深入理解lombok:@data、@getter、@setter全面指南
作为java开发者,你是否厌倦了写大量重复的getter/setter方法?是否在为维护冗长的tostring、equals、hashcode方法而烦恼?本文将带你深入了解lombok注解的使用技巧,让你的代码更加简洁优雅。
🚀 前言:告别样板代码的时代
在传统的java开发中,一个简单的user类可能需要写50+行代码:
public class user {
private string name;
private integer age;
private string email;
// 需要手动写的方法:
// - 3个getter方法
// - 3个setter方法
// - tostring方法
// - equals方法
// - hashcode方法
// - 构造函数
// 总共50+行重复代码!😱
}
而使用lombok,同样的功能只需要:
@data
public class user {
private string name;
private integer age;
private string email;
}
// 7行代码搞定!🎉
这就是lombok的魅力所在。让我们深入探索这个"懒人神器"的奥秘。
📚 lombok简介
什么是lombok?
lombok是一个java库,通过注解的方式在编译时自动生成常用的样板代码,如getter、setter、tostring等方法。它的核心理念是:让开发者专注于业务逻辑,而不是重复的样板代码。
工作原理
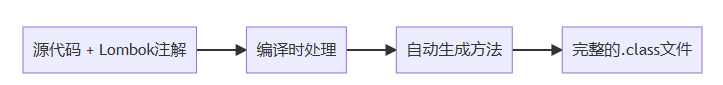
lombok在编译阶段通过apt(annotation processing tool)技术,分析注解并生成相应的java代码,最终编译成标准的字节码文件。
🎯 核心注解详解
1. @data:万能选手
@data是lombok中最强大的注解,它是以下注解的组合:
@getter- 所有字段的getter方法@setter- 所有非final字段的setter方法@tostring- tostring方法@equalsandhashcode- equals和hashcode方法@requiredargsconstructor- 必需参数构造函数
基础用法
@data
public class student {
private string name;
private integer age;
private string major;
private list<string> hobbies;
}
编译后自动生成的方法:
// 自动生成的getter方法
public string getname() { return this.name; }
public integer getage() { return this.age; }
public string getmajor() { return this.major; }
public list<string> gethobbies() { return this.hobbies; }
// 自动生成的setter方法
public void setname(string name) { this.name = name; }
public void setage(integer age) { this.age = age; }
public void setmajor(string major) { this.major = major; }
public void sethobbies(list<string> hobbies) { this.hobbies = hobbies; }
// 自动生成的tostring方法
public string tostring() {
return "student(name=" + this.name + ", age=" + this.age +
", major=" + this.major + ", hobbies=" + this.hobbies + ")";
}
// 自动生成的equals和hashcode方法
public boolean equals(object o) { /* 完整的equals实现 */ }
public int hashcode() { /* 完整的hashcode实现 */ }
// 自动生成的构造函数
public student() {}高级配置
@data
@tostring(exclude = {"password"}) // tostring时排除敏感字段
@equalsandhashcode(exclude = {"id"}) // equals比较时排除id字段
public class user {
private long id;
private string username;
private string password;
private string email;
}
2. @getter:只读属性的守护者
@getter注解专门用于生成getter方法,适合需要数据封装和只读访问的场景。
类级别使用
@getter
public class configinfo {
private string appname = "myapp";
private string version = "1.0.0";
private date buildtime = new date();
// 只生成getter方法,保护数据不被外部修改
}
// 使用示例
configinfo config = new configinfo();
string appname = config.getappname(); // ✅ 可以读取
config.setappname("newapp"); // ❌ 编译错误,没有setter字段级别使用
public class bankaccount {
@getter
private string accountnumber; // 只读:账号不能修改
@getter @setter
private bigdecimal balance; // 可读写:余额可以修改
private string password; // 完全私有:密码不能直接访问
// 自定义密码验证方法
public boolean verifypassword(string inputpassword) {
return this.password.equals(inputpassword);
}
}访问级别控制
public class securityuser {
@getter(accesslevel.public)
private string username; // public getter
@getter(accesslevel.protected)
private string internalid; // protected getter
@getter(accesslevel.package)
private string sessiontoken; // package-private getter
@getter(accesslevel.private)
private string encryptionkey; // private getter(基本无用)
@getter(accesslevel.none)
private string secretdata; // 不生成getter
}3. @setter:数据修改的管家
@setter注解用于生成setter方法,适合需要数据输入和修改的场景。
基础用法
@setter
public class userregistrationform {
private string username;
private string password;
private string email;
private string captcha;
// 只有setter方法,适合表单数据收集
}
// 使用示例
userregistrationform form = new userregistrationform();
form.setusername("john_doe"); // ✅ 可以设置
form.setpassword("secret123"); // ✅ 可以设置
string name = form.getusername(); // ❌ 编译错误,没有getter链式调用支持
@setter
@accessors(chain = true) // 启用链式调用
public class fluentuser {
private string name;
private integer age;
private string email;
}
// 链式调用示例
fluentuser user = new fluentuser()
.setname("alice")
.setage(25)
.setemail("alice@example.com");参数验证
public class validateduser {
@setter
private string email;
@setter
private integer age;
// 自定义setter with validation
public void setemail(string email) {
