前言
gdb 是 linux 平台下进行程序调试的最常用的工具。简单的程序调试就是加断点,然后一步一步让程序运行,直到找到 bug 。
一般的程序调试起来比较简单,但是在多进程或多线程情况下调试起来就比较麻烦。
若 test.c 是你想要调试的程序,那么在编译时需要加 -g,即 gcc test.c -g -o test。完成编译后使用命令:gdb test。
常用命令
命令 | 命令缩写及例子 | 说明 |
list + n | l + n | 显示源码第n行前后的代码,显示范围有限。 |
break + n | b + n | 在第n行设置断点 |
info | i | 描述程序状态 |
run | r | 开始运行程序 |
display | disp | 跟踪查看某个变量的值 |
info display | 用于显示当前所有要显示值的表达式的情况 | |
undisplay | undisplay + 编号 | 用于结束某个表达式值的显示 |
step | s | 执行下一条语句,如果该语句为函数调用,则进入函数执行其中的第一条语句 |
next | n | 执行下一条语句,如果该语句为函数调用,不会进入函数内部执行 |
p | 打印内部变量的值 | |
continue | c | 继续运行,直到遇到下一个断点 |
start | st | 开始执行程序,在main函数的第一条语句前面停下来 |
kill | k | 终止正在调试的程序 |
quit | q | 退出gdb |
set args | set args arg1 arg2 | 设置运行参数 |
show args | show args | 查看运行参数 |
finish | finish | 一直运行到函数返回并打印函数返回时的堆栈地址和返回值及参数值等信息 |
堆栈相关命令
命令 | 例子 | 说明 |
backtrace | bt | 查看堆栈信息 |
frame | f 1 | 查看栈帧 |
info reg | info reg/ i r | 查看寄存器使用情况 |
info stack | info stack | 查看堆栈使用情况 |
up/down | up/down | 跳到上一层/下一层函数 |
这里以一个简单的程序为例,进行调试。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define m 5
