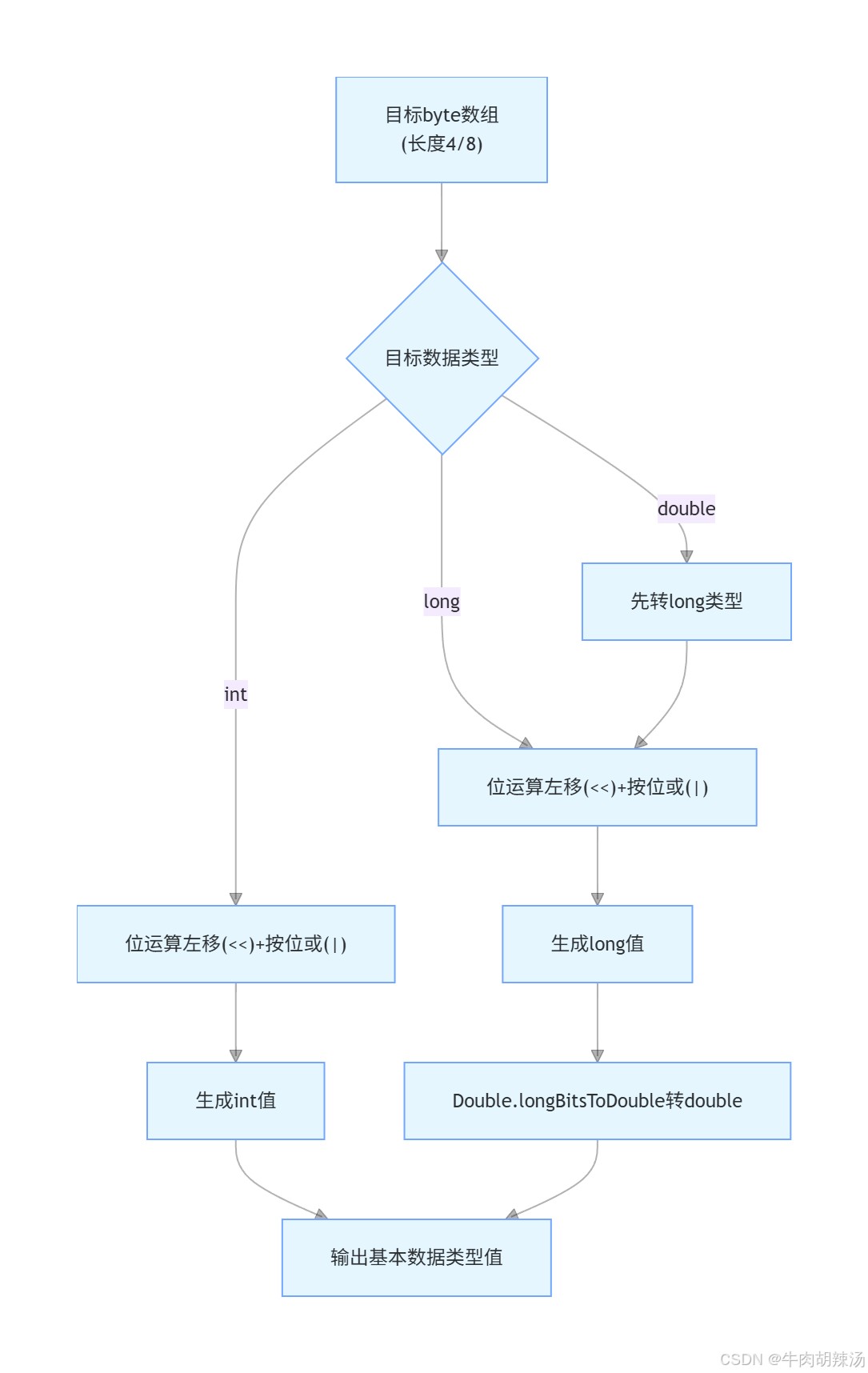
1. 基本数据类型转 byte[]
1.1 int 转 byte[]
public static byte[] inttobytearray(int value) {
return new byte[] {
(byte)((value >> 24) & 0xff),
(byte)((value >> 16) & 0xff),
(byte)((value >> 8) & 0xff),
(byte)(value & 0xff)
};
}1.2 long 转 byte[]
public static byte[] longtobytearray(long value) {
return new byte[] {
(byte)((value >> 56) & 0xff),
(byte)((value >> 48) & 0xff),
(byte)((value >> 40) & 0xff),
(byte)((value >> 32) & 0xff),
(byte)((value >> 24) & 0xff),
(byte)((value >> 16) & 0xff),
(byte)((value >> 8) & 0xff),
(byte)(value & 0xff)
};
}1.3 float 转 byte[]
public static byte[] floattobytearray(float value) {
return inttobytearray(float.floattointbits(value));
}1.4 double 转 byte[]
public static byte[] doubletobytearray(double value) {
return longtobytearray(double.doubletolongbits(value));
}1.5 char 转 byte[]
public static byte[] chartobytearray(char value) {
return new byte[] {
(byte)((value >> 8) & 0xff),
(byte)(value & 0xff)
};
}1.6 boolean 转 byte[]
