一、早期时间类
1.java.util.date
- 简介:最早的时间类,表示某一时刻。
- 常用方法:
gettime():返回自1970年1月1日00:00:00 gmt以来的毫秒数。tostring():返回日期字符串。before(date date)/after(date date):比较日期先后。
- 缺点:大部分方法已废弃,线程不安全,易出错。
date date = new date(); system.out.println(date); // 当前时间
2.java.util.calendar
- 简介:用于更复杂的日期计算(如加减天数),是抽象类,常用子类
gregoriancalendar。 - 常用方法:
add(int field, int amount):增加指定时间字段的值。get(int field):获取指定字段的值(如 year, month)。set(int field, int value):设置指定字段的值。
- 缺点:api设计复杂,线程不安全。
calendar cal = calendar.getinstance(); cal.add(calendar.day_of_month, 5); // 当前日期加5天 date newdate = cal.gettime();
3.java.text.simpledateformat
- 简介:用于日期格式化和解析。
- 常用方法:
format(date date):格式化日期为字符串。parse(string source):解析字符串为日期对象。
simpledateformat sdf = new simpledateformat("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss");
string str = sdf.format(new date());
date date = sdf.parse("2024-06-01 12:00:00");二、java 8 引入的现代时间api(推荐)
所有类都在 java.time 包下,线程安全,易于使用。
1.localdate
- 简介:只表示日期(不含时间),如 2024-06-01。
- 常用方法:
now():当前日期。of(int year, int month, int dayofmonth):指定日期。plusdays(long days):加天数。minusdays(long days):减天数。getyear(),getmonth(),getdayofmonth():获取年月日。
localdate today = localdate.now(); localdate tomorrow = today.plusdays(1);
2.localtime
- 简介:只表示时间(不含日期),如 14:30:00。
- 常用方法:
now():当前时间。of(int hour, int minute, int second):指定时间。plushours(long hours):加小时。
localtime time = localtime.now(); localtime later = time.plushours(2);
3.localdatetime
- 简介:表示日期和时间,不含时区。
- 常用方法:
now():当前日期时间。of(int year, int month, int day, int hour, int minute, int second):指定日期时间。plusdays(),plushours():加天/小时。
localdatetime ldt = localdatetime.now(); localdatetime future = ldt.plusdays(3).plushours(5);
4.zoneddatetime
- 简介:日期时间+时区。
- 常用方法:
now(zoneid zone):当前时区的日期时间。of(...):指定日期时间和时区。
zoneddatetime zdt = zoneddatetime.now(zoneid.of("asia/shanghai"));5.instant
- 简介:时间戳,精确到纳秒,表示自1970年1月1日00:00:00 utc的瞬间。
- 常用方法:
now():当前时间戳。ofepochmilli(long epochmilli):通过毫秒数创建。
instant instant = instant.now(); long epochmilli = instant.toepochmilli();
6.duration&period
duration:表示两个时间点之间的时间量(秒、纳秒),适用于localtime、localdatetime、instant。period:表示两个日期之间的时间量(年、月、日),适用于localdate。
duration duration = duration.between(localtime.now(), localtime.now().plushours(2)); period period = period.between(localdate.now(), localdate.now().plusdays(10));
7.datetimeformatter
- 简介:格式化和解析日期时间,线程安全。
- 常用方法:
format(temporalaccessor temporal):格式化为字符串。parse(charsequence text):解析字符串为日期时间对象。
datetimeformatter formatter = datetimeformatter.ofpattern("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss");
string str = formatter.format(localdatetime.now());
localdatetime ldt = localdatetime.parse("2024-06-01 12:00:00", formatter);8.zoneid&zoneoffset
zoneid:时区id。zoneoffset:时区偏移量。
zoneid zoneid = zoneid.of("asia/shanghai");
zoneoffset offset = zoneoffset.of("+08:00");三、其他相关类
1.java.sql.date、java.sql.time、java.sql.timestamp
- 用于数据库操作,继承自