int fact(int n) //线性递归
{
if (n < 0)
return 0;
else if(n == 0 || n == 1)
return 1;
else
return n * fact(n - 1);
}
int facttail(int n, int a) //尾递归
{
if (n < 0)
return 0;
else if (n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n == 1)
return a;
else
return facttail(n - 1, n * a);
}
int facttail1(int n, int a)
{
while(n > 0)
{
a = n * a;
n--;
}
return a;
}
int main()
{
//printf("%p", facttail);
int a = fact(m);
int b = facttail(m, 1);
cout << "a:" << a <<endl;
cout << "b:" << b <<endl;
}(1)开始 gdb 调试
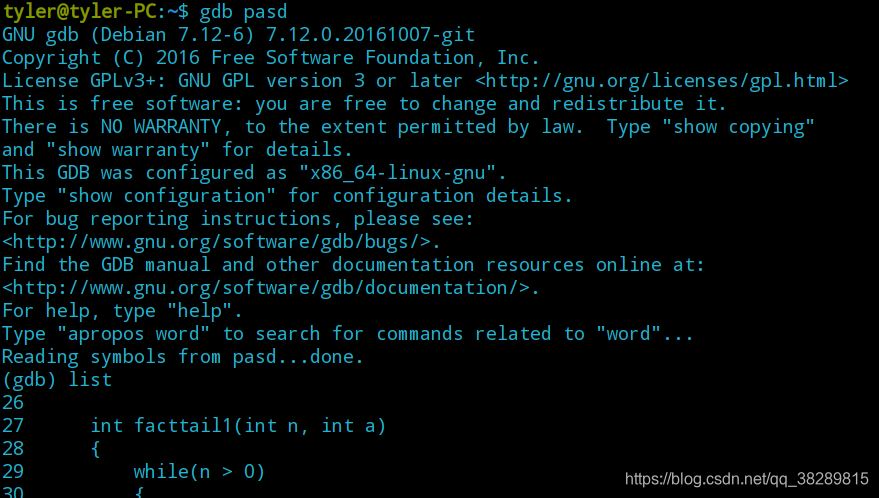
(2)设置断点
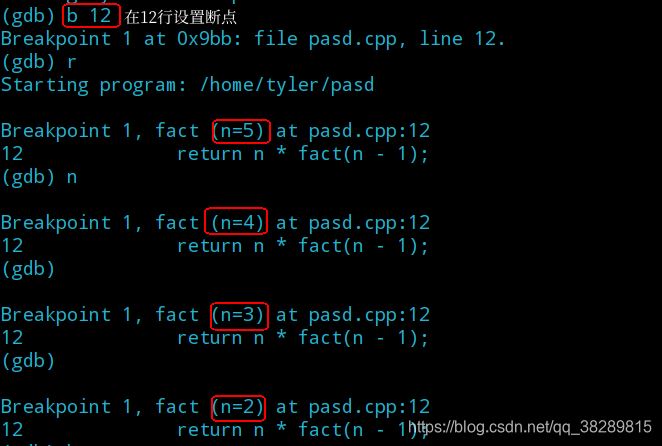
(3)查看栈的使用情况
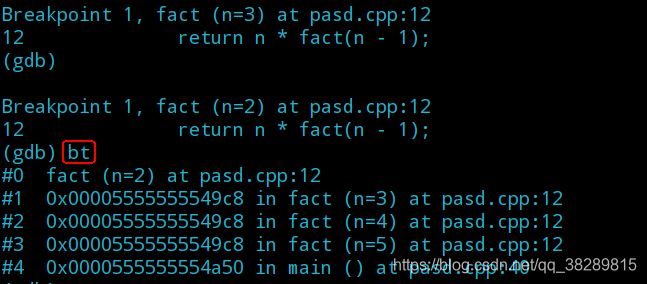
更为详细的断点调试
命令 | 例子 | 说明 |
break + 设置断点的行号 | break n | 在n行处设置断点 |
tbreak + 行号或函数名 | tbreak n/func | 设置临时断点,到达后被自动删除 |
break + filename + 行号 | break main.c:10 | 用于在指定文件对应行设置断点 |
break + <0x...> | break 0x3400a | 用于在内存某一位置处暂停 |
break + 行号 + if + 条件 | break 10 if i==3 | 用于设置条件断点,在循环中使用非常方便 |
info breakpoints/watchpoints [n] | info break | n表示断点编号,查看断点/观察点的情况 |
