前情提要:在学习 arraylist 时,认识到由于其底层是一段连续空间,当在 arraylist 任意位置插入或者删除元素时,就需要将后序元素整体往前或者往后搬移,时间复杂度为o(n),效率比较低,因此 arraylist 不适合做任意位置插入和删除比较多的场景。因此:java 集合中又引入了linkedlist,即链表结构。
一、链表概念与结构
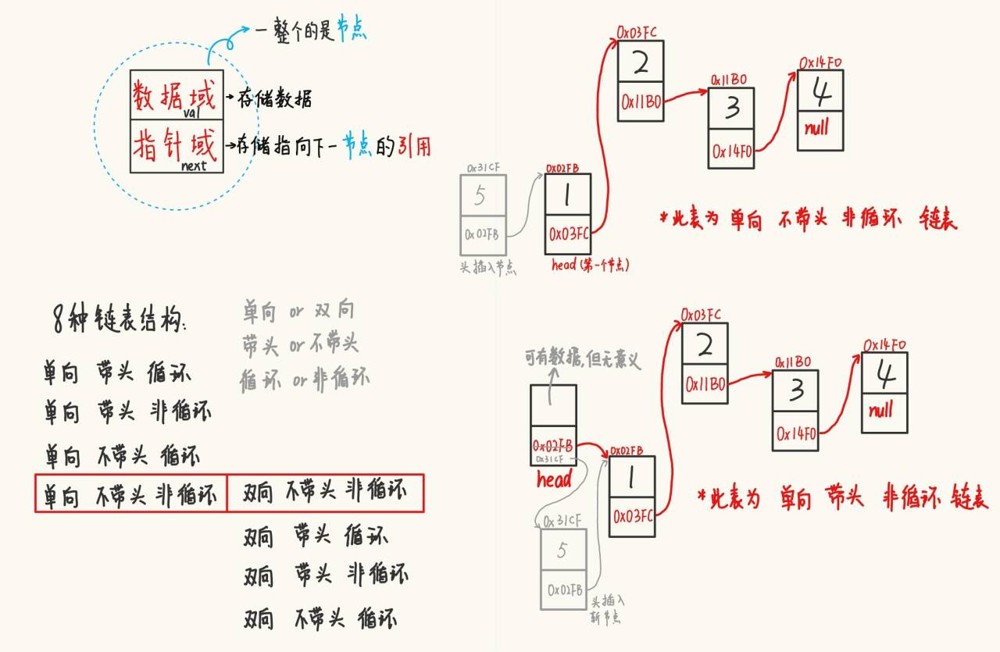
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序的通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的。
其结构总共有8种:
带头链表中的第一个节点相当于一个标记,如果采用头插法新增节点,只能在当前头的下一个节点插入;而如果是不带头的链表,头插法是在第一个节点前面新增节点。
二、当向单链表的实现
整个实现将围绕下图展开:
定义一个 cur 对象,表示当前节点。用法:遍历链表。
注意
1、cur 为空和 cur.next 为空的区别。
2、单向链表不能回退。
2.1 准备工作
1、先定义一个类用来表示整个链表,名为 singlelinkedlist。
2、而链表中包含节点,每个节点带有两个域,一个是数据域存储整型数据;另一个是指针域,指针域中存放的是下一个 节点 的引用,因此其类型也就是节点;且注意两个属性都用 public 修饰,在测试时大有用途。将每个节点封装成链表的内部类。
3、定义一个头部节点,用于查找或者输出链表数据,但这里并不代表链表带头。
4、将对链表的操作封装成一个接口,其功能包括打印链表数据 display、计算链表长度 size、查找数据 contains、头插法插入数据 addfirst、尾插法插入数据 addlast、任意位置插入数据 addindex、删除第一次出现 key 的节点 remove、删除所有值为 key 的节点 removeallkey、清空。
singlelinkedlist 链表:
package test;
// 不带头 单向 链表
public class singlelinkedlist implements ilink{
static class listnode{ // 每一个 节点 都是对象,具有共同属性,因此可以抽象成内部类
public int val;
public listnode next; // 节点的地址,类型也应该是节点的类型
public listnode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public listnode head; // 头节点
@override
// ......
}ilink 接口:
package test;
/**
* 链表的操作
*/
public interface ilink {
//头插法
void addfirst(int data);
//尾插法
void addlast(int data);
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
void addindex(int index,int data);
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
boolean contains(int key);
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
void remove(int key);
//删除所有值为key的节点
void removeallkey(int key);
//得到单链表的长度
int size();
// 清空
void clear();
// 打印链表数据
void display();
}在实现具体的操作之前,还需要考虑链表是否为空,即 head == null ?
2.2 初始化链表
在具体实现各项功能之前,需要有一个原始的链表,利于展示操作效果。其定义方法如下
package test;
public class singlelinkedlist implements ilink{
// ......
public void creatlist(){ // 创建一个原始链表
listnode node1 = new listnode(1);
listnode node2 = new listnode(2);
listnode node3 = new listnode(3);
listnode node4 = new listnode(4);
this.head = node1;
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
}
// ......
}2.3 打印数据、链表长度、查找数据
这三个功能都需要将链表从头到尾遍历一遍。而遍历的条件只是当前节点不为空。
package test;
public class singlelinkedlist implements ilink{
// ......
