缓存异常实践案例
redis基本上是高并发场景上会用到的一个高性能的key-value数据库,属于nosql类型,一般用作于缓存,一般是结合数据库一块使用的,但是在使用的过程中可能会出现异常的问题,就是面试常常唠嗑的缓存异常问题
分别是缓存击穿,缓存穿透和雪崩,简单解释如下:
缓存穿透:
就是当用户查询数据时,缓存和数据库该数据都是不存在的,此时如果用户不断的请求,就会不断的查询缓存和数据库,对数据库造成很大压力
缓存击穿:
当热点key过期或者丢失时,大量的请求访问该数据,缓存不存在,就会将大量的请求直接访问数据库,造成数据库有大量连接,存在崩溃风险
缓存雪崩:
是指大量请求在缓存中没有查到数据,直接访问数据库,导致数据库压力增大,最终导致数据库崩溃,从而波及整个系统不可用,好像雪崩一样。
下面就讲讲案例,并提供解决方案
常规写法
平常的写法,未考虑异常时
现在是有一个查询商户的接口
这个是正常的,结合了redis的逻辑,
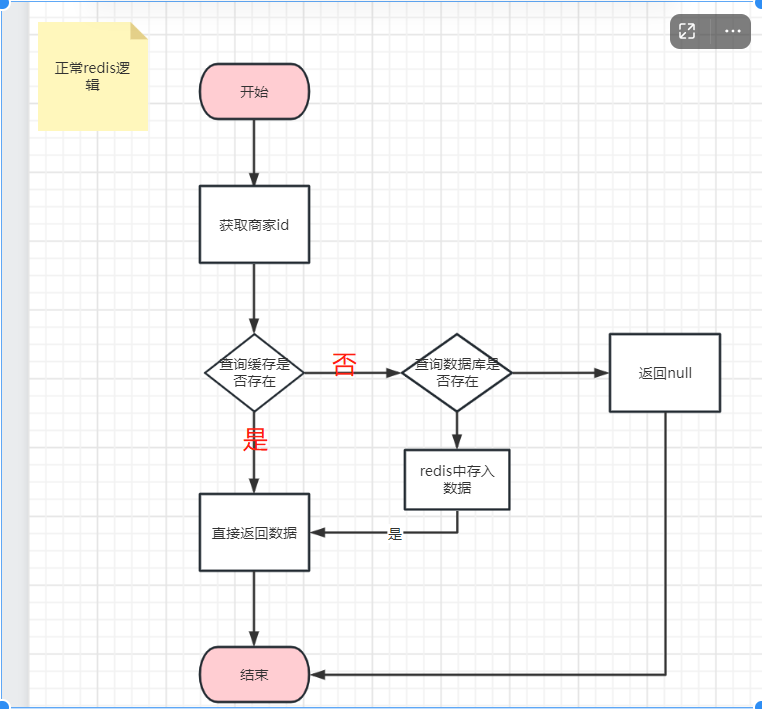
public tbshopentity rawquery(long id) {
tbshopentity shop = null;
//1.是否命中缓存
string shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
//1.1 如果命中,且数据非空,则直接返回
if (!strutil.isempty(shopjson)) {
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}
//1.2 查询数据库
shop = getbyid(id);
//1.2.1 如果数据库不存在,则直接返回
if (shop == null) return null;
//1.2.2 如果存在则设置到redis中
