引言
我发现官网只有python的调用代码示例,在网上也没找到有人分享java的例子,因此就有了这篇文章,前人栽树后人乘凉(如果你只想看代码部分可跳到文章后半部分)。
一、获取调用api所需要的参数信息:
首先我们进入腾讯元器获取调用api所需要的参数信息;链接:https://yuanqi.tencent.com/
点击【我的创建】,找到自己想要api调用的智能体,点击【更多】,点击【调用api】。
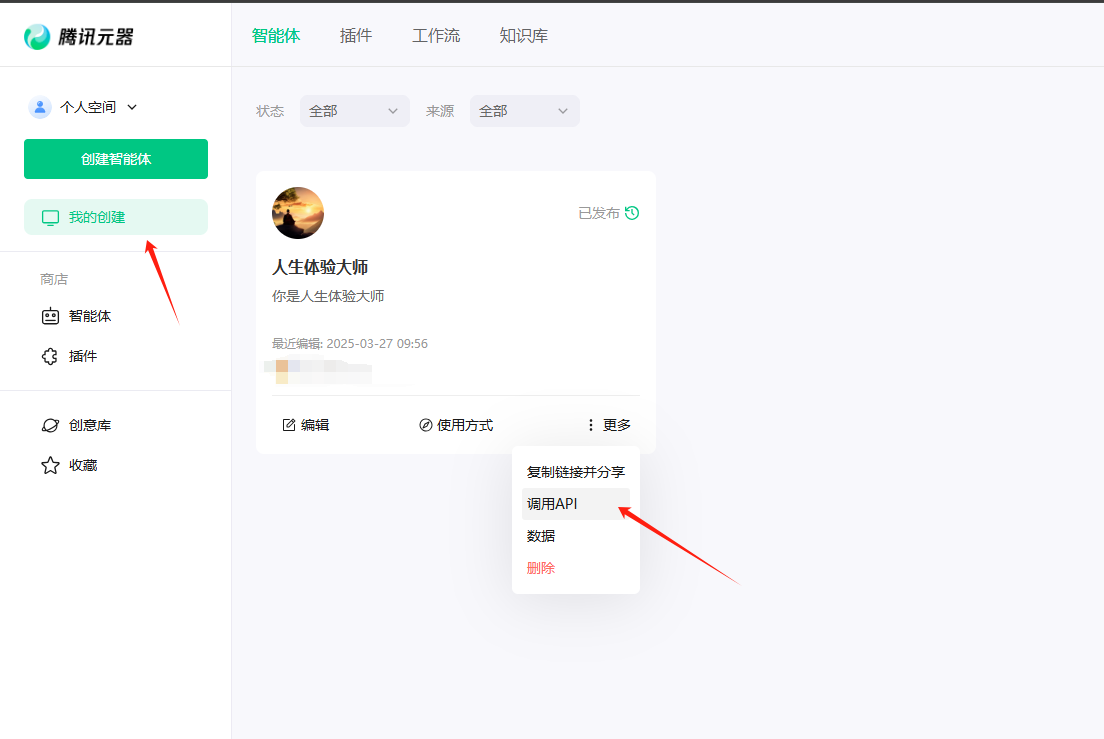
我们会得到调用所需要的信息:url、assistant_id、token等。
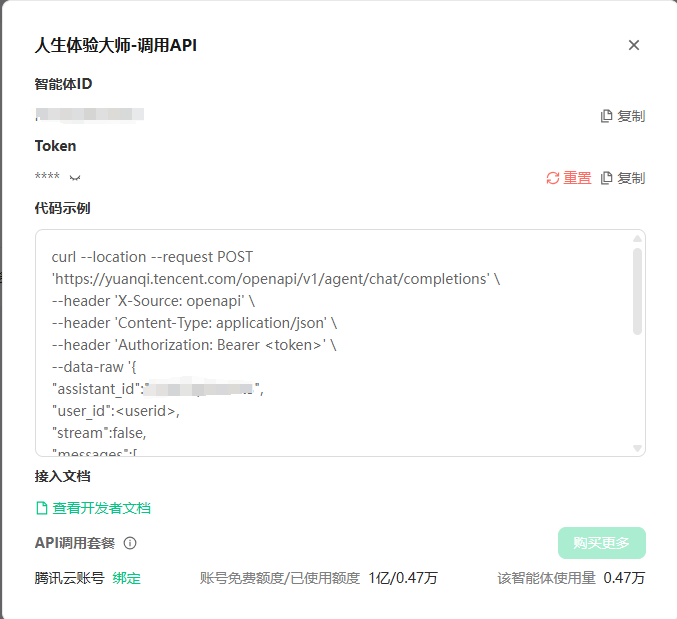
调用信息的具体意义可参考官网文档:https://docs.qq.com/aio/p/scxmsn78nzsuj64?p=unuu8c3hbocfqsogah2byuc
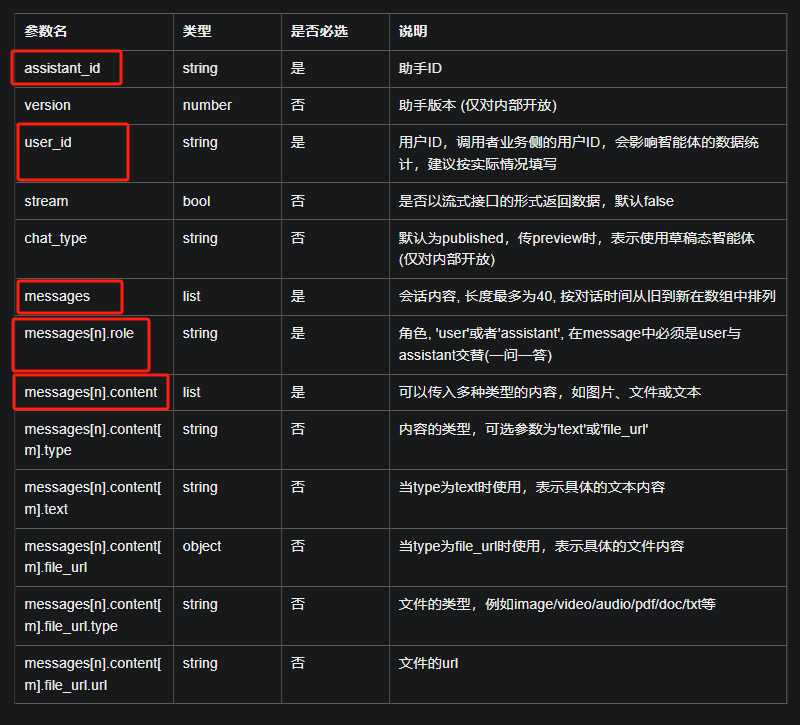
请求参数(其中红框为必填项):
二、代码实现:
【代码1】:
主要是对请求参数的处理;官方给的参数例子格式是:
string jsoninputstring = "{\n" +
" \"assistant_id\": \"你的assistant_id\",\n" +
" \"user_id\": \"username\",\n" +
" \"stream\": false,\n" +
" \"messages\": [\n" +
" {\n" +
" \"role\": \"user\",\n" +
" \"content\": [\n" +
" {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"text\": \"开始\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" ]\n" +
" }\n" +
" ]\n" +
"}";但是我们一般情况下不能这样写死,所以需要动态处理请求参数,如下:
string url = 你的url";
string token = "你的token";
try {
map m = new hashmap();
m.put("assistant_id","你的assistant_id");
m.put("user_id","username");
m.put("stream",false);
list mesg = new arraylist();
map m2 = new hashmap();
m2.put("role","user");
map m3 = new hashmap();
m3.put("type","text");
m3.put("text","开始");
list content = new arraylist();
content.add(m3);
m2.put("content",content);
mesg.add(m2);
m.put("messages",mesg);
gson gson = new gson();
string json = gson.tojson(m);
list list = accessretailapi.dopostjson5(url,json,token);
}catch (exception e){
e.printstacktrace();
}【代码1】所引用的包参考:
import com.google.gson.gson; import org.junit.test; import org.junit.runner.runwith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.springboottest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.springrunner; import java.math.bigdecimal; import java.util.arraylist; import java.util.hashmap; import java.util.list; import java.util.map;
【代码2】:
上面调用的accessretailapi.dopostjson5(url,json,token)方法的代码内容:
//api方式调用腾讯智能体(元宝)
public list dopostjson5(string apiurl, string jsoninput,string auth) throws ioexception {
