前言
本文参考若依源码,介绍了如何在springboot项目中使用aop和自定义注解实现mysql主从数据库的动态切换,当从库故障时,能自动切换到主库,确保服务的高可用性。
实现效果:如果 服务器搭建的是一主多从多个mysql数据源,主服务器用来读。从服务器用来写。此时你在代码层面用注解指定了一个增删改方法到从数据源,但是碰巧此时从数据源失效了,那么就会自动的切换到其它服务器。
为什么要切换数据源,有哪些应用场景?
动态切换数据源通常是为了满足以下需求:
- 读写分离:在数据库架构中,为了提高性能和可用性,常常使用主从复制的方式。主数据库处理写操作,而从数据库处理读操作。动态切换数据源可以在不同的操作中使用不同的数据库,以达到优化性能的目的。
- 多租户架构:在saas(software as a service)应用中,不同的租户可能需要操作不同的数据库。动态数据源允许系统根据租户的身份来切换到对应的数据源。
- 分库分表:在处理大规模数据时,可能会采用分库分表的策略来分散数据存储的压力。动态切换数据源可以在执行跨库或跨表操作时,根据需要切换到正确的数据源。
- 环境隔离:在开发、测试和生产环境中,可能需要连接到不同的数据库。动态数据源可以在不同环境之间无缝切换,以确保数据的隔离和安全性。
- 灵活的数据库管理:在复杂的业务场景下,可能需要根据不同的业务逻辑来选择不同的数据源。动态数据源提供了这种灵活性,允许开发者根据运行时的条件来选择最合适的数据源。
- 故障转移和高可用性:当主数据库不可用时,动态切换数据源可以自动或手动切换到备用数据库,以保证服务的连续性和数据的可用性。
如何切换数据源?
springboot版本:3.0.4
jdk版本:jdk17
1.pom文件
<dependency>
<groupid>org.projectlombok</groupid>
<artifactid>lombok</artifactid>
</dependency>
<!-- aop切面-->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactid>
</dependency>
<!--druid连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupid>com.alibaba</groupid>
<artifactid>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactid>
<version>1.2.20</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupid>com.mysql</groupid>
<artifactid>mysql-connector-j</artifactid>
</dependency>
<!--mybatisplus-->
<dependency>
<groupid>com.baomidou</groupid>
<artifactid>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactid>
<version>3.5.3.1</version>
</dependency>2.配置文件:application.yml、application-druid.yml
application.yml配置文件:
#application.yml
server:
port: 8000
spring:
profiles:
active: druidapplication-druid.yml配置文件:
# 数据源配置
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.druiddatasource
driverclassname: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.driver
druid:
# 主库数据源
master:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/study?useunicode=true&characterencoding=utf8&zerodatetimebehavior=converttonull&usessl=true&servertimezone=gmt%2b8
username: root
password: 123456
# 从库数据源
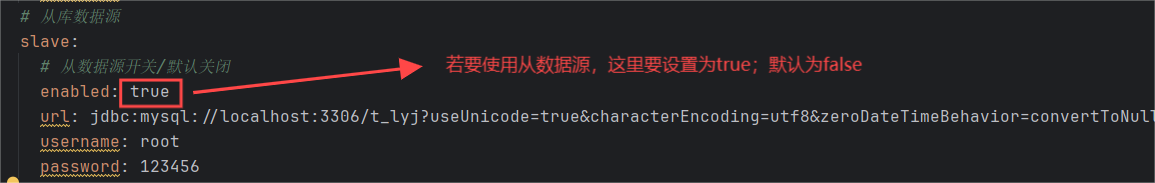
slave:
# 从数据源开关/默认关闭
enabled: true
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/t_lyj?useunicode=true&characterencoding=utf8&zerodatetimebehavior=converttonull&usessl=true&servertimezone=gmt%2b8
username: root
password: 123456
# 初始连接数
initialsize: 5
# 最小连接池数量
minidle: 10
# 最大连接池数量
maxactive: 20
# 配置获取连接等待超时的时间
maxwait: 60000
# 配置连接超时时间
connecttimeout: 30000
# 配置网络超时时间
sockettimeout: 60000
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
timebetweenevictionrunsmillis: 60000
# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
minevictableidletimemillis: 300000
# 配置一个连接在池中最大生存的时间,单位是毫秒
maxevictableidletimemillis: 9000003、数据源名称枚举datasourcetype
/**
* 数据源
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
public enum datasourcetype
{
/**
* 主库
*/
master,
