1. 核心设计思路
tokenstore类的核心设计目标是实现一个高效、安全的token管理系统,主要功能包括:
- token的生成与存储:用户登录时生成
accesstoken和refreshtoken,并将其存储在redis中。 - token的刷新:通过
refreshtoken获取新的accesstoken。 - token的删除:删除用户的所有token,通常用于用户注销或管理员禁用用户。
- 用户信息的获取:通过
accesstoken获取用户的详细信息。
为了实现这些功能,tokenstore类依赖redis作为存储介质,利用redis的高性能和丰富的数据结构(如string、set)来管理token和用户信息。
2. 关键代码逻辑分析
2.1 token的生成与存储
在用户登录时,系统会生成一个accesstoken和一个refreshtoken,并将它们存储在redis中。以下是storeaccesstoken方法的核心逻辑:
public tokeninfobo storeaccesstoken(userinfointokenbo userinfointoken) {
tokeninfobo tokeninfobo = new tokeninfobo();
string accesstoken = idutil.simpleuuid(); // 生成随机的accesstoken
string refreshtoken = idutil.simpleuuid(); // 生成随机的refreshtoken
tokeninfobo.setuserinfointoken(userinfointoken);
tokeninfobo.setexpiresin(getexpiresin(userinfointoken.getsystype())); // 设置token过期时间
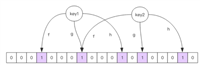
string uidtoaccesskeystr = getuidtoaccesskey(getapprovalkey(userinfointoken)); // 生成uid_to_access的redis key
string accesskeystr = getaccesskey(accesstoken); // 生成access_token的redis key
string refreshtoaccesskeystr = getrefreshtoaccesskey(refreshtoken); // 生成refresh_to_access的redis key
// 将新的token加入现有token列表
list<string> existsaccesstokens = new arraylist<>();
existsaccesstokens.add(accesstoken + strutil.colon + refreshtoken);
// 检查并清理过期的token
long size = redistemplate.opsforset().size(uidtoaccesskeystr);
if (size != null && size != 0) {
list<string> tokeninfobolist = stringredistemplate.opsforset().pop(uidtoaccesskeystr, size);
if (tokeninfobolist != null) {
for (string accesstokenwithrefreshtoken : tokeninfobolist) {
string[] accesstokenwithrefreshtokenarr = accesstokenwithrefreshtoken.split(strutil.colon);
string accesstokendata = accesstokenwithrefreshtokenarr[0];
if (booleanutil.istrue(stringredistemplate.haskey(getaccesskey(accesstokendata)))) {
existsaccesstokens.add(accesstokenwithrefreshtoken);
}
}
}
}
// 使用redis管道批量操作
redistemplate.executepipelined((rediscallback<object>) connection -> {
long expiresin = tokeninfobo.getexpiresin();
byte[] uidkey = uidtoaccesskeystr.getbytes(standardcharsets.utf_8);
byte[] refreshkey = refreshtoaccesskeystr.getbytes(standardcharsets.utf_8);
byte[] accesskey = accesskeystr.getbytes(standardcharsets.utf_8);
// 将token列表存入redis
for (string existsaccesstoken : existsaccesstokens) {
connection.sadd(uidkey, existsaccesstoken.getbytes(standardcharsets.utf_8));
}
// 设置uid_to_access的过期时间
connection.expire(uidkey, expiresin);
// 存储refresh_to_access的映射
connection.setex(refreshkey, expiresin, accesstoken.getbytes(standardcharsets.utf_8));
// 存储access_token对应的用户信息
connection.setex(accesskey, expiresin, objects.requirenonnull(redisserializer.serialize(userinfointoken)));
return null;
});
// 返回加密后的token
tokeninfobo.setaccesstoken(encrypttoken(accesstoken, userinfointoken.getsystype()));
tokeninfobo.setrefreshtoken(encrypttoken(refreshtoken, userinfointoken.getsystype()));
return tokeninfobo;
}
关键点分析:
- token生成:使用
idutil.simpleuuid()生成随机的accesstoken和refreshtoken,确保token的唯一性。 - redis数据结构:
uid_to_access:使用set数据结构存储用户的所有token,方便管理和清理。refresh_to_access:使用string数据结构存储refreshtoken到accesstoken的映射。access_token:使用string数据结构存储accesstoken对应的用户信息。