clear + 要清除的断点行号 | clear 10 | 用于清除对应行的断点,要给出断点的行号,清除时gdb会给出提示 |
delete + 要清除的断点编号 | delete 3 | 用于清除断点和自动显示的表达式的命令,要给出断点的编号,清除时gdb不会给出任何提示 |
disable/enable + 断点编号 | disable 3 | 让所设断点暂时失效/使能,如果要让多个编号处的断点失效/使能,可将编号之间用空格隔开 |
awatch/watch + 变量 | awatch/watch i | 设置一个观察点,当变量被读出或写入时程序被暂停 |
rwatch + 变量 | rwatch i | 设置一个观察点,当变量被读出时,程序被暂停 |
catch | 设置捕捉点来补捉程序运行时的一些事件。如:载入共享库(动态链接库)或是c++的异常 | |
tcatch | 只设置一次捕捉点,当程序停住以后,应点被自动删除 |
gdb多进程调试
命令 | 例子 | 说明 |
set follow-fork-mode [parent|child] | set follow-fork-mode parent or child | 设置调试器的模式,mode参数可以是: parent :fork之后调试原进程,子进程不受影响,这是缺省的方式 child :fork之后调试新的进程,父进程不受影响。 |
show follow-fork-mode | show follow-fork-mode | 显示当前调试器的模式 |
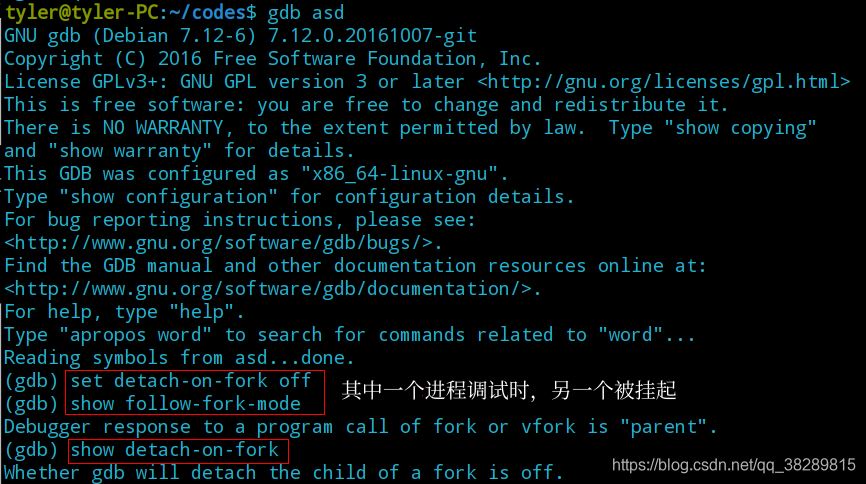
set detach-on-fork [on|off] | set detach-on-fork on or off | 设置gdb在fork之后是否detach进程中的其中一个,或者继续保留控制这两个进程 。 on:子进程(或者父进程,依赖于follow-fork-mode的值)会detach然后独立运行,这是缺省的mode off:两个进程都受gdb控制,一个进程(子进程或父进程,依赖于follow-fork-mode)被调试,另外一个进程被挂起 |
info inferiors | info inferiors | 显示所有进程 |
inferiors processid | inferiors 2 | 切换进程 |
