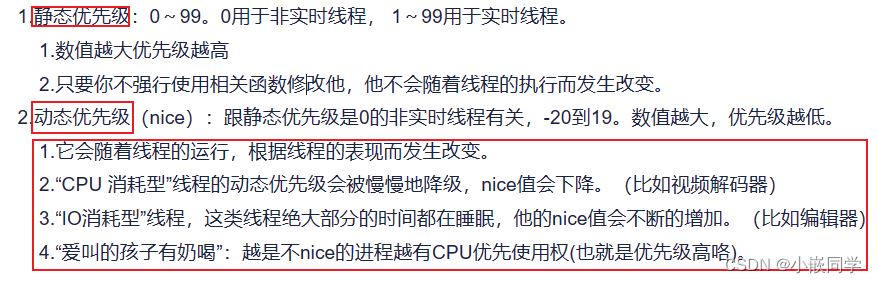
在操作系统中,线程优先级决定了线程在 cpu 调度时的重要性。较高优先级的线程会在竞争 cpu 资源时被更频繁地调度,以保证其及时响应。
一、背景
在linux中,线程是一种轻量级的执行单元,可以在进程内独立运行。线程可以分为普通线程和实时线程,它们之间的区别在于其调度和优先级设置。
sched_other,普通的调度(非实时线程),应用层设置优先级0,调度器总会给此类线程分配一定的cpu资源,只不过是被分配到的频次和时间片长度较少。每1s中实时线程和普通线程的时间比例是95 :5。
普通线程没有固定的响应时间要求,它们的优先级由系统动态调整。
linux使用cfs调度器来管理普通线程。cfs调度器采用一种称为红黑树的数据结构来维护线程的优先级。每个线程都有一个vruntime值,它表示线程在运行队列中消耗的虚拟时间。cfs调度器会根据线程的vruntime值来确定运行的顺序。优先级较高的线程vruntime值较小,因此能够更早地获得cpu的时间片。适用场景:实时性要求不高,但要求必须能被执行的线程。sched_fifo,抢占式调度(实时线程),实时先行,应用层设置优先级1-99,同一优先级的多个线程中,一旦某个抢占式线程获取cpu,除非被更高优先级线程抢占(比如在非实时线程中创建一个更高优先级的实时线程),或该线程主动让出cpu资源,否则该线程将会一直占用cpu(但总会分配一点资源给sched_other非实时线程)。适用场景:实时性要求高,不希望被频繁打断的任务。sched_rr,轮询式调度(实时线程),实时循环,设置优先级1-99,以循环方式运行,每个线程都有一个时间片来执行任务,时间片耗尽后,该线程将被放入队列的末尾,而较低优先级的线程有机会执行。适用场景:实时性要求高,允许被频繁打断的任务。
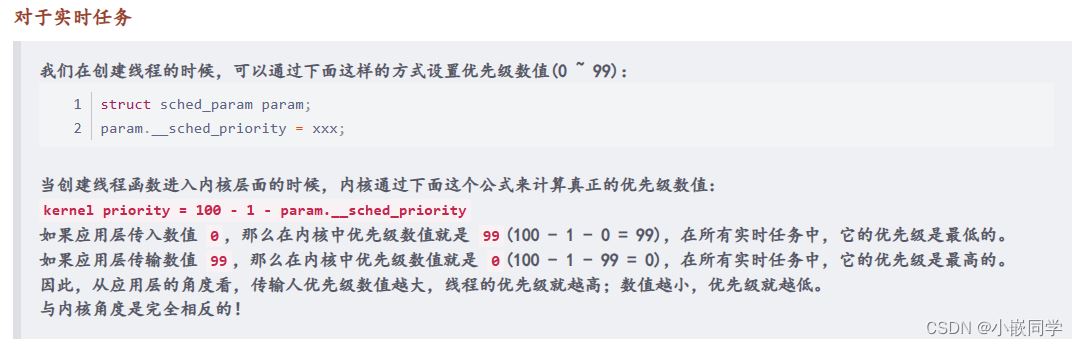
在linux中,可以使用sched_setscheduler函数。这个函数允许我们选择普通线程或实时线程。对于普通线程,可以使用nice函数来动态调整优先级。对于实时线程,可以使用sched_setscheduler函数来设置其类型和优先级。

关于优先级高低和数值大小的关系,在应用层和内核中二者是相反的。
设置线程的优先级需要谨慎,因为过高的优先级可能会导致系统资源的过度占用,从而影响其他线程和进程的正常运行。另外,需要注意的是,只有具有足够权限的用户才能设置较高的实时线程优先级。
总结起来,linux中的线程分为普通线程和实时线程。普通线程的优先级由系统动态调整,而实时线程的优先级由用户显式设置。通过合理地设置线程的优先级,可以提高系统的性能和响应时间。然而,设置线程的优先级需要慎重考虑,以避免影响其他线程和进程的正常运行。
二、调整普通线程的优先级
通过系统命令
在 linux 系统中,普通线程(非实时线程)的优先级可以通过 nice 和 renice 命令来进行设置。这些命令允许用户在命令行中调整线程的优先级,而无需特权。
nice命令:nice 命令用于启动新的进程并设置其优先级。它在运行指定命令时按照给定的优先级进行调度。较低的优先级对应较高的 nice 值,这意味着 nice 值越高,优先级越低。
命令的基本语法如下:
nice -n <priority> <command>
其中,-n 后面跟着要设置的优先级值(取值范围一般是-20到19),然后是要执行的命令。
例如,要以较低的优先级(较高的 nice 值)运行一个命令,可以使用如下命令:
nice -n 10 <command>
renice命令:renice 命令用于修改已经运行的进程的优先级。这使得用户可以在进程运行时动态地调整其优先级,而无需停止和重新启动它。命令的基本语法如下:
renice <priority> -p <pid>
其中,<priority> 是要设置的优先级值,<pid> 是要修改优先级的进程的进程 id。
例如,要将进程的优先级调整为较高,可以使用如下命令:
renice -5 -p 12345
其中 12345 是目标进程的进程 id。
通过 nice 和 renice 命令,用户可以在 linux 系统中方便地设置普通线程的优先级,以满足对执行顺序的特定要求。这种方式虽然不能达到实时线程调度的级别,但对于一般的任务调度已经足够有效了。
通过linux c代码
nice 函数用于调整进程的调度优先级,允许进程降低自身的优先级,从而降低对系统资源的竞争,也可以提高自身优先级来更快地响应。
在linux系统中,nice 函数的作用是通过改变进程的静态优先级值,来影响进程在cpu上的调度顺序。
下面是nice函数的原型:
#include <unistd.h> int nice(int inc);
参数 inc 是一个整数,表示要增加或减少的进程优先级。这个值的范围通常是 -20 到 19,其中 -20 表示最高优先级,而 19 表示最低优先级。
nice 函数的返回值是新的进程优先级。如果调用成功,返回值通常是 0 到 39 之间的数,其中 0 表示最高优先级,而 39 表示最低优先级。如果调用失败,返回值为 -1,并设置全局变量 errno 以指示错误原因。

