前面使用 jedis 时, 是借助 jedis 对象中的各种方法来对 redis 进行操作. 而在 spring 框架中, 则是通过 stringredistemplate 来操作 redis. 最开始提供的类是 redistemplate, stringredistemplate 是 redistemplate 的子类, 专门用于处理文本数据.
0. 配置 spring 的 redis环境
(1) 引入 redis 的 spring 依赖
选中 nosql 中的 spring data redis (access+driver) 依赖.
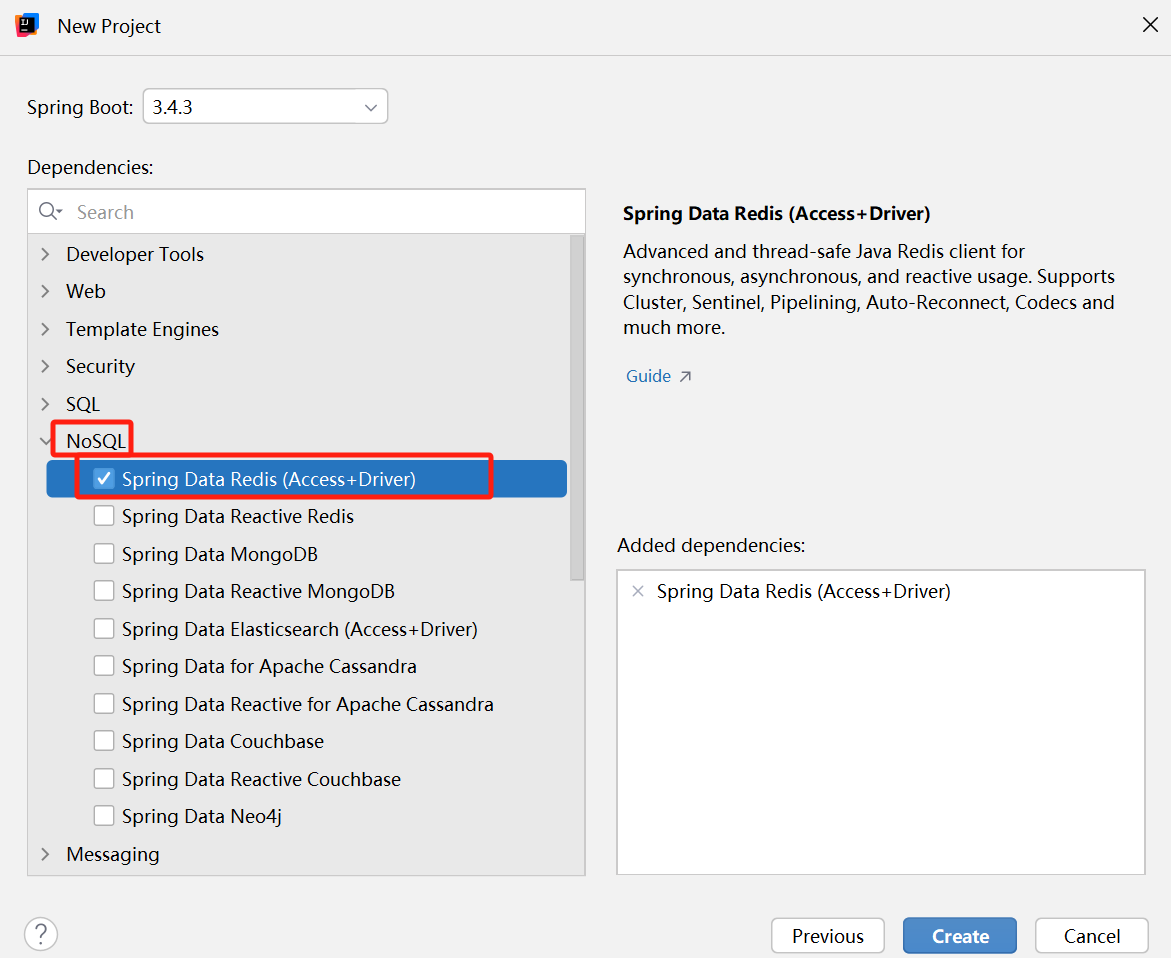
(2) 写 spring 配置文件
application.yml:
spring:
data:
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 8888
(3) 创建 controller 类, 并注入 stringredistemplate 对象.
@restcontroller
public class mycontroller {
@autowired
stringredistemplate stringredistemplate;
}
[!note]
这里的 redistemplate 将 redis 中的命令, 又做了进一步封装, 分成了几个类别 (每个类别操作特定的数据类型)
- opsforvalue(): 专门操作 string 类型.
- opsforlist(): 专门操作 list 类型.
