引言
缓存击穿:给某一个key设置了过期时间,当key过期的时候,恰好这个时间点对这个key有大量的并发请求过来,这些并发的请求可能会瞬间把db压垮
解决办法
互斥锁(强一致,性能差)
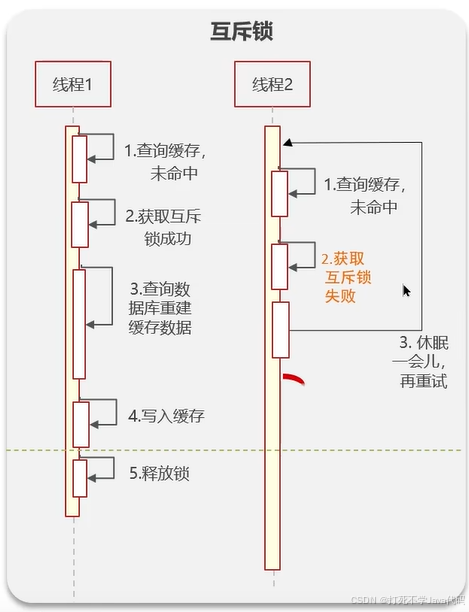
根据图片就可以看出,我们的思路就是只能让一个线程能够进行访问redis,要想实现这个功能,我们也可以使用redis自带的setnx
封装两个方法,一个写key来尝试获取锁另一个删key来释放锁
/**
* 尝试获取锁
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
private boolean trylock(string key) {
boolean flag = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().setifabsent(key, "1", 10, timeunit.seconds);
return booleanutil.istrue(flag);
}
/**
* 释放锁
*
* @param key
*/
private void unlock(string key) {
stringredistemplate.delete(key);
}在并行情况下每当其他线程想要获取锁,来访问缓存都要通过将自己的key写到trylock()方法里,setifabsent()返回false则说明有线程在在更新缓存数据,锁未释放。若返回true则说明当前线程拿到锁了可以访问缓存甚至操作缓存。
我们在下面一个热门的查询场景中用代码用代码来实现互斥锁解决缓存击穿,代码如下:
/**
* 解决缓存击穿的互斥锁
* @param id
* @return
*/
public shop querywithmutex(long id) {
string key = cache_shop_key + id;
//1.从redis查询缓存
string shopjson = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key); //json格式
//2.判断是否存在
if (strutil.isnotblank(shopjson)) { //不为空就返回 此工具类api会判断" "为false
//存在则直接返回
shop shop = jsonutil.tobean(shopjson, shop.class);
//return result.ok(shop);
return shop;
}
//3.判断是否为空值 这里过滤 " "的情况,不用担心会一直触发这个条件因为他有ttl
if (shopjson != null) {
//返回一个空值
return null;
}
//4.缓存重建 redis中值为null的情况
//4.1获得互斥锁
string lockkey = "lock:shop"+id;
shop shopbyid=null;
try {
boolean islock = trylock(lockkey);
//4.2判断是否获取成功
if (!islock){
//4.3失败,则休眠并重试
thread.sleep(50);
return querywithmutex(id);
}
//4.4成功,根据id查询数据库
shopbyid = getbyid(id);
//5.不存在则返回错误
if (shopbyid == null) {
//将空值写入redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, "", cache_null_ttl, timeunit.minutes);
//为什么这里要存一个" "这是因为如果后续db中有数据补充的话还可以去重建缓存
//return result.fail("暂无该商铺信息");
return null;
}
//6.存在,写入redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, jsonutil.tojsonstr(shopbyid), cache_shop_ttl, timeunit.minutes);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
} finally {
//7.释放互斥锁
unlock(lockkey);
}
return shopbyid;
}逻辑过期(高可用,性能优)
方案:用户查询某个热门产品信息,如果缓存未命中(即信息为空),则直接返回空,不去查询数据库。如果缓存信息命中,则判断是否逻辑过期,未过期返回缓存信息,过期则重建缓存,尝试获得互斥锁,获取失败则直接返回已过期缓存数据,获取成功则开启独立线程去重构缓存然后直接返回旧的缓存信息,重构完成之后就释放互斥锁。
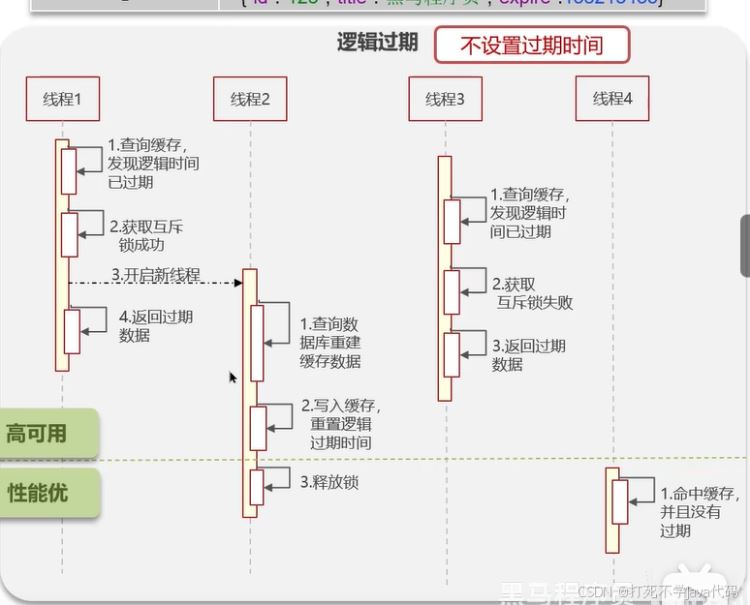
封装一个方法用来模拟更新逻辑过期时间与缓存的数据在测试类里运行起来达到数据与热的效果
/**
* 添加逻辑过期时间
*
* @param id
* @param expiretime
*/
public void saveshopredis(long id, long expiretime) {
//查询店铺信息
shop shop = getbyid(id);
