在日常的开发工作进程中,常常会碰到需要替换指定字符串的情形。接下来,就让我们详细地谈谈java中替换字符串的几种方法吧。
replace
replace 方法有两个重载版本:
public string replace(char oldchar, char newchar)
这个方法的作用是将字符串中所有的 oldchar 字符替换为 newchar 字符。它非常适合于当你需要替换字符串中的特定字符时使用。
public string replace(charsequence target, charsequence replacement)
这个方法用于将字符串中所有与 target 相等的子字符串替换为 replacement。需要注意的是,这个方法不支持正则表达式,它执行的是简单的文本匹配和替换。示例代码如下
public static void main(string[] args) {
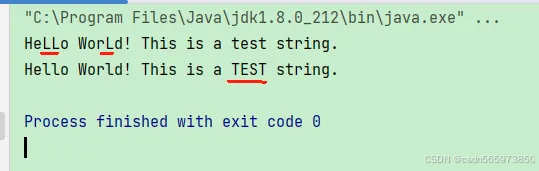
string original = "hello world! this is a test string.";
// 使用 replace 方法替换字符 'l' 为 'l'
string replaced = original.replace('l', 'l');
system.out.println(replaced);
// 使用 replace 方法替换子字符串 "test" 为 "test"
replaced = original.replace("test", "test");
system.out.println(replaced);
}
执行结果如图
replaceall
replaceall 方法如下:
public string replaceall(string regex, string replacement)
这个方法使用正则表达式 regex 来识别要替换的部分,并将其替换为 replacement。
replaceall 支持正则表达式,这意味着你可以用更复杂的方式来定义要被替换的内容,例如匹配特定模式的文本,而不仅仅是固定的字符串。
方法说明:
replaceall 方法接受两个参数:第一个参数 regex 是一个正则表达式,用于匹配字符串中需要被替换的部分;第二个参数 replacement 是用来替换匹配到的子字符串的新字符串。这个方法会找到所有匹配 regex 的子字符串,并将它们替换为 replacement。
示例代码
public static void main(string[] args) {
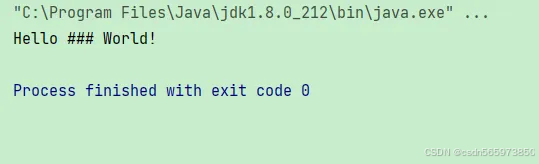
// 使用 replaceall 方法替换所有数字为 "#"
string withregex = "hello 123 world!";
string replaced = withregex.replaceall("\\d", "#");
system.out.println(replaced);
}
执行结果如图
replacefirst
replacefirst 方法如下:
public string replacefirst(string regex, string replacement)
这个方法类似于 replaceall(), 但它只替换第一个匹配的模式。
方法说明:
replacefirst 方法同样接受一个正则表达式 regex 作为第一个参数,用于匹配字符串中需要被替换的部分。第二个参数 replacement 是用来替换匹配到的第一个子字符串的新字符串。与 replaceall 不同的是,replacefirst 只会替换掉第一个匹配到的子字符串,而不是全部。
示例代码
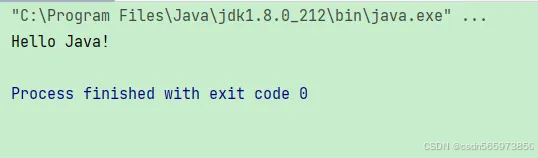
public static void main(string[] args) {
// 使用 replaceall 方法替换所有数字为 "#"
string withregex = "hello 123 world!";
string replaced = withregex.replacefirst("\\d", "#");
system.out.println(replaced);
}
执行结果如图

stringbuffer 或 stringbuilder 的 replace()
stringbuffer 或 stringbuilder 的 replace() 方法 这些类提供了 replace(int start, int end, string str) 方法,可以在指定位置替换字符串的一部分,但通常这不是用于全局替换的首选方法,因为这涉及到创建一个新的 stringbuffer 或 stringbuilder 对象
方法说明:
replace() 方法接受三个参数:start 是替换开始的位置(包括),end 是替换结束的位置(不包括),str 是用来替换原有内容的新的字符串。这个方法会在 start 和 end 指定的范围内,用 str 替换掉原有的字符序列。
示例代码
public static void main(string[] args) {
stringbuffer buffer = new stringbuffer("hello world!");
buffer.replace(6, 11, "java");
system.out.println(buffer.tostring());
}
执行结果如图
第三方库
在java生态中,除了标准库提供的字符串操作方法外,还有许多优秀的第三方库,如hutool,它们提供了更为丰富和强大的字符串处理功能,能够满足开发者对于特定需求的处理。hutool是一个java工具包,其中的strutil类提供了大量实用的字符串操作方法。
示例代码
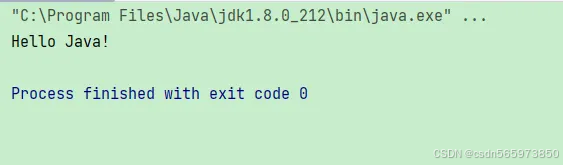
public static void main(string[] args) {
string original = "hello world!";
string replaced = strutil.replace(original, "world", "java");
system.out.println(replaced);
}
执行结果如图
第三方库如hutool提供了额外的字符串操作功能,这些功能可能更适合某些特定的需求,比如复杂的字符串解析、格式化或是高性能的字符串处理。 使用第三方库可以简化代码,提高开发效率,同时这些库通常也会提供更好的文档和支持。 在选择使用第三方库时,应考虑项目的依赖管理、库的活跃度和社区支持等因素。 通过合理利用这些第三方库,开发者可以更加高效地完成字符串处理任务,提升代码的质量和可维护性。
总结
在java中,替换字符串的常用方法主要包括string类的replace()、replaceall()、replacefirst()方法,以及stringbuilder和stringbuffer类的replace()方法。这些方法能够满足大多数日常开发中的字符串替换需求。
然而,在一些特殊场景下,当这些常规方法无法满足特定的替换要求时,我们可以借助第三方库来实现更为复杂或高效的字符串处理。例如,hutool等工具库提供了丰富多样的字符串操作函数,能够轻松应对各种复杂的字符串替换场景。
总之,虽然java内置的字符串替换方法已经相当强大,但在面对一些特殊需求时,结合第三方库的使用,将为我们提供更为灵活和高效的解决方案。
到此这篇关于java替换字符串replace和replaceall方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java替换字符串replace和replaceall内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论