java.util.date,通常用于 jdbc。
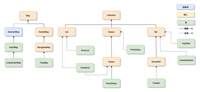
四、时间类关系图
java.util.date
├─ java.sql.date
├─ java.sql.time
└─ java.sql.timestamp
java.util.calendar
└─ java.util.gregoriancalendar
java.text.simpledateformat
java.time.localdate
java.time.localtime
java.time.localdatetime
java.time.zoneddatetime
java.time.instant
java.time.duration
java.time.period
java.time.datetimeformatter
java.time.zoneid
java.time.zoneoffset五、常用时间操作示例
// 当前日期时间
localdatetime now = localdatetime.now();
// 日期加减
localdatetime tomorrow = now.plusdays(1);
localdatetime lastweek = now.minusweeks(1);
// 日期格式化
string str = now.format(datetimeformatter.ofpattern("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss"));
// 字符串转日期
localdatetime ldt = localdatetime.parse("2024-06-01 12:00:00", datetimeformatter.ofpattern("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss"));
// 时间差
duration duration = duration.between(now, tomorrow);
long hours = duration.tohours();六、建议
- 新项目优先使用
java.time包下的类,线程安全、功能丰富、易用。 - 旧项目如果使用了
date、calendar,建议逐步迁移到新的时间api。 - 格式化和解析请用
datetimeformatter,避免simpledateformat的线程安全问题。
七. 各时间类详细用法与实战场景
1.1 localdate
场景:只关心日期(如生日、节假日、账单日期)
localdate birthday = localdate.of(1995, 6, 1); localdate today = localdate.now(); // 判断是否是今天 boolean istoday = birthday.equals(today); // 获取本月第一天 localdate firstday = today.withdayofmonth(1); // 获取本月最后一天 localdate lastday = today.withdayofmonth(today.lengthofmonth()); // 日期加减 localdate nextweek = today.plusweeks(1); localdate lastyear = today.minusyears(1);
1.2 localtime
场景:只关心时间(如打卡时间、会议时间)
localtime starttime = localtime.of(9, 0, 0); localtime endtime = localtime.of(18, 0, 0); // 判断是否在工作时间内 localtime now = localtime.now(); boolean isworktime = !now.isbefore(starttime) && !now.isafter(endtime); // 时间加减 localtime lunchtime = starttime.plushours(4);
1.3 localdatetime
场景:关心日期和时间(如订单创建时间、日志时间)
localdatetime ordertime = localdatetime.now(); localdatetime expiretime = ordertime.plushours(2); // 比较先后 boolean isexpired = localdatetime.now().isafter(expiretime); // 获取年月日时分秒 int year = ordertime.getyear(); int month = ordertime.getmonthvalue(); int day = ordertime.getdayofmonth(); int hour = ordertime.gethour(); int minute = ordertime.getminute();
1.4 zoneddatetime
场景:全球化应用,关心时区(如国际会议、航班时间)
zoneddatetime shanghaitime = zoneddatetime.now(zoneid.of("asia/shanghai"));
zoneddatetime newyorktime = shanghaitime.withzonesameinstant(zoneid.of("america/new_york"));
// 获取时区
zoneid zoneid = shanghaitime.getzone();1.5 instant
场景:存储时间戳(如数据库、消息队列)、高精度时间计算
instant now = instant.now(); long timestamp = now.toepochmilli(); // 毫秒时间戳 // instant与localdatetime互转 localdatetime ldt = localdatetime.ofinstant(now, zoneid.systemdefault()); instant instant = ldt.atzone(zoneid.systemdefault()).toinstant();
1.6 duration & period
场景:计算时间差
