为什么要用线程池?
- 减少了创建和销毁线程的次数,每个工作线程都可以被重复利用
- 可以根据系统的承受能力,调整线程池中工作线线程的数目,防止因线程过多消耗内存,也避免了因线程过少,浪费系统资源
如何做到每个工作线程都可以被重复利用呢?
先看下线程池的工作原理:
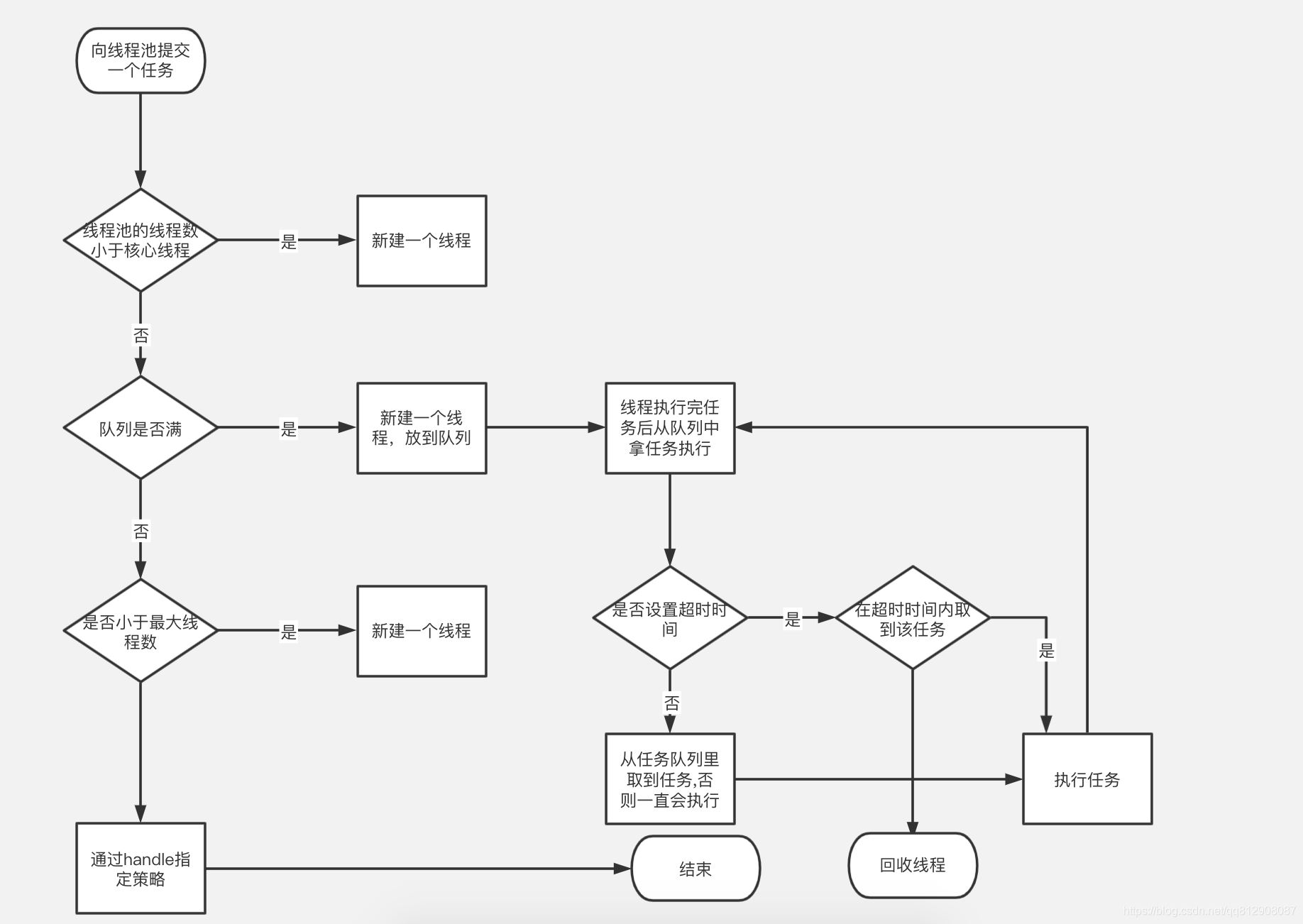
原理如上图,线程池有七个核心参数
corepoolsize线程池核心线程数maximumpoolsize线程池最大线程数量keepalivetime空闲线程存活时间unit空闲线程存活时间单位workqueue工作队列threadfactory线程工厂handler拒绝策略
线程池之所以能做到重复利用,是因为线程池的核心线程不会被摧毁,执行完任务后会重复利用
线程池是如何保持核心线程不被摧毁呢?
