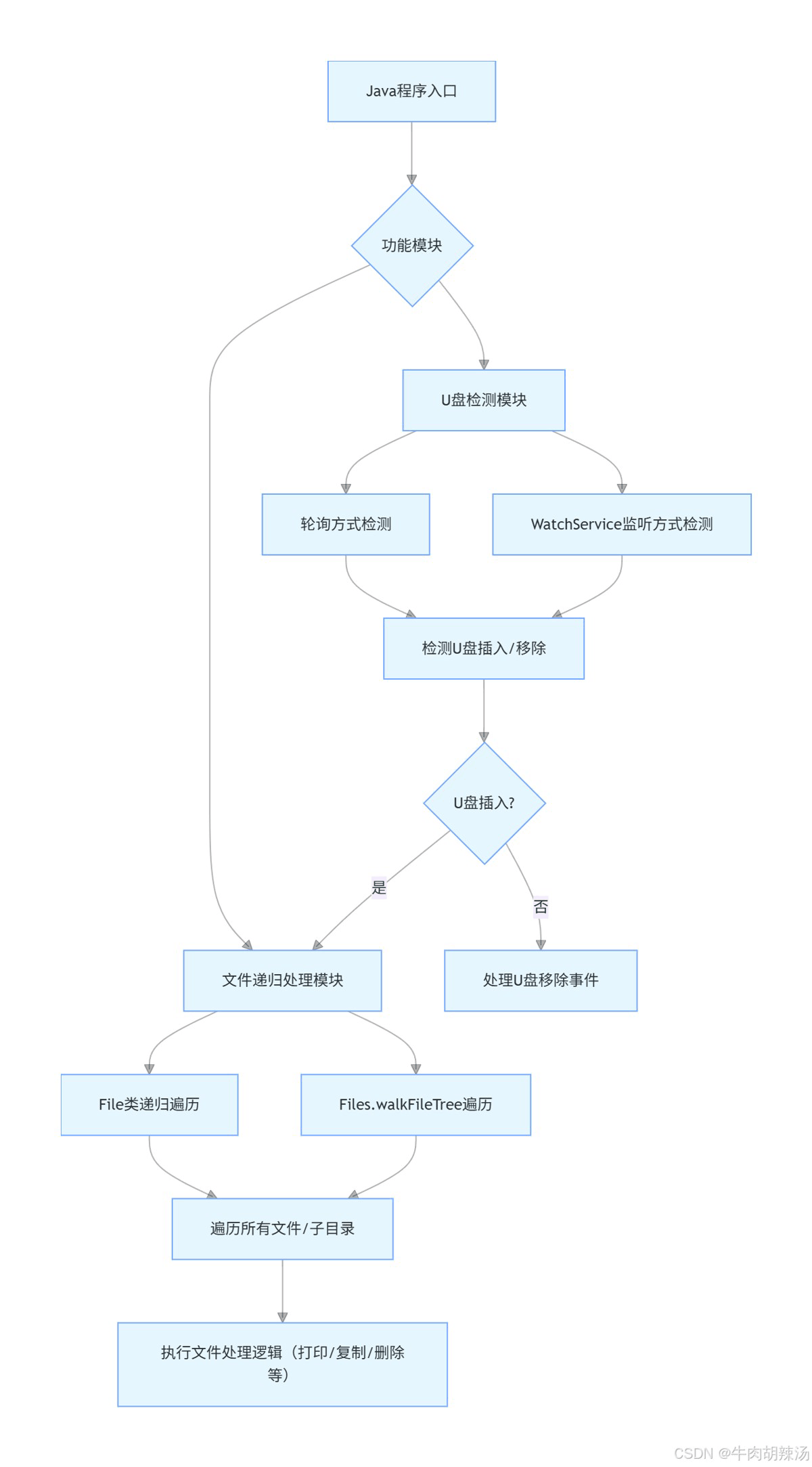
在现代计算机系统中,u盘的使用非常普遍,无论是数据传输还是备份。然而,如何在java程序中实现对u盘的插入和移除进行检测,并对u盘中的文件进行递归处理呢?本文将详细介绍这一过程。
1. 环境准备
首先,确保你的开发环境已经安装了jdk(java development kit),并配置好环境变量。此外,本示例将在windows环境下运行,但代码可以很容易地移植到其他操作系统上。
2. u盘检测
2.1 监听u盘事件
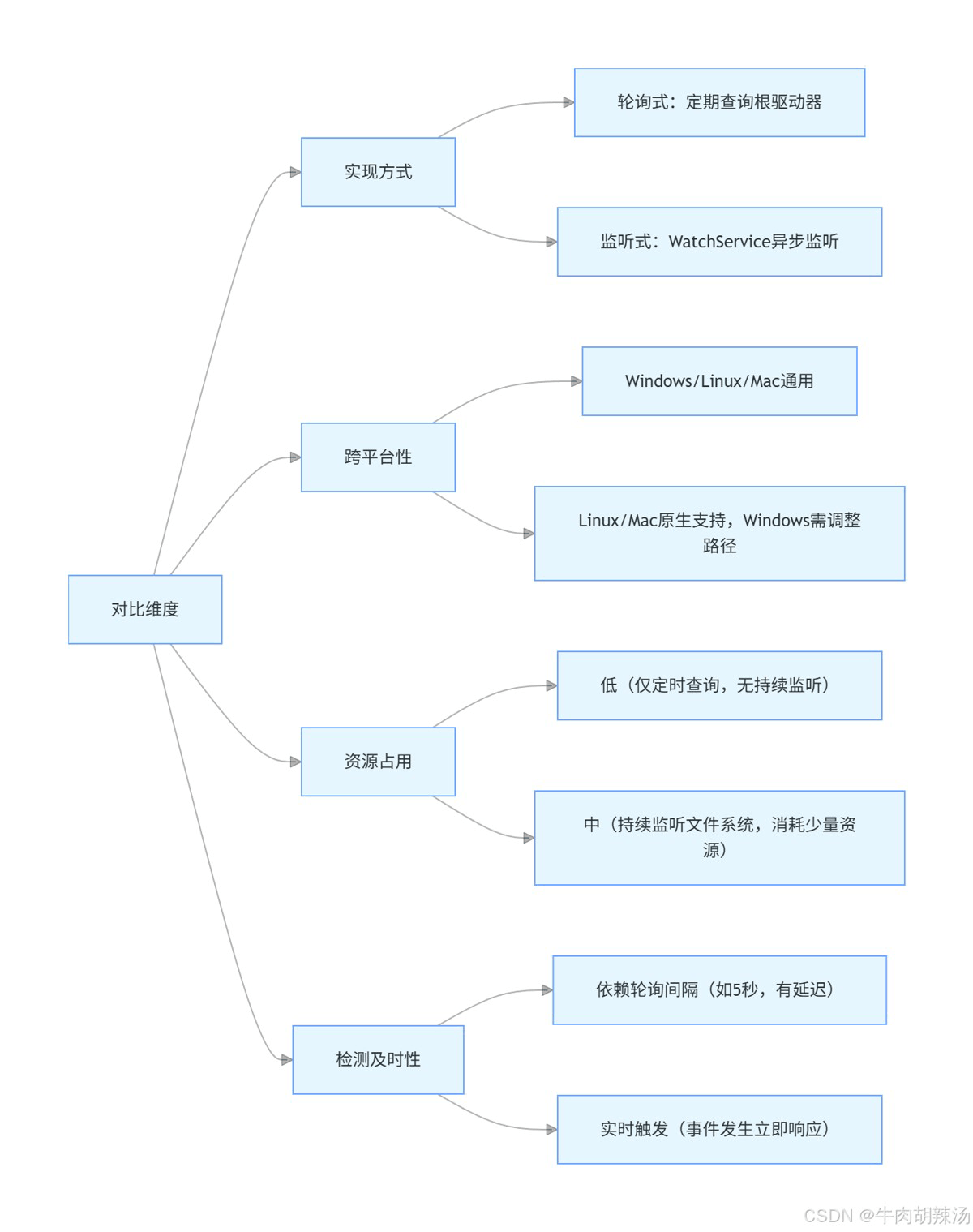
java本身并没有直接提供u盘插入或移除的监听接口,但我们可以通过轮询的方式来实现这一功能。下面是一个简单的示例,展示如何通过定时检查驱动器列表来判断u盘是否被 插入或移除。
获取当前所有驱动器
import java.io.file;
public class drivedetector {
public static list<string> getcurrentdrives() {
list<string> drives = new arraylist<>();
file[] roots = file.listroots();
for (file root : roots) {
drives.add(root.getabsolutepath());
}
return drives;
}
}检测u盘插入和移除
import java.util.list;
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.set;
import java.util.hashset;
public class usbmonitor {
private set<string> currentdrives = new hashset<>(drivedetector.getcurrentdrives());
public void checkusbchanges() {
list<string> newdrives = drivedetector.getcurrentdrives();