- opsforset(): 专门操作 set 类型.
- opsforhash(): 专门操作 hash 类型.
- opsforzset(): 专门操作 zset 类型.
这样一来, 它提供的一些接口风格和原生的redis命令就存在一定差异.
还有一点要注意的是: spring 并没有封装 redis 的所有命令 (如 flushall 就没有封装), 此时我们可以使用 execute 方法来使用 redis 的原始命令.
例如:
stringredistemplate.execute((redisconnection connection) -> {
// execute 要求回调方法中必须写 return 语句,返回个东西
// 这个回调返回的对象,就会作为 execute 本身的返回值
connection.flushall();
return null;
});
//这里的redisconnection对象, 就相当于jedis里的jedis对象.
1.使用 string
@restcontroller
public class mycontroller {
@autowired
stringredistemplate stringredistemplate;
@getmapping("/teststring")
public string teststring() {
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set("key", "111");
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set("key2", "222");
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set("key3", "333");
string value = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get("key");
system.out.println("value: " + value);
return "ok";
}
}
- 请求结果:
postman:
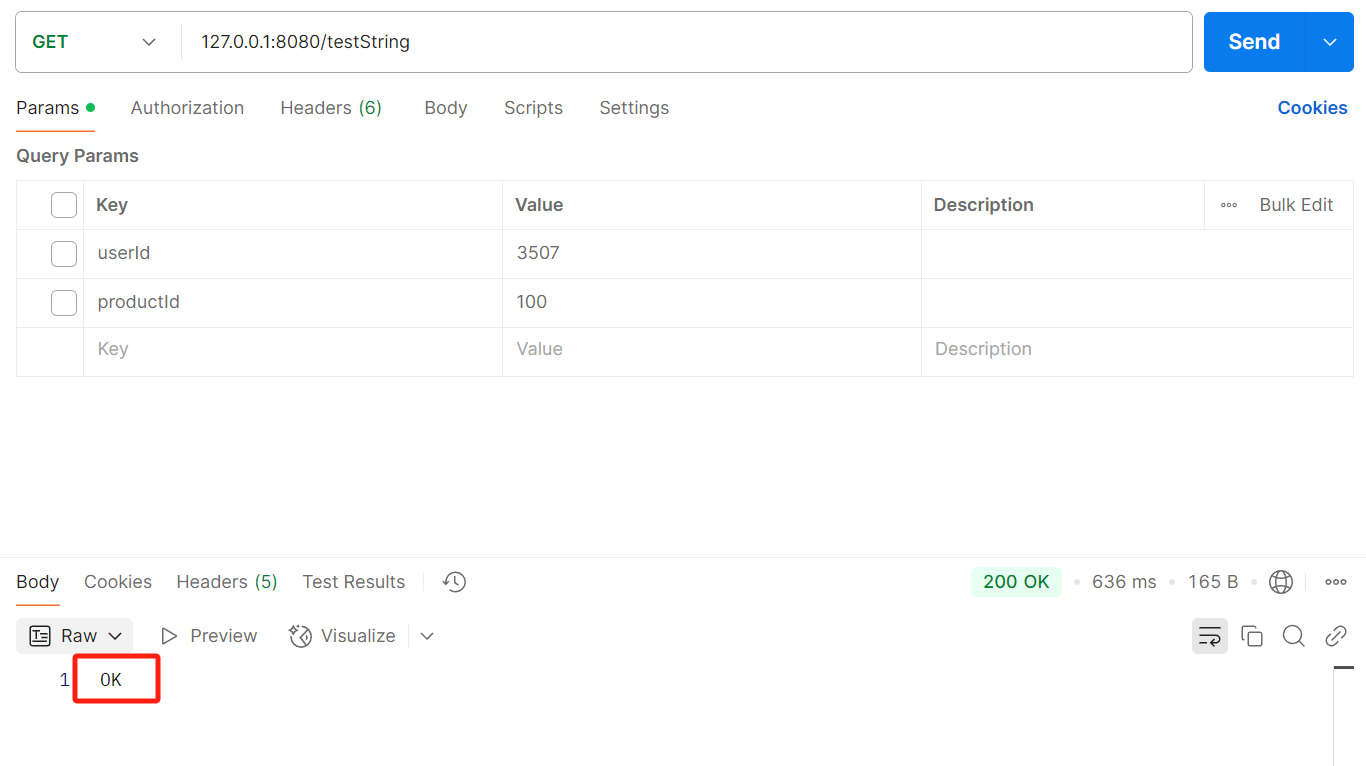
日志:

2. 使用 list
@getmapping("/testlist")
public string testlist() {
// 先清除之前的数据
tringredistemplate.execute((redisconnection connection) -> {
// execute 要求回调方法中必须写 return 语句,返回个东西
// 这个回调返回的对象,就会作为 execute 本身的返回值
connection.flushall();
return null;
});
stringredistemplate.opsforlist().leftpush("key", "111");
stringredistemplate.opsforlist().leftpush("key", "222");
stringredistemplate.opsforlist().leftpush("key", "333");
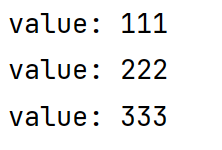
string value = stringredistemplate.opsforlist().rightpop("key");
system.out.println("value: " + value);
value = stringredistemplate.opsforlist().rightpop("key");
system.out.println("value: " + value);
value = stringredistemplate.opsforlist().rightpop("key");
system.out.println("value: " + value);
return "ok";
}
运行结果:
3. 使用 set
@getmapping("/testset")
public string testset() {
stringredistemplate.execute((redisconnection connection) -> {
connection.flushall();
return null;
});
stringredistemplate.opsforset().add("key", "111", "222", "333");
set<string> result = stringredistemplate.opsforset().members("key");
system.out.println("result: " + result);
boolean exists = stringredistemplate.opsforset().ismember("key", "111");
system.out.println("exists: " + exists);
