一、前言
官方文档:https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3.12/library/json.html
在python中,json模块可以方便地处理json数据与python对象之间的转换。然而,如果仅用json模块来提取特定数据,就有点力不从心了,这时可以使用jsonpath模块,但它的操作稍显复杂,那么jmespath模块就是不错的选择
二、格式转换
python的json模块用于处理json数据,json字符串与python类型之间的转换关系如下图所示:
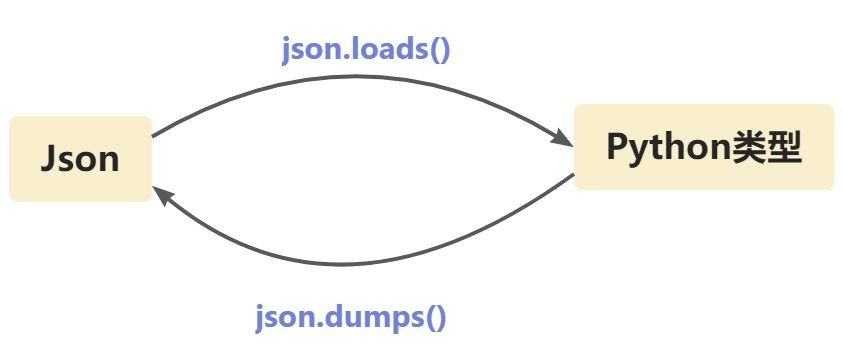
2.1 dumps函数
函数格式:json.dumps(obj, *, skipkeys=false, ensure_ascii=true, check_circular=true, allow_nan=true, cls=none, indent=none, separators=none, default=none, sort_keys=false, **kw)
参数解析:以下是一些常用的参数,更多参数参考:https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/json.html#basic-usage
| 常用参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| indent | 美化输出 |
| ensure_ascii | 为false时可保留非ascii字符(如中文) |
| sort_keys | 为true时按键名排序输出 |
使用示例:
import json
mydict={'name':'张三','age':15}
json_str = json.dumps(mydict, indent=2, ensure_ascii=false)
print(json_str)
print(type(json_str)) # <class 'str'>
2.2 loads函数
函数格式:json.loads(s, *, cls=none, object_hook=none, parse_float=none, parse_int=none, parse_constant=none, object_pairs_hook=none, **kw)</font>**
具体参数参考:https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/json.html#basic-usage