detach inferiors processid | detach inferiors processid | detach 一个由指定的进程,然后从fork 列表里删除。这个进程会被允许继续独立运行。 |
kill inferiors processid | kill inferiors processid | 杀死一个由指定的进程,然后从fork 列表里删除。 |
catch fork | catch fork | 让程序在fork,vfork或者exec调用的时候中断 |
调试多进程时,需要设置 detach-on-fork 的值,默认值为 on,设置为 off 的含义:一个进程被调试,另外一个进程被挂起,这样就可以交替的调试进程。follow-fork-mode 的默认值为 parent,即默认调试父进程。调试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int num = 0;
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0) //子进程
{
while(1)
{
num++;
printf("child:pid:[%d] num:[%d]\n", getpid(), num);
sleep(2);
}
}
else
{
while(1){
num = num + 2;
printf("parent:pid:[%d] num:[%d]\n", getpid(), num);
sleep(2);
}
}
return 0;
}(1) 查看系统默认的 follow-fork-mode 和 detach-on-fork 及 设置follow-fork-mode 和 detach-on-fork
show follow-fork-mode show detach-on-fork set follow-fork-mode [parent|child] set detach-on-fork [on|off]
(2) 设置断点并查看断点信息
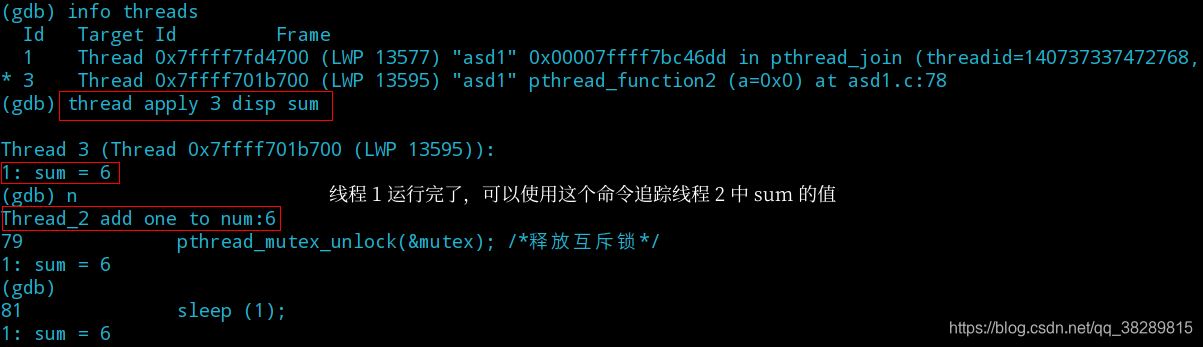
(3) 运行程序并使用 info inferiors 命令 (显示gdb调试的所有进程,其中带有*的进程是正在调试的进程)
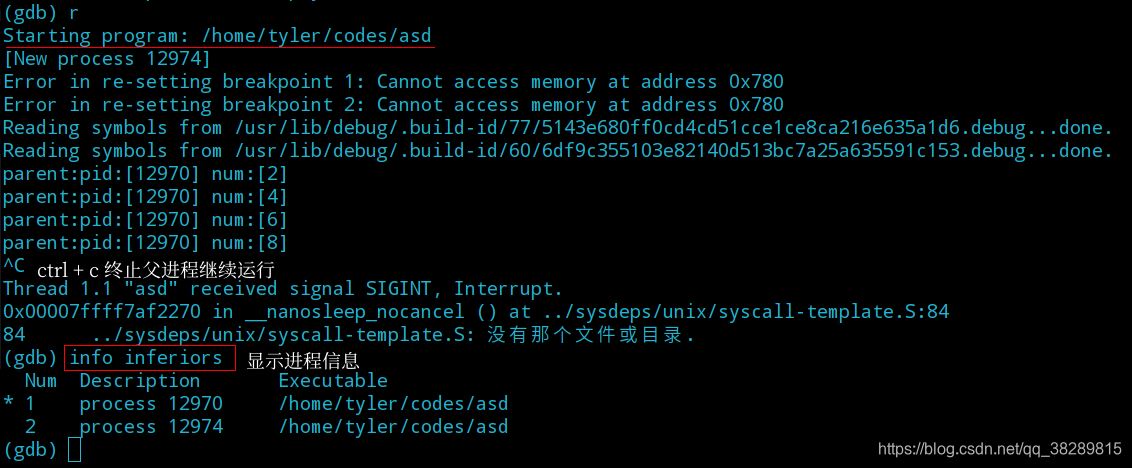
(4) 使用 inferior + [编号] 切换进程,对子进程进行调试