@override
public void display() {
listnode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
system.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
system.out.println(); // 换行
}
@override
public int size() {
listnode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
@override
public boolean contains(int key) {
listnode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
}package test;
public class testsingle {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// ilink ilink = new singlelinkedlist(); // 通过接口无法调用 creatlist()
singlelinkedlist linkedlist = new singlelinkedlist();
linkedlist.creatlist(); // 还没实现新增节点功能前调用的原始链表
linkedlist.display();
system.out.println(linkedlist.size());
}
}2.4 头插法
@override
public void addfirst(int data) {
listnode newnode = new listnode(data);
newnode.next = head;
this.head = newnode;
}即使原先的链表是空的,代码一样能实现头插法插入节点。
2.5 尾插法
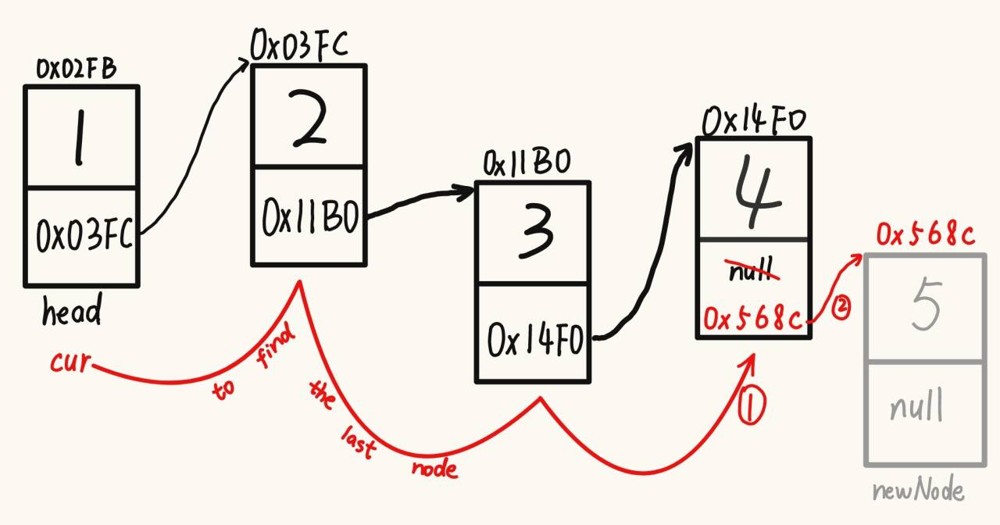
@override
public void addlast(int data) {
listnode newnode = new listnode(data);
if (head == null){ // 原来链表中一个节点都没有的情况下
head = newnode;
return;
}
listnode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
} // 循环走完说明 cur.next == null 了
cur.next = newnode;
}package test_8_7;
public class testsingle {
public static void main(string[] args) {
singlelinkedlist linkedlist = new singlelinkedlist();
// 实现新增节点功能之后,不需要调用 creatlist(),也可以创建链表
// 头插法
linkedlist.addfirst(11);
linkedlist.addfirst(22);
linkedlist.addfirst(33);
linkedlist.addfirst(44);
// 尾插法
linkedlist.addlast(55);
linkedlist.display();
system.out.println(linkedlist.size());
}
}2.6 任意位置插入节点
注意
1、指定位置的合法性;
2、指定下标为 0 和 指定位置等于链表长度 的情况分开处理;