使用示例:以百度翻译为例
import json
import requests
url = "https://fanyi.baidu.com/sug"
headers = {
"user-agent": "mozilla/5.0 (windows nt 10.0; win64; x64) applewebkit/537.36 (khtml, like gecko) chrome/109.0.0.0 safari/537.36 edg/109.0.1518.78"
}
data = {
"kw": "face to face"
}
response = requests.post(url=url, data=data, headers=headers)
result = json.loads(response.text)
# result = response.json()
for item in result["data"]:
print(item["k"], item["v"])
2.3 错误处理
捕获json解析错误:exception json.jsondecodeerror(msg, doc, pos),jsondecodeerror有msg错误信息、doc正在解析的json文档、pos文档中解析失败的起始位置索引等属性。
try:
data = json.loads(invalid_json_str)
except json.jsondecodeerror as e:
print(f"解析失败: {e}")
三、jsonpath模块
官方文档:https://goessner.net/articles/jsonpath/
jsonpath模块可以对json 数据快速提取,安装:pip install jsonpath-ng
他与xpath语法相似:
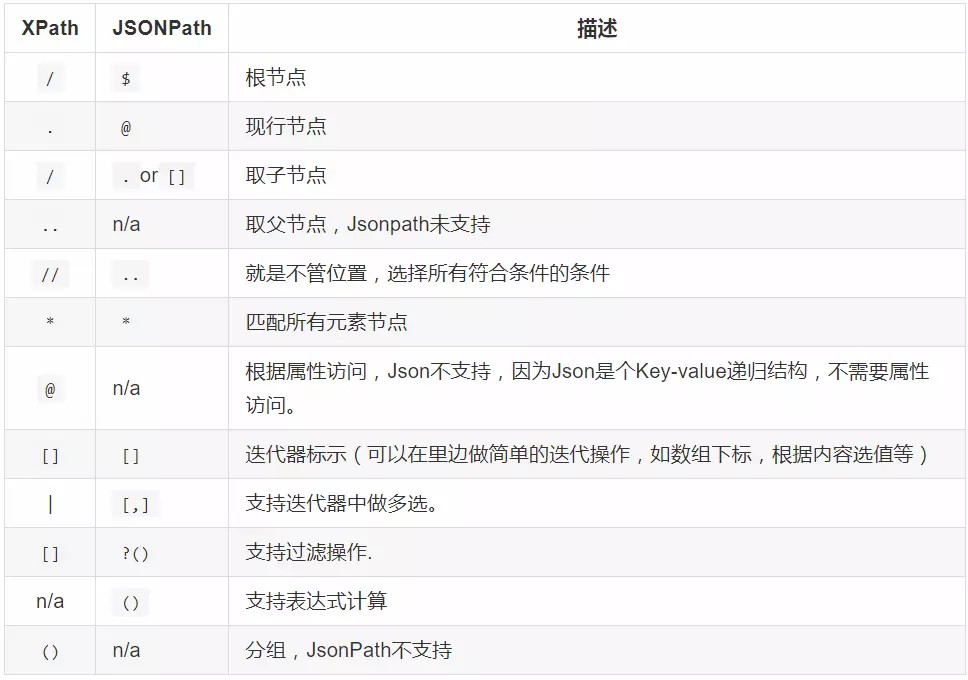
以下面数据为例:
{ "store": {
"book": [
{ "category": "reference",
"author": "nigel rees",
"title": "sayings of the century",
"price": 8.95
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "evelyn waugh",
"title": "sword of honour",
"price": 12.99
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "herman melville",