以下是一些需要注意的事项:
- 只有具有 cap_sys_nice 权限(linux内核中的一种权限,用于控制进程对于设置任意nice值的能力)或者以 root 用户身份运行的进程才能提高进程的调度优先级。通常,普通用户只能降低自己进程的优先级。
nice函数的参数inc只是相对调整,而不是设定一个绝对的优先级值。只能提高或降低一定的优先级,而不能直接将进程的优先级调整到一个特定的值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main() {
// 获取当前进程的优先级
int currentpriority = nice(0);
if (currentpriority == -1) {
perror("failed to get current process priority");
return 1;
}
printf("current process priority: %d\n", currentpriority);
// 增加进程的优先级
int newpriority = nice(-5);
if (newpriority == -1) {
perror("failed to increase process priority");
return 1;
}
printf("increased process priority to: %d\n", newpriority);
return 0;
}
在 linux 系统中,除了 nice 函数之外,还有一个名为 setpriority 的系统调用可用于设置进程的调度优先级。setpriority 函数提供了更灵活的方式来设置进程的优先级,它允许指定进程的进程组id和用户id,而不仅仅是当前进程。
下面是 setpriority 函数的原型:
#include <sys/resource.h> int setpriority(int which, id_t who, int priority);
which参数指定了谁的优先级要被改变。它可以是prio_process(表示改变指定进程的优先级)、prio_pgrp(表示改变指定进程组的所有进程的优先级)或者prio_user(表示改变指定用户的所有进程的优先级)。who参数是进程、进程组或用户的 id,用于指定要进行优先级调整的目标。priority参数是新的进程优先级。其取值范围与nice函数相同,通常为 -20 到 19。
下面是 setpriority 函数的一个简单示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/resource.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno>
int main() {
// 设置当前进程的优先级
if (setpriority(prio_process, 0, 10) == -1) {
perror("failed to set process priority");
return 1;
}
printf("process priority set to 10\n");
return 0;
}
在这个示例中,setpriority 函数被用来将当前进程的优先级设置为 10。这将影响当前进程的调度优先级。setpriority 函数的使用可以让我们更加灵活地控制进程的调度优先级,可以针对不同的进程组或用户进行设置,提供了比 nice 函数更细粒度的控制能力。
三、调整实时线程的优先级
通过系统命令
chrt 是一个用于改变进程调度策略或优先级的命令行工具。它在 linux 系统中提供了对实时进程调度的控制。
chrt 命令的基本语法如下:
chrt [options] priority command
chrt 命令的常用选项包括:
-p, --pid:指定要操作的进程id。-f, --fifo:设置进程的调度策略为 fifo(先进先出)。-r, --rr:设置进程的调度策略为 round robin(循环调度)。-o, --other:设置进程的调度策略为其他进程调度策略。-m, --max:设置进程的优先级为最高优先级。-e, --min:设置进程的优先级为最低优先级。-p, --priority priority:设置进程的静态优先级。
- 以下是几个使用示例:
将进程的调度策略设置为 fifo(先进先出):
chrt -f -p 90 <command>
将进程的调度策略设置为 round robin(循环调度):
chrt -r -p 80 <command>
将进程的调度策略设置为其他调度策略(如 sched_batch):
chrt -o -p 50 <command>
将进程的优先级设置为最高优先级:
chrt -m -p 99 <command>
将进程的优先级设置为最低优先级:
chrt -e -p 0 <command>
在上述示例中,<command> 是要运行的命令或进程。通过使用不同的选项和参数,chrt 命令可以改变进程的调度策略和优先级,从而影响进程在系统中的调度行为。