set<string> addeddrives = new hashset<>(newdrives);
addeddrives.removeall(currentdrives);
set<string> removeddrives = new hashset<>(currentdrives);
removeddrives.removeall(newdrives);
if (!addeddrives.isempty()) {
system.out.println("detected new usb drives: " + addeddrives);
// 这里可以添加处理新插入u盘的逻辑
}
if (!removeddrives.isempty()) {
system.out.println("detected removed usb drives: " + removeddrives);
// 这里可以添加处理u盘拔出的逻辑
}
currentdrives = new hashset<>(newdrives);
}
}2.2 定时任务
为了定期检查u盘状态,我们可以使用scheduledexecutorservice来创建一个定时任务。
import java.util.concurrent.executors;
import java.util.concurrent.scheduledexecutorservice;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
public class main {
public static void main(string[] args) {
scheduledexecutorservice executor = executors.newsinglethreadscheduledexecutor();
usbmonitor usbmonitor = new usbmonitor();
executor.scheduleatfixedrate(() -> usbmonitor.checkusbchanges(), 0, 5, timeunit.seconds);
}
}3. 文件递归处理
当检测到u盘插入后,我们可能需要遍历u盘中的文件,进行某些操作,如复制、删除等。下面是一个简单的文件递归遍历示例。
import java.io.file;
public class fileprocessor {
public void processfiles(file directory) {
if (directory.isdirectory()) {
file[] files = directory.listfiles();
if (files != null) {
for (file file : files) {
if (file.isdirectory()) {
processfiles(file); // 递归调用
} else {
// 处理文件
system.out.println("processing file: " + file.getabsolutepath());
}
}
}
}
}
}调用文件处理
在usbmonitor类中,当检测到新的u盘插入时,可以调用fileprocessor来处理u盘中的文件。
public class usbmonitor {
// ... 其他代码 ...
public void checkusbchanges() {
list<string> newdrives = drivedetector.getcurrentdrives();
set<string> addeddrives = new hashset<>(newdrives);
addeddrives.removeall(currentdrives);
if (!addeddrives.isempty()) {
system.out.println("detected new usb drives: " + addeddrives);
for (string drive : addeddrives) {
fileprocessor processor = new fileprocessor();
processor.processfiles(new file(drive));
}
}
// ... 其他代码 ...