"title": "moby dick",
"isbn": "0-553-21311-3",
"price": 8.99
},
{ "category": "fiction",
"author": "j. r. r. tolkien",
"title": "the lord of the rings",
"isbn": "0-395-19395-8",
"price": 22.99
}
],
"bicycle": {
"color": "red",
"price": 19.95
}
}
}
使用jsonpath获取数据:
代码实现
from jsonpath_ng import parse
# 定义 jsonpath 表达式
expr = parse("$.store.book[*].title")
# 提取数据
matches = [match.value for match in expr.find(data)]
print(matches)
# 输出: ['sayings of the century', 'sword of honour', 'moby dick', 'the lord of the rings']
四、jmespath模块
官方文档:https://jmespath.org/tutorial.html
相比于jsonpath,jmespath语法更简洁,性能更好,安装:pip install jmespath
根据上述例子,则有:
import jmespath
# 提取所有书籍标题
result = jmespath.search("store.book[*].title", data)
print(result)
# 输出: ['sayings of the century', 'sword of honour', 'moby dick', 'the lord of the rings']
具体使用参见下文
4.1 search函数
jmespath.search是 jmespath 库的核心函数,用于在 json 数据中执行查询表达式并返回匹配结果,格式为jmespath.search(expression, data),更多参考https://jmespath.org/specification.html
expression:jmespath 查询字符串(如"users[*].name")
data:待查询的 json 数据(python 字典或列表)
查询成功则返回匹配的数据,否则返回none
对于要重复执行的查询,可以预编译
from jmespath import compile as jmes_compile
