nscache
nscache是foundation框架提供的缓存类的实现,使用方式类似于可变字典,最重要的是它是线程安全的,而nsmutabledictionary不是线程安全的,在多线程环境下使用nscache是更好的选择。 类的基本属性和方法:
#import <foundation/nsobject.h>
@class nsstring;
@protocol nscachedelegate;
ns_assume_nonnull_begin
api_available(macos(10.6), ios(4.0), watchos(2.0), tvos(9.0))
@interface nscache <keytype, objecttype> : nsobject {
@private
id _delegate;
void *_private[5];
void *_reserved;
}
@property (copy) nsstring *name;
@property (nullable, assign) id<nscachedelegate> delegate;
- (nullable objecttype)objectforkey:(keytype)key;
- (void)setobject:(objecttype)obj forkey:(keytype)key; // 0 cost
- (void)setobject:(objecttype)obj forkey:(keytype)key cost:(nsuinteger)g;
- (void)removeobjectforkey:(keytype)key;
- (void)removeallobjects;
@property nsuinteger totalcostlimit; // limits are imprecise/not strict
@property nsuinteger countlimit; // limits are imprecise/not strict
@property bool evictsobjectswithdiscardedcontent;
@end
@protocol nscachedelegate <nsobject>
@optional
- (void)cache:(nscache *)cache willevictobject:(id)obj;
@end
ns_assume_nonnull_end
缓存淘汰策略
通过 gnustep 提供的源码,我们得知其对于 nscache 的处理是计算出一个平均访问次数,然后释放的是访问次数较少的对象,直到满足需要释放大小,也就是 lru 的机制。通过 swift-corelibs-foundation 源码我们得知,其首先存储链表结构中是按对象花费内存大小排序的,然后通过用户有无指定 totalcostlimit 大小限制来依次释放(先释放占用较小的对象),直到满足需要释放大小。然后再通过个数限制来释放,直到满足需要释放大小(依旧是先释放较小的对象)。
gnustepfoundation 源码地址:github.com/gnustep/lib…
swift foundation 源码地址:github.com/apple/swift…
在内存不足时nscache会自动释放存储的对象。
nscache的键key不会被复制,所以key不需要实现nscopying协议。
可以设置缓存的最大数量,当缓存数量满的时候,再添加将先删除先添加的对象再增加。
唯一一个代理方法是一个对象将被删除时调用,调用方式有以下几种:
- nscache缓存对象自身被释放
- 手动调用removeobjectforkey:方法
- 手动调用removeallobjects
- 缓存中对象的个数大于countlimit,或,缓存中对象的总cost值大于totalcostlimit
- 程序进入后台后
- 收到系统的内存警告
基本用法:
@interface nscacheviewcontroller ()<nscachedelegate>
@property(nonatomic,strong) nscache *cache;
@end
@implementation nscacheviewcontroller
- (void)viewdidload {
[super viewdidload];
self.cache = [[nscache alloc] init];
//设置最大缓存数
self.cache.countlimit = 5;
//设置代理,实现代理方法,
self.cache.delegate = self;
self.cache.name = @"测试内存";
for (int i=0; i<10; i++) {
nsstring *str = [nsstring stringwithformat:@"%d",i];
[self.cache setobject:str forkey:str];
}
// do any additional setup after loading the view.