}
}4.方法补充
下面我将提供一个简单的java程序示例,该程序能够检测u盘的插入和移除,并在u盘插入时递归地遍历u盘中的所有文件和目录。
1. u盘检测
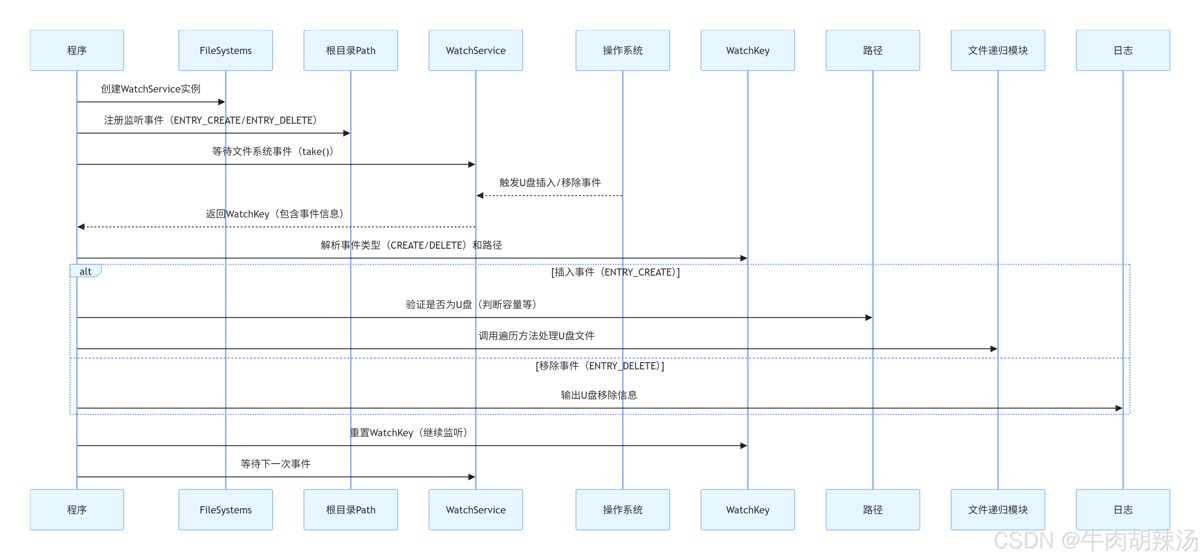
首先,我们需要一个方法来检测u盘的插入和移除。这可以通过监听文件系统的变更来实现。java 7 引入了 watchservice api,可以用来监控文件系统的变化。
2. 文件递归遍历
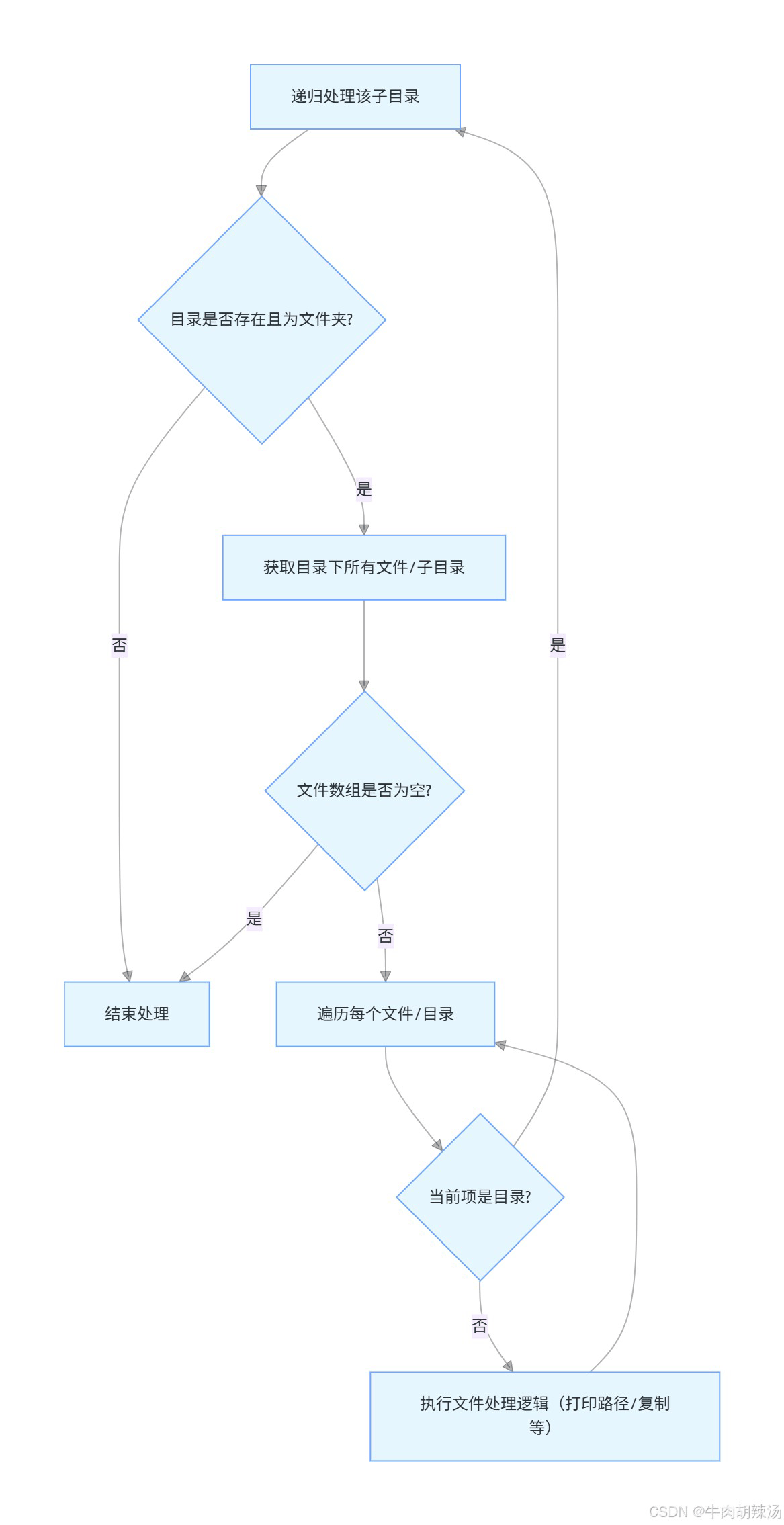
接下来,我们需要一个方法来递归地遍历u盘中的所有文件和目录。
示例代码
import java.io.file;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.nio.file.attribute.basicfileattributes;
import static java.nio.file.standardwatcheventkinds.*;
public class usbdrivemonitor {
public static void main(string[] args) {
try {
// 创建watchservice实例
watchservice watchservice = filesystems.getdefault().newwatchservice();
// 注册根目录以监视u盘的插入和移除
path rootpath = paths.get("/");
rootpath.register(watchservice, entry_create, entry_delete);
system.out.println("usb drive monitor started. waiting for events...");
while (true) {
// 等待事件
watchkey key = watchservice.take();
for (watchevent<?> event : key.pollevents()) {
watchevent.kind<?> kind = event.kind();
if (kind == overflow) {
continue;
}
// 获取事件类型和路径
path name = (path) event.context();
path child = rootpath.resolve(name);
if (kind == entry_create) {
system.out.println("usb drive inserted: " + child);
// 检查是否为u盘
if (isusbdrive(child)) {
// 递归遍历u盘中的文件
traversedirectory(child);
}
} else if (kind == entry_delete) {
system.out.println("usb drive removed: " + child);
