一、简单case when函数:
case score when 'a' then '优' else '不及格' end # 使用 if 函数进行替换 if(score = 'a', '优', '不及格')
then后边的值与else后边的值类型应一致,否则会报错。
如下:
case score when ‘a’ then ‘优’ else 0 end’优’和0数据类型不一致则报错:
[err] ora-00932: 数据类型不一致: 应为 char, 但却获得 number
简单case when函数只能应对一些简单的业务场景,而case when条件表达式的写法则更加灵活。
二、case when条件表达式函数
类似java中的if else语句。
格式:
case when condition then result [when...then...] else result end
sql语言演示:
case
when score = 'a' then '优'
when score = 'b' then '良'
when score = 'c' then '中'
else '不及格' end
# 等同于
case score
when 'a' then '优'
when 'b' then '良'
when 'c' then '中'
else '不及格' endcondition是一个返回布尔类型的表达式,
如果表达式返回true,则整个函数返回相应result的值,
如果表达式皆为false,则返回else后result的值,如果省略了else子句,则返回null。
三、常用场景
前言
students表的ddl
-- auto-generated definition
create table students
(
stu_code varchar(10) null,
stu_name varchar(10) null,
stu_sex int null,
stu_score int null
);students表的dml
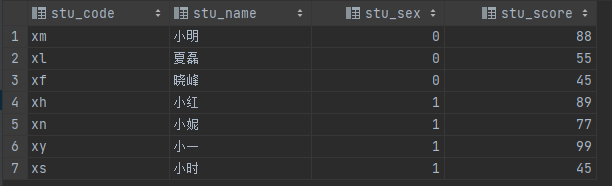
# 其中stu_sex字段,0表示男生,1表示女生。
insert into students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) values ('xm', '小明', 0, 88);
insert into students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) values ('xl', '夏磊', 0, 55);
insert into students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) values ('xf', '晓峰', 0, 45);
insert into students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) values ('xh', '小红', 1, 89);
insert into students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) values ('xn', '小妮', 1, 77);
insert into students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) values ('xy', '小一', 1, 99);
insert into students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) values ('xs', '小时', 1, 45);energy_test表的ddl
-- auto-generated definition
create table energy_test
(
e_code varchar(2) null,
e_value decimal(5, 2) null,
e_type int null
);energy_test表的dml
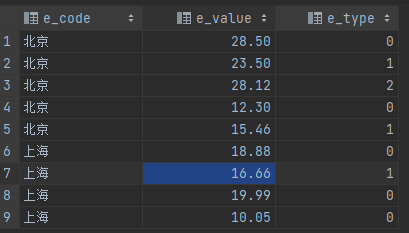
# 其中,e_type表示能耗类型,0表示水耗,1表示电耗,2表示热耗
insert into energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) values ('北京', 28.50, 0);
insert into energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) values ('北京', 23.50, 1);
insert into energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) values ('北京', 28.12, 2);
insert into energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) values ('北京', 12.30, 0);
insert into energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) values ('北京', 15.46, 1);
insert into energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) values ('上海', 18.88, 0);
insert into energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) values ('上海', 16.66, 1);
insert into energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) values ('上海', 19.99, 0);
insert into energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) values ('上海', 10.05, 0);p_price表的ddl
-- auto-generated definition
create table p_price
(
p_price decimal(5, 2) null comment '价格',
p_level int null comment '等级',
p_limit int null comment '阈值'
)
comment '电能耗单价表';p_price表的dml
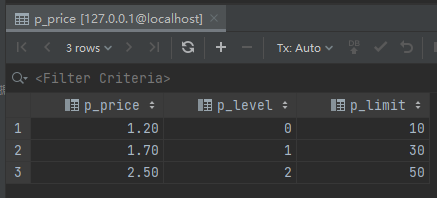
insert into test.p_price (p_price, p_level, p_limit) values (1.20, 0, 10); insert into test.p_price (p_price, p_level, p_limit) values (1.70, 1, 30); insert into test.p_price (p_price, p_level, p_limit) values (2.50, 2, 50);
user_col_comments 表的ddl
-- auto-generated definition
create table user_col_comments
(
column_name varchar(50) null comment '列名',
comment varchar(100) null comment '列的备注'
);user_col_comments 表的dml
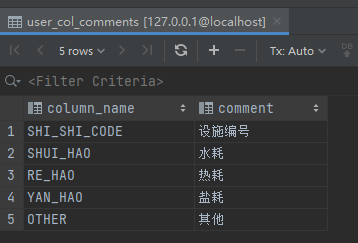
insert into test.user_col_comments (column_name, comment) values ('shi_shi_code', '设施编号');
insert into test.user_col_comments (column_name, comment) values ('shui_hao', '水耗');
insert into test.user_col_comments (column_name, comment) values ('re_hao', '热耗');
insert into test.user_col_comments (column_name, comment) values ('yan_hao', '盐耗');
insert into test.user_col_comments (column_name, comment) values ('other', '其他');场景1:不同状态展示为不同的值
有分数score,score<60返回不及格,score>=60返回及格,score>=80返回优秀
# 有分数score,score<60返回不及格,score>=60返回及格,score>=80返回优秀
select
stu_name,
(case when stu_score < 60 then '不及格'
when stu_score >= 60 and stu_score < 80 then '及格'
when stu_score >= 80 then '优秀'
else '异常' end) as remark
from students;注意:如果你想判断score是否null的情况,when score = null then ‘缺席考试’,这是一种错误的写法,正确的写法应为:case when score is null then '缺席考试' else '正常' end
场景2:统计不同状态下的值
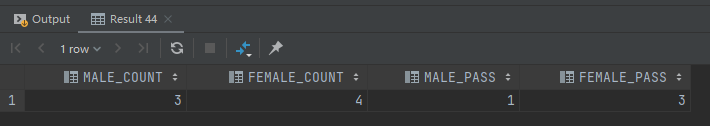
现老师要统计班中,有多少男同学,多少女同学,并统计男同学中有几人及格,女同学中有几人及格,要求用一个sql输出结果。其中stu_sex字段,0表示男生,1表示女生。