首先看先线程池是如何处理任务的,如下图
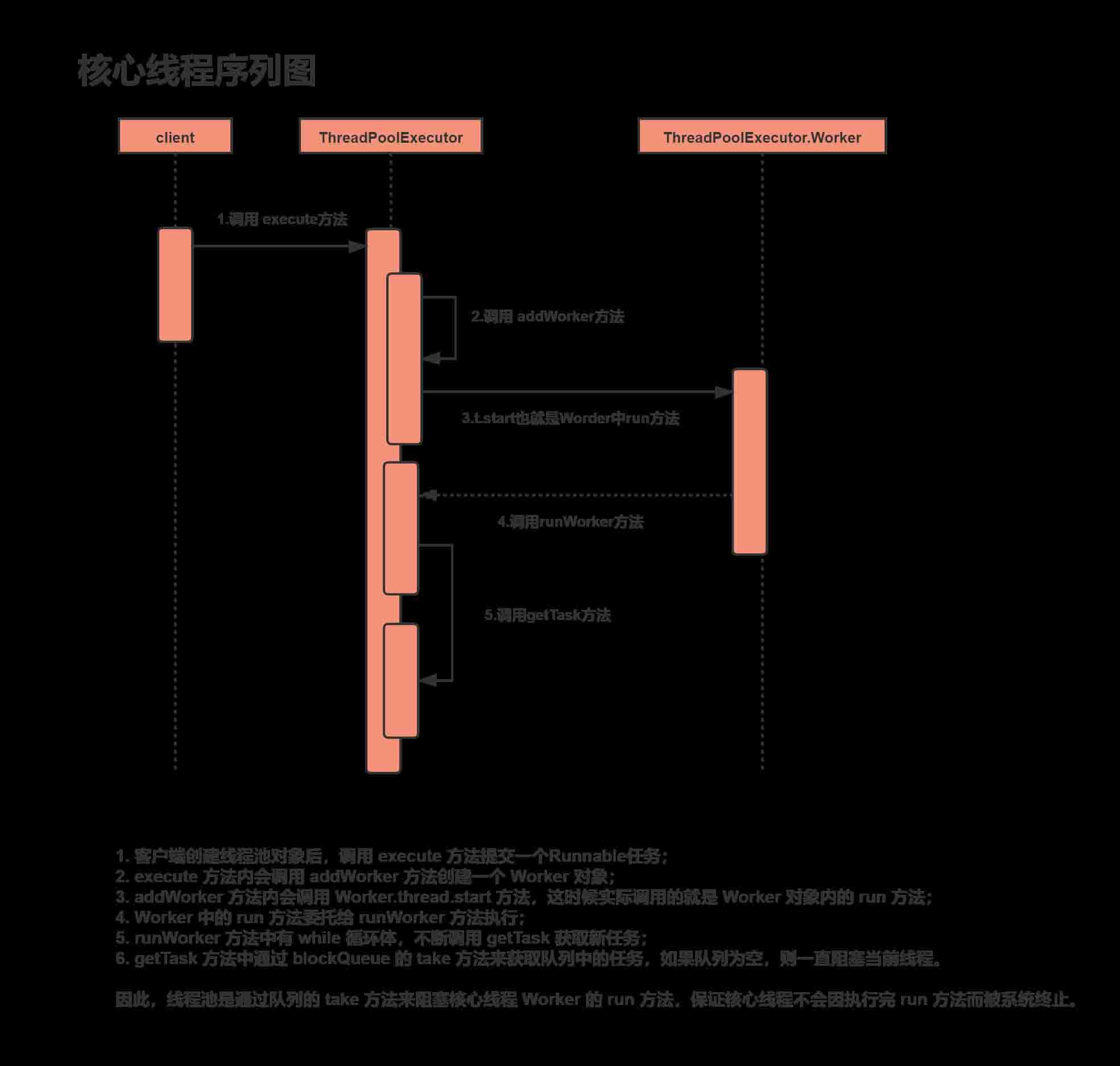
下面我们看下核心部分源码:
- 当有一个任务添加进来时,线程池会创建一个worker,worker是实现runnable方法的,所以worker执行时会调用run方法,run方法会接着调用runwoker方法
- 主要看这一行代码,调用gettask方法获取任务并且执行 while (task != null || (task = gettask()) != null)
final void runworker(worker w) {
thread wt = thread.currentthread();
runnable task = w.firsttask;
w.firsttask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedabruptly = true;
try {
// 主要看这一行代码,调用gettask方法获取任务并且执行
while (task != null || (task = gettask()) != null) {
w.lock();
// if pool is stopping, ensure thread is interrupted;
// if not, ensure thread is not interrupted. this
// requires a recheck in second case to deal with
// shutdownnow race while clearing interrupt
if ((runstateatleast(ctl.get(), stop) ||
(thread.interrupted() &&
runstateatleast(ctl.get(), stop))) &&
!wt.isinterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
beforeexecute(wt, task);
throwable thrown = null;
try {
task.run();
} catch (runtimeexception x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new error(x);
} finally {
afterexecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
task = null;