}
}
// 重置watchkey
boolean valid = key.reset();
if (!valid) {
break;
}
}
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
private static boolean isusbdrive(path path) {
// 这里可以根据实际情况判断是否为u盘
// 例如,u盘通常有一个较小的总大小
try {
filestore filestore = files.getfilestore(path);
long totalspace = filestore.gettotalspace();
return totalspace < 100 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024; // 小于100gb
} catch (exception e) {
return false;
}
}
private static void traversedirectory(path path) throws exception {
files.walkfiletree(path, new simplefilevisitor<path>() {
@override
public filevisitresult visitfile(path file, basicfileattributes attrs) throws ioexception {
system.out.println("file: " + file);
return filevisitresult.continue;
}
@override
public filevisitresult postvisitdirectory(path dir, ioexception exc) throws ioexception {
system.out.println("directory: " + dir);
return filevisitresult.continue;
}
});
}
}代码说明
watchservice:用于监听文件系统的变更。
注册根目录:我们注册根目录(/)以监听u盘的插入和移除事件。
事件处理:
-
entry_create:表示u盘插入。 -
entry_delete:表示u盘移除。
判断是否为u盘:通过检查文件系统的总大小来简单判断是否为u盘。
递归遍历:使用 files.walkfiletree 方法递归遍历u盘中的所有文件和目录。
注意事项
- 权限:确保你的应用程序有权限访问文件系统和u盘。
- 跨平台:上述代码在linux和macos上运行良好。如果你需要在windows上运行,可能需要调整路径和文件系统的处理方式。
- 性能:频繁的文件系统操作可能会对性能产生影响,特别是在处理大量文件时。