/**
* 从库
*/
slave
}4、bean工具类springutils
@component
public final class springutils implements beanfactorypostprocessor, applicationcontextaware
{
/** spring应用上下文环境 */
private static configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory;
private static applicationcontext applicationcontext;
@override
public void postprocessbeanfactory(configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory) throws beansexception
{
springutils.beanfactory = beanfactory;
}
@override
public void setapplicationcontext(applicationcontext applicationcontext) throws beansexception
{
springutils.applicationcontext = applicationcontext;
}
/**
* 获取对象
*
* @param name
* @return object 一个以所给名字注册的bean的实例
* @throws beansexception
*
*/
@suppresswarnings("unchecked")
public static <t> t getbean(string name) throws beansexception
{
return (t) beanfactory.getbean(name);
}
/**
* 获取类型为requiredtype的对象
*
* @param clz
* @return
* @throws beansexception
*
*/
public static <t> t getbean(class<t> clz) throws beansexception
{
t result = (t) beanfactory.getbean(clz);
return result;
}
/**
* 如果beanfactory包含一个与所给名称匹配的bean定义,则返回true
*
* @param name
* @return boolean
*/
public static boolean containsbean(string name)
{
return beanfactory.containsbean(name);
}
/**
* 判断以给定名字注册的bean定义是一个singleton还是一个prototype。 如果与给定名字相应的bean定义没有被找到,将会抛出一个异常(nosuchbeandefinitionexception)
*
* @param name
* @return boolean
* @throws nosuchbeandefinitionexception
*
*/
public static boolean issingleton(string name) throws nosuchbeandefinitionexception
{
return beanfactory.issingleton(name);
}
/**
* @param name
* @return class 注册对象的类型
* @throws nosuchbeandefinitionexception
*
*/
public static class<?> gettype(string name) throws nosuchbeandefinitionexception
{
return beanfactory.gettype(name);
}
/**
* 如果给定的bean名字在bean定义中有别名,则返回这些别名
*
* @param name
* @return
* @throws nosuchbeandefinitionexception
*
*/
public static string[] getaliases(string name) throws nosuchbeandefinitionexception
{
return beanfactory.getaliases(name);
}
/**
* 获取aop代理对象
*
* @param invoker
* @return
*/
@suppresswarnings("unchecked")
public static <t> t getaopproxy(t invoker)
{
return (t) aopcontext.currentproxy();
}
/**
* 获取当前的环境配置,无配置返回null
*
* @return 当前的环境配置
*/
public static string[] getactiveprofiles()
{
return applicationcontext.getenvironment().getactiveprofiles();
}
/**
* 获取当前的环境配置,当有多个环境配置时,只获取第一个
*
* @return 当前的环境配置
*/
public static string getactiveprofile()
{
final string[] activeprofiles = getactiveprofiles();
return stringutils.isnotempty(arrays.tostring(activeprofiles)) ? activeprofiles[0] : null;
}
/**
* 获取配置文件中的值
*
* @param key 配置文件的key
* @return 当前的配置文件的值
*
*/
public static string getrequiredproperty(string key)
{
return applicationcontext.getenvironment().getrequiredproperty(key);
}
}5、多数据源切换注解datasource
/**
