前言
本文是自定义view中最简单的使用方法,分别进行 ‘onmeasure’、‘ondraw’、‘自定义样式’、‘lifecycle’的简单使用,了解自定义view的使用。
通过lifecycle来控制 动画的状态
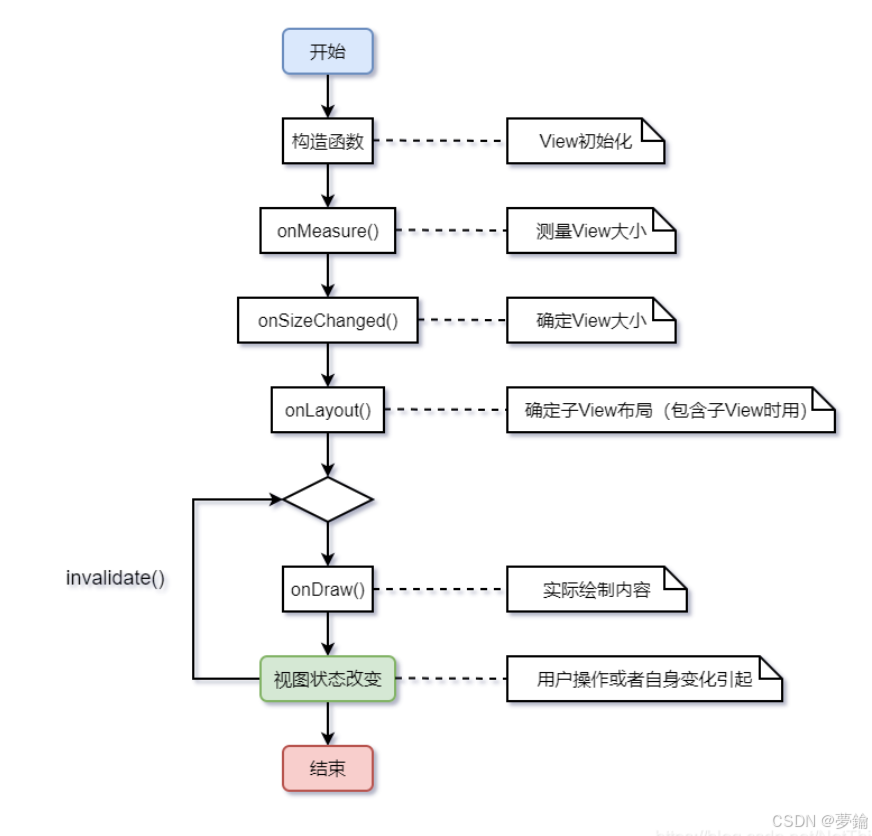
一、onmeasure做了什么?
在onmeasure中获取view 的宽和高 是 ‘0’
测量view的宽 / 高
- 在某些情况下,需要多次测量
(measure)才能确定view最终的宽/高; - 该情况下,
measure过程后得到的宽 / 高可能不准确; - 此处建议:在
layout过程中onlayout()去获取最终的宽 / 高
必须要了解 measurespec 作用
测量规格(measurespec)是由测量模式(mode)和测量大小(size)组成,共32位(int类型),其中:
- 测量模式(mode):占测量规格(measurespec)的高2位;
- 测量大小(size):占测量规格(measurespec)的低30位。
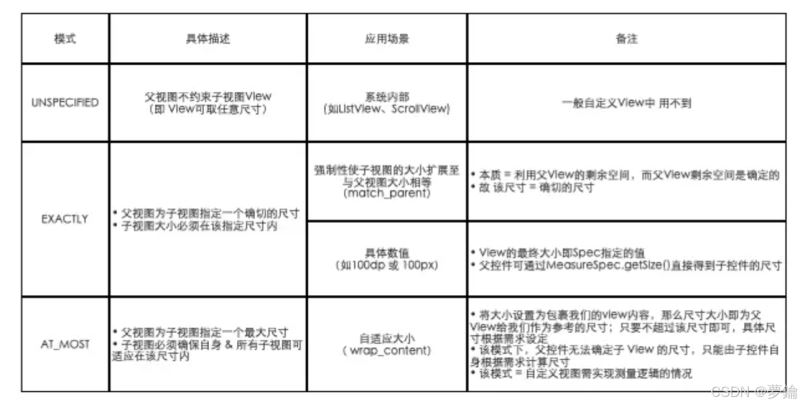
measurespec类用一个变量封装了测量模式(mode)和测量大小(size):通过使用二进制,将测量模式(mode)和测量大小(size)打包成一个int值,并提供了打包和解包的方法,这样的做法是为了减少对象内存分配和提高存取效率。具体使用如下所示:
override fun onmeasure(widthmeasurespec: int, heightmeasurespec: int) {
super.onmeasure(widthmeasurespec, heightmeasurespec)
val widthmodel = measurespec.getmode(widthmeasurespec)
val widthsize = measurespec.getsize(widthmeasurespec)
val heightmodel = measurespec.getmode(heightmeasurespec)
val heightsize = measurespec.getsize(heightmeasurespec)
// @todo 在 onmeasure 中获取view的 宽高 获取到是 0
log.e(tag, "onmeasure: ${widthsize}-${width}__${heightsize}__${height}")
val defwidth = 400
val defheight = 400
// @todo measurespec.at_most:wrap_content ; measurespec.exactly:match_parent ;
if (widthmodel == measurespec.at_most && heightmodel == measurespec.at_most) {
setmeasureddimension(defwidth, defheight)
} else if (widthmodel == measurespec.at_most) {
setmeasureddimension(defwidth, heightsize)
} else if (heightmodel == measurespec.at_most) {
setmeasureddimension(widthsize, defheight)
}
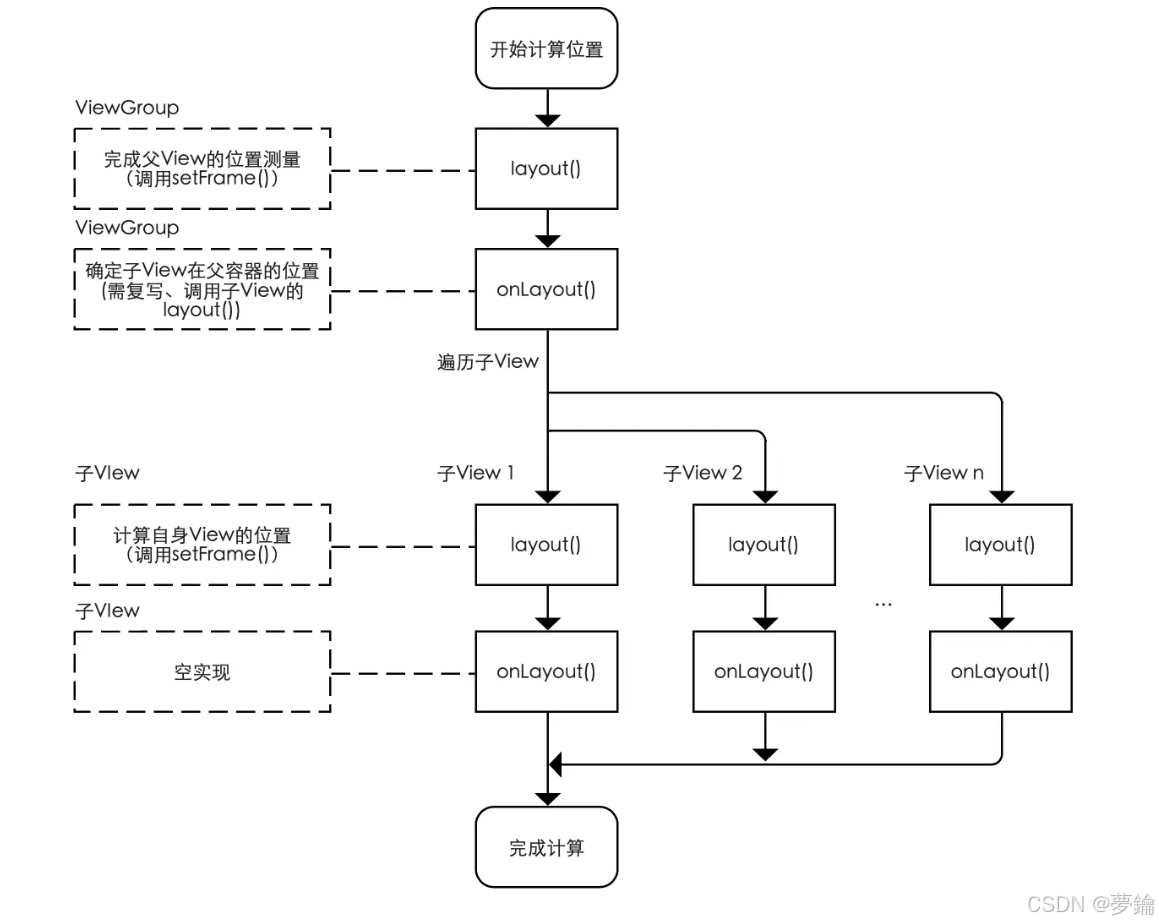
}1、onlayout 做了什么
计算位置,里面包含子view 的情况下才会用到这个函数
一般继承自viewgroup或者重新写layout布局
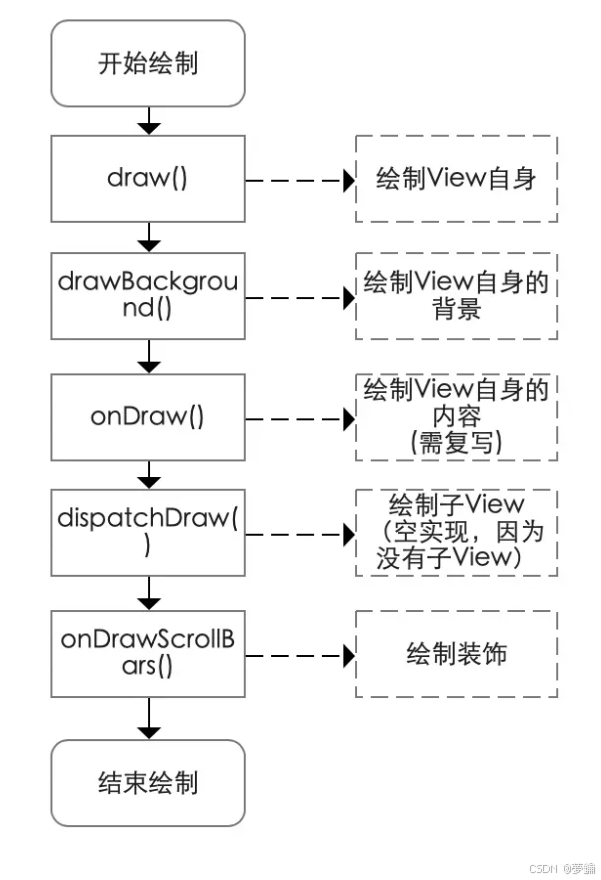
2、ondraw 做了什么
绘制view自身,设置padding 时要在ondraw中计算
1. 绘制view背景
2. 绘制view内容
3. 绘制子view
4. 绘制装饰(渐变框,滑动条等等)
override fun ondraw(canvas: canvas?) {
super.ondraw(canvas)
canvas?.let {
val pl = paddingleft
val pr = paddingright
val pt = paddingtop
val pb = paddingbottom
var mheight = height - pt - pb
