一、快速入门
先说总结:如果你要在实体类的属性上加注解,那么你这俩注解都加上,啥问题都没有。
1.1、准备工作
定义一个pojo,它有两个 java.util.date 类型的属性 createdate和uploaddate。
现在属性上什么注解都没加,接着往下走看效果。
public class student{
private integer id;
private string name;
private date createdate;
private date uploaddate;
// 省略get和set方法
}
定义一个controller
@requestmapping("/student")
@restcontroller
public class studentcontroller {
@getmapping("/test")
public student test(student student) {
system.out.println("前端传来的日期:" + student.getcreatedate());
// 将前端传来的日期格式化
simpledateformat sdf = new simpledateformat("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss");
string date = sdf.format(student.getcreatedate());
system.out.println("格式化后的日期:"+date);
// 传一个当前日期给前端,想看看是什么格式的
student stu = new student();
stu.setcreatedate(new date());
return stu;
}
}
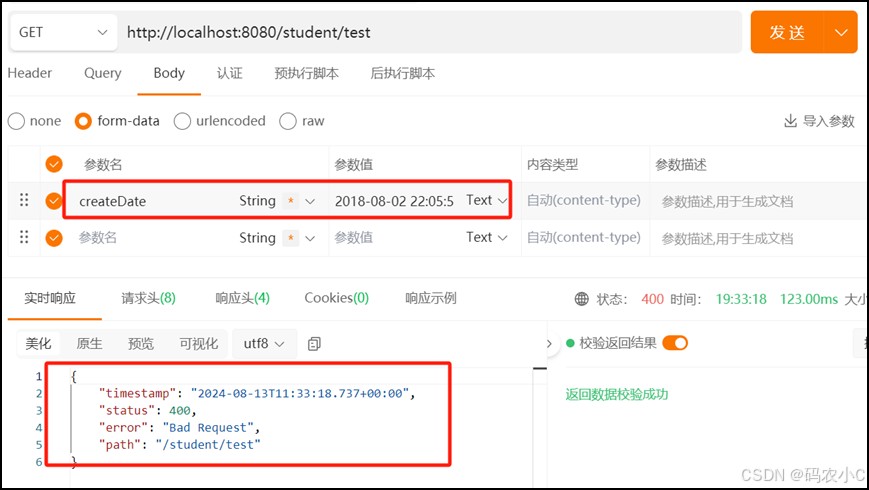
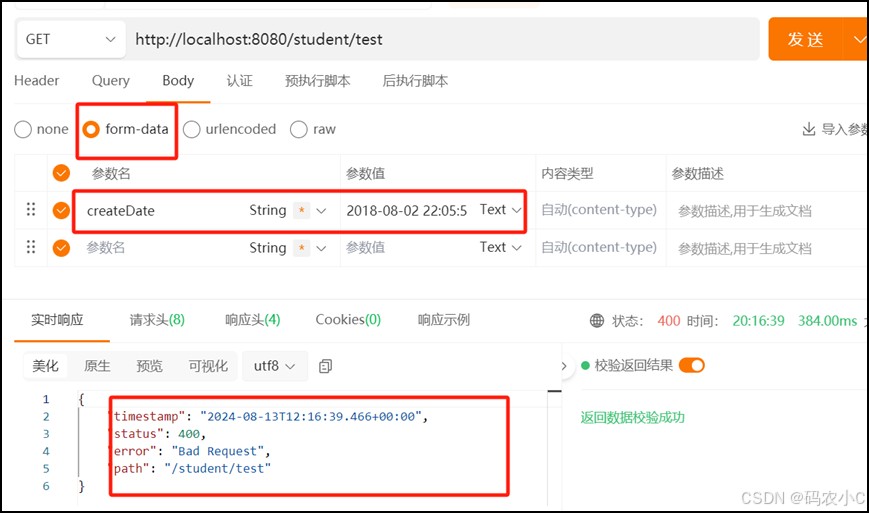
在apipost传参测试,访问 /student/test ,并传入参数:2018-08-02 22:05:55,发现并不能访问成功,会抛出400异常,因为传入的参数是 string 类型的,而用来接收参数的 datevo 的 date 属性是 java.util.date 类型的,类型无法转换。
怎么办呢?请往下看,也就是入参格式化。
1.2、入参格式化(前端传参到后端)
解决办法就是在接收参数的pojo类上的队友参数属性上加上注解:
@datetimeformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss")
加完之后的pojo类:
public class student{
private integer id;
private string name;
@datetimeformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss")
private date createdate;
private date uploaddate;
// 省略get和set方法
}
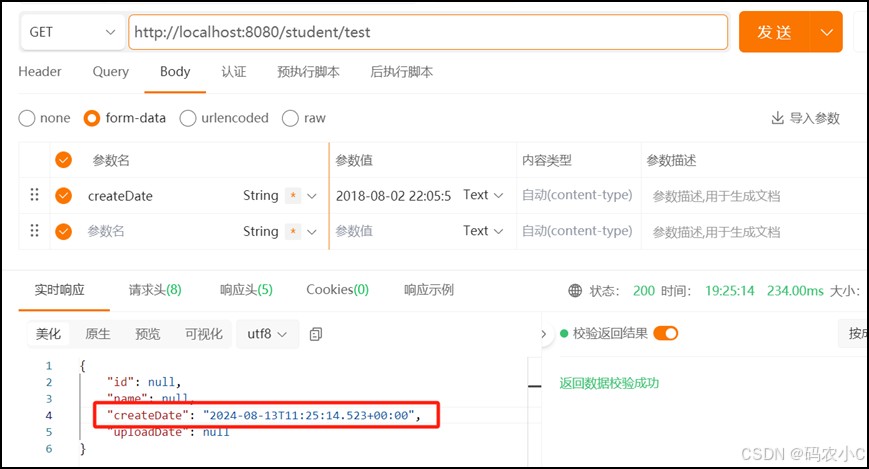
再测试,这样就能请求成功,后端就能接收前端传的参数了,结果如下:
控制台输出:
前端传来的日期:thu aug 02 22:05:55 cst 2018 格式化后的日期:2018-08-02 22:05:55
响应:
{
"id": null,
"name": null,
"createdate": "2024-08-13t11:37:59.022+00:00",
"uploaddate": null
}
请注意:
这样请求成功后,后端就能接收前端传的参数了,但后端接收到的日期时间的格式还是需要自己再手动转换一下。因为 @datetimeformat 注解的 pattern 属性值指定的日期时间格式并不是将要转换成的日期格式,这个指定的格式是和传入的参数对应的,假如注解为:
@datetimeformat(pattern="yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss")
则传入的参数应该是这样的:2018/08/02 22:05:55,如果传入2018/08/02就会抛出400异常。
1.3、出参格式化(后端返回给前端)
在上述示例中,调用接口的返回结果为:
{
"id": null,
"name": null,
"createdate": "2024-08-13t11:37:59.022+00:00",
"uploaddate": null
}
这个格式并不是我们想要的,那么如何将其进行格式化?这时就需要用到 jackson 的 @jsonformat 注解。
改造 student:
public class student{
private integer id;
private string name;
@datetimeformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss")
@jsonformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss", timezone = "gmt+8")
private date createdate;
private date uploaddate;
// 省略get和set方法
}
这样响应的日期就是正确的。
{
"id": null,
"name": null,
"createdate": "2024-08-13 19:49:28",
"uploaddate": null
}
1.4、如果是请求体@requestbody传参
pojo的属性类型是date,不加@datetimeformat(pattern="yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss")这个一样能接收到前端传来的日期。那么只能传 "createdate":"2018-08-02 ",因为date不支持时分秒,没法接收"createdate":"2018-08-02 22:11:05"这种,如果传带时分秒的,用@datetimeformat(pattern="yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss")也不管用。
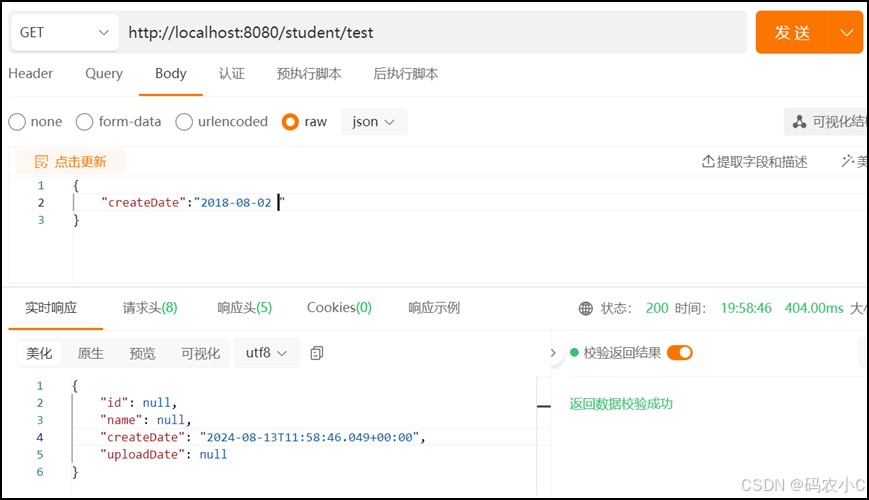
如果你想在请求体中,传带时分秒的,并且返回时分秒的。可以如下操作,也就是平常开发最常用的。
pojo类:
public class student{
private integer id;
private string name;
@datetimeformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss")// 这个加不加不影响结果,但是不能只有它,没有下边的jsonform注解。但是可以只有下边的jsonform注解。
@jsonformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss", timezone = "gmt+8")
private date createdate;
private date uploaddate;
// 省略get和set方法
}
稍微改了下刚才的controller
@getmapping("/test")
public student test(@requestbody student student) {
system.out.println("前端传来的日期:" + student.getcreatedate());
// 将前端传来的日期格式化后返回
simpledateformat sdf = new simpledateformat("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss");
string date = sdf.format(student.getcreatedate());
system.out.println("格式化后的日期:"+date);
// 返回前端的日期
student stu = new student();
stu.setcreatedate(student.getcreatedate());
return stu;
}

注意:如果是请求体接收参数,只加@jsonform注解,而不写@datetimeformat注解可以正常接收。
public class student{
private integer id;
private string name;
@jsonformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss", timezone = "gmt+8")
private date createdate;
private date uploaddate;
// 省略get和set方法
}
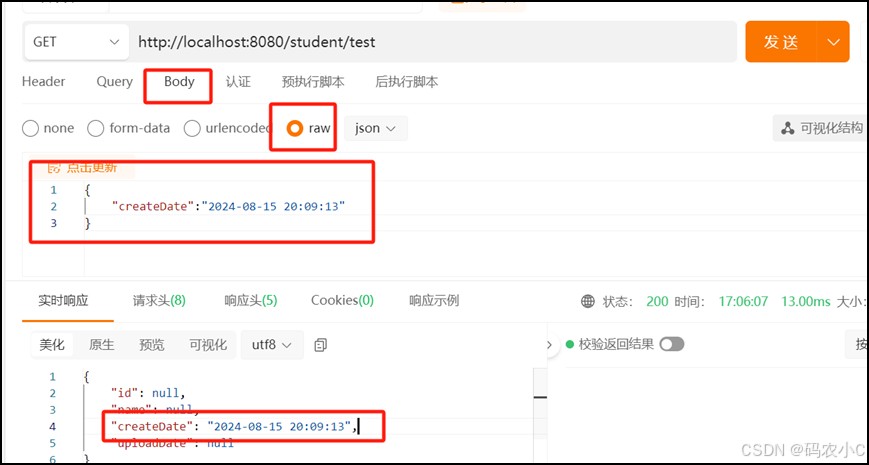
但如果是刚才的请求参数问题,不能只写@jsonform注解,而不写@datetimeformat注解。这样会报400,也就是pojo如下,响应结果如下图。
public class student{
private integer id;
private string name;
@jsonformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss", timezone = "gmt+8")
private date createdate;
private date uploaddate;
// 省略get和set方法
}
记得在controller里吧@requestbody去掉
二、解释这两个注解
1、@jsonformat
@jsonformat 是 jackson 库中的注解,用于在序列化和反序列化过程中控制日期和时间的格式。