if (email == null || !email.contains("@")) {
throw new illegalargumentexception("invalid email format");
}
this.email = email;
}
public void setage(integer age) {
if (age == null || age < 0 || age > 150) {
throw new illegalargumentexception("invalid age");
}
this.age = age;
}
}🛠️ 实战应用场景
场景1:数据传输对象(dto)
// 前端请求参数
@data
@apimodel("用户查询请求")
public class userquerydto {
@apimodelproperty("用户名(支持模糊查询)")
private string username;
@apimodelproperty("邮箱")
private string email;
@apimodelproperty("年龄范围-最小值")
private integer minage;
@apimodelproperty("年龄范围-最大值")
private integer maxage;
@apimodelproperty("分页信息")
private pageinfo pageinfo;
}
// 响应数据
@data
@apimodel("用户信息响应")
public class userresponsevo {
@apimodelproperty("用户id")
private long id;
@apimodelproperty("用户名")
private string username;
@apimodelproperty("邮箱")
private string email;
@apimodelproperty("年龄")
private integer age;
@apimodelproperty("注册时间")
@jsonformat(pattern = "yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss")
private date registertime;
}场景2:数据库实体类(entity)
@data
@entity
@table(name = "users")
@equalsandhashcode(exclude = {"id", "createtime", "updatetime"})
public class userentity {
@id
@generatedvalue(strategy = generationtype.identity)
private long id;
@column(name = "username", unique = true, nullable = false)
private string username;
@column(name = "email", unique = true)
private string email;
@column(name = "password_hash")
private string passwordhash;
@column(name = "status")
@enumerated(enumtype.string)
private userstatus status;
@creationtimestamp
@column(name = "create_time")
private localdatetime createtime;
@updatetimestamp
@column(name = "update_time")
private localdatetime updatetime;
// 关联关系
@onetomany(mappedby = "user", cascade = cascadetype.all)
@tostring.exclude // 避免循环引用
private list<orderentity> orders;
}场景3:配置类
@data
@configurationproperties(prefix = "app.security")
@component
public class securityconfig {
private string jwtsecret = "defaultsecret";
private long jwtexpiration = 86400l; // 24 hours
private integer maxloginattempts = 5;
private long lockoutduration = 1800l; // 30 minutes
private cors cors = new cors();
@data
public static class cors {
private list<string> allowedorigins = arrays.aslist("*");
private list<string> allowedmethods = arrays.aslist("get", "post", "put", "delete");
private list<string> allowedheaders = arrays.aslist("*");
private boolean allowcredentials = true;
}
}场景4:构建器模式增强
@data
@builder
@noargsconstructor
@allargsconstructor
public class complexuser {
private string firstname;
private string lastname;
private string email;
private integer age;
private address address;
private list<string> roles;
private map<string, object> metadata;
@data
@builder
@noargsconstructor
@allargsconstructor
public static class address {
private string street;
private string city;
private string state;
private string zipcode;
private string country;
}
}
// 使用示例
complexuser user = complexuser.builder()
.firstname("john")
.lastname("doe")
.email("john.doe@example.com")
.age(30)
.address(complexuser.address.builder()
.street("123 main st")
.city("new york")
.state("ny")
.zipcode("10001")
.country("usa")
.build())
.roles(arrays.aslist("user", "admin"))
.metadata(map.of("department", "it", "level", "senior"))
.build();⚡ 性能与最佳实践
性能考虑
1. 编译时 vs 运行时
// lombok:编译时生成代码,运行时无性能损耗
@data
public class lombokuser {
private string name;
private integer age;
}
// 反射:运行时动态调用,有性能损耗
public class reflectionuser {
private string name;
private integer age;
public void setproperty(string propertyname, object value) {
field field = this.getclass().getdeclaredfield(propertyname);
field.setaccessible(true);
field.set(this, value); // 运行时反射调用
}
}2. 内存使用优化
@data
@tostring(exclude = {"largedataset"}) // 排除大数据集,避免tostring时内存问题
@equalsandhashcode(exclude = {"id", "createtime"}) // 排除不参与比较的字段
public class optimizedentity {
private long id;
private string name;
private localdatetime createtime;
@tostring.exclude
private list<byte[]> largedataset; // 大数据不参与tostring
}最佳实践
1. 团队规范建议
// ✅ 推荐:明确的注解使用规范
@data
@apimodel("用户信息")
public class userdto {
@apimodelproperty(value = "用户id", example = "1001")