* 自定义多数据源切换注解
*
* 优先级:先方法,后类,如果方法覆盖了类上的数据源类型,以方法的为准,否则以类上的为准
*
* @author lyj
*/
@target({ elementtype.method, elementtype.type })
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@documented
@inherited
public @interface datasource
{
/**
* 切换数据源名称
*/
public datasourcetype value() default datasourcetype.master;
}6、数据源解析配置类druidconfig
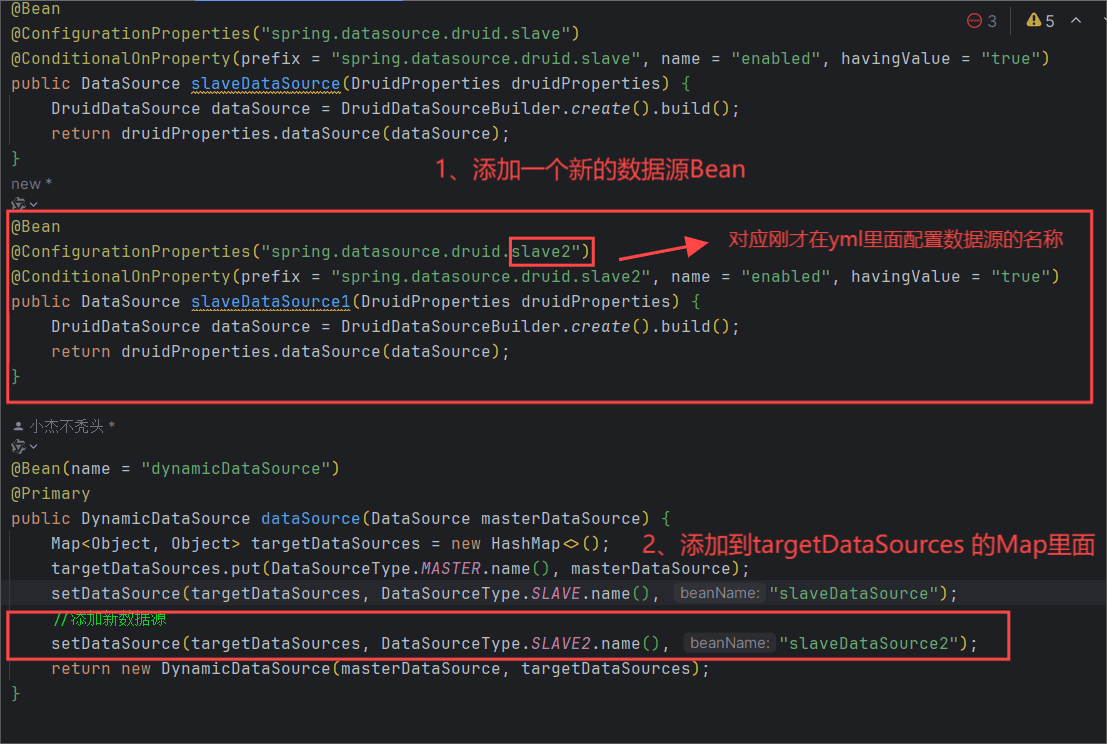
@configuration
public class druidconfig {
@bean
@configurationproperties("spring.datasource.druid.master")
public datasource masterdatasource(druidproperties druidproperties){
druiddatasource datasource = druiddatasourcebuilder.create().build();
return druidproperties.datasource(datasource);
}
@bean
@configurationproperties("spring.datasource.druid.slave")
@conditionalonproperty(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.slave", name = "enabled", havingvalue = "true")
public datasource slavedatasource(druidproperties druidproperties) {
druiddatasource datasource = druiddatasourcebuilder.create().build();
return druidproperties.datasource(datasource);
}
@bean(name = "dynamicdatasource")
@primary
public dynamicdatasource datasource(datasource masterdatasource) {
map<object, object> targetdatasources = new hashmap<>();
targetdatasources.put(datasourcetype.master.name(), masterdatasource);
setdatasource(targetdatasources, datasourcetype.slave.name(), "slavedatasource");
return new dynamicdatasource(masterdatasource, targetdatasources);
}
/**
* 设置数据源
*
* @param targetdatasources 备选数据源集合
* @param sourcename 数据源名称
* @param beanname bean名称
*/
public void setdatasource(map<object, object> targetdatasources, string sourcename, string beanname) {
try {
datasource datasource = springutils.getbean(beanname);
targetdatasources.put(sourcename, datasource);
} catch (exception e) {
}
}
}7、数据源注入核心类dynamicdatasource
/**
* 动态数据源
*
* @author lyj
*/
public class dynamicdatasource extends abstractroutingdatasource {
public dynamicdatasource(datasource defaulttargetdatasource, map<object, object> targetdatasources)
{
//设置默认数据源
super.setdefaulttargetdatasource(defaulttargetdatasource);
//设置目标数据源的映射
super.settargetdatasources(targetdatasources);
//初始化
super.afterpropertiesset();
}
@override
protected object determinecurrentlookupkey()
{
return dynamicdatasourcecontextholder.getdatasourcetype();
}
}8、数据源切换处理类dynamicdatasourcecontextholder
/**
* 数据源切换处理
*
* @author lyj
*/
public class dynamicdatasourcecontextholder
{
public static final logger log = loggerfactory.getlogger(dynamicdatasourcecontextholder.class);
/**
* 使用threadlocal维护变量,threadlocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本,
* 所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本。
*/
private static final threadlocal<string> context_holder = new threadlocal<>();
/**
* 设置数据源的变量
*/
public static void setdatasourcetype(string dstype)