- 过期时间管理:根据用户类型(
systype)设置不同的token过期时间,普通用户和管理员的token过期时间不同。 - redis管道操作:通过
executepipelined方法批量执行redis操作,减少网络开销,提升性能。
2.2 token的刷新
当accesstoken过期时,用户可以通过refreshtoken获取新的accesstoken。以下是refreshtoken方法的核心逻辑:
public serverresponseentity<tokeninfobo> refreshtoken(string refreshtoken) {
if (strutil.isblank(refreshtoken)) {
return serverresponseentity.showfailmsg("refreshtoken is blank");
}
serverresponseentity<string> decrypttokenentity = decrypttoken(refreshtoken); // 解密refreshtoken
if (!decrypttokenentity.issuccess()) {
return serverresponseentity.transform(decrypttokenentity);
}
string realrefreshtoken = decrypttokenentity.getdata();
string accesstoken = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(getrefreshtoaccesskey(realrefreshtoken)); // 获取对应的accesstoken
if (strutil.isblank(accesstoken)) {
return serverresponseentity.showfailmsg("refreshtoken 已过期");
}
serverresponseentity<userinfointokenbo> userinfobyaccesstokenentity = getuserinfobyaccesstoken(accesstoken, false);
if (!userinfobyaccesstokenentity.issuccess()) {
return serverresponseentity.showfailmsg("refreshtoken 已过期");
}
userinfointokenbo userinfointokenbo = userinfobyaccesstokenentity.getdata();
// 删除旧的refresh_token和access_token
stringredistemplate.delete(getrefreshtoaccesskey(realrefreshtoken));
stringredistemplate.delete(getaccesskey(accesstoken));
// 生成新的token
tokeninfobo tokeninfobo = storeaccesstoken(userinfointokenbo);
return serverresponseentity.success(tokeninfobo);
}
关键点分析:
- token解密:通过
decrypttoken方法解密refreshtoken,确保token的安全性。 - token映射:通过
refresh_to_access的映射关系,找到对应的accesstoken。 - token清理:删除旧的
refreshtoken和accesstoken,防止token被重复使用。 - 新token生成:调用
storeaccesstoken方法生成新的token。
2.3 token的删除
在某些情况下(如用户注销或管理员禁用用户),需要删除用户的所有token。以下是deletealltoken方法的核心逻辑:
public void deletealltoken(string appid, long uid) {
string uidkey = getuidtoaccesskey(getapprovalkey(appid, uid)); // 生成uid_to_access的redis key
long size = redistemplate.opsforset().size(uidkey);
if (size == null || size == 0) {
return;
}
list<string> tokeninfobolist = stringredistemplate.opsforset().pop(uidkey, size);
if (collutil.isempty(tokeninfobolist)) {
return;
}
// 遍历并删除所有token
for (string accesstokenwithrefreshtoken : tokeninfobolist) {
string[] accesstokenwithrefreshtokenarr = accesstokenwithrefreshtoken.split(strutil.colon);
string accesstoken = accesstokenwithrefreshtokenarr[0];
string refreshtoken = accesstokenwithrefreshtokenarr[1];
redistemplate.delete(getrefreshtoaccesskey(refreshtoken));
redistemplate.delete(getaccesskey(accesstoken));
}
redistemplate.delete(uidkey); // 删除uid_to_access的key
}
关键点分析:
- 批量删除:通过
uid_to_access的set数据结构,获取用户的所有token并批量删除。 - 清理映射关系:删除
refresh_to_access和access_token的映射关系,确保token完全失效。
3. 总结
通过对tokenstore类的深入分析,我们可以看到其设计思路清晰,代码逻辑严谨。通过redis的高效存储和丰富的数据结构,实现了token的生成、刷新、删除以及用户信息的获取。这种设计不仅保证了系统的安全性,还提升了系统的性能和可扩展性。
希望本文的源码分析能够帮助你更好地理解token管理的实现原理。
到此这篇关于基于redis实现双加密token的示例代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关redis双加密token内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论