//封装逻辑过期时间
redisdata redisdata = new redisdata();
redisdata.setdata(shop);
redisdata.setexpiretime(localdatetime.now().plusseconds(expiretime));
//将封装过期时间和商铺数据的对象写入redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(cache_shop_key + id, jsonutil.tojsonstr(redisdata));
}查询接口:
/**
* 逻辑过期解决缓存击穿
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
public shop querywithlogicalexpire(long id) throws interruptedexception {
string key = cache_shop_key + id;
thread.sleep(200);
//1.从redis查询缓存
string shopjson = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key); //json格式
//2.判断是否存在
if (strutil.isblank(shopjson)) {
//不存在则直接返回
return null;
}
//3.判断是否为空值
if (shopjson != null) {
//返回一个空值
//return result.fail("店铺不存在!");
return null;
}
//4.命中
//4.1将json反序列化为对象
redisdata redisdata = jsonutil.tobean(shopjson, redisdata.class);
shop shop = jsonutil.tobean((jsonobject) redisdata.getdata(), shop.class);
localdatetime expiretime = redisdata.getexpiretime();
//4.2判断是否过期
if (expiretime.isafter(localdatetime.now())) {
//5.未过期则返回店铺信息
return shop;
}
//6.过期则缓存重建
//6.1获取互斥锁
string lockkey = lock_shop_key + id;
boolean islock = trylock(lockkey);
//6.2判断是否成功获得锁
if (islock) {
//6.3成功,开启独立线程,实现缓存重建
cache_rebuild_executor.submit(() -> {
try {
//重建缓存
this.saveshop2redis(id, 20l);
} catch (exception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
} finally {
//释放锁
unlock(lockkey);
}
});
}
//6.4返回商铺信息
return shop;
}设计逻辑过期时间
可以用这个方法设置逻辑过期时间
import org.redisson.redisson;
import org.redisson.api.rbucket;
import org.redisson.api.redissonclient;
import org.redisson.config.config;
public class redissonexample {
public static void main(string[] args) {
config config = new config();
config.usesingleserver().setaddress("redis://127.0.0.1:6379");
redissonclient redisson = redisson.create(config);
string key = "examplekey";
string value = "examplevalue";
int timeout = 10; // 过期时间(秒)
// 获取rbucket对象
rbucket<string> bucket = redisson.getbucket(key);
// 设置值并指定过期时间
bucket.set(value, timeout, timeunit.seconds);
system.out.println("设置成功");
redisson.shutdown();
}
}大家可以看到,逻辑过期锁就是可以实现并发,所以他的效率更快,性能更好
但是
牺牲了数据的实时性,以保证高并发场景下的服务可用性和数据库的稳定性。
在实际应用中,需要确保获取互斥锁的操作是原子的,并且锁具有合适的超时时间,以避免死锁的发生。
逻辑过期策略适用于那些对数据实时性要求不高,但要求服务高可用性的场景。
到此这篇关于redis解决缓存击穿问题的两种方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关redis解决缓存击穿内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论