// api 的 url
string url = apiurl;
// 请求头
string authorizationtoken = auth; // 替换为实际的token
string jsoninputstring = jsoninput;
// 创建url对象
url obj = new url(url);
// 打开连接
httpurlconnection connection = (httpurlconnection) obj.openconnection();
// 设置请求方法为 post
connection.setrequestmethod("post");
// 设置请求头
connection.setrequestproperty("x-source", "openapi");
connection.setrequestproperty("content-type", "application/json");
connection.setrequestproperty("authorization", "bearer " + authorizationtoken);
// 启用输入输出流
connection.setdooutput(true);
// 将请求体写入输出流
try (outputstream os = connection.getoutputstream()) {
byte[] input = jsoninputstring.getbytes(standardcharsets.utf_8);
os.write(input, 0, input.length);
}
// 获取响应状态码;为200即成功
int responsecode = connection.getresponsecode();
system.out.println("response code: " + responsecode);
list result = new arraylist();
// 读取响应内容
try (bufferedreader in = new bufferedreader(new inputstreamreader(connection.getinputstream(), standardcharsets.utf_8))) {
string inputline;
stringbuilder response = new stringbuilder();
while ((inputline = in.readline()) != null) {
response.append(inputline);
}
string resultstr = response.tostring();
system.out.println("response: " + response.tostring());
result = strtolist(resultstr,"choices");
system.out.println("result: " + result);
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
return result;
}
//把json类型字符串转换成list<map>
public static list strtolist(string liststr, string path) throws exception{
objectmapper mapper = new objectmapper();
jsonnode rootnode = mapper.readtree(liststr);
// 访问路径的数组
jsonnode datasnode = rootnode.path(path);
// 创建一个list来存储map
list<map<string, object>> dataslist = new arraylist<>();
// 遍历数组中的每个元素(jsonnode),并将其转换为map
for (jsonnode datanode : datasnode) {
map<string, object> datamap = new hashmap<>();
datanode.fields().foreachremaining(entry -> {
// 注意:这里简单地将所有值都视为object类型
// 对于更复杂的类型(如嵌套对象或数组),你可能需要进一步的逻辑来处理它们
datamap.put(entry.getkey(), entry.getvalue().astext());