}
//超出缓存部分会被释放, 收到内存警告时候系统也会释放一部分。
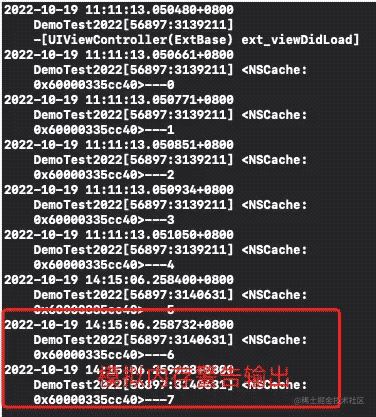
-(void)cache:(nscache *)cache willevictobject:(id)obj{
nslog(@"%@---%@",cache,obj);
}
@end
实际应用 sdwebimage
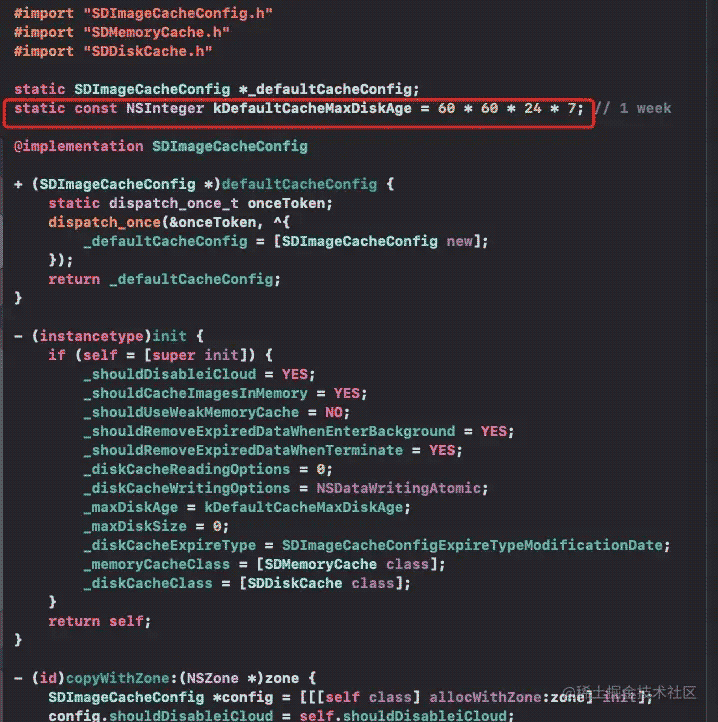
sdimagecacheconfig中可以配置是否使用内存做缓存,默认为yes
磁盘缓存的最大时长,默认为一周
sdimage中内存缓存sdmemorycache继承与nscache,缓存时候会在nscache和sdmemorycache的nsmaptable各存一份。读取时候也优先读取系统cache,如果不存在再读取sdmemorycache,这样做的目标是防止一些系统缓存不可控因素。
// `setobject:forkey:` just call this with 0 cost. override this is enough
- (void)setobject:(id)obj forkey:(id)key cost:(nsuinteger)g {
[super setobject:obj forkey:key cost:g];
if (!self.config.shoulduseweakmemorycache) {
return;
}
if (key && obj) {
// store weak cache
sd_lock(_weakcachelock);
[self.weakcache setobject:obj forkey:key];
sd_unlock(_weakcachelock);
}
}
nsurlcache
使用缓存的目的是为了使应用程序能更快速的响应用户输入,是程序高效的运行。有时候我们需要将远程web服务器获取的数据缓存起来,以空间换取时间,减少对同一个url多次请求,减轻服务器的压力,优化客户端网络,让用户体验更良好。
背景:nsurlcache : 在ios5以前,apple不支持磁盘缓存,在ios5的时候,允许磁盘缓存,(nsurlcache 是根据nsurlrequest 来实现的)只支持http,在ios6以后,支持http和https。
缓存的实现说明:由于get请求一般用来查询数据,post请求一般是发大量数据给服务器处理(变动性比较大),因此一般只对get请求进行缓存,而不对post请求进行缓存。
缓存原理:一个nsurlrequest对应一个nscachedurlresponse
etag全称是entity tag,一般用于标识url对象是否发生了改变。 使用etag一般会出现如下的请求流程:
etag有点类似于文件hash或者说是信息摘要。
当进行一次url请求,服务端会返回'etag'响应头,下次浏览器请求相同的url时,浏览器会自动将它设置为请求头'if-none-match'的值。服务器收到这个请求之后,就开始做信息校验工作将自己本次产生的etag与请求传递过来的'if-none-match'对比,如果相同,则返回http状态码304,并且response数据体中没有数据。
第二次请求的时候从哪里获取到'etag'的值并赋给请求头'if-none-match'的?自然是浏览器的缓存中取出的。那么浏览器收到304状态码之后又干了什么?刚才说到response数据体中没有数据,但是浏览器仍需加载页面,它会从缓存中读取上次缓存的页面。
//
// nsurlcacheviewcontroller.m
// demotest2022
//
// created by wy on 2022/10/19.