long count = stringredistemplate.opsforset().size("key");
system.out.println("count: " + count);
stringredistemplate.opsforset().remove("key", "111", "222");
result = stringredistemplate.opsforset().members("key");
system.out.println("result: " + result);
return "ok";
}
运行结果:

4. 使用 hash
@getmapping("/testhash")
public string testhash() {
stringredistemplate.execute((redisconnection connection) -> {
connection.flushall();
return null;
});
stringredistemplate.opsforhash().put("key", "f1", "111");
stringredistemplate.opsforhash().put("key", "f2", "222");
stringredistemplate.opsforhash().put("key", "f3", "333");
string value = (string) stringredistemplate.opsforhash().get("key", "f1");
system.out.println("value: " + value);
boolean exists = stringredistemplate.opsforhash().haskey("key", "f1");
system.out.println("exists: " + exists);
stringredistemplate.opsforhash().delete("key", "f1", "f2");
long size = stringredistemplate.opsforhash().size("key");
system.out.println("size: " + size);
return "ok";
}
运行结果:

5. 使用 zset
@getmapping("/testzset")
public string testzset() {
stringredistemplate.execute((redisconnection connection) -> {
connection.flushall();
return null;
});
stringredistemplate.opsforzset().add("key", "zhangsan", 10d);
stringredistemplate.opsforzset().add("key", "lisi", 20d);
stringredistemplate.opsforzset().add("key", "wangwu", 30d);
set<string> members = stringredistemplate.opsforzset().range("key", 0, -1);
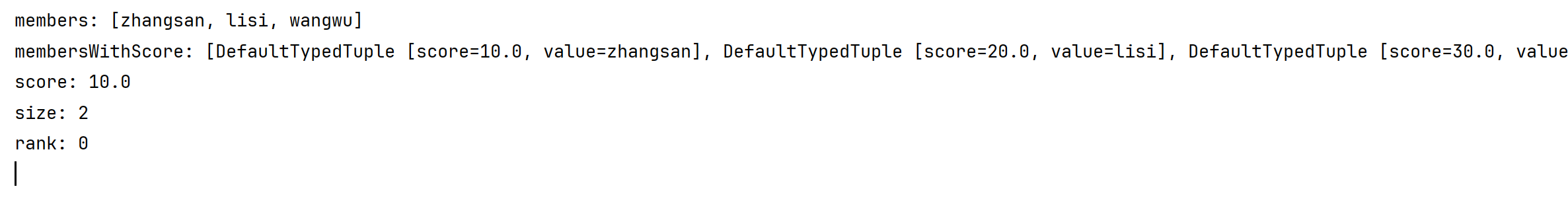
system.out.println("members: " + members);
set<zsetoperations.typedtuple<string>> memberswithscore = stringredistemplate.opsforzset().rangewithscores("key", 0, -1);
system.out.println("memberswithscore: " + memberswithscore);
double score = stringredistemplate.opsforzset().score("key", "zhangsan");
system.out.println("score: " + score);
stringredistemplate.opsforzset().remove("key", "zhangsan");
long size = stringredistemplate.opsforzset().size("key");
system.out.println("size: " + size);
long rank = stringredistemplate.opsforzset().rank("key", "lisi");
system.out.println("rank: " + rank);
return "ok";
}
运行结果:
到此这篇关于redis的spring客户端使用小结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关redis spring客户端使用内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论