// duration: 时间点之间的差(如秒、纳秒) duration duration = duration.between(ldt1, ldt2); long seconds = duration.getseconds(); long minutes = duration.tominutes(); // period: 日期之间的差(如年、月、日) period period = period.between(date1, date2); int days = period.getdays(); int months = period.getmonths(); int years = period.getyears();
2. 时间比较与排序
localdatetime t1 = localdatetime.of(2024, 6, 1, 12, 0); localdatetime t2 = localdatetime.of(2024, 6, 2, 12, 0); boolean isbefore = t1.isbefore(t2); // true boolean isafter = t1.isafter(t2); // false boolean isequal = t1.isequal(t2); // false // 排序 list<localdatetime> list = arrays.aslist(t1, t2); list.sort(comparator.naturalorder());
3. 与旧api兼容与转换
date <-> localdatetime
// date转localdatetime date date = new date(); instant instant = date.toinstant(); localdatetime ldt = localdatetime.ofinstant(instant, zoneid.systemdefault()); // localdatetime转date localdatetime ldt2 = localdatetime.now(); instant instant2 = ldt2.atzone(zoneid.systemdefault()).toinstant(); date date2 = date.from(instant2);
4. 时间格式化与解析(自定义格式)
datetimeformatter fmt = datetimeformatter.ofpattern("yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss");
// 格式化
string str = localdatetime.now().format(fmt);
// 解析
localdatetime ldt = localdatetime.parse("2024/06/01 13:45:30", fmt);5. 时区处理
// 获取所有可用时区
set<string> zoneids = zoneid.getavailablezoneids();
// 当前时间在不同地区
zoneddatetime utctime = zoneddatetime.now(zoneid.of("utc"));
zoneddatetime tokyotime = zoneddatetime.now(zoneid.of("asia/tokyo"));6. 常见坑与注意事项
- 月份从1开始(不是0)
localdatetime没有时区信息,存储时要注意转换simpledateformat线程不安全,推荐用datetimeformatterduration不能用于日期(用period)date和calendar已过时,避免新项目使用- 时间操作建议统一使用一种api,避免混用造成混乱
7. 进阶用法
7.1 时间区间判断
localdatetime now = localdatetime.now(); localdatetime start = localdatetime.of(2024, 6, 1, 9, 0); localdatetime end = localdatetime.of(2024, 6, 1, 18, 0); boolean inrange = !now.isbefore(start) && !now.isafter(end);
7.2 按天、月、年循环
// 按天循环
localdate start = localdate.of(2024, 6, 1);
localdate end = localdate.of(2024, 6, 10);
for (localdate d = start; !d.isafter(end); d = d.plusdays(1)) {
system.out.println(d);
}7.3 时间差友好显示
duration duration = duration.between(ldt1, ldt2); long hours = duration.tohours(); long minutes = duration.tominutes() % 60; system.out.println(hours + "小时" + minutes + "分钟");
8. 代码片段汇总
// 获取当前时间戳(秒/毫秒)
long epochsecond = instant.now().getepochsecond();
long epochmilli = instant.now().toepochmilli();
// 时间加减
localdatetime t = localdatetime.now().plusdays(3).minushours(2);
// 时间格式化
string s = t.format(datetimeformatter.ofpattern("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss"));
// 时间解析
localdatetime parsed = localdatetime.parse("2024-06-01 12:00:00", datetimeformatter.ofpattern("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss"));
// 时间区间
localdate start = localdate.of(2024, 6, 1);
localdate end = localdate.of(2024, 6, 10);
for (localdate d = start; !d.isafter(end); d = d.plusdays(1)) {
// ...