请注意,使用 chrt 命令可能需要 root 权限或 cap_sys_nice 权限。
通过linux c代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sched.h>
#define thread_priority 80 // 设置实时线程的优先级
void* thread_function(void* arg) {
// 实时线程的具体操作
// ...
return null;
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid;
pthread_attr_t attr;
struct sched_param sched_param;
// 初始化线程属性
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
// 设置线程为实时线程
pthread_attr_setinheritsched(&attr, pthread_explicit_sched);
pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(&attr, sched_fifo);
// 设置线程优先级
sched_param.sched_priority = thread_priority;
pthread_attr_setschedparam(&attr, &sched_param);
// 创建实时线程
int result = pthread_create(&tid, &attr, thread_function, null);
if (result != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to create thread\n");
exit(exit_failure);
}
// 等待实时线程结束
pthread_join(tid, null);
// 清理资源
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return 0;
}
pthread_attr_setinheritsched函数用于设置线程属性的继承调度策略。具体来说,它可以控制新创建线程是否继承调用线程的调度策略。函数原型如下:
#include <pthread.h> int pthread_attr_setinheritsched(pthread_attr_t *attr, int inherit);
attr是一个指向线程属性对象的指针,inherit参数用于设置继承调度策略。inherit可以是以下两个常量之一:
pthread_inherit_sched:新线程将继承创建它的线程的调度策略。pthread_explicit_sched:使用显式调度策略,即通过pthread_attr_setschedpolicy设置特定的调度策略。
默认情况下,线程属性的继承调度策略是 pthread_inherit_sched,意味着新创建的线程将继承调用线程的调度策略。
下面是一个示例代码,演示如何使用 pthread_attr_setinheritsched 函数来设置线程属性的继承调度策略:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
int main() {
pthread_attr_t attr;
int ret;
int inherit;
// 初始化线程属性
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
// 获取当前线程属性的继承调度策略
ret = pthread_attr_getinheritsched(&attr, &inherit);
if (ret == 0) {
if (inherit == pthread_inherit_sched) {
printf("继承调度策略:pthread_inherit_sched\n");
} else if (inherit == pthread_explicit_sched) {
printf("继承调度策略:pthread_explicit_sched\n");
} else {
printf("未知的继承调度策略\n");
}
} else {
printf("获取线程属性的继承调度策略失败\n");
}
// 设置线程属性的继承调度策略
inherit = pthread_explicit_sched;
ret = pthread_attr_setinheritsched(&attr, inherit);
if (ret == 0) {
printf("成功设置线程属性的继承调度策略\n");
} else {
printf("设置线程属性的继承调度策略失败\n");
}
// 销毁线程属性
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return 0;
}
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。





发表评论