var mwidth = width - pl - pr
val cy = pt.plus(pb).div(2) + mheight.div(2).tofloat()
val cx = pl.plus(pr).div(2) + mwidth.div(2).tofloat()
val cc = math.min(mheight, mwidth).div(2).tofloat()
it.drawcircle(
cx,
cy,
cc,
mpaint
)
}
}3、lifecycle控制动画的状态
自定义view 继承 defaultlifecycleobserver 类 然后实现 生命周期=中的方法
override fun onstart(owner: lifecycleowner) {
super.onstart(owner)
animsetcolor.start()
}
override fun ondestroy(owner: lifecycleowner) {
super.ondestroy(owner)
animsetcolor.cancel()
}
override fun onpause(owner: lifecycleowner) {
super.onpause(owner)
animsetcolor.pause()
}
override fun onresume(owner: lifecycleowner) {
super.onresume(owner)
animsetcolor.resume()
}
在act中 进行生命周期监听的绑定
lifecycle.addobserver(customview)4、代码示例
自定义view代码
/**
* @todo 自定义view
*
*
*/
class myview(context: context?, attrs: attributeset?) :
view(context, attrs), defaultlifecycleobserver {
private val mpaint by lazy { paint() }
private val tag = "myview"
private var i = 0
// @todo 动画实现改变颜色 然后 通过 lifecycle 控制动画的状态:开始、暂停、恢复、取消
private val animsetcolor by lazy {
valueanimator.ofint(0, 100).apply {
addlistener(object : animatorlistener {
override fun onanimationstart(animation: animator) {
}
override fun onanimationend(animation: animator) {
}
override fun onanimationcancel(animation: animator) {
}
override fun onanimationrepeat(animation: animator) {
i++
if (i % 2 == 0) {
mpaint.color = android.graphics.color.blue
}
mpaint.color = when (i % 5) {
0 -> android.graphics.color.blue
1 -> android.graphics.color.yellow
2 -> android.graphics.color.cyan
3 -> android.graphics.color.magenta
4 -> android.graphics.color.ltgray
else -> android.graphics.color.transparent
}
// @todo 每次设置颜色后 调用postinvalidate 重新绘制view
postinvalidate()
}
})
// 动画无线循环执行
repeatcount = valueanimator.infinite
// 间隔一秒执行一次
duration = 1000
}
}
init {
mpaint.color = color.blue.hashcode()
mpaint.style = paint.style.fill
mpaint.strokewidth = 20f
context?.obtainstyledattributes(attrs, r.styleable.myview)?.apply {