3、单向链表不能回退,因此注意 cur 的位置;
4、所有的插入,优先绑定后面的节点。
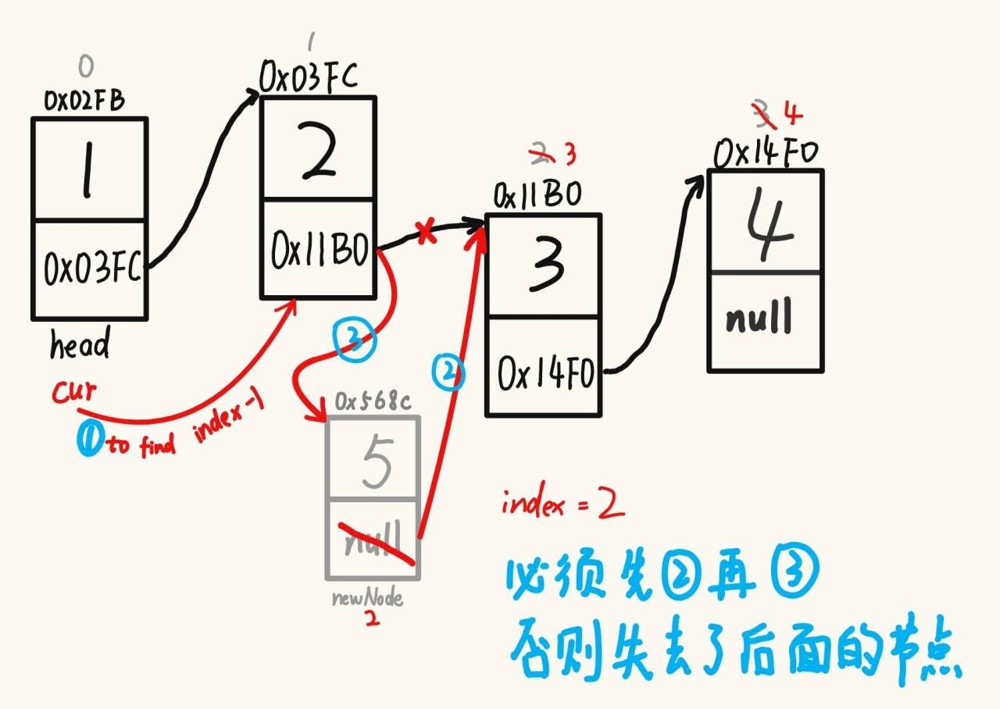
@override
public void addindex(int index, int data) throws illegalindexexception{
int len = this.size(); // 存储当前长度,好处:提高效率
if (index < 0 || index > len){
throw new illegalindexexception("指定位置不合法!!!");
}else {
if (index == 0){
this.addfirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == len){
this.addlast(data);
return;
}
listnode newnode = new listnode(data);
listnode cur = head;
while (index - 1 != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
newnode.next = cur.next;
cur.next = newnode;
}
}package test;
// 处理指定位置的不合法异常
public class illegalindexexception extends runtimeexception{
public illegalindexexception(){
}
public illegalindexexception(string msg){
super(msg);
}
}2.7 删除第一次出现 key 的节点
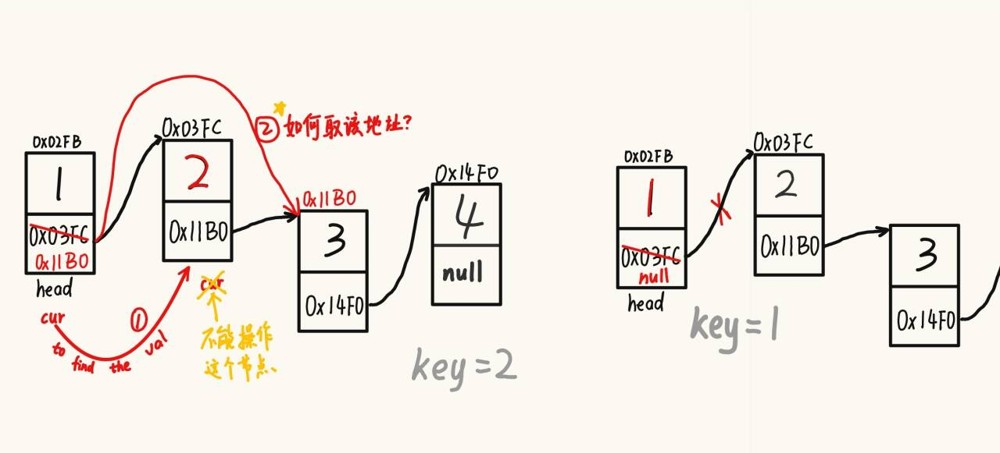
@override
public void remove(int key) {
if (head == null){
return;
}
if(head.val == key){
head = null;
}
listnode cur = findnodeofkey(key);
if (cur == null){
return;
}
listnode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
public listnode findnodeofkey(int key){ // 找到存储的数据是key的对象,并返回
listnode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null){
if (cur.next.val == key){
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}提示
1、在链表中查找 key 可封装成一个方法
2、查找 key 的条件 cur.next 不为空的前提下,已经判断了 cur.next 存储的数据是否等于 key 了
2.8 删除链表中所有数据为 key 的节点
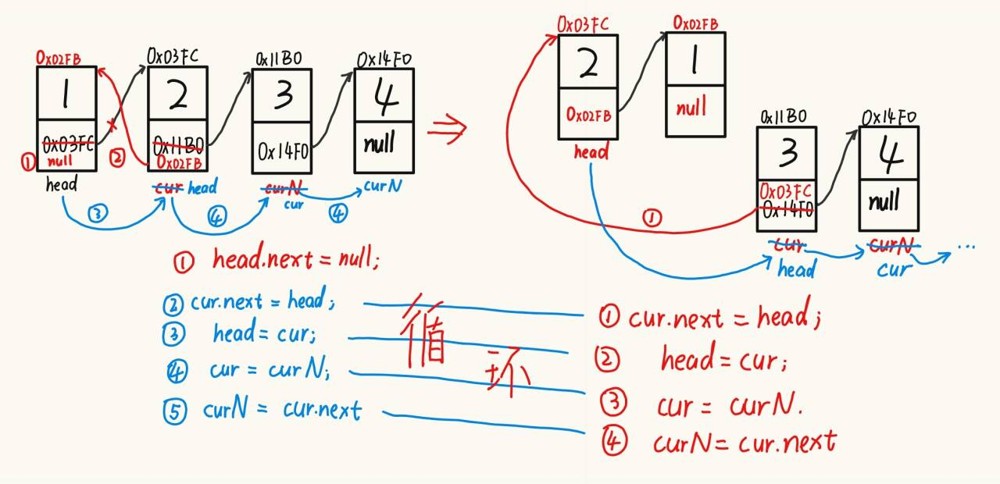
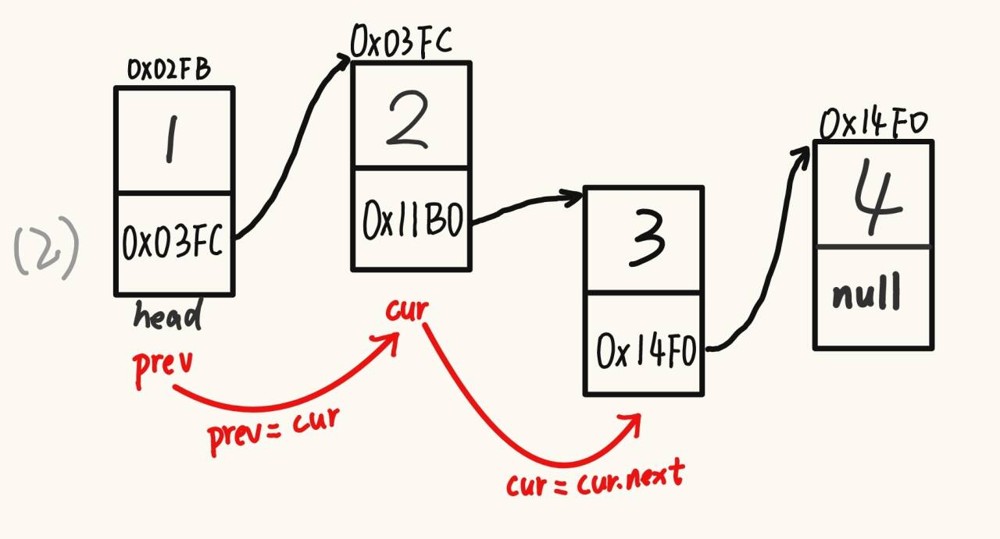
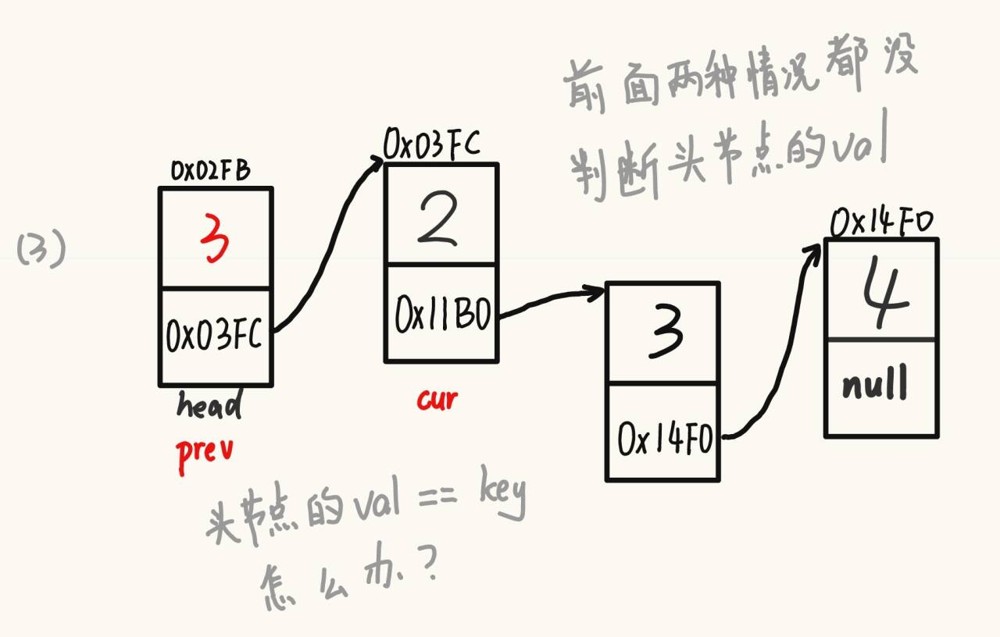
@override
public void removeallkey(int key) {
if (head == null){
return;
}