redisclient.set(cache_shop_key + id, json.tojsonstring(shop));
//2.返回数据
return shop;
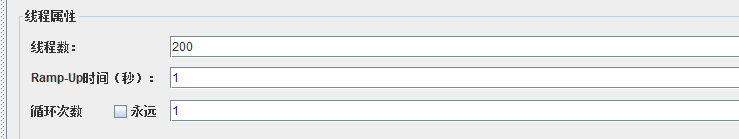
}现在使用一个不存在的商品id,然后使用jmeter进行压测,例如使用id=0的商品,然后使用200个线程共发起200个请求进行压测

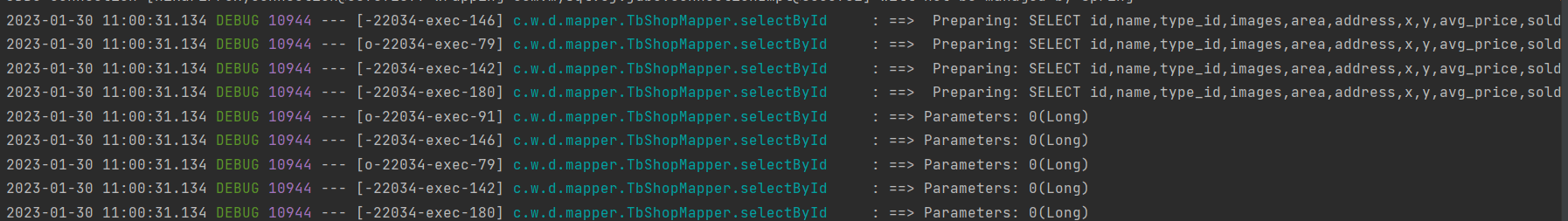
结果:
发现有大量的请求直接请求数据库,如果时大量的请求,有可能会把数据库搞崩,也就是我们的缓存穿透问题
缓存穿透问题
分析:
如果是这种情况,当用户并发测试访问一个不存在的key时,会有大量的不存在的key访问数据,导致数据库压力剧增,也就是缓存穿透问题
改进方式
缓存穿透一般有两种解决方式,分别是:
- 设置带有过期时间的空值
- 布隆过滤器
设置带有过期时间的空值
逻辑图如下:主要是改进这里
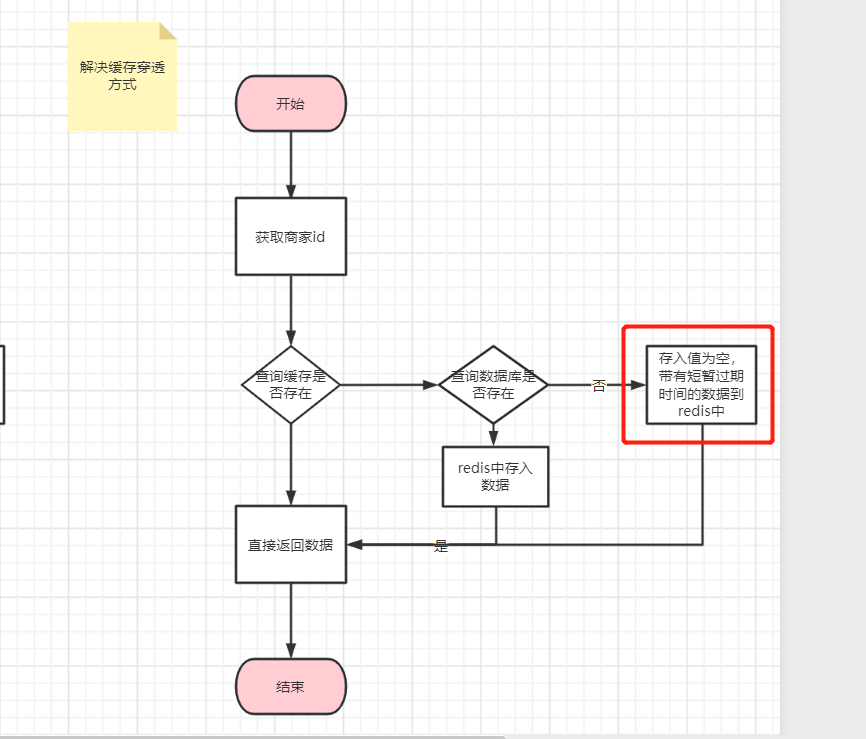
/**
* 缓存穿透解决方案, 1、设置一个空值,且带有较短的过期时间 2、布隆过滤器
* <p>
* 但是目前还是没有解决穿透的问题的,因为该key不存在,所以会有多个请求去直接请求数据库(并发问题),从而需要进行优化,解决缓存穿透问题
*/
private tbshopentity querywithpassthrough(long id) {
//1.是否命中缓存
string shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
//1.1 如果命中缓存,则直接返回
//这里不能使用!strutil.isempty去判断,因为在下边会使用”“去存空值
if (shopjson != null) {
//如果返回的值是"",则直接返回null
if (strutil.isempty(shopjson)) return null;