public static byte[] booleantobytearray(boolean value) {
return new byte[] { (byte)(value ? 1 : 0) };
}2. byte[] 转基本数据类型
2.1 byte[] 转 int
public static int bytearraytoint(byte[] bytes) {
return (bytes[0] & 0xff) << 24 |
(bytes[1] & 0xff) << 16 |
(bytes[2] & 0xff) << 8 |
(bytes[3] & 0xff);
}2.2 byte[] 转 long
public static long bytearraytolong(byte[] bytes) {
return (bytes[0] & 0xffl) << 56 |
(bytes[1] & 0xffl) << 48 |
(bytes[2] & 0xffl) << 40 |
(bytes[3] & 0xffl) << 32 |
(bytes[4] & 0xffl) << 24 |
(bytes[5] & 0xffl) << 16 |
(bytes[6] & 0xffl) << 8 |
(bytes[7] & 0xffl);
}2.3 byte[] 转 float
public static float bytearraytofloat(byte[] bytes) {
return float.intbitstofloat(bytearraytoint(bytes));
}2.4 byte[] 转 double
public static double bytearraytodouble(byte[] bytes) {
return double.longbitstodouble(bytearraytolong(bytes));
}2.5 byte[] 转 char
public static char bytearraytochar(byte[] bytes) {
return (char)(((bytes[0] & 0xff) << 8) | (bytes[1] & 0xff));
}2.6 byte[] 转 boolean
public static boolean bytearraytoboolean(byte[] bytes) {