listnode prev = head;
listnode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.val == key){
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if (head.val == key){
head = head.next;
}
}2.9 清空
像之前“清空” arraylist 的方法在链表中是不可行的,因为如果引用一直存在,那么引用所指的对象无法被内存回收,容易造成内存泄漏,因此只有将 next 都置空了才算清空了链表数据。
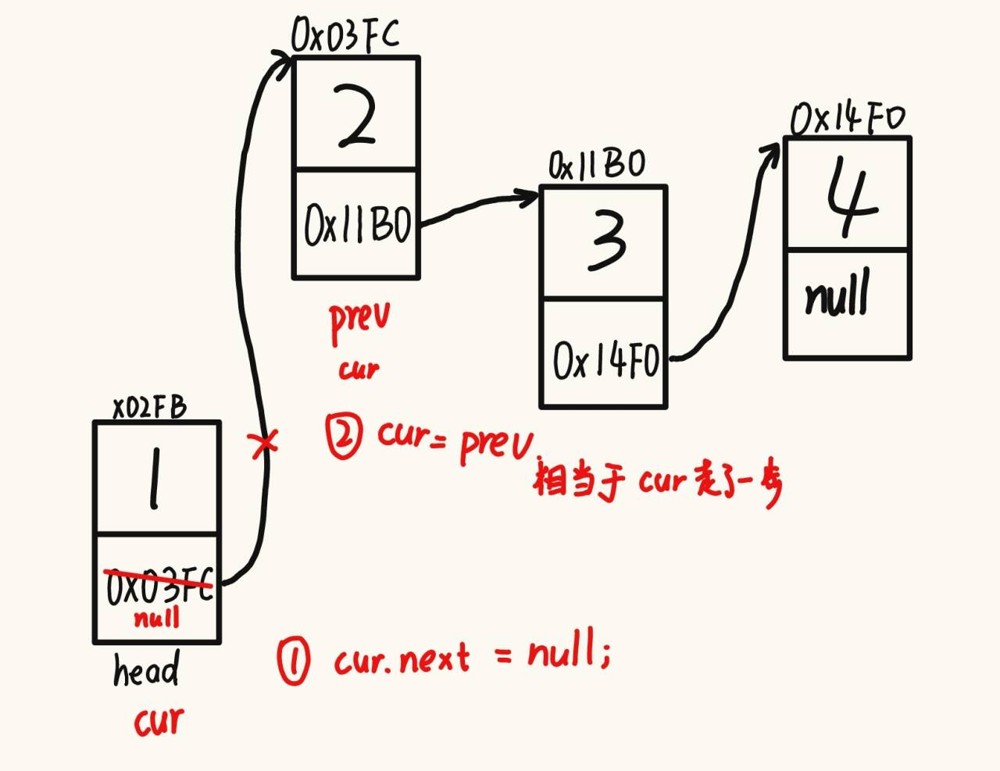
@override
public void clear() {
listnode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null){
listnode prev = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
cur = prev;
}
head = null;
}三、面试题
3.1 删除链表中等于给定值 key 的所有节点。(与上面的 2.8 一个意思)
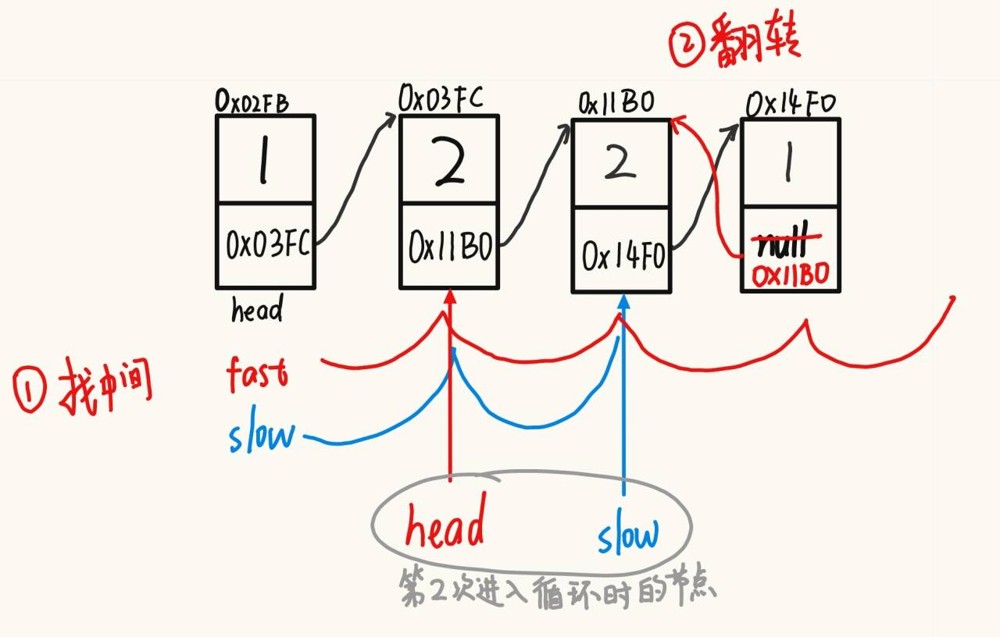
3.2反转一个单链表。

public listnode reverselist() { // 反转
if(head == null){
return null;
}
listnode cur = head.next;
head.next = null;
while(cur != null){
listnode curnode = cur.next;
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
cur = curnode;
}
return head;
}3.3返回链表中的中间节点,如果有两个中间节点,则返回第2个节点。
提示,不能通过计算链表长度的方法进行编程。
那么,采用双指针的方法,快指针走两步,慢指针走1步,最后慢指针指向的就是中间。
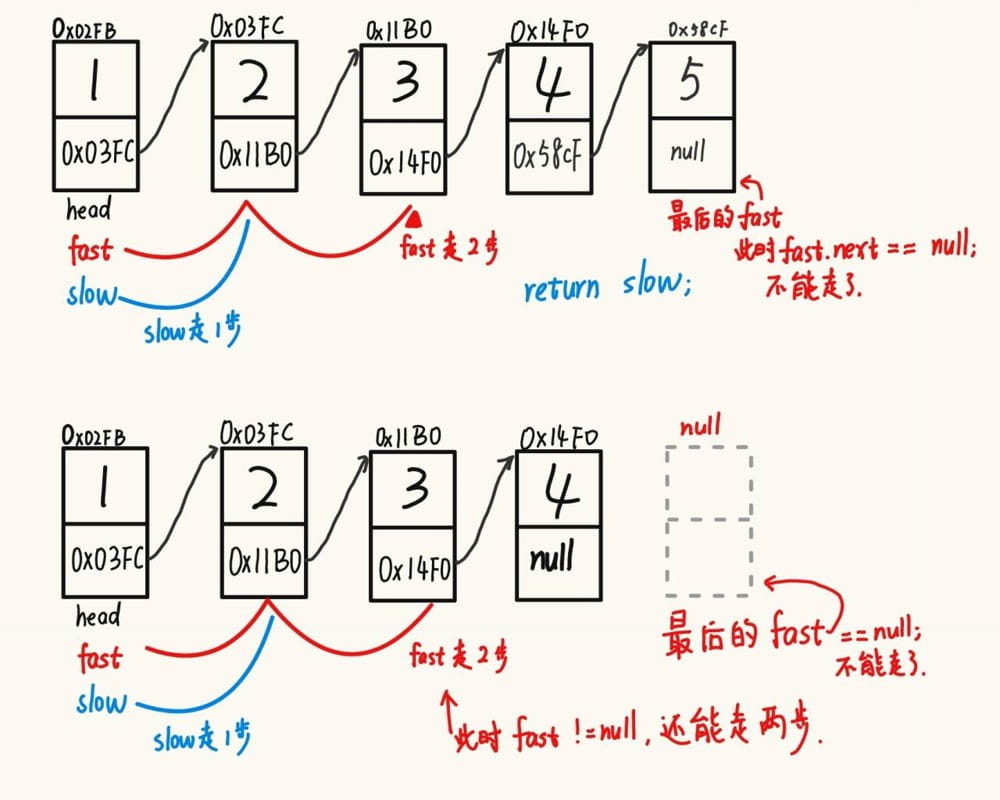
public listnode middlenode() { // 找中间节点
listnode fast = head; // 快指针,走两步
listnode slow = head; // 慢指针,走一步
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){ // &&前面必须是 fast != null 的条件
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
/*while(fast.next != null && fast != null){ // 输出 nullpointerexception
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}*/
return slow;
}3.4输出该链表中倒数第 k 个节点。
虽然 leetcode 上已经保证了 k 的合法性,但自己实现的时候还是需要注意 k 的有效范围。
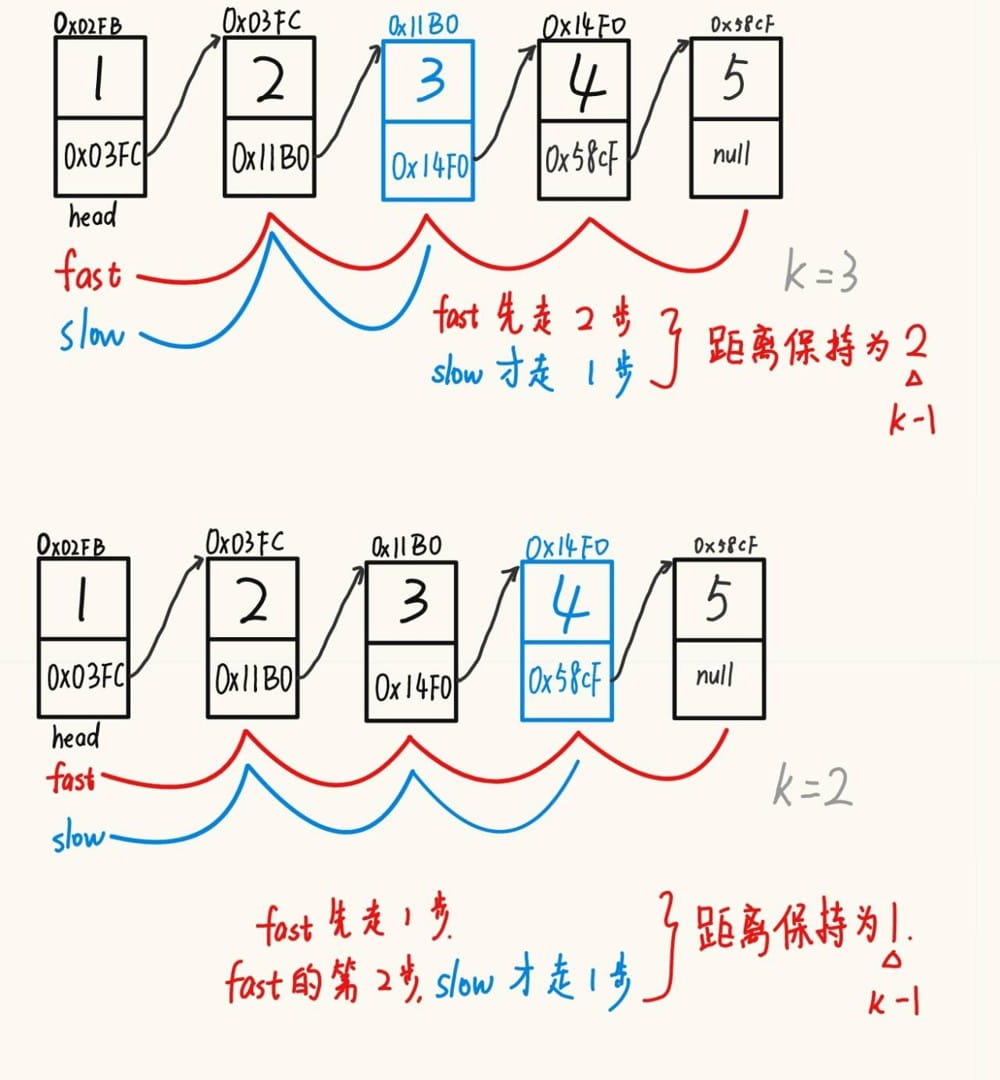
public int kthtolast(int k) { // 返回倒数第k个字节的数据
if(head == null){
return -1;
}
// 注意k的范围
if (k <= 0){