java u盘检测程序和文件递归处理是两个相对独立但又可以结合使用的功能。下面我将详细介绍这两个部分的实现方法,并提供相应的代码示例。
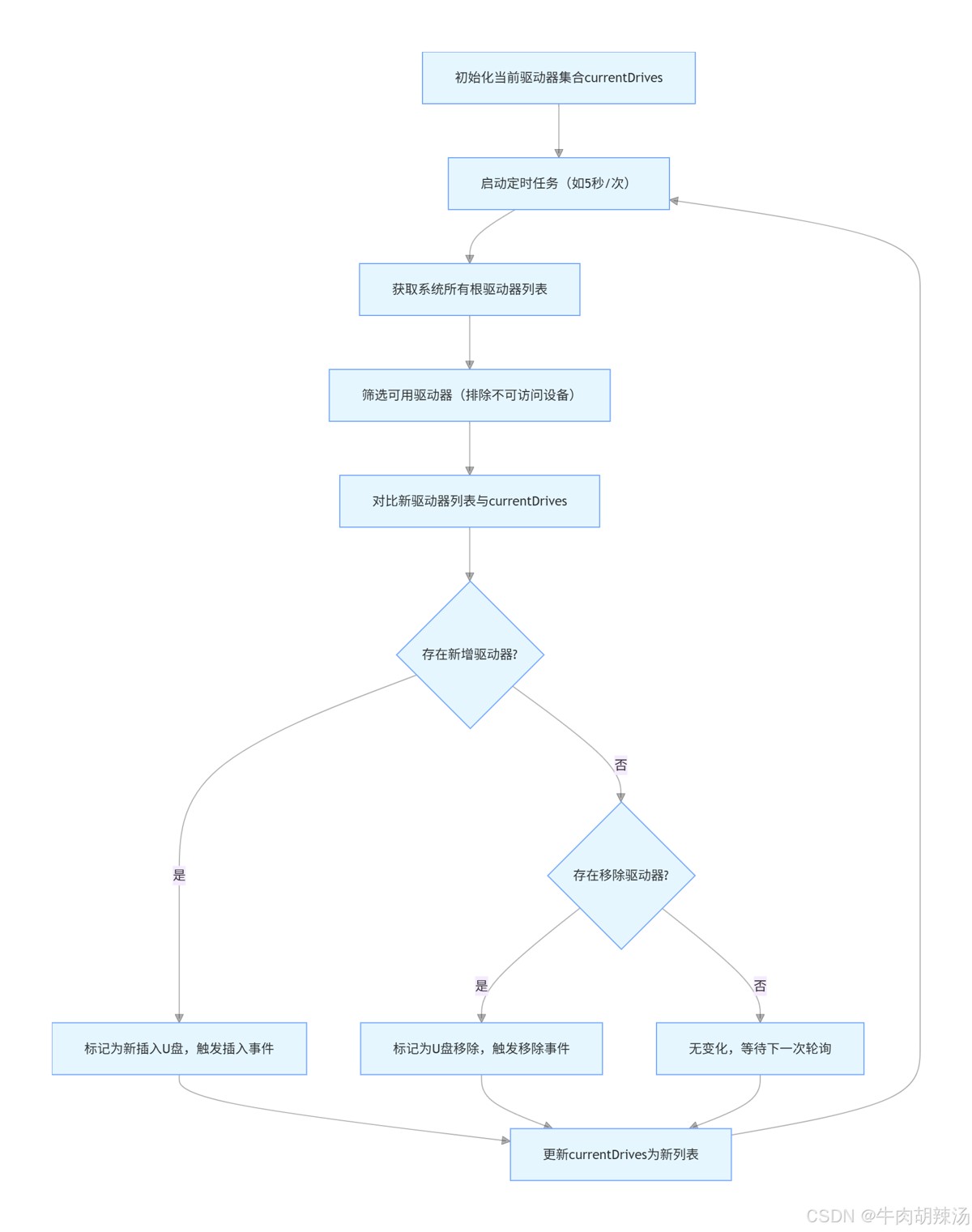
1. java u盘检测程序
在java中,检测u盘插入和移除可以通过监听文件系统的变动来实现。虽然java标准库没有直接提供这样的api,但我们可以通过一些间接的方法来实现这一功能。一个常见的方法是定期检查特定目录(如windows系统下的d:\, e:\等)是否存在新的驱动器。
示例代码:u盘检测
import java.io.file;
import java.util.hashset;
import java.util.set;
public class usbdrivedetector {
private set<string> currentdrives = new hashset<>();
public void startmonitoring() {
thread monitorthread = new thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
thread.sleep(5000); // 每5秒检查一次
checkforusbdrives();
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
});
monitorthread.start();
}
private void checkforusbdrives() {
file[] roots = file.listroots();
set<string> currentroots = new hashset<>();
for (file root : roots) {
if (root.gettotalspace() > 0) { // 确保驱动器是可用的
currentroots.add(root.getpath());
}
}
// 检测新插入的u盘
for (string drive : currentroots) {
if (!currentdrives.contains(drive)) {
system.out.println("u盘已插入: " + drive);
onusbinserted(drive);
}
}
// 检测移除的u盘
for (string drive : currentdrives) {
if (!currentroots.contains(drive)) {
system.out.println("u盘已移除: " + drive);
onusbremoved(drive);
}
}
currentdrives = currentroots;
}
private void onusbinserted(string drive) {
// 处理u盘插入事件
system.out.println("处理u盘插入事件: " + drive);
// 例如,启动文件递归处理