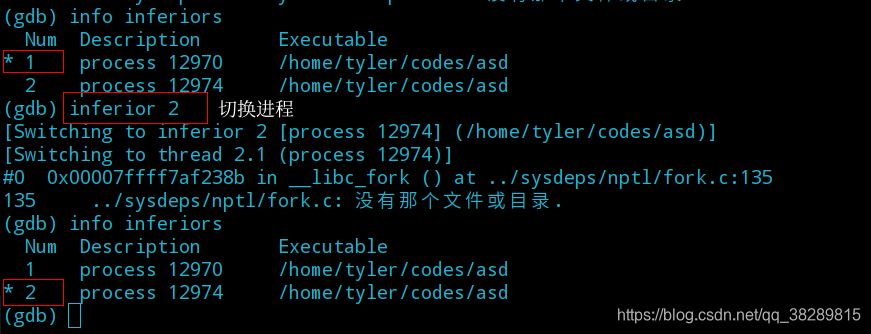
(5) 继续运行程序,观察子进程的输出
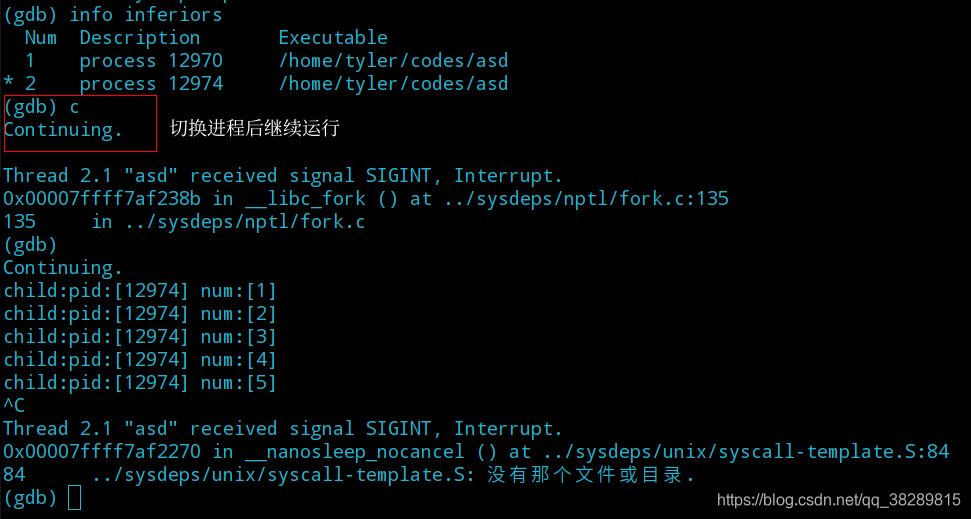
(6) 中断子进程运行后,开始逐步调试
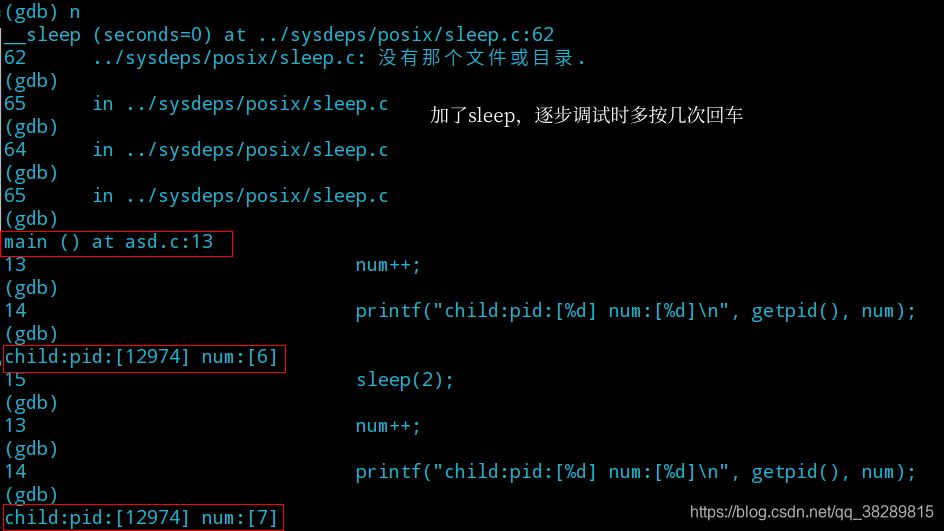
(7) 再次切换回父进程完成调试
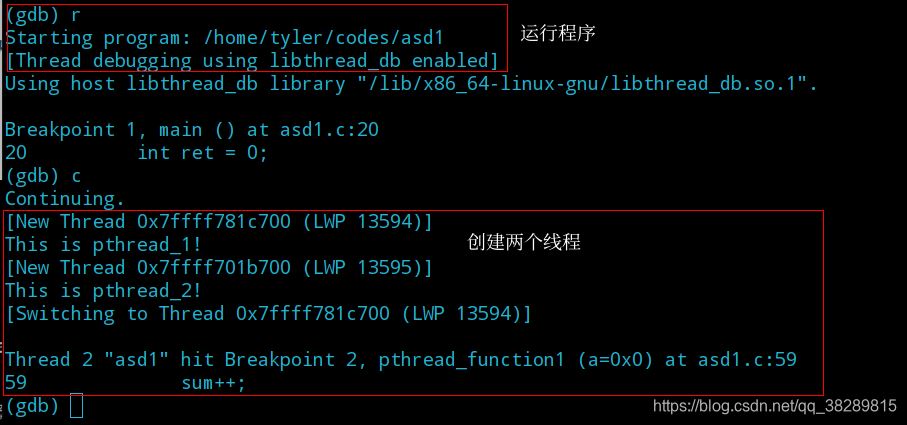
gdb多线程调试
命令 | 例子 | 说明 |
info threads | info threads | 查询线程信息 |
thread + 线程号 | thread 2 | 切换线程 |
thread apply [threadno] [all] + 命令 | thread apply [threadno] [all] bt | 线程根据相应的命令完成操作 |
set print thread-events | set print thread-events | 控制线程开始和结束时的打印信息 |
show print thread-events | show print thread-events | 显示线程打印信息的开关状态 |
调试代码:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
/*全局变量*/
int sum = 0;
/*互斥量 */
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
/*声明线程运行服务程序*/
void* pthread_function1 (void*);
void* pthread_function2 (void*);
int main (void)
{
/*线程的标识符*/
pthread_t pt_1 = 0;
pthread_t pt_2 = 0;
int ret = 0;
/*互斥初始化*/
pthread_mutex_init (&mutex, null);
/*分别创建线程1、2*/
ret = pthread_create( &pt_1, //线程标识符指针
null, //默认属性
pthread_function1, //运行函数
null); //无参数
if (ret != 0)
{