return -1;
}
/*if (k > 5){ // 这样写还得求链表的长度,不好
return -1;
}*/
listnode fast = head;
listnode slow = head;
int count = 0;
while(count != k-1){ // 为了与慢指针拉开一定的距离
fast = fast.next;
if(fast == null) // 这里就是判断k是否超出链表长度的条件
return -1;
count++;
}
while(fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow.val;
}3.5合并两个有序链表并按升序排序成有序链表返回。
提示
1、创建一个头节点,作为标志,可存储数据,但该数据无实际意义;
2、返回的节点不是创建的头节点。
3、在自己实现的链表中实现时,需要注意,因为该方法操作的是两个链表,因此不好将它定义到 singlelinkedlist 这个类中,因此直接定义到测试类。但直接定义到测试类时因为 listnode 是 singlelinkedlist 的内部类,需要用 singlelinkedlist. 来调用 listnode
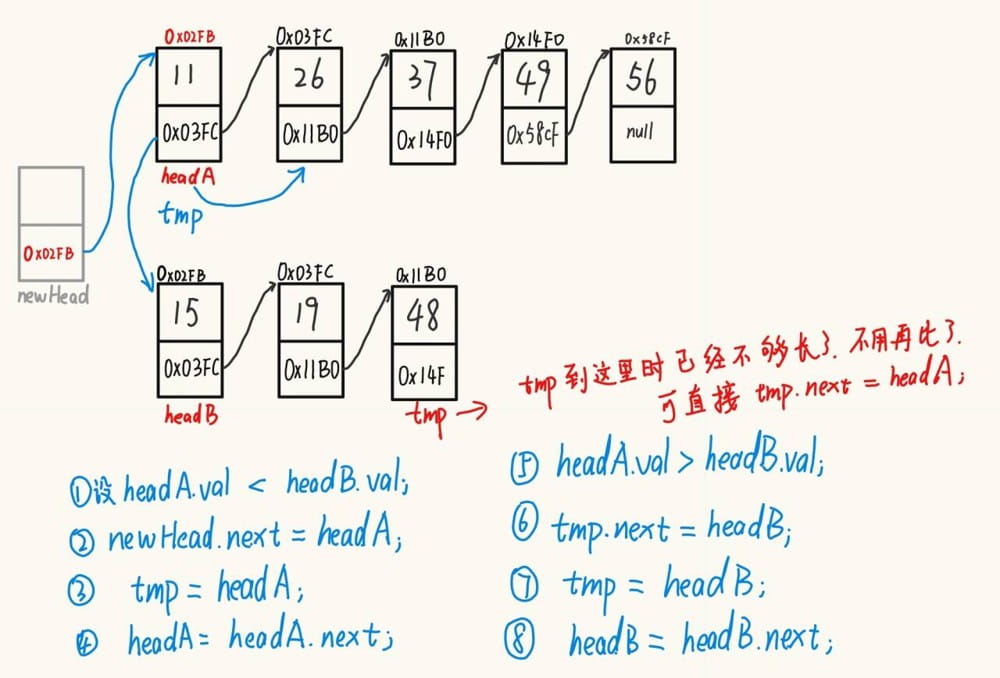
package test;
public class testsingle {
public static singlelinkedlist.listnode mergetwolists
(singlelinkedlist.listnode heada, singlelinkedlist.listnode headb) { // 合并两个有序链表并排序
singlelinkedlist.listnode newhead = new singlelinkedlist.listnode(-1); // 随便传一个数据,因为这个数据无效
singlelinkedlist.listnode tmp = newhead;
while(heada != null && headb != null){
if (heada.val < headb.val){
tmp.next = heada;
heada = heada.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}else{
tmp.next = headb;
headb = headb.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
if (heada != null){
tmp.next = heada;
}
if (headb != null){
tmp.next = headb;
}
return newhead.next;
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 测试合并两个链表
singlelinkedlist linkedlist = new singlelinkedlist();
linkedlist.addfirst(4);
linkedlist.addlast(11);
linkedlist.addlast(19);
linkedlist.addlast(44);
singlelinkedlist linkedlist2 = new singlelinkedlist();
linkedlist2.addfirst(3);
linkedlist2.addlast(6);
linkedlist2.addlast(32);
linkedlist2.addlast(57);