select sum(case when stu_sex = 0 then 1 else 0 end) as male_count, sum(case when stu_sex = 1 then 1 else 0 end) as female_count, sum(case when stu_score >= 60 and stu_sex = 0 then 1 else 0 end) as male_pass, sum(case when stu_score >= 60 and stu_sex = 1 then 1 else 0 end) as female_pass from students;
输出结果如下:
注意点:
- 用的是 :
sum?而不是count then 1 else 0的位置不能改变:否则会有以下效果:
sum(case when stu_sex = 0 then '1' else '0' end) as '男性', 改变了 sum(case when stu_sex = 0 then '0' else '1' end) as '女性':
字符 ‘0’ 和 数值 0,使用 都是一样的
场景3:配合聚合函数做统计
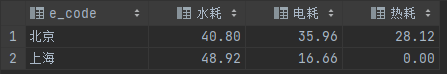
现要求统计各个城市,总共使用了多少水耗、电耗、热耗,使用一条sql语句输出结果
有能耗表如下:其中,e_type表示能耗类型,0表示水耗,1表示电耗,2表示热耗
select e_code,
sum(case when e_type = 0 then e_value else 0 end) as '水耗',
sum(case when e_type = 1 then e_value else 0 end) as '电耗',
sum(case when e_type = 2 then e_value else 0 end) as '热耗'
from energy_test
group by e_code;输出结果如下:
场景4:case when中使用子查询
根据城市用电量多少,计算用电成本。假设电能耗单价分为三档,根据不同的能耗值,使用相应价格计算成本。
当能耗值小于10时,使用p_level=0时的p_price的值,能耗值大于10小于30使用p_level=1时的p_price的值…
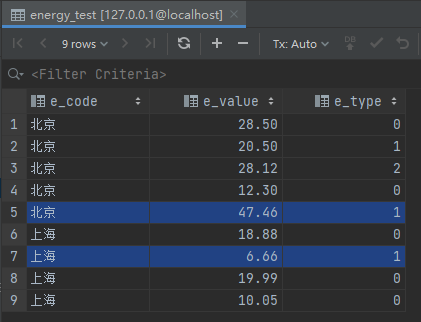
energy_test 我修改了e_type 为1的值的两条数据的e_value。
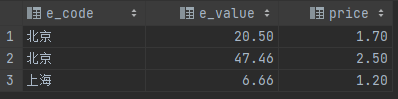
select e_code, e_value,
(case when e_value <= (select p_limit from p_price where p_level = 0)
then (select p_price from p_price where p_level = 0)
when e_value > (select p_limit from p_price where p_level = 0) and e_value <= (select p_limit from p_price where p_level = 1)
then (select p_price from p_price where p_level = 1)
when e_value > (select p_limit from p_price where p_level = 1) and e_value <= (select p_limit from p_price where p_level = 2)
then (select p_price from p_price where p_level = 2) end ) as price
from energy_test
where e_type = 1;输出结果如下:
场景5:经典行转列,结合max聚合函数
行转列中 sum作用:无用,但是select后得跟聚合函数,不能去掉sum。直接写max或者min也行。
select
max(case when column_name = 'shi_shi_code' then comment else ''end) as shi_shi_code_comment,
max(case when column_name = 'shui_hao' then comment else ''end) as shui_hao_comment,
max(case when column_name = 're_hao' then comment else ''end) as re_hao_comment,
max(case when column_name = 'yan_hao' then comment else ''end) as yan_hao_comment,
max(case when column_name = 'other' then comment else '' end) as other_comment
from user_col_comments;输出结果如下:

到此这篇关于sql中的case when用法详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关sql case when用法内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!







发表评论