# 预编译表达式
expr = jmes_compile("users[*].name")
# 多次使用编译后的表达式
result1 = expr.search(data1)
result2 = expr.search(data2)
在错误处理上,可以用try-except捕获jmespath.exceptions.jmespatherror
try:
result = jmespath.search("invalid.expression[", data)
except jmespath.exceptions.jmespatherror as e:
print(f"表达式错误: {e}")
4.2 基本语法
4.2.1 基本查询
基本表达式:json对象中的一个键,如果不存在则返回null
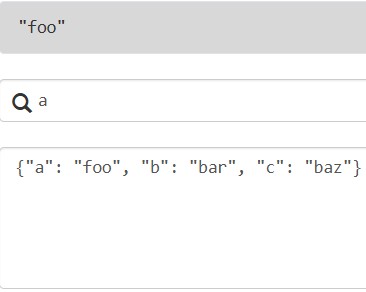
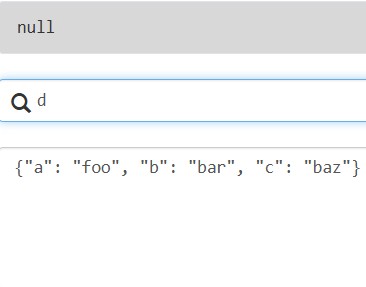
相应的代码实现:
#自定义环境 library/python:3.9-slim-top1000
import jmespath
data = {"a": "foo", "b": "bar", "c": "baz"}
result = jmespath.search("a", data)
print(result) # 输出: foo
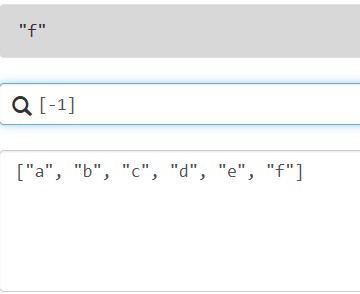
支持索引访问,从0开始,也支持负索引(从列表末尾开始索引)
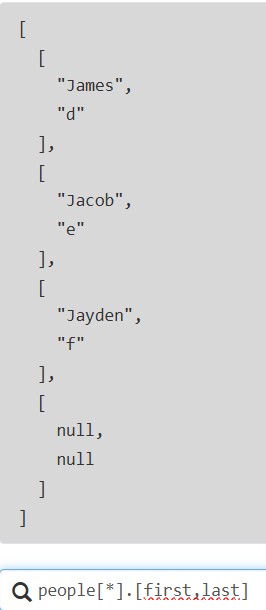
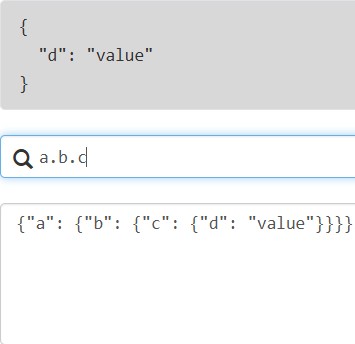
使用.访问子节点:

支持切片,与python的切片类似,格式为[start:stop:step]
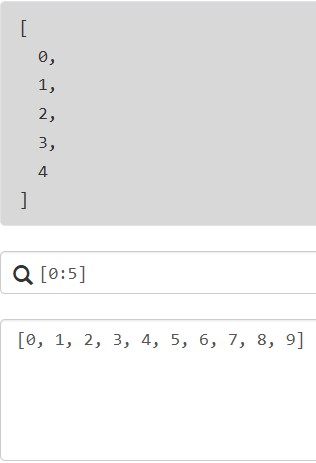
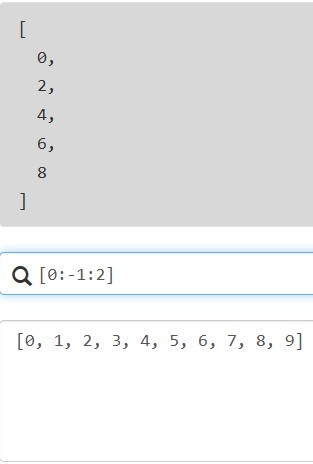
4.2.2 投影
投影,是jmespath的一个关键特性,允许将一个表达式应用于一组元素,有五种类型:
- list projections:列表投影
- slice projections:切片投影
- object projections:对象投影
- flatten projections:平坦投影
- filter projections:过滤投影
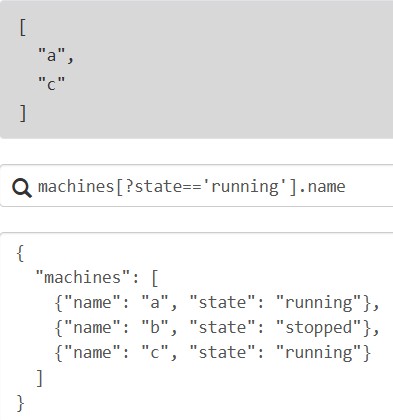
列表投影:仅适用于列表,*用来匹配列表中所有元素或对象的所有键;[]用于列表投影,类似于sql中的select