mpaint.color = getcolor(r.styleable.myview_circlr_color, android.graphics.color.green)
recycle()
}
}
override fun onmeasure(widthmeasurespec: int, heightmeasurespec: int) {
super.onmeasure(widthmeasurespec, heightmeasurespec)
val widthmodel = measurespec.getmode(widthmeasurespec)
val widthsize = measurespec.getsize(widthmeasurespec)
val heightmodel = measurespec.getmode(heightmeasurespec)
val heightsize = measurespec.getsize(heightmeasurespec)
// @todo 在 onmeasure 中获取view的 宽高 获取到是 0
log.e(tag, "onmeasure: ${widthsize}-${width}__${heightsize}__${height}")
val defwidth = 400
val defheight = 400
// @todo measurespec.at_most:wrap_content ; measurespec.exactly:match_parent ;
if (widthmodel == measurespec.at_most && heightmodel == measurespec.at_most) {
setmeasureddimension(defwidth, defheight)
} else if (widthmodel == measurespec.at_most) {
setmeasureddimension(defwidth, heightsize)
} else if (heightmodel == measurespec.at_most) {
setmeasureddimension(widthsize, defheight)
}
}
//挂在到act上时
// override fun onattachedtowindow() {
// super.onattachedtowindow()
// log.e(tag, "onattachedtowindow: ")
// anim.start()
// }
//在act 销毁时
// override fun ondetachedfromwindow() {
// super.ondetachedfromwindow()
// log.e(tag, "ondetachedfromwindow: ")
// anim.cancel()
//
// }
override fun onstart(owner: lifecycleowner) {
super.onstart(owner)
animsetcolor.start()
}
override fun ondestroy(owner: lifecycleowner) {
super.ondestroy(owner)
animsetcolor.cancel()
}
override fun onpause(owner: lifecycleowner) {
super.onpause(owner)
animsetcolor.pause()
}
override fun onresume(owner: lifecycleowner) {
super.onresume(owner)
animsetcolor.resume()
}
override fun onlayout(changed: boolean, left: int, top: int, right: int, bottom: int) {
super.onlayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom)
log.e(tag, "onlayout: ")
}
/**
* 作用:根据给定的 canvas 自动渲染view包括其所有子 view)。
* 绘制过程:
* 1. 绘制view背景
* 2. 绘制view内容
* 3. 绘制子view
* 4. 绘制装饰(渐变框,滑动条等等)
* 注:
* a. 在调用该方法之前必须要完成 layout 过程