w.completedtasks++;
w.unlock();
}
}
completedabruptly = false;
} finally {
processworkerexit(w, completedabruptly);
}
}- 看下gettask方法是如何实现的
private runnable gettask() {
boolean timedout = false; // did the last poll() time out?
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runstateof(c);
// check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= shutdown && (rs >= stop || workqueue.isempty())) {
decrementworkercount();
return null;
}
int wc = workercountof(c);
// are workers subject to culling?
boolean timed = allowcorethreadtimeout || wc > corepoolsize;
if ((wc > maximumpoolsize || (timed && timedout))
&& (wc > 1 || workqueue.isempty())) {
if (compareanddecrementworkercount(c))
return null;
continue;
}
try {
runnable r = timed ?
workqueue.poll(keepalivetime, timeunit.nanoseconds) :
workqueue.take();
if (r != null)
return r;
timedout = true;
} catch (interruptedexception retry) {
timedout = false;
}
}
}- 主要看这几行代码
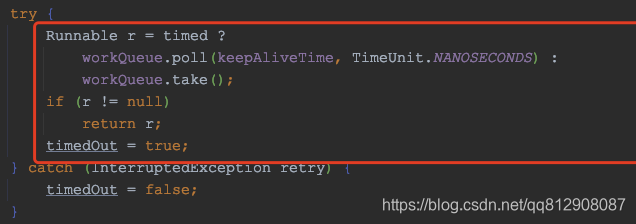
- gettask方法通过调用任务队列的take方法,不断的获取线程
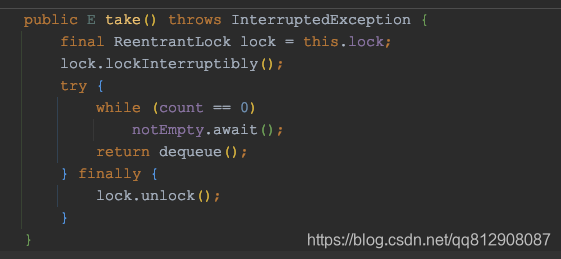
- 如果任务队列里面数量为0,则会一直阻塞,一直等到有任务加入,从而保证了核心线程不被摧毁
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。





发表评论