{"missing": "different"} 在应用表达式first时评估为null,并且null值不会被添加到收集结果数组中
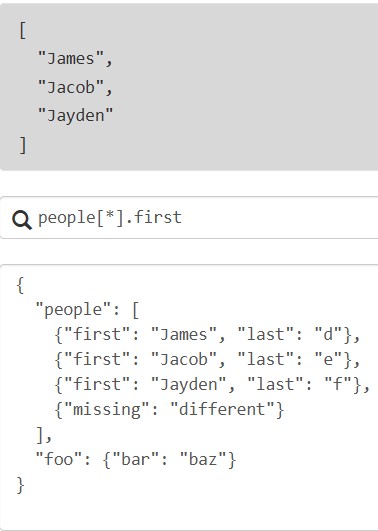
也可以提取多个字段组成多个列表

切片投影:与列表投影几乎相同,区别在于左侧是切片评估的结果,
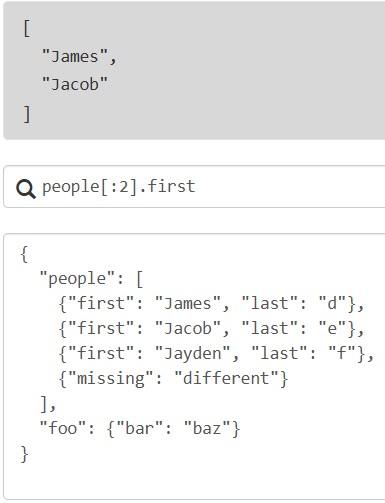
对象投影:从对象中提取多个字段,生成新的字典或列表
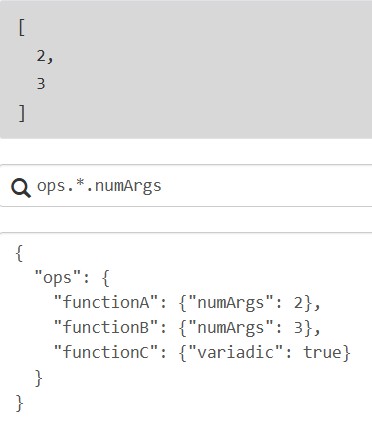
展平投影:将嵌套的列表结构转换为单层列表,便于处理多层嵌套数据,列表[]将嵌套列表展平,通常结合*使用

如果元素不是列表,展平操作会忽略它
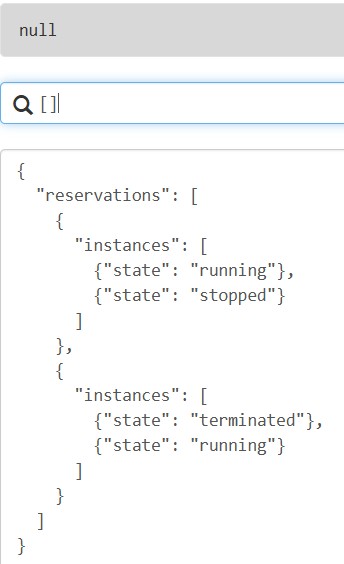
过滤投影:使用过滤表达式[?条件]实现更精准的数据提取,过滤表达式支持比较运算符(==、!=、<、<=、>、>=)、逻辑运算符
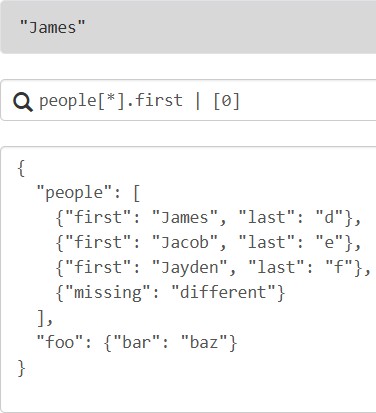
4.2.3 管道
使用管道表达式<expression> | <expression>来表示投影必须停止。当遇到管道符时,该点之前的结果会被传递给管道表达式的右侧
4.2.4 多选
同时提取多个字段,返回字典或列表;多选与投影不同,即使表达式结果为空,也会包含在内
- 哈希多选:
{key1: expr1, key2: expr2}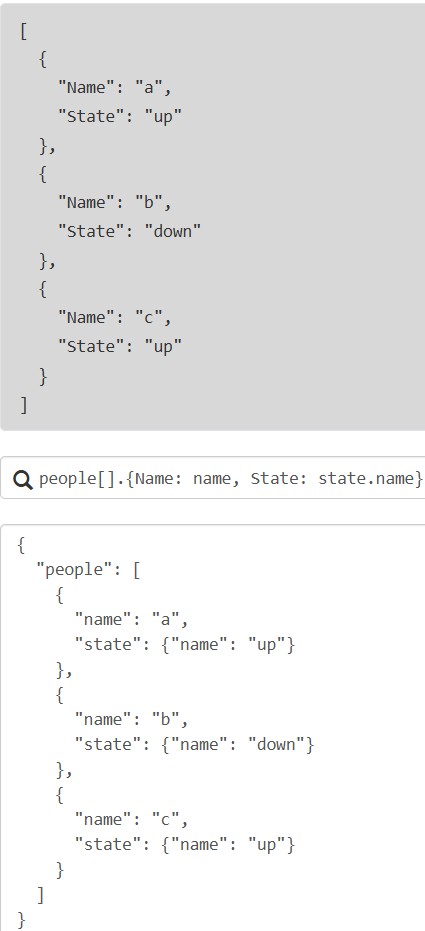
- 列表多选:
[expr1, expr2]
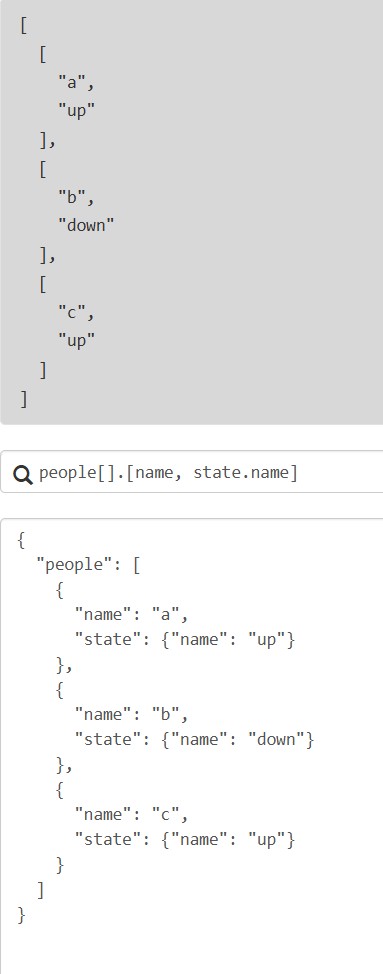
4.2.5 函数
支持函数表达式,更多参考:https://jmespath.org/specification.html#functions
| 常用函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
length() | 计算长度(字符串、列表、字典) |
keys()/values() | 获取字典的键或值 |
sort() | 排序列表 |
join() | 连接字符串列表 |
to_array()/to_object() | 转换类型 |

总结
到此这篇关于在python中使用json提取数据的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python用json提取数据内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论