singlelinkedlist.listnode newnode = mergetwolists(linkedlist.head, linkedlist2.head);
linkedlist.display(newnode);
}
}3.6以 x 值为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于 x 的节点排在大于或等于 x 的节点之后。
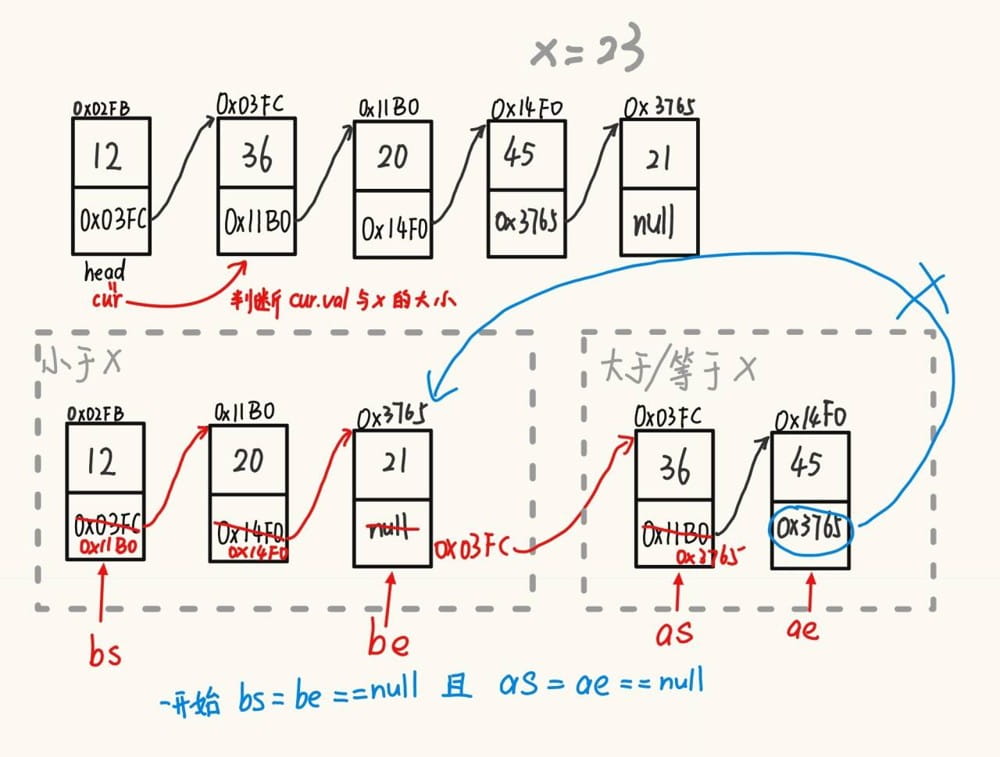
public listnode partition(int x) { // 不改变原来数据的顺序下,将所有小于x的结点排在其余结点之前
listnode beforestart = null; // 小于x的头节点
listnode beforeend = null; // 小于x的尾节点
listnode afterstart = null; // 大于x的头节点
listnode afterend = null; // 大于x的尾节点
listnode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val < x){
if(beforestart == null){ // 第一次插入
beforestart = beforeend = cur;
}else{
beforeend.next = cur;
beforeend = beforeend.next;
}
}else{
if(afterstart == null){
afterstart = afterend = cur;
}else{
afterend.next = cur;
afterend = afterend.next;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 如果没有小于x的节点
if (beforestart == null){
return afterstart;
}
// 前后两部分衔接起来
beforeend.next = afterstart;
// 第2部分的最后一个节点的引用要置空,否则编译超出范围
if(afterstart != null){
afterend.next = null;
}
return beforestart;
}3.7判断是否为回文链表。
提示
1、找到链表的中间节点;
2、将中间节点后面的节点反转;
3、头节点的值与最后一个节点的值进行比较,然后头节点往后,最后一个节点往前。
注意此题需要区分链表的节点数,如果是奇数比较好判断,但如果是偶数,需要考虑另一个判断条件。
奇数情况下:
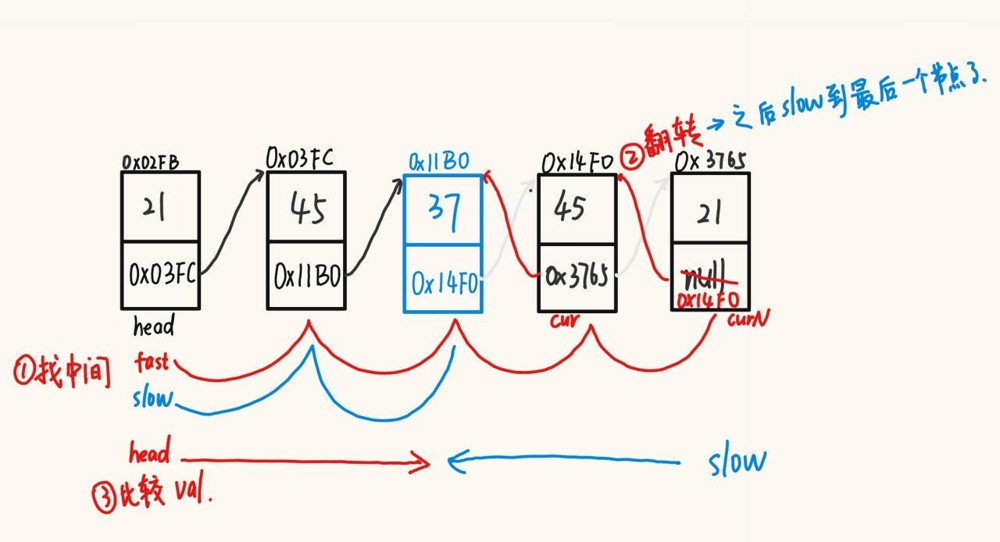
偶数情况下:

判断条件是 fast.next = slow; 不能是 slow.next = fast;
且该判断条件前提是两者的数据是相等的,因此判断顺序很重要。
public boolean chkpalindrome(){ // 判断是否是回文链表
if(head == null){
return true;
}
// 1、找到中间节点
listnode fast = head;
listnode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 2、反转
listnode cur = slow.next;
while(cur != null){
listnode curn = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curn;
}