//否则则返回结果
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}
//1.2 如果没有命中,查询数据库
tbshopentity shop = getbyid(id);
//1.2.1 如果数据库查询数据不存在,则直设置值为空,以及过期时间,现在是设置为10s,如果10s已经过,再重新查询
if (shop == null) {
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(cache_shop_key + id, strutil.empty, seckill_seconds, timeunit.seconds);
return null;
}
//1.2.2 如果数据库存在,则设置到redis中
redisclient.set(cache_shop_key + id, json.tojsonstring(shop));
//并转成shop返回
//2.返回数据
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}测试一:直接调用接口
之后进行测试,首先是使用链接直接访问一个不存在的商品

可以发现,在第一次访问的时候,会去查找数据库,然后在之后的10s内,都不会进行数据库的查询了,然后当数据过期之后,才会进行查询,从这个结果来看,是没有问题的,也就是平常我们可以这样子使用的!
测试二:使用并发测试进行
但是如果使用200个并发去测试,结果又是如何呢?
可以发现,还是有大部分请求直接去查询数据库,
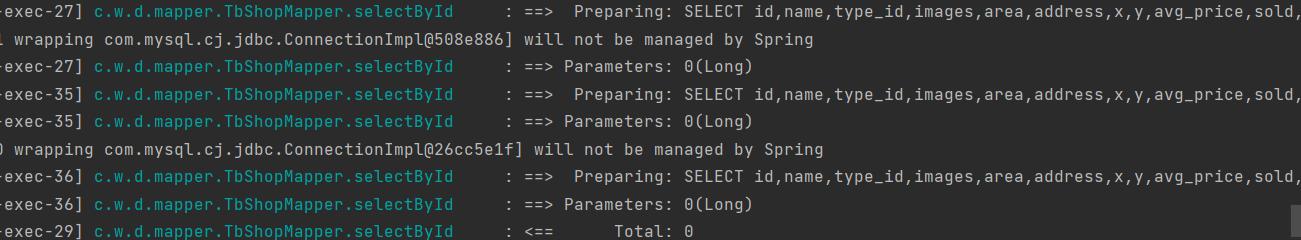
原因是由于线程的并发问题,大部分请求都执行到这一步,这个时候redis的数据还没有补充上去,所以导致了大量请求还是重新去查数据库,其实也类似于缓存穿透问题,当某个key失效时,大量请求会去查询数据库,那么这个问题应该如何解决呢?