perror ("pthread_1_create");
}
ret = pthread_create( &pt_2, //线程标识符指针
null, //默认属性
pthread_function2, //运行函数
null); //无参数
if (ret != 0)
{
perror ("pthread_2_create");
}
/*等待线程1、2的结束*/
pthread_join (pt_1, null);
pthread_join (pt_2, null);
printf ("main programme exit!\n");
return 0;
}
/*线程1的服务程序*/
void* pthread_function1 (void*a)
{
int i = 0;
printf ("this is pthread_1!\n");
for( i=0; i<3; i++ )
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); /*获取互斥锁*/
/*临界资源*/
sum++;
printf ("thread_1 add one to num:%d\n",sum);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); /*释放互斥锁*/
/*注意,这里以防线程的抢占,以造成一个线程在另一个线程sleep时多次访问互斥资源,所以sleep要在得到互斥锁后调用*/
sleep (1);
}
pthread_exit ( null );
}
/*线程2的服务程序*/
void* pthread_function2 (void*a)
{
int i = 0;
printf ("this is pthread_2!\n");
for( i=0; i<5; i++ )
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); /*获取互斥锁*/
/*临界资源*/
sum++;
printf ("thread_2 add one to num:%d\n",sum);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); /*释放互斥锁*/
/*注意,这里以防线程的抢占,以造成一个线程在另一个线程sleep时多次访问互斥资源,所以sleep要在得到互斥锁后调用*/