// 3、判断是否是回文
while(head != slow){
if (head.val != slow.val){
return false;
}
// 如果链表是偶数的话,应该是下面的判断条件
// 前提是两个val值是相等的
if (head.next == slow){ // 注意是head的下一个节点是slow才对,因为slow的下一个节点回到了slow后面了。
return true;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}3.8输入两个链表,找出它们的公共节点。
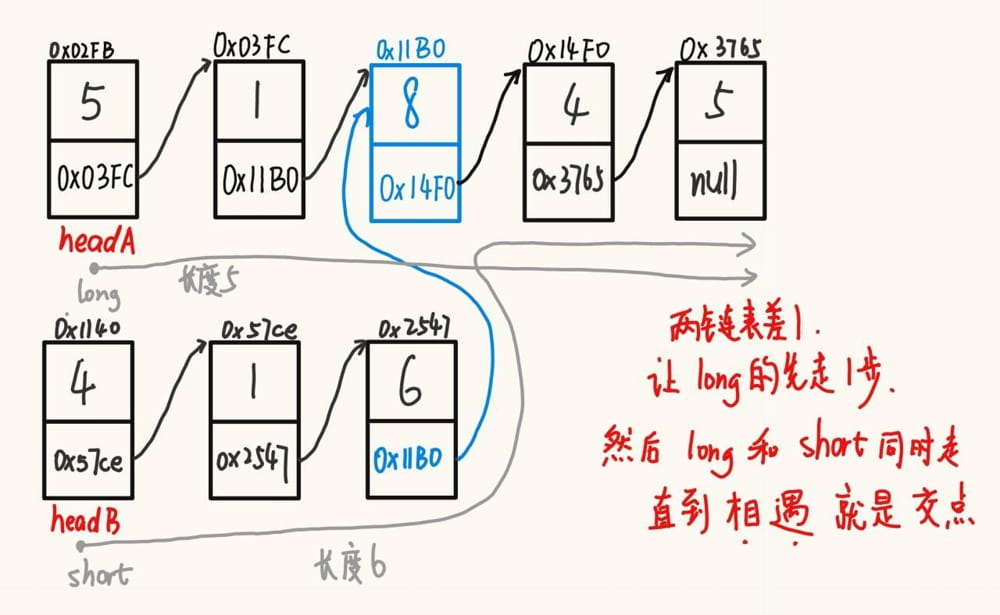
public singlelinkedlist.listnode getintersectionnode
(singlelinkedlist.listnode heada, singlelinkedlist.listnode headb) { // 两链表是否相交
singlelinkedlist.listnode plong = heada; // 假设链表a的长度比链表b的长
singlelinkedlist.listnode pshort = headb;
int lena = 0; // 链表a的长度
int lenb = 0; // 链表b的长度
while (plong != null){
lena++;
plong = plong.next;
}
while (pshort != null){
lenb++;
pshort = pshort.next;
}
// 因为在计算长度时改变了两个值,因此要从新定义
plong = heada;
pshort = headb;
// 计算两个链表长度的差值
int len = lena - lenb;
if (len < 0){ // 如果len为负数,说明lenb大于lena,规定plong一定指向长的链表
plong = headb;
pshort = heada;
len = lenb - lena; // 记住要把差值换成正数
}
// 长的链表先走len步
while (len != 0){
plong = plong.next;
len--;
}
// 两个引用同时走,知道它们相遇
while (plong != pshort){
plong = plong.next;
pshort = pshort.next;
}
if (plong == null){
return null; // 说明没有相交
}
return plong;
}测试:
public static void creatintersect
(singlelinkedlist.listnode heada, singlelinkedlist.listnode headb){ // 自己实现相交
heada.next.next = headb.next.next.next;
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
singlelinkedlist linkedlist = new singlelinkedlist();
linkedlist.addfirst(5);
linkedlist.addlast(1);
linkedlist.addlast(8);
linkedlist.addlast(4);
linkedlist.addlast(5);
singlelinkedlist linkedlist2 = new singlelinkedlist();
linkedlist2.addfirst(4);
linkedlist2.addlast(1);