* b. 所有的视图最终都是调用 view 的 draw()绘制视图( viewgroup 没有复写此方法)
* c. 在自定义view时,不应该复写该方法,而是复写 ondraw(canvas) 方法进行绘制
* d. 若自定义的视图确实要复写该方法,那么需先调用 super.draw(canvas)完成系统的绘制,然后再进行自定义的绘制
*/
override fun ondraw(canvas: canvas?) {
super.ondraw(canvas)
canvas?.let {
val pl = paddingleft
val pr = paddingright
val pt = paddingtop
val pb = paddingbottom
var mheight = height - pt - pb
var mwidth = width - pl - pr
val cy = pt.plus(pb).div(2) + mheight.div(2).tofloat()
val cx = pl.plus(pr).div(2) + mwidth.div(2).tofloat()
val cc = math.min(mheight, mwidth).div(2).tofloat()
it.drawcircle(
cx,
cy,
cc,
mpaint
)
}
}
}自定义view的xml样式文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="myview">
<attr name="circlr_color" format="color"/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>layout布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.constraintlayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#11008811"
tools:context=".customviewactivity">
<com.andriod.police.view.myview
android:id="@+id/customview"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="130dp"
android:background="#11f08811"
app:circlr_color="@color/cardview_light_background"
android:padding="20dp"
app:layout_constraintstart_tostartof="parent"
app:layout_constrainttop_totopof="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.constraintlayout>act
class customviewactivity : appcompatactivity() {
private val customview: myview by lazy { findviewbyid(r.id.customview) }
override fun oncreate(savedinstancestate: bundle?) {
super.oncreate(savedinstancestate)
setcontentview(r.layout.activity_custom_view)
// @todo 通过 lifecycle 控制动画的状态:开始、暂停、恢复、取消
lifecycle.addobserver(customview)
}
}总结
在自定义view中了解在 onmeasure中进行view 的测量,在onlayout中进行对view位置的控制,在ondraw中进行view的绘制。
通过 lifecycle控制view的生命周期,防止出现内存泄露问题如在相应的生命周期中操作动画的执行状态
到此这篇关于android 自定义view 加 lifecycle 简单使用详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关android 自定义view内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论