if(entry.getkey().equals("message")) {
objectmapper objectmapper = new objectmapper();
map<string, object> resultmap = new hashmap<>();
try {
// 首先,将整个json字符串解析为jsonnode
jsonnode rootnode2 = objectmapper.readtree(entry.getvalue().tostring());
// 将jsonnode转换为map<string, object>
resultmap = objectmapper.convertvalue(rootnode2, map.class);
datamap.replace("message", resultmap);
} catch (jsonmappingexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
} catch (jsonprocessingexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
});
dataslist.add(datamap);
}
return dataslist;
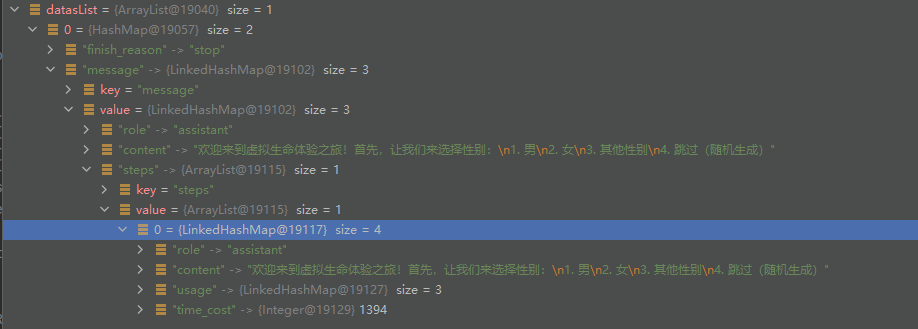
}其中特意要讲解一下的是strtolist方法,这个方法是把调用成功返回的字符串结果转换成数组;
例如:获得的resultstr是这样一段字符串:
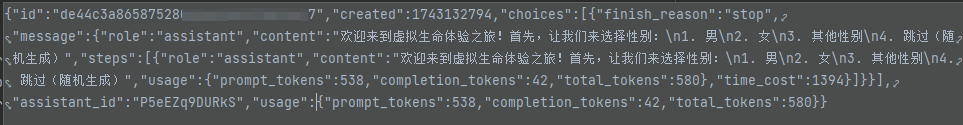
通过 strtolist(resultstr,"choices")方法把“choices”路径下提取成数组list,方便后续处理:
【代码2】所引用的包参考:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.jsonobject; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.jsonprocessingexception; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.jsonmappingexception; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.jsonnode; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.objectmapper; import org.apache.http.httpresponse; import org.apache.http.httpstatus; import org.apache.http.client.httpclient; import org.apache.http.client.methods.httppost; import org.apache.http.entity.stringentity; import org.apache.http.impl.client.httpclients; import org.apache.http.util.entityutils; import org.springframework.stereotype.component; import java.io.bufferedreader; import java.io.ioexception; import java.io.inputstreamreader; import java.io.outputstream; import java.net.httpurlconnection; import java.net.url; import java.nio.charset.standardcharsets; import java.util.arraylist; import java.util.hashmap; import java.util.list; import java.util.map;
总结
到此这篇关于springboot java通过api的方式调用腾讯智能体(腾讯元宝)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java api调用腾讯元宝内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论