filerecursion.recursiveprocess(new file(drive));
}
private void onusbremoved(string drive) {
// 处理u盘移除事件
system.out.println("处理u盘移除事件: " + drive);
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
usbdrivedetector detector = new usbdrivedetector();
detector.startmonitoring();
}
}2. 文件递归处理
文件递归处理是指从某个目录开始,遍历该目录及其所有子目录中的文件,并对每个文件执行特定的操作。java提供了file类来处理文件和目录操作。
示例代码:文件递归处理
import java.io.file;
public class filerecursion {
public static void recursiveprocess(file directory) {
if (directory.exists() && directory.isdirectory()) {
file[] files = directory.listfiles();
if (files != null) {
for (file file : files) {
if (file.isdirectory()) {
recursiveprocess(file); // 递归处理子目录
} else {
processfile(file); // 处理文件
}
}
}
}
}
private static void processfile(file file) {
// 在这里处理文件,例如打印文件路径
system.out.println("处理文件: " + file.getabsolutepath());
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
file directory = new file("c:\\path\\to\\directory"); // 替换为实际目录路径
recursiveprocess(directory);
}
}结合使用
在上面的usbdrivedetector类中,当检测到u盘插入时,调用了filerecursion.recursiveprocess(new file(drive));方法来递归处理u盘中的文件。这样,当u盘插入时,程序会自动遍历u盘中的所有文件并进行处理。
总结
- u盘检测:通过定期检查系统根目录来检测u盘的插入和移除。
- 文件递归处理:从指定目录开始,递归遍历所有子目录和文件,并对每个文件执行特定的操作。
以上就是java实现u盘的插入和移除检测程序的详细内容,更多关于java u盘检测的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!







发表评论