}9. 时间操作常见应用场景实战
9.1 时间区间的交集与重叠判断
在预订系统、排班系统等场景,经常需要判断两个时间段是否有重叠。
public static boolean isoverlap(localdatetime start1, localdatetime end1,
localdatetime start2, localdatetime end2) {
return !start1.isafter(end2) && !start2.isafter(end1);
}
// 示例
localdatetime s1 = localdatetime.of(2024, 6, 1, 10, 0);
localdatetime e1 = localdatetime.of(2024, 6, 1, 12, 0);
localdatetime s2 = localdatetime.of(2024, 6, 1, 11, 0);
localdatetime e2 = localdatetime.of(2024, 6, 1, 13, 0);
boolean overlap = isoverlap(s1, e1, s2, e2); // true9.2 日期的周期性操作(如每周一的定时任务)
// 获取本周的所有日期
localdate monday = localdate.now().with(dayofweek.monday);
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
localdate d = monday.plusdays(i);
system.out.println(d + " " + d.getdayofweek());
}9.3 计算某月的第一天和最后一天
localdate now = localdate.now(); localdate firstday = now.withdayofmonth(1); localdate lastday = now.withdayofmonth(now.lengthofmonth());
9.4 获取某天的开始和结束时间
localdate date = localdate.of(2024, 6, 1); localdatetime startofday = date.atstartofday(); localdatetime endofday = date.attime(localtime.max); // 23:59:59.999999999
9.5 时间格式化为友好字符串(如“刚刚”、“1分钟前”、“1天前”)
public static string friendlytime(localdatetime time) {
duration duration = duration.between(time, localdatetime.now());
long seconds = duration.getseconds();
if (seconds < 60) return "刚刚";
if (seconds < 3600) return (seconds / 60) + "分钟前";
if (seconds < 86400) return (seconds / 3600) + "小时前";
return (seconds / 86400) + "天前";
}9.6 日期时间的序列化与反序列化(如 json)
- 推荐用 iso 标准格式,如
"2024-06-01t12:00:00"。 - jackson、gson 等主流 json 库在 java 8 后已支持直接序列化/反序列化
localdatetime、localdate等类型。 - 若需自定义格式,可用注解:
@jsonformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss") private localdatetime createtime;
10. 时间操作的性能与线程安全
新 api(java.time)都是不可变对象,线程安全。
旧 api(date、calendar、simpledateformat)都非线程安全。
示例:多线程格式化日期时,推荐如下写法:
datetimeformatter formatter = datetimeformatter.ofpattern("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss");
runnable task = () -> {
string formatted = localdatetime.now().format(formatter);
system.out.println(formatted);
};
new thread(task).start();11. 时间的国际化与本地化
11.1 不同区域的日期格式
datetimeformatter formatter = datetimeformatter.ofpattern("yyyy年mm月dd日", locale.china);
string str = localdate.now().format(formatter); // 2024年06月01日11.2 不同国家的周起始日
localdate date = localdate.now(); dayofweek firstdayofweek = weekfields.of(locale.us).getfirstdayofweek(); // sunday dayofweek firstdayofweekcn = weekfields.of(locale.china).getfirstdayofweek(); // monday
12. 时间工具类封装示例
你可以将常用操作封装为工具类,便于项目复用:
public class datetimeutils {
public static string format(localdatetime time, string pattern) {
return time.format(datetimeformatter.ofpattern(pattern));
}
public static localdatetime parse(string str, string pattern) {
return localdatetime.parse(str, datetimeformatter.ofpattern(pattern));
}
public static long diffminutes(localdatetime start, localdatetime end) {
return duration.between(start, end).tominutes();
}
// 更多方法...
}13. 时间操作常见面试题
- 如何获取某个月的最后一天?
- 如何判断两个时间段是否有重叠?
- 如何将 date 转换为 localdatetime?
- 如何计算两个日期之间的天数?
- 如何格式化为“刚刚”、“几分钟前”?
14. 未来趋势和常用第三方库
- 推荐只用 java.time 包,避免 date、calendar。
- 主流 orm 框架(如 jpa、mybatis)已支持 java 8 时间类。
- 如果需要更高级的日历功能,可用 joda-time(但现在已被 java.time 替代)。
- 时间处理相关的第三方库如 hutool、apache commons lang 也有丰富的工具类。
15. 其他常见问题与补充
- 时间戳存储建议用 utc,显示时再转换为本地时区。
- 跨时区应用注意夏令时(dst)变化。
- 数据库时间字段建议用标准时间(如 utc),避免因时区导致数据混乱。
到此这篇关于java 中的所有时间操作类详解及使用实战的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java时间操作类内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论