缓存击穿问题(其中也解决了穿透问题)
当有一个访问量较高的key,在失效时,会导致大量的请求发向数据库,导致数据库崩溃
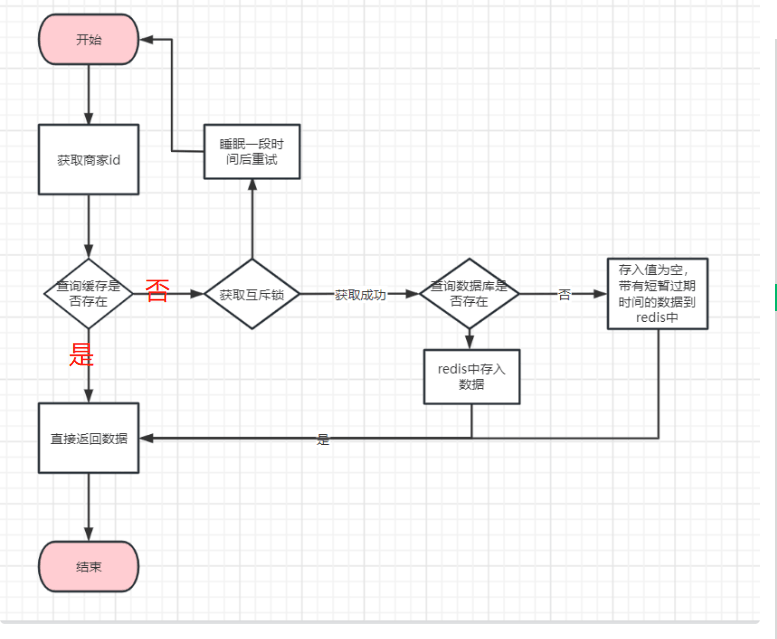
解决方式主要有:
- 加互斥锁
- 逻辑过期
加互斥锁
public tbshopentity querywithmutexlock(long id) {
tbshopentity shop = null;
//是否命中缓存
string shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
//如果命中缓存,则先判断缓存是否为”“,如果是返回null,否则返回结果
if (shopjson != null) {
//如果缓存为空的话,则直接返回结果
if (strutil.isempty(shopjson)) return null;
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}
//获取锁,锁的粒度需要精确到id,不能太大
rlock lock = redissonclient.getlock(lock_shop + id);
try {
//加锁
boolean islock = lock.trylock(10,timeunit.seconds);
//如果没有获取到锁,则休眠50ms,然后重试
if (!islock) {
thread.sleep(50);
querywithmutexlock(id);
}
//这里需要做doublecheck,需要重新查询缓存的数据是否存在,否则还会出现重复查询数据库的情况
shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
if (shopjson != null) {
if (strutil.isempty(shopjson)) return null;
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}
//如果缓存不存在,则查询数据库
shop = getbyid(id);
//如果数据库查询数据不存在,则直设置值为空,以及过期时间,直接返回null
if (shop == null) {
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(cache_shop_key + id, strutil.empty, seckill_seconds, timeunit.seconds);
return null;
}
//如果数据库数据存在则设置到redis中
redisclient.set(cache_shop_key + id, json.tojsonstring(shop));
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
//2.返回数据
return shop;
}压测:
使用200个线程测试,结果是只查询了一次,是ok的

逻辑过期
逻辑过期的原理,指的是不使用redis自带的expire进行存储,而是在存储的数据中,添加一个过期字段,然后在获取数据的时候,进行该字段的判断,如果已经过期了,则返回旧的数据,启动一个线程去更新新的数据
数据结构如下:
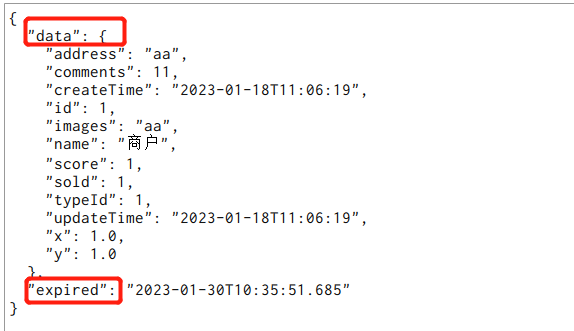
data用来存储数据,expired存储过期时间,所以我们只要比较,如果expired小于当前时间的话,就代表该数据是过期的了
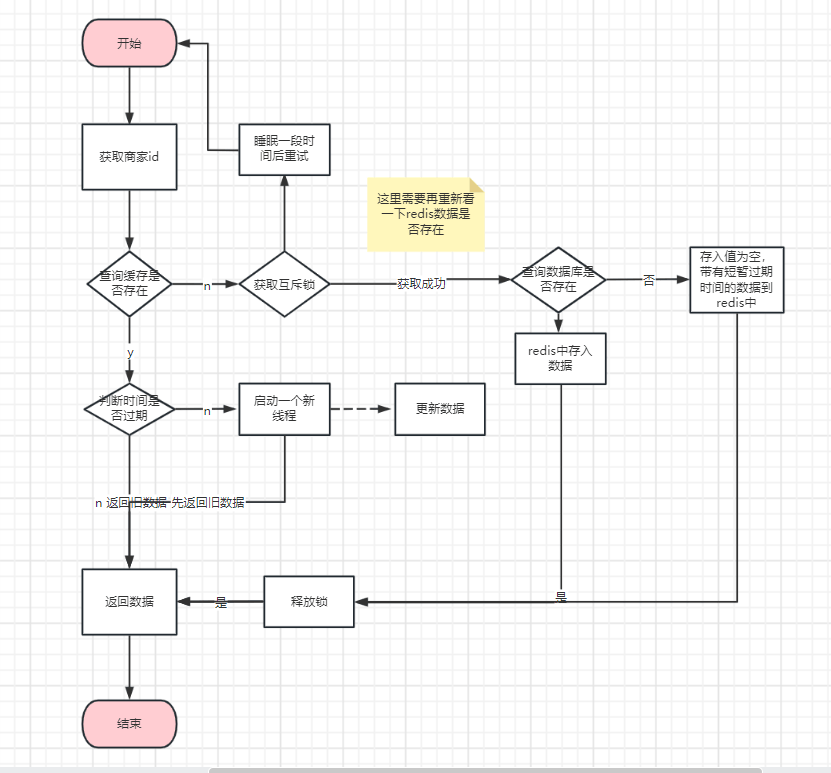
逻辑图如下:
这个逻辑图稍微比较复杂,基本将空值和互斥锁都加进去了
querywithlogicexpire
public tbshopentity querywithlogicexpire(long id) {
tbshopentity shop = null;
//查询是否命中缓存
string shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
//如果命中,则判断结果是空置,还是过期的值,或者没过期的值
if (shopjson != null) {
//这里的代码往下滑查看
return redisdto2entity(id, shopjson);
}
//获取锁,粒度具体到商户
rlock lock = redissonclient.getlock("lock:shop:" + id);
try {
//加锁,10s过期
boolean islock = lock.trylock(10,timeunit.seconds);
// 如果没有获取到锁,则休眠50ms,然后重试
if (!islock) {
thread.sleep(50);
querywithlogicexpire(id);
}
//这里需要做doublecheck,否则还会出现重复查询数据库的情况
//这里先不做判断是否逻辑过期的逻辑
shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
if (shopjson != null) {
redisdto2entity(id,shopjson);
}
shop = getbyid(id);
//1.2 如果数据库查询数据不存在,则直设置值为空,以及过期时间,直接返回null
if (shop == null) {
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(cache_shop_key + id, "", seckill_seconds, timeunit.minutes);
return null;
}
//1.3 如果存在则设置到redis中
redisclient.set(cache_shop_key + id, json.tojsonstring(shop));
