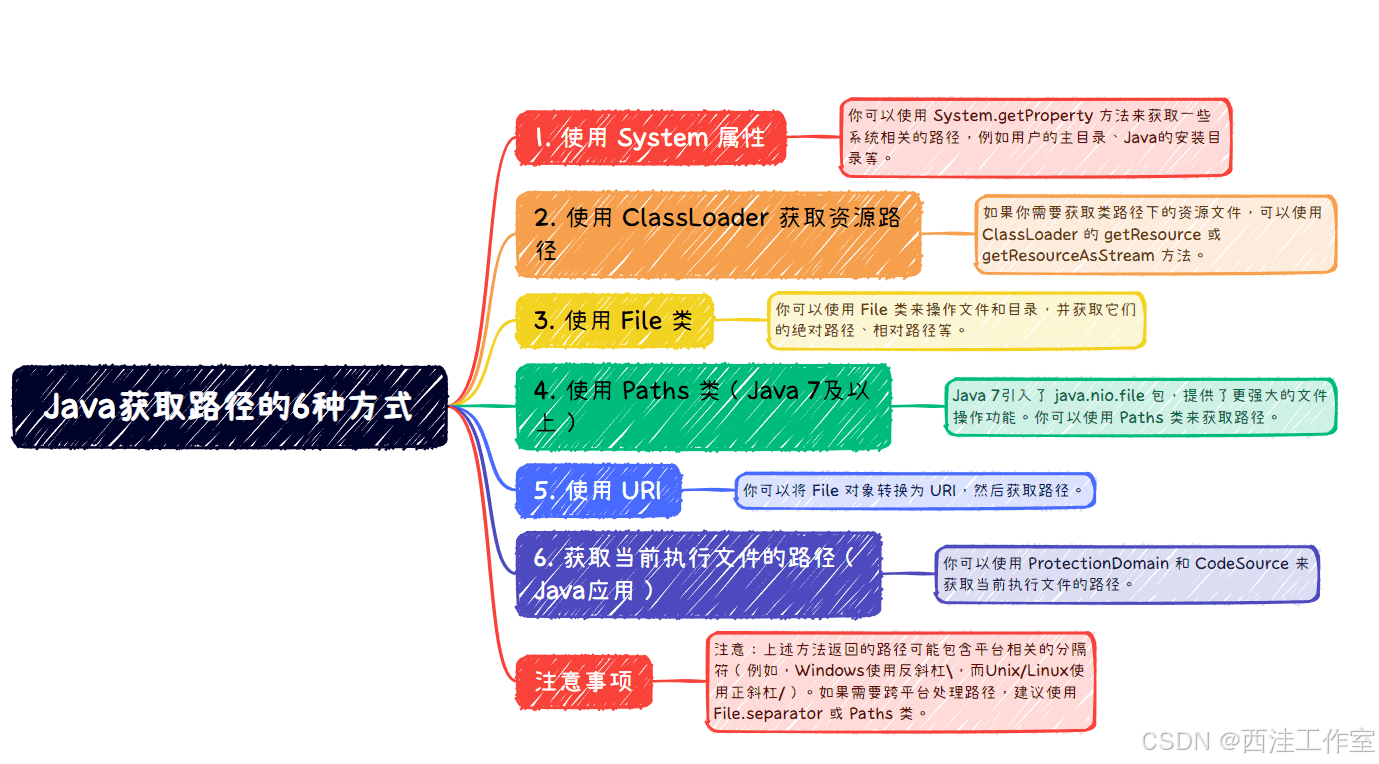
public class demo1 {
public static void main(string[] args) {
/*
1.使用 system 属性
*/
// 获取用户的主目录
string userhome = system.getproperty("user.home");
system.out.println("user home: " + userhome);
// 获取java的安装目录
string javahome = system.getproperty("java.home");
system.out.println("java home: " + javahome);
/*
* 2.使用 classloader 获取资源路径
*/
// 获取类路径下的资源文件路径
classloader classloader = demo1.class.getclassloader();
url resourceurl = classloader.getresource("config.properties");
string resourcepath = resourceurl != null ? resourceurl.getpath() : null;
system.out.println("resource path: " + resourcepath);
/*
3.使用 file 类
*/
// 创建一个file对象
file file = new file("example.txt");
// 获取绝对路径
string absolutepath = file.getabsolutepath();
system.out.println("absolute path: " + absolutepath);
// 获取相对路径(相对于当前工作目录)
string canonicalpath;
try {
canonicalpath = file.getcanonicalpath();
system.out.println("canonical path: " + canonicalpath);
} catch (ioexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
// 获取父目录路径
string parentpath = file.getparent();
system.out.println("parent path: " + parentpath);
/*
4.使用 paths 类(java 7及以上)
*/
// 获取当前工作目录
path currentdir = paths.get(".").toabsolutepath();
system.out.println("current directory: " + currentdir);
// 拼接路径
path filepath = paths.get(currentdir.tostring(), "example.txt");
system.out.println("file path: " + filepath);
/*
5.使用 uri
*/
file file2 = new file("example.txt");
uri uri = file2.touri();
string uripath = uri.getpath();
system.out.println("uri path: " + uripath);
/*
6. 获取当前执行文件的路径(java应用)
*/
string path = demo1.class.getprotectiondomain().getcodesource().getlocation().getpath();
system.out.println("executable path: " + path);
}
}
总结
到此这篇关于java获取路径的6种方式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java获取路径方式内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论