{
log.info("切换到{}数据源", dstype);
context_holder.set(dstype);
}
/**
* 获得数据源的变量,默认使用主数据源
*/
public static string getdatasourcetype()
{
return context_holder.get() == null ? datasourcetype.master.name() : context_holder.get();
}
/**
* 清空数据源变量
*/
public static void cleardatasourcetype()
{
context_holder.remove();
}
}9、aop切面类
@aspect
@order(1)
@component
public class datasourceaspect {
@pointcut("@annotation(com.lyj.study.dynamicdatasource.annocation.datasource)"
+ "|| @within(com.lyj.study.dynamicdatasource.annocation.datasource)")
public void dspointcut(){}
@around("dspointcut()")
public object around(proceedingjoinpoint joinpoint) throws throwable{
datasource datasource = getdatasource(joinpoint);
if (datasource != null){
dynamicdatasourcecontextholder.setdatasourcetype(datasource.value().name());
}
try {
return joinpoint.proceed();
}
finally {
// 销毁数据源 在执行方法之后
dynamicdatasourcecontextholder.cleardatasourcetype();
}
}
/**
* 获取需要切换的数据源
*/
public datasource getdatasource(proceedingjoinpoint point)
{
methodsignature signature = (methodsignature) point.getsignature();
com.lyj.study.dynamicdatasource.annocation.datasource datasource = annotationutils.findannotation(signature.getmethod(), com.lyj.study.dynamicdatasource.annocation.datasource.class);
if (objects.nonnull(datasource)) {
return datasource;
}
return annotationutils.findannotation(signature.getdeclaringtype(), datasource.class);
}
}10、在业务中使用
@service
@requiredargsconstructor
@datasource(value=datasourcetype.master)
//@datasource(value=datasourcetype.slave)
public class userserviceimpl extends serviceimpl<usermapper, user> implements userservice {
private final usermapper usermapper;
@override
@datasource(value=datasourcetype.master)
//@datasource(value=datasourcetype.slave)
public list<user> queryall() {
return usermapper.selectlist(null);
}
}我们在service、mapper的类和方法上使用都可以。
补充:有很多从数据源怎么办?
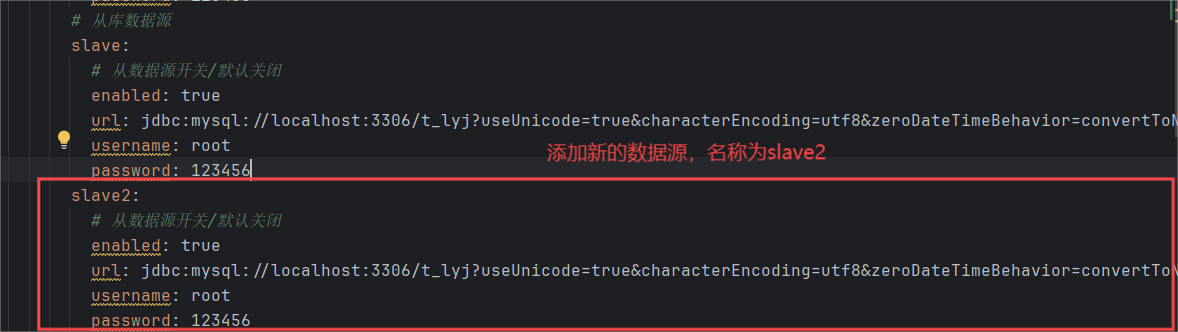
我们上面已经配置了一个从数据源了,接下来我们继续配置多个从数据源
首先在application-druid.yml文件添加新的数据源
在枚举添加数据源名称
//如果配置多数据源,继续添加即可
public enum datasourcetype
{
/**
* 主库
*/
master,
/**
* 从库
*/
slave,
/**
* 从库2
*/
slave2
}
如何切换数据库?
我们就以oracle为例
<!--oracle驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupid>com.oracle</groupid>
<artifactid>ojdbc6</artifactid>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
</dependency>在application-druid.yml添加
slave3:
# 从数据源开关/默认关闭
enabled: true
url: jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:oracle
username: root
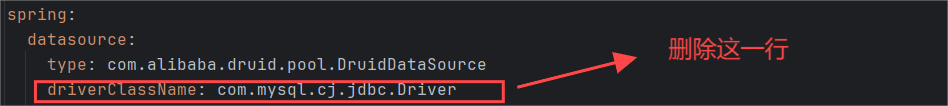
password: password然后删除指定的mysql驱动,默认会自动寻找驱动
添加数据源和用法参考上面即可,都是一样的。
注意:在切换数据库时,因为mysql跟oracle的sql语法有差别,启动时可能报错。
到此这篇关于springboot项目中如何动态切换数据源、数据库的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot动态切换数据源内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!




发表评论