private long id;
@apimodelproperty(value = "用户名", required = true)
@notblank(message = "用户名不能为空")
private string username;
}
// ❌ 不推荐:缺乏文档和验证
@data
public class userdto {
private long id;
private string username;
}2. 继承关系处理
// 父类
@getter
@setter
@tostring
public class baseentity {
private long id;
private localdatetime createtime;
private localdatetime updatetime;
}
// 子类
@data
@equalsandhashcode(callsuper = true) // 重要:包含父类字段
@tostring(callsuper = true) // 重要:包含父类字段
public class userentity extends baseentity {
private string username;
private string email;
}3. 循环引用处理
@data
public class department {
private string name;
@tostring.exclude
@equalsandhashcode.exclude
private list<employee> employees; // 避免循环引用
}
@data
public class employee {
private string name;
@tostring.exclude
@equalsandhashcode.exclude
private department department; // 避免循环引用
}🔧 高级特性与技巧
1. 自定义命名策略
@data
@accessors(prefix = "m") // 字段前缀为m
public class prefixeduser {
private string mname; // getter: getname(), setter: setname()
private integer mage; // getter: getage(), setter: setage()
}
@data
@accessors(fluent = true) // 流式接口
public class fluentuser {
private string name; // getter: name(), setter: name(string)
private integer age; // getter: age(), setter: age(integer)
}
// 使用示例
fluentuser user = new fluentuser().name("alice").age(25);
string name = user.name();2. 条件生成
public class conditionaluser {
@getter
@setter(onparam_ = {@valid}) // setter参数添加@valid注解
private @notnull string username;
@getter(onmethod_ = {@jsonignore}) // getter方法添加@jsonignore注解
private string password;
@getter(lazy = true) // 懒加载getter
private final string expensivecalculation = calculateexpensive();
private string calculateexpensive() {
// 模拟耗时计算
try { thread.sleep(1000); } catch (interruptedexception e) {}
return "expensive result";
}
}3. 与其他框架集成
// 与jackson集成
@data
@jsonnaming(propertynamingstrategies.snakecasestrategy.class)
@jsoninclude(jsoninclude.include.non_null)
public class jsonuser {
private string firstname; // json: first_name
private string lastname; // json: last_name
private integer userage; // json: user_age
@jsonproperty("email_address")
private string email; // json: email_address
@jsonignore
private string password; // 不序列化
}
// 与jpa集成
@data
@entity
@table(name = "users")
@entitylisteners(auditingentitylistener.class)
public class jpauser {
@id
@generatedvalue(strategy = generationtype.identity)
private long id;
@column(unique = true)
private string username;
@createddate
private localdatetime createtime;
@lastmodifieddate
private localdatetime updatetime;
}🚨 常见陷阱与解决方案
1. equals和hashcode陷阱
// ❌ 问题代码:包含可变字段导致hashmap行为异常
@data
public class problematicuser {
private string name;
private list<string> hobbies; // 可变集合参与equals/hashcode
}
// 测试问题
map<problematicuser, string> map = new hashmap<>();
problematicuser user = new problematicuser();
user.setname("alice");
user.sethobbies(new arraylist<>(arrays.aslist("reading")));
map.put(user, "value");
user.gethobbies().add("swimming"); // 修改了hashcode
string value = map.get(user); // null!找不到了
// ✅ 解决方案:排除可变字段或使用不可变集合
@data
@equalsandhashcode(exclude = {"hobbies"})
public class safeuser {
private string name;
private list<string> hobbies;
}2. 循环引用陷阱
// ❌ 问题代码:tostring时出现stackoverflowerror
@data
public class parent {
private string name;
private list<child> children;
}
@data
public class child {
private string name;
private parent parent; // 循环引用
}
// ✅ 解决方案:使用@tostring.exclude
@data
public class safeparent {
private string name;
@tostring.exclude
private list<safechild> children;
}
@data
public class safechild {
private string name;
@tostring.exclude
private safeparent parent;
}3. 性能陷阱
// ❌ 问题代码:大集合参与tostring
@data
public class bigdatauser {
private string name;
private list<byte[]> bigdatalist; // 大数据集合
}
bigdatauser user = new bigdatauser();
user.setbigdatalist(generatemassivedata());
system.out.println(user); // 可能导致内存问题
// ✅ 解决方案:排除大数据字段
@data
@tostring(exclude = {"bigdatalist"})
public class optimizeduser {
private string name;
private list<byte[]> bigdatalist;
// 自定义tostring显示摘要信息
public string getdatasummary() {
return bigdatalist != null ?