linkedlist2.addlast(6);
linkedlist2.addlast(8);
linkedlist2.addlast(4);
linkedlist2.addlast(5);
creatintersect(linkedlist.head, linkedlist2.head);
singlelinkedlist.listnode ret = getintersectionnode(linkedlist.head, linkedlist2.head);
system.out.println(ret.val);
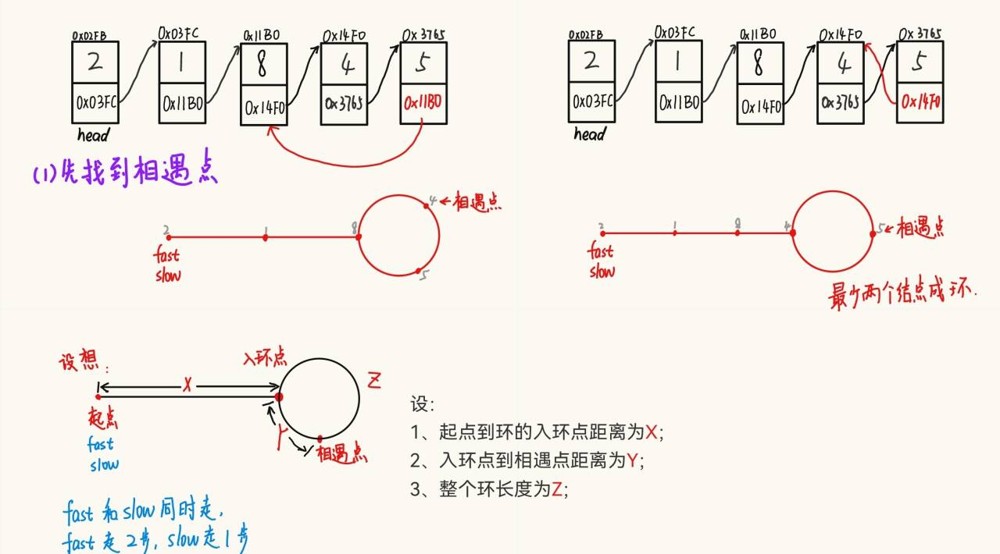
}3.9判断链表中是否有环。* 进阶:给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。


public boolean hascycle(){ // 判断当前链表是否有环
if (head == null){
return false;
}
listnode fast = head;
listnode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public void creatloop(){ // 创建环
listnode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = head.next.next.next;
}
public listnode detectcycle() { // 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null
listnode fast = head;
listnode slow = head;
while( fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
break;
}
}
if(fast == null || fast.next == null){
return null; // 说明没有环
}
slow = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}测试类:
public class testsingle {
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 测试返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。
singlelinkedlist linkedlist = new singlelinkedlist();
linkedlist.addfirst(5);
linkedlist.addlast(1);
linkedlist.addlast(8);
linkedlist.addlast(4);
linkedlist.addlast(5);
linkedlist.creatloop();
system.out.println(linkedlist.hascycle());
singlelinkedlist.listnode ret = linkedlist.detectcycle();
system.out.println(ret.val);
}
}到此这篇关于java集合中的链表与结构详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java集合链表内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论