//
#import "nsurlcacheviewcontroller.h"
@interface nsurlcacheviewcontroller ()
//去服务器比对资源是否需要更新
@property (nonatomic, strong) nsstring *lastmodified;
@property (nonatomic, strong) nsstring *etag;
@property(nonatomic,strong) uiimageview *imagev;
@end
@implementation nsurlcacheviewcontroller
- (void)viewdidload {
[super viewdidload];
self.imagev = [[uiimageview alloc] initwithframe:cgrectmake(0, 100, 100, 100)];
[self.view addsubview:self.imagev];
// do any additional setup after loading the view.
}
-(void)requesttest{
nsurl *url = [nsurl urlwithstring:@"http://via.placeholder.com/50x50.png"];
nsmutableurlrequest *request = [nsmutableurlrequest requestwithurl:url cachepolicy:(nsurlrequestreloadignoringcachedata) timeoutinterval:15] ;
if (self.lastmodified) {
[request setvalue:self.lastmodified forhttpheaderfield:@"if-modified-since"];
}
if (self.etag) {
[request setvalue:self.etag forhttpheaderfield:@"if-none-match"];
}
[[[nsurlsession sharedsession] datataskwithrequest:request completionhandler:^(nsdata * _nullable data, nsurlresponse * _nullable response, nserror * _nullable error) {
if (error) {
nslog(@"error---%@",error);
}else{
nsdata *tempdata = data;
nsstring *responsestr = [[nsstring alloc] initwithdata:tempdata encoding:nsutf8stringencoding];
self.lastmodified = [(nshttpurlresponse *)response allheaderfields][@"last-modified"];
self.etag =[(nshttpurlresponse *)response allheaderfields][@"etag"];
nslog(@"response:%@", response);
dispatch_sync(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