"datalist[size=" + bigdatalist.size() + "]" : "datalist[empty]";
}
}🔄 迁移指南
从传统代码迁移到lombok
步骤1:添加依赖和插件
<!-- maven -->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.projectlombok</groupid>
<artifactid>lombok</artifactid>
<version>1.18.30</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>// gradle
dependencies {
compileonly 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.30'
annotationprocessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok:1.18.30'
}步骤2:渐进式迁移
// 原始代码
public class user {
private string name;
public string getname() { return name; }
public void setname(string name) { this.name = name; }
// ... 其他样板代码
}
// 迁移步骤1:添加@getter @setter,保留原有方法
@getter
@setter
public class user {
private string name;
// 保留原有方法,确保兼容性
public string getname() { return name; }
public void setname(string name) { this.name = name; }
}
// 迁移步骤2:测试通过后删除原有方法
@getter
@setter
public class user {
private string name;
}
// 迁移步骤3:根据需要升级为@data
@data
public class user {
private string name;
}步骤3:团队培训清单
## lombok使用规范 ### ✅ 推荐做法 - 优先使用@data处理简单数据类 - 使用@getter处理只读数据 - 复杂继承关系谨慎使用@equalsandhashcode - 循环引用场景使用@tostring.exclude ### ❌ 避免做法 - 不要在所有类上盲目使用@data - 不要忽略equals/hashcode的语义 - 不要在大数据字段上使用默认tostring - 不要在api接口类上使用@data
📊 对比总结
| 特性 | 传统写法 | @getter | @setter | @data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 代码量 | 50+行 | 减少60% | 减少40% | 减少90% |
| 可读性 | 差 | 良好 | 良好 | 优秀 |
| 维护性 | 差 | 良好 | 良好 | 优秀 |
| 性能 | 标准 | 标准 | 标准 | 标准 |
| 灵活性 | 最高 | 高 | 高 | 中等 |
| 学习成本 | 无 | 低 | 低 | 低 |
| 团队接受度 | 100% | 高 | 高 | 高 |
🎉 总结
lombok通过编译时代码生成技术,极大地简化了java开发中的样板代码编写。合理使用@data、@getter、@setter等注解,可以让代码更加简洁、易读、易维护。
选择建议
- 🥇 @data:适用于80%的数据类场景,功能全面,使用简单
- 🥈 @getter:适用于只读数据,如配置类、查询结果等
- 🥉 @setter:适用于只写数据,如表单参数、更新对象等
- 🔧 组合使用:适用于需要精确控制的复杂场景
最后的建议
- 从小处开始:先在新的数据类上尝试使用
- 保持一致性:团队内部统一使用规范
- 关注细节:注意equals/hashcode语义和循环引用问题
- 持续学习:关注lombok的新特性和最佳实践
记住:工具是为了让开发更高效,而不是炫技。选择最适合你项目和团队的方案,才是最好的方案。
希望这篇文章能帮助你更好地理解和使用lombok。如果你有任何问题或建议,欢迎在评论区交流讨论!
📚 参考资源
到此这篇关于java lombok中的@data、@getter、@setter使用技巧全面指南的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关深入理解lombok:@data、@getter、@setter全面指南内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论