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
//2.返回数据
return shop;
}redisdto2entity
private tbshopentity redisdto2entity(long id,string shopjson){
//如果是空值,则直接返回null
if (strutil.isempty(shopjson)) return null;
//或者则转换成redis实体类
redisdto redisdto = jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, redisdto.class);
//获取逻辑过期时间
localdatetime expired = redisdto.getexpired();
// 判断时间是否过期,如果过期,则启动线程更新数据,其他直接返回
if (expired.isbefore(localdatetime.now())) {
//使用异步线程,更新数据
saveshop(id);
}
return jsonobject.parseobject(json.tojsonstring(redisdto.getdata()), tbshopentity.class);
}使用异步线程进行数据的更新
saveshop
@async
public void saveshop(long id){
tbshopentity entity = getbyid(id);
if(entity==null) return;
redisclient.setlogicexpired(redisconstant.cache_shop_key+id,entity,redisconstant.seckill_seconds, timeunit.seconds);
log.info("线程{},更新商户信息",thread.currentthread().getname());
}测试
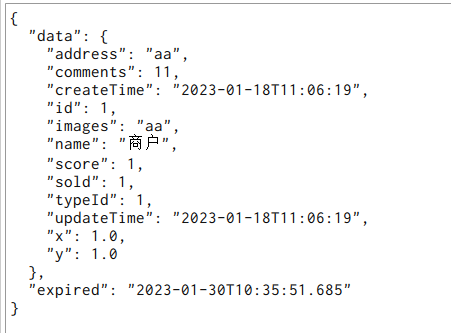
需要先添加一条数据
执行下面的test方法,进行添加数据,添加成功后
数据如下:
package com.walker.dianping;
import com.walker.dianping.common.constants.redisconstant;
import com.walker.dianping.common.utils.redisclient;
import com.walker.dianping.model.tbshopentity;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.springboottest;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
@springboottest
public class redistest {
@autowired
private redisclient redisclient;
@test
void addshop() {
tbshopentity tbshopentity = new tbshopentity();
tbshopentity.setid(1l);
tbshopentity.setname("逻辑过期测试商户");
//该方法可以查看大纲,放在了完整代码中
redisclient.setlogicexpired(redisconstant.cache_shop_key + 1l, tbshopentity, 20, timeunit.minutes);
}
}调用接口发起测试

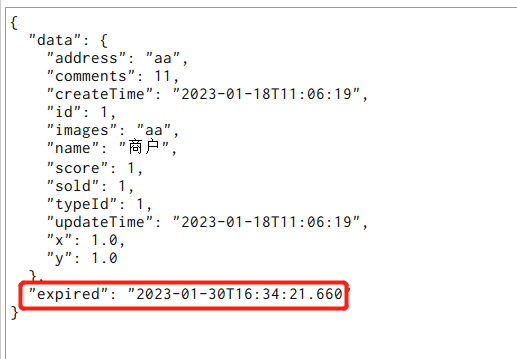
因为一开始是有的,所以可以直接拿到数据
当过期时间expired小于当前时间时,这个时候重新去调用接口(可以直接更改redis的数据)
这个时候就会去更新商户的数据了,这个时候就能拿到新的数据了

完整代码
controller
package com.walker.dianping.controller;
import com.walker.dianping.model.r;
import com.walker.dianping.service.tbshopservice;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.getmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.pathvariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller;
/**
* <p>
* 前端控制器
* </p>
*
* @author walker
* @since 2023-01-18
*/
@restcontroller
@requestmapping("/tb-shop-entity")
public class tbshopcontroller {
@autowired
private tbshopservice tbshopservice;
/**
* 获取商铺
*/
@getmapping("/shop/{id}")
public r getshop(@pathvariable(value = "id") long id){
return tbshopservice.getshop(id);
}
}service
package com.walker.dianping.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.iservice;
import com.walker.dianping.model.r;
import com.walker.dianping.model.tbshopentity;
/**
* <p>
* 服务类