self.imagev.image = [uiimage imagewithdata:tempdata];
});
}
}] resume] ;
}
- (void)touchesbegan:(nsset<uitouch *> *)touches withevent:(uievent *)event{
[self requesttest];
}
@end
这样每次请求都使用忽略缓存的策略,但是要附带着"if-none-match"头,它的值是上次请求的响应头"etag"的值,于是服务器会每次都实时检查文件的修改状态,得到一个准确的状态值,最后决定返回304还是200。若是200,ios则直接使用新的response和新的数据;如果是304,则使用新的response和缓存中的data。
这样既能够获取到最新的数据有能够节约带宽。两全其美。
ios中定以的urlrequest缓存策略有以下几种:
typedef ns_enum(nsuinteger, nsurlrequestcachepolicy)
{
nsurlrequestuseprotocolcachepolicy = 0,
// 从不读取缓存,但请求后将response缓存起来
nsurlrequestreloadignoringlocalcachedata = 1,
nsurlrequestreloadignoringlocalandremotecachedata = 4,
nsurlrequestreloadignoringcachedata = nsurlrequestreloadignoringlocalcachedata,
// 以下两种在取缓存时,可能取到的是过期数据
nsurlrequestreturncachedataelseload = 2,// 缓存中没有才去发起请求加载,有就不进行网络请求了
nsurlrequestreturncachedatadontload = 3,// 缓存中没有不加载,绝不发起网络请求,缓存中没有则返回错误
nsurlrequestreloadrevalidatingcachedata = 5,//unimplemented
};
官方文档解释:
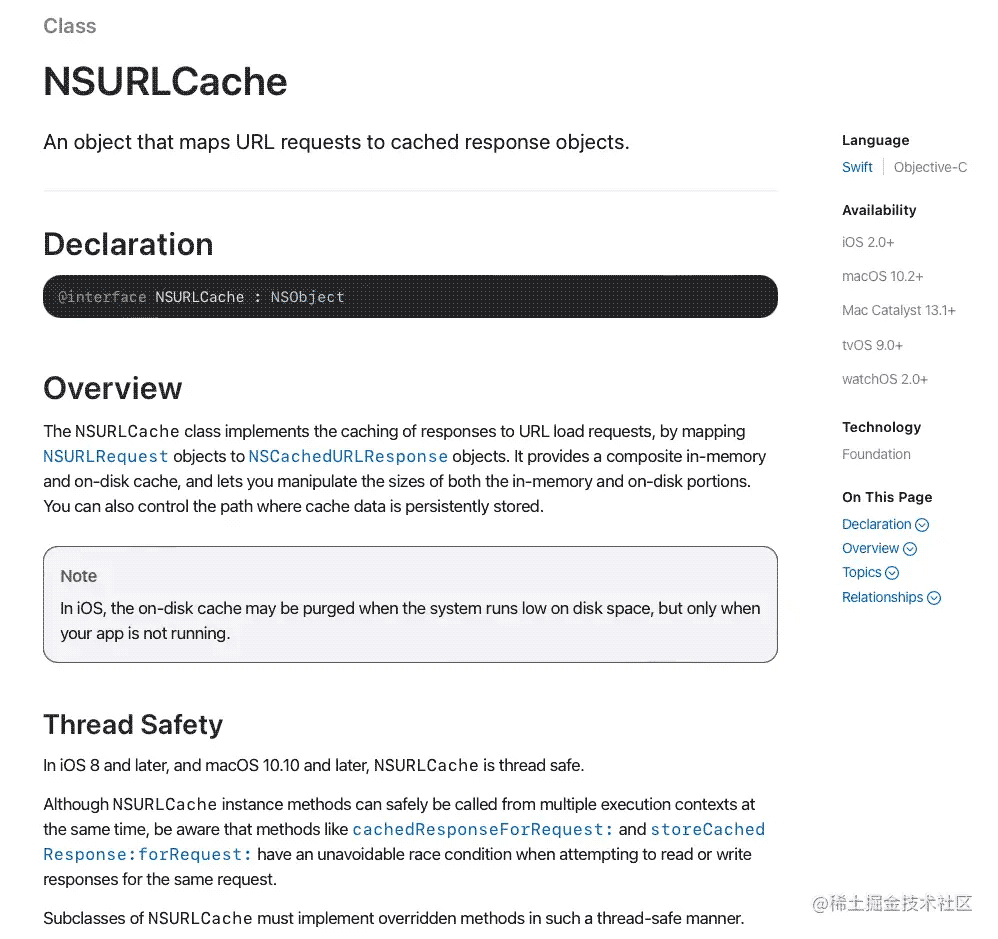
nsurlcache类通过将nsurlrequest对象映射到nscachedurlresponse对象来实现url加载请求响应的缓存。它提供了一个复合的内存和磁盘缓存,并允许您操作内存和磁盘部分的大小。您还可以控制缓存数据持久存储的路径。
在ios中,当系统磁盘空间不足时,磁盘上的缓存可能会被清除,但只有在应用程序未运行时才会清除。
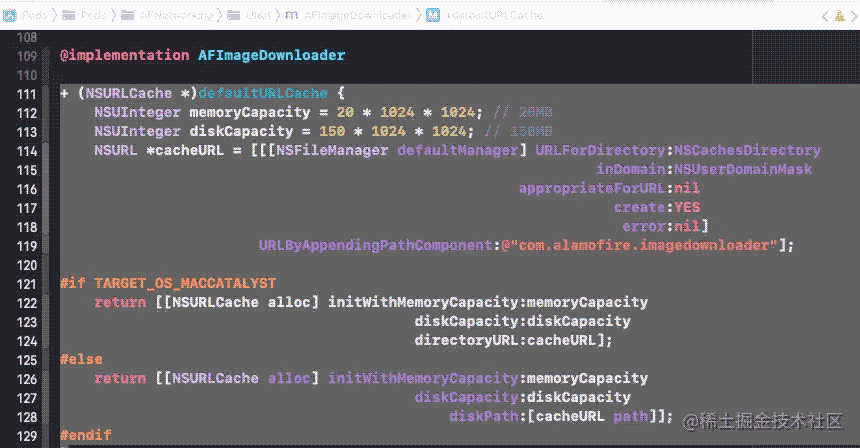
afnetwork中用法:
总结:
nscache 特点
- 使用方便,类似字典
- l线程安全
- l内存不足时,nscache会自动释放存储对象
- nscache的key不会被拷贝,不需要实现nscopying协议
- lnsdiscardablecontent协议
nsurlcache主要应用与网络请求数据缓存策略,优化网络请求性能优化。
以上就是ios nscache和nsurlcache缓存类实现示例详解的详细内容,更多关于ios nscache nsurlcache的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!



发表评论