什么是 resttemplate
resttemplate 是从 spring3.0 开始支持的一个 http 请求工具,它提供了常见的 rest请求方案的模板,例如 get 请求、post 请求、put 请求、delete 请求以及一些通用的请求执行方法 exchange 以及 execute。resttemplate 继承自 interceptinghttpaccessor 并且实现了 restoperations 接口,其中 restoptions 接口定义了基本的 restful 操作,这些操作在 resttemplate 中都得到了实现。
restemplate请求乱码之content-encoding="gzip"
今天有一个通过restemplate请求一个天气api,发现其body数据是乱码,同事处理了好久,然并卵,经检查后,发现头部信息出了问题。
content-encoding="gzip" content-type="application/json;charset=utf-8"
返回值是utf-8,restemplate设置的也是utf-8。在翻看其他博客,发现问题原因是http存在一个压缩格式:gzip。
gzip是一个压缩算法,当请求数据或返回数据体积过大,为减少网络负载压力而使用的压缩算法。通常在服务器端使用,客户端为获得原始数据需通过gzip解压。
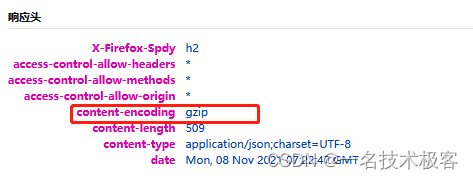
响应头中的gzip
content-encoding
是一个实体消息首部,用于对特定媒体类型的数据进行压缩。当这个首部出现的时候,它的值表示消息主体进行了何种方式的内容编码转换。这个消息首部用来告知客户端应该怎样解码才能获取在 content-type 中标示的媒体类型内容。
一般建议对数据尽可能地进行压缩,因此才有了这个消息首部的出现。
注:客户端和服务器都可以使用,表示body中的数据采用了什么编码(压缩算法)
accept-encoding
http 请求头 accept-encoding 会将客户端能够理解的内容编码方式——通常是某种压缩算法——进行通知(给服务端)。通过内容协商的方式,服务端会选择一个客户端提议的方式,使用并在响应头 content-encoding 中通知客户端该选择。
注:一般是客户端使用,表示给服务器说明,客户端支持的压缩算法列表。服务从中选择一个对响应体进行压缩。
/**
* @title: getclimatebyrequst
* @description: ( 通过request 获取天气信息)
* @author:lijie
* @since 2021/11/9 14:05
* @version:1.1.0
* @return: climate:封装的天气结果类
*/
public result<climate> getclimatebyrequst(httpservletrequest request) {
result<climate> result=new result<>();
try{
//通过request请求获得ip地址
string ip = webutils.getipbyrequset(request);
//通过ip获得大致定位
result<map<string, object>> locationbyip = this.getlocationbyip(ip);
if(locationbyip!=null&&locationbyip.issuccess()){
map<string, object> data = locationbyip.getdata();
string url=""//请求的url地址
if(maputils.isnotempty(data)){
string jd = maputils.getstring(data, "jd");//精度
string wd = maputils.getstring(data, "wd");//纬度
httpheaders httpheaders = new httpheaders();
// accept 表示客户端支持什么格式的响应体
httpheaders.set("contenttype", "application/json;charset=utf-8");
// accept-encoding 头,表示客户端可以接收gzip格式的压缩
httpheaders.set(httpheaders.accept_encoding, "gzip");
//发送请求
responseentity<byte[]> forentity = resttemplate.exchange
(url, httpmethod.get, new httpentity<>(httpheaders), byte[].class);
if(forentity.getstatuscode()== httpstatus.ok){
// 获取服务器响应体编码
string contentencoding = forentity.getheaders().getfirst(httpheaders.content_encoding);
if ("gzip".equals(contentencoding)) { // 是gzip编码
// gzip解压服务器的body响应体
byte[] weatherdata = webutils.ungzip(
new bytearrayinputstream(objects.requirenonnull(forentity.getbody())));
string weatherjson = new string(weatherdata, standardcharsets.utf_8);
climate climate = jsonobject.parseobject(weatherjson, climate.class);
if(climate!=null){
result.setsuccess();
result.setdata(climate);
}
} else {
// todo 其他的编码
result.seterrored("和风api响应值编码不是gzip,请联系我,谢谢");
}
}else{
result.seterrored("和风api响应出错了");
}
}
}
}catch (exception e){
result.seterrored("天气获取出错了");
}
return result;
}/**
* gzip解压缩
* @param inputstream
* @return
* @throws ioexception
*/
public static byte[] ungzip(inputstream inputstream) throws ioexception {
bytearrayoutputstream bytearrayoutputstream = new bytearrayoutputstream();
try (gzipinputstream gzipinputstream = new gzipinputstream(inputstream)) {
byte[] buf = new byte[4096];
int len = -1;
while ((len = gzipinputstream.read(buf, 0, buf.length)) != -1) {
bytearrayoutputstream.write(buf, 0, len);
}
return bytearrayoutputstream.tobytearray();
} finally {
bytearrayoutputstream.close();
}
}
/**
* gzip压缩数据
* @param data
* @return
* @throws ioexception
*/
public static byte[] gzip(byte[] data) throws ioexception {
bytearrayoutputstream bytearrayoutputstream = new bytearrayoutputstream();
try (gzipoutputstream gzipoutputstream = new gzipoutputstream(bytearrayoutputstream)) {
gzipoutputstream.write(data);
gzipoutputstream.finish();
return bytearrayoutputstream.tobytearray();
}
}
springboot的响应体压缩配置
实际上,并不需要自己手动去写这种响应体的压缩代码。springboot提供了相关的配置。只针对响应压缩
server:
compression:
# 开启响应压缩
enabled: true
# 支持的压缩类型
mime-types:
- application/json
- application/xml
- application/javascript
- text/html
- text/xml
- text/plain
- text/css
- text/javascript
# 默认只有响应体大于 2028kb 时才会进行压缩
min-response-size: 2048
# 指定不压缩的user-agent,默认为null
# excluded-user-agents对应的配置类:org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.compression
最后
使用resttemplate请求文本数据接口,发现解码后的字符串是乱码。此时除了编码格式问题外就可以怀疑是不是服务器响应了压缩后的数据。解决这个问题,先尝试移除accept-encoding请求头,告诉服务器,客户端不需要压缩响应体。如果服务器还是响应压缩后的数据,尝试读取服务器的content-encoding头,根据服务器的压缩编码,自己再进行解压缩。
到此这篇关于restemplate请求乱码之content-encoding=“gzip“的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关restemplate请求乱码内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论