* </p>
*
* @author walker
* @since 2023-01-18
*/
public interface tbshopservice extends iservice<tbshopentity> {
r getshop(long id);
}tbshopserviceimpl
package com.walker.dianping.service.impl;
import cn.hutool.core.bean.beanutil;
import cn.hutool.core.util.strutil;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.json;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.jsonobject;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.serviceimpl;
import com.walker.dianping.common.constants.redisconstant;
import com.walker.dianping.common.utils.redisclient;
import com.walker.dianping.mapper.tbshopmapper;
import com.walker.dianping.model.r;
import com.walker.dianping.model.tbshopentity;
import com.walker.dianping.model.dto.redisdto;
import com.walker.dianping.service.tbshopservice;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.redisson.api.rlock;
import org.redisson.api.redissonclient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.stringredistemplate;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.async;
import org.springframework.stereotype.service;
import java.time.localdatetime;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
import static com.walker.dianping.common.constants.redisconstant.*;
@slf4j
@service
public class tbshopserviceimpl extends serviceimpl<tbshopmapper, tbshopentity> implements tbshopservice {
@autowired
private stringredistemplate redistemplate;
@autowired
private redisclient redisclient;
@autowired
private redissonclient redissonclient;
@override
public r getshop(long id) {
//初始查询
// tbshopentity shop = rawquery(id);
//缓存穿透
// tbshopentity shop = querywithpassthrough(id);
//解决缓存击穿问题
// tbshopentity shop = querywithmutexlock(id);
//解决缓存击穿+穿透问题,使用逻辑过期
tbshopentity shop = querywithlogicexpire(id);
if (shop == null) {
return r.fail("店铺不存在");
}
return r.ok(shop);
}
/**
* 最初始的版本
*/
public tbshopentity rawquery(long id) {
tbshopentity shop = null;
//1.是否命中缓存
string shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
//1.1 如果命中,且数据非空,则直接返回
if (!strutil.isempty(shopjson)) {
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}
//1.2 查询数据库
shop = getbyid(id);
//1.2.1 如果数据库不存在,则直接返回
if (shop == null) return null;
//1.2.2 如果存在则设置到redis中
redisclient.set(cache_shop_key + id, json.tojsonstring(shop));
//2.返回数据
return shop;
}
/**
* 缓存穿透解决方案, 1、设置一个空值,且带有较短的过期时间 2、布隆过滤器
* <p>
* 但是目前还是没有解决穿透的问题的,因为该key不存在,所以会有多个请求去直接请求数据库(并发问题),从而需要进行优化,解决缓存穿透问题
*/
private tbshopentity querywithpassthrough(long id) {
//1.是否命中缓存
string shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
//1.1 如果命中缓存,则直接返回
//这里不能使用!strutil.isempty去判断,因为在下边会使用”“去存空值