主要用于控制如何将 java 对象中的日期时间格式化为 json 输出(即从后端到前端的格式化),适用于序列化和反序列化 json 数据,通常用在实体类中的日期字段上
@jsonformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss", timezone = "gmt+8") private date time;
2、@datetimeformat
@datetimeformat 是 spring 框架中用于处理日期和时间格式的注解,主要用于将前端传来的日期时间字符串转换为 java 对象(即从前端到后端的解析),适用于处理 web 请求中的日期时间参数,通常与 @requestparam、@pathvariable 等注解结合使用。
1、用途:
@datetimeformat 用于格式化日期和时间,确保请求参数能够按照指定的格式被解析。
只对 @requestparam 和 @pathvariable 类型的参数有效,而对 @requestbody 无效。对 @requestbody 的日期格式化需要用到 @jsonformat。
支持的格式:
可以指定日期和时间的格式,例如 "yyyy-mm-dd"、"yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss" 等。
2、示例代码:
后端代码(spring boot controller)
import org.springframework.format.annotation.datetimeformat;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.getmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestparam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller;
import java.time.localdate;
import java.time.localdatetime;
@restcontroller
public class datecontroller {
@getmapping("/date")
public string getdate(
@requestparam("date")
@datetimeformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd") localdate date,
@requestparam("datetime")
@datetimeformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss") localdatetime datetime) {
return "date: " + date + ", datetime: " + datetime;
}
}
api 测试代码(使用 apipost)
假设你启动了上述 spring boot 应用,下面是如何在 apipost 中测试这个接口:
get 请求 url:
http://localhost:8080/date?date=2024-08-13&datetime=2024-08-13%2015:45:30
响应:
date: 2024-08-13, datetime: 2024-08-13t15:45:30
特别注意
1、这两者的注解一般联合使用
@datetimeformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss") @jsonformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss", timezone="gmt+8") private date time;
一般系统都是前后交互
对此总结如下:
@jsonformat: 用于序列化和反序列化 json 数据中的日期时间字段,确保数据从后端到前端的一致性
@datetimeformat: 用于解析和格式化 web 请求中的日期时间参数,确保数据从前端到后端的正确处理
2、注意2
- 对 url 参数有效:
@datetimeformat常用于 url 参数的解析例如,@requestparam中的日期参数会受到@datetimeformat的影响 - 对请求体中的参数: 在请求体中,
@datetimeformat的直接作用有限,如果请求体中的日期时间字段是 json格式的,@datetimeformat不会直接影响解析,在这种情况下,通常使用@jsonformat来指定 json 中的日期时间格式
如果需要在请求体中解析日期时间,应该确保 json 转换器(如 jackson)能够正确处理日期格式。
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。






发表评论