sleep (1);
}
pthread_exit ( null );
}(1) 设置断点并查看信息
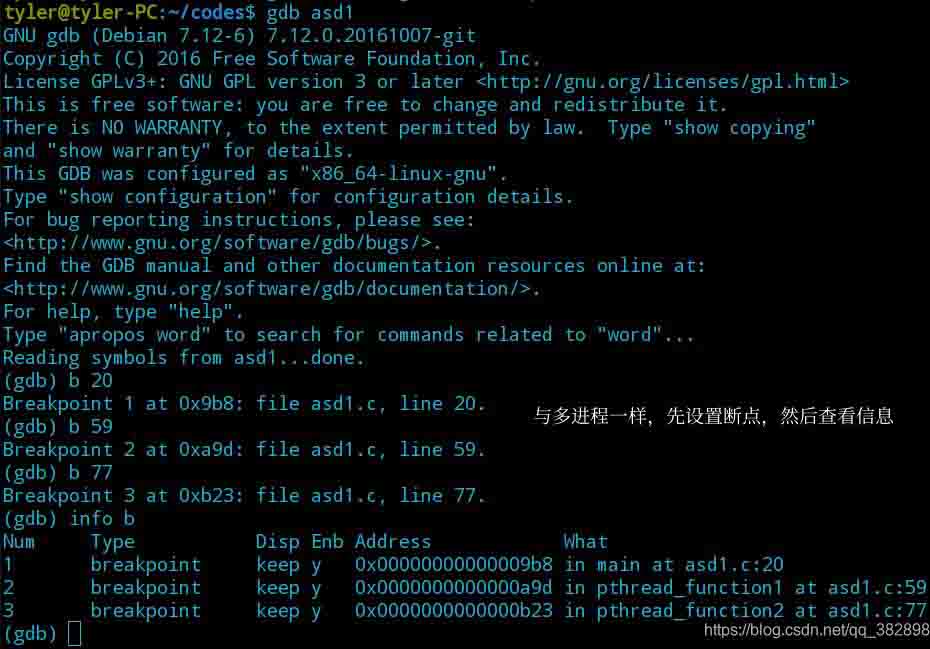
(2) 运行程序,这里可以不设第一个断点

(3) 两个线程交替运行,观察不同线程的输出结果
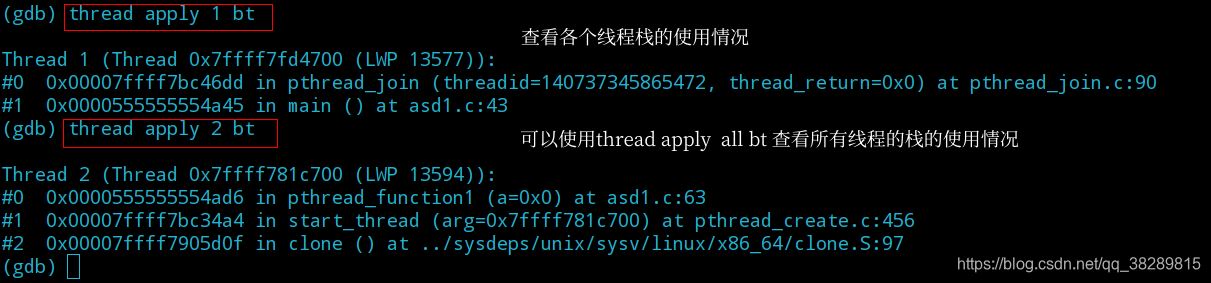
(4) 使用 info threads 查看线程信息,使用 thread + [编号] 切换线程

(5) 使用 thread apply + [编号] + 命令


锁定其他线程,只让当前线程运行
(1) 设置 set scheduler-locking on
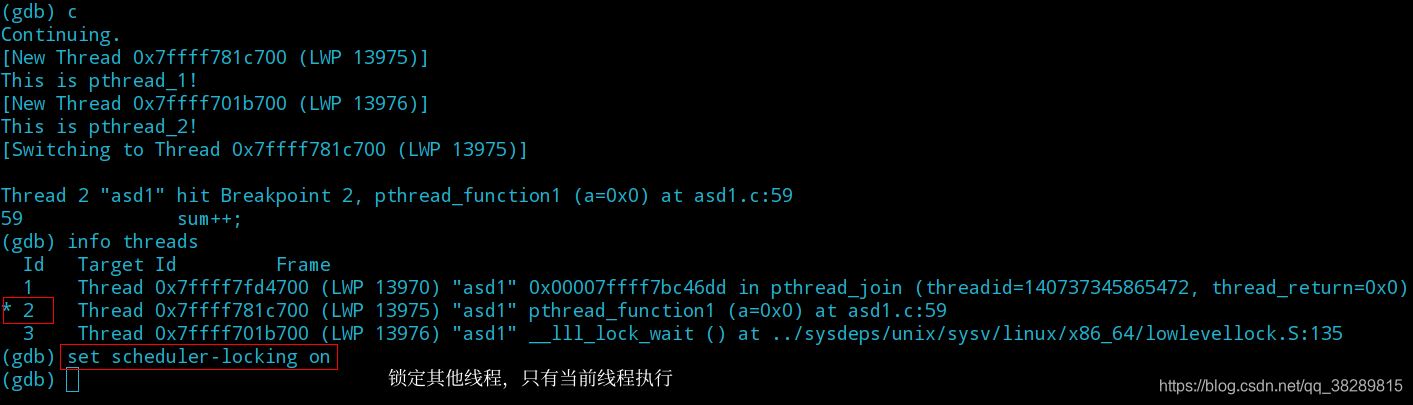
(2) 观察线程 1 运行的情况并完成调试
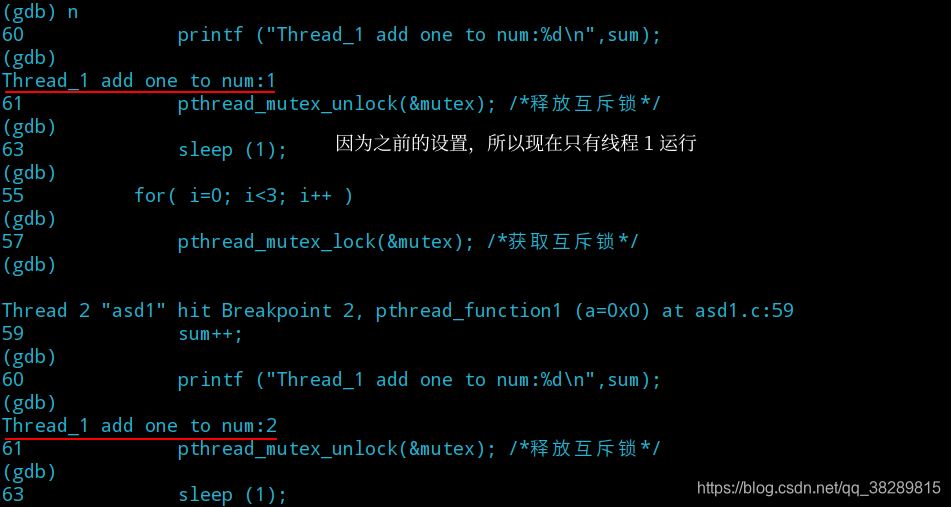
其他命令
(1) thread apply id1 id2 idn command: 让线程编号是id1,id2…等等的线程都执行command命令。
(2) thread apply all command:所有线程都执行command命令。
(3) set scheduler-locking off|on|step: 在调试某一个线程时,其他线程是否执行。在使用step或continue命令调试当前被调试线程的时候,其他线程也是同时执行的,如果我们只想要被调试的线程执行,而其他线程停止等待,那就要锁定要调试的线程,只让他运行。
off:不锁定任何线程,默认值。on:锁定其他线程,只有当前线程执行。step:在step(单步)时,只有被调试线程运行。
(4) set non-stop on/off:当调试一个线程时,其他线程是否运行。
(5) set pagination on/off: 在使用backtrace时,在分页时是否停止。
(6) set target-async on/ff: 同步和异步。同步,gdb在输出提示符之前等待程序报告一些线程已经终止的信息。而异步的则是直接返回。
(7) show scheduler-locking: 查看当前锁定线程的模式
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。



发表评论