if (shopjson != null) {
//如果返回的值是"",则直接返回null
if (strutil.isempty(shopjson)) return null;
//否则则返回结果
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}
//1.2 如果没有命中,查询数据库
tbshopentity shop = getbyid(id);
//1.2.1 如果数据库查询数据不存在,则直设置值为空,以及过期时间,现在是设置为10s,如果10s已经过,再重新查询
if (shop == null) {
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(cache_shop_key + id, strutil.empty, seckill_seconds, timeunit.seconds);
return null;
}
//1.2.2 如果数据库存在,则设置到redis中
redisclient.set(cache_shop_key + id, json.tojsonstring(shop));
//并转成shop返回
//2.返回数据
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}
/**
* 缓存击穿,key失效,导致高并发的请求
* 加锁:可以使用redisson
*/
public tbshopentity querywithmutexlock(long id) {
tbshopentity shop = null;
//是否命中缓存
string shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
//如果命中缓存,则先判断缓存是否为”“,如果是返回null,否则返回结果
if (shopjson != null) {
//如果缓存为空的话,则直接返回结果
if (strutil.isempty(shopjson)) return null;
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}
//获取锁,锁的粒度需要精确到id,不能太大
rlock lock = redissonclient.getlock(lock_shop + id);
try {
//加锁
boolean islock = lock.trylock(10,timeunit.seconds);
//如果没有获取到锁,则休眠50ms,然后重试
if (!islock) {
thread.sleep(50);
querywithmutexlock(id);
}
//这里需要做doublecheck,需要重新查询缓存的数据是否存在,否则还会出现重复查询数据库的情况
shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
if (shopjson != null) {
if (strutil.isempty(shopjson)) return null;
return jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, tbshopentity.class);
}
//如果缓存不存在,则查询数据库
shop = getbyid(id);
//如果数据库查询数据不存在,则直设置值为空,以及过期时间,直接返回null
if (shop == null) {
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(cache_shop_key + id, strutil.empty, seckill_seconds, timeunit.seconds);
return null;
}
//如果数据库数据存在则设置到redis中
redisclient.set(cache_shop_key + id, json.tojsonstring(shop));
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
//2.返回数据
return shop;
}
private tbshopentity redisdto2entity(long id,string shopjson){
//如果是空值,则直接返回null
if (strutil.isempty(shopjson)) return null;
//或者则转换成redis实体类
redisdto redisdto = jsonobject.parseobject(shopjson, redisdto.class);
//获取逻辑过期时间
localdatetime expired = redisdto.getexpired();
// 判断时间是否过期,如果过期,则启动线程更新数据,其他直接返回
if (expired.isbefore(localdatetime.now())) {
//使用异步线程,更新数据
saveshop(id);
}
return jsonobject.parseobject(json.tojsonstring(redisdto.getdata()), tbshopentity.class);
}
/**
* 缓存击穿解决方式二:逻辑过期
*/
public tbshopentity querywithlogicexpire(long id) {
tbshopentity shop = null;
//查询是否命中缓存
string shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
//如果命中,则判断结果是空置,还是过期的值,或者没过期的值
if (shopjson != null) {
return redisdto2entity(id, shopjson);
}