return bytes[0] != 0;
}3. 使用 bytebuffer 进行转换
java的bytebuffer类提供了更方便的方法来进行基本数据类型和byte[]之间的转换。以下是一些示例:
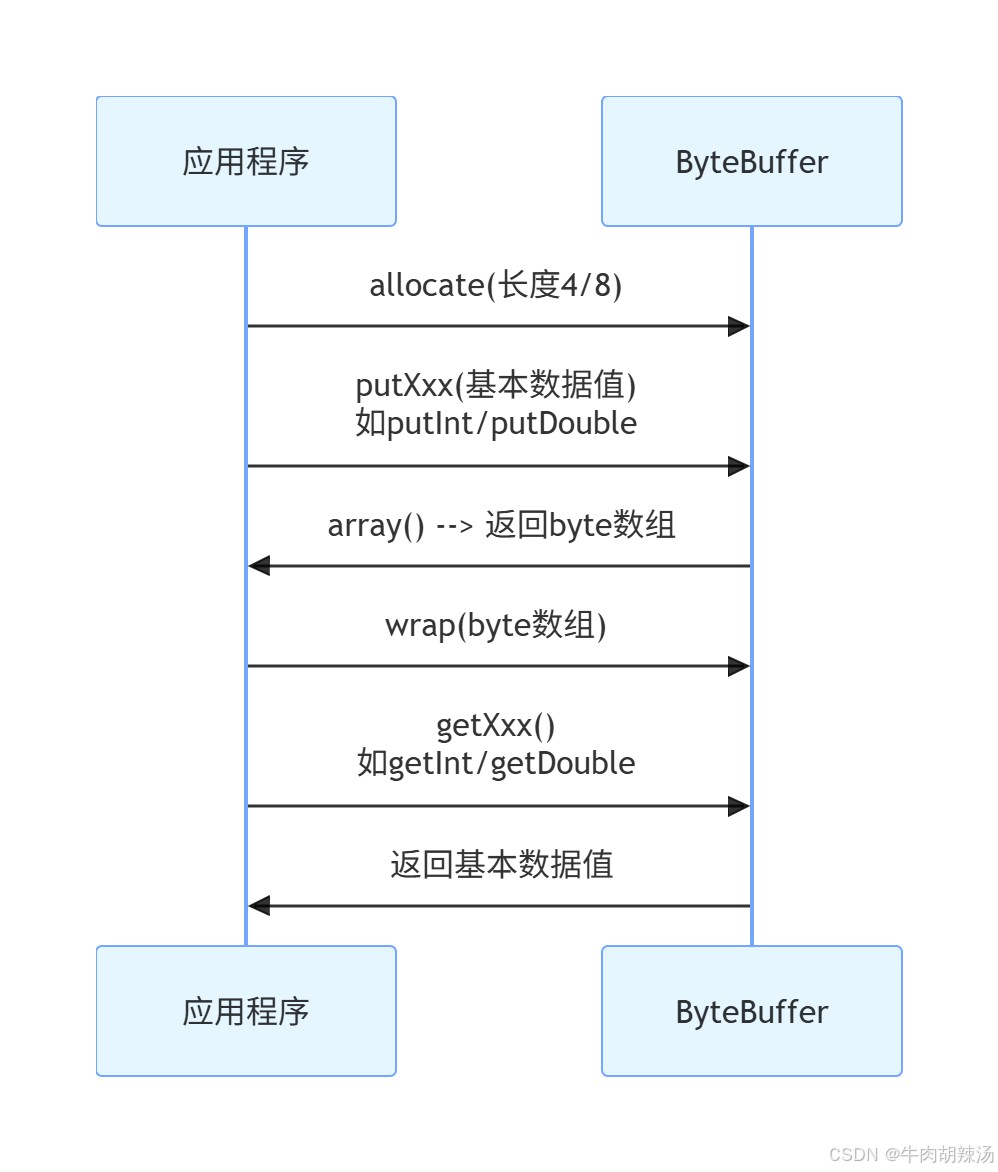
3.1 int 转 byte[]
import java.nio.bytebuffer;
public static byte[] inttobytearray(int value) {
return bytebuffer.allocate(4).putint(value).array();
}3.2 byte[] 转 int
public static int bytearraytoint(byte[] bytes) {
return bytebuffer.wrap(bytes).getint();
}3.3 double 转 byte[]
public static byte[] doubletobytearray(double value) {
return bytebuffer.allocate(8).putdouble(value).array();
}3.4 byte[] 转 double
public static double bytearraytodouble(byte[] bytes) {
return bytebuffer.wrap(bytes).getdouble();
}4. 注意事项
字节序:上述示例默认使用大端字节序(big-endian)。如果需要小端字节序(little-endian),可以在bytebuffer中调用order(byteorder.little_endian)方法。
异常处理:在实际应用中,建议添加异常处理,以应对可能的输入错误或异常情况。
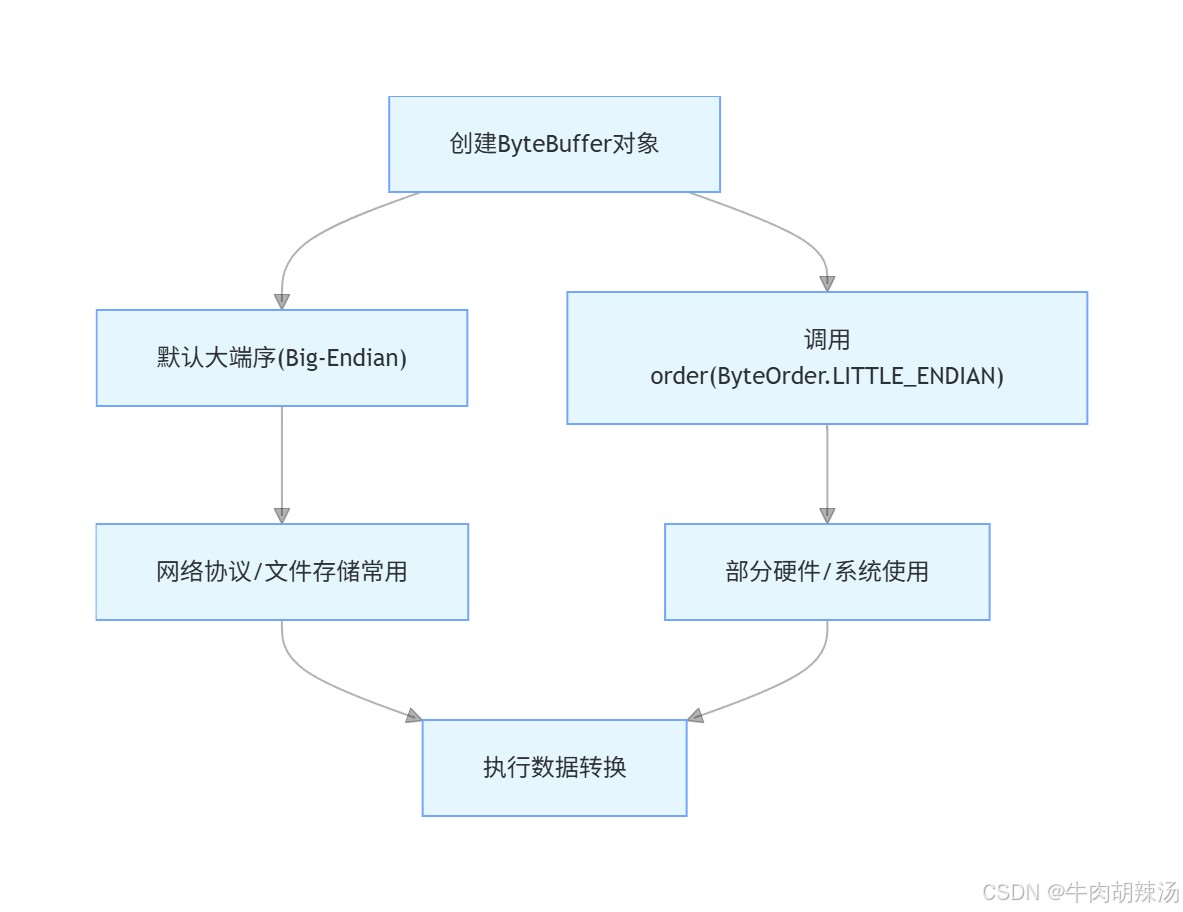
通过这些方法,你可以在java中轻松地进行基本数据类型和byte[]之间的转换。希望这些示例对你有所帮助!
以上就是java实现基本数据类型与byte数组相互转换的详细内容,更多关于java数据类型转byte数组的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!




发表评论