//获取锁,粒度具体到商户
rlock lock = redissonclient.getlock("lock:shop:" + id);
try {
//加锁,10s过期
boolean islock = lock.trylock(10,timeunit.seconds);
// 如果没有获取到锁,则休眠50ms,然后重试
if (!islock) {
thread.sleep(50);
querywithlogicexpire(id);
}
//这里需要做doublecheck,否则还会出现重复查询数据库的情况
//这里先不做判断是否逻辑过期的逻辑
shopjson = redisclient.get(cache_shop_key + id);
if (shopjson != null) {
redisdto2entity(id,shopjson);
}
shop = getbyid(id);
//1.2 如果数据库查询数据不存在,则直设置值为空,以及过期时间,直接返回null
if (shop == null) {
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(cache_shop_key + id, "", seckill_seconds, timeunit.minutes);
return null;
}
//1.3 如果存在则设置到redis中
redisclient.set(cache_shop_key + id, json.tojsonstring(shop));
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
//2.返回数据
return shop;
}
@async
public void saveshop(long id) {
//查询数据
tbshopentity entity = getbyid(id);
if (entity == null) return;
redisclient.setlogicexpired(redisconstant.cache_shop_key + id, entity, redisconstant.seckill_seconds, timeunit.seconds);
log.info("线程{},更新商户信息", thread.currentthread().getname());
}
}redisclient代码
package com.walker.dianping.common.utils;
import cn.hutool.core.bean.beanutil;
import cn.hutool.core.util.strutil;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.json;
import com.walker.dianping.model.dto.redisdto;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.stringredistemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.convert.redisdata;
import org.springframework.stereotype.component;
import java.time.localdatetime;
import java.util.concurrent.timeunit;
@slf4j
@component
public class redisclient {
@autowired
private stringredistemplate redistemplate;
/**
* 定义set方法
*/
public void set(string key,object value){
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, json.tojsonstring(value));
}
/**
* 定义set方法
*/
public void setlogicexpired(string key,object value,long timeout, timeunit unit){
redisdto dto = new redisdto();
dto.setdata(value);
dto.setexpired(localdatetime.now().plusseconds(unit.toseconds(timeout)));
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, json.tojsonstring(dto));
}
/**
* get方法
*/
public string get(string key){
string s = redistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
return s;
}
}redisconstant
package com.walker.dianping.common.constants;
public interface redisconstant {
string seckill_lua_script="seckill.lua";
string cache_shop_key= "cache:shop:";
integer seckill_seconds=10;
string lock_shop="lock:shop:";
}到此这篇关于springboot项目redis缓存异常实战案例详解(提供解决方案)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot redis缓存异常内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论