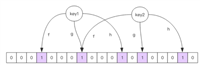
1. 热点数据识别机制
1.1 计数器方式
@service
public class hotdatacounter {
@autowired
private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
// 访问计数
public void incrementcounter(string key) {
string countkey = "counter:" + key;
redistemplate.opsforvalue().increment(countkey, 1);
// 设置计数器过期时间,比如1小时
redistemplate.expire(countkey, 1, timeunit.hours);
}
// 获取访问次数
public long getcounter(string key) {
string countkey = "counter:" + key;
return (long) redistemplate.opsforvalue().get(countkey);
}
}
1.2 lru算法实现
public class lrucache<k, v> extends linkedhashmap<k, v> {
private final int capacity;
public lrucache(int capacity) {
super(capacity, 0.75f, true);
this.capacity = capacity;
}
@override
protected boolean removeeldestentry(map.entry<k, v> eldest) {
return size() > capacity;
}
}
2. 动态缓存策略实现
2.1 基础缓存服务
@service
public class dynamiccacheservice {
@autowired
private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
@autowired
private hotdatacounter hotdatacounter;
// 热点阈值
private static final long hot_threshold = 100;
// 获取数据
public object getdata(string key) {
// 增加访问计数
hotdatacounter.incrementcounter(key);
// 从缓存获取数据
object value = redistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
// 从数据库获取数据
value = getfromdb(key);
// 判断是否为热点数据
if (ishotdata(key)) {
// 热点数据设置较长的过期时间
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, value, 1, timeunit.hours);
} else {
// 非热点数据设置较短的过期时间
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, value, 5, timeunit.minutes);
}
return value;
}
// 判断是否为热点数据
private boolean ishotdata(string key) {
long count = hotdatacounter.getcounter(key);
return count != null && count > hot_threshold;
}
}
2.2 定时任务更新策略
@component
public class hotdatascheduler {
@autowired
private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
@scheduled(fixedrate = 300000) // 每5分钟执行一次
public void updatehotdata() {
// 获取所有计数器
set<string> counterkeys = redistemplate.keys("counter:");
if (counterkeys == null) return;
// 更新热点数据过期时间
for (string counterkey : counterkeys) {
string datakey = counterkey.substring("counter:".length());
long count = (long) redistemplate.opsforvalue().get(counterkey);
if (count != null && count > hot_threshold) {
// 延长热点数据过期时间
redistemplate.expire(datakey, 1, timeunit.hours);
}
}
}
}
3. 多级缓存策略
3.1 本地缓存配合redis
@service
public class multilevelcache {
@autowired
private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
// 本地缓存
private final loadingcache<string, object> localcache = cachebuilder.newbuilder()
.maximumsize(1000)
.expireafterwrite(5, timeunit.minutes)
.build(new cacheloader<string, object>() {
@override
public object load(string key) {
return getfromredis(key);
}
});
public object get(string key) {
try {
return localcache.get(key);
} catch (executionexception e) {
return getfromredis(key);
}
}
private object getfromredis(string key) {
object value = redistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
if (value == null) {
value = getfromdb(key);
if (value != null) {
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, value);
}
}
return value;
}
}
4. 热点数据预加载
4.1 预热服务
@service
public class hotdatapreloader {
@autowired
private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
@postconstruct
public void preloadhotdata() {
// 从统计数据中获取历史热点数据
list<string> historicalhotkeys = gethistoricalhotkeys();
// 预加载数据到redis
for (string key : historicalhotkeys) {
object value = getfromdb(key);
if (value != null) {
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, value, 1, timeunit.hours);
}
}
}
}
5. 缓存更新策略
5.1 更新服务
@service
public class cacheupdateservice {
@autowired
private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
// 更新缓存数据
@transactional
public void updatedata(string key, object value) {
// 更新数据库
updatedb(key, value);
// 判断是否为热点数据
if (ishotdata(key)) {
// 直接更新缓存
redistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, value, 1, timeunit.hours);
} else {
// 删除缓存
redistemplate.delete(key);
}
}
}
6. 监控和告警
6.1 监控服务
@service
public class cachemonitorservice {
@autowired
private redistemplate<string, object> redistemplate;
// 监控缓存命中率
public double gethitrate() {
long hits = (long) redistemplate.opsforvalue().get("cache:hits");
long misses = (long) redistemplate.opsforvalue().get("cache:misses");
if (hits == null || misses == null) {
return 0.0;
}
return (double) hits / (hits + misses);
}
// 记录缓存访问
public void recordaccess(boolean ishit) {
string key = ishit ? "cache:hits" : "cache:misses";
redistemplate.opsforvalue().increment(key, 1);
}
}
7. 配置管理
7.1 动态配置
@configuration
@refreshscope
public class cacheconfig {
@value("${cache.hot.threshold:100}")
private long hotthreshold;
@value("${cache.hot.expire:3600}")
private long hotexpireseconds;
@value("${cache.normal.expire:300}")
private long normalexpireseconds;
}
8. 总结
热点识别:
- 使用计数器记录访问频率
- 实现lru算法管理缓存
动态缓存:
- 根据访问频率动态调整过期时间
- 定时任务更新热点数据
多级缓存:
- 本地缓存配合redis
- 减少网络开销
预加载机制:
- 系统启动时预加载历史热点数据
- 提高系统启动后的访问性能
更新策略:
- 热点数据直接更新缓存
- 非热点数据采用删除策略
监控告警:
- 监控缓存命中率
- 记录访问统计
配置管理:
- 支持动态调整配置
- 灵活控制缓存策略
到此这篇关于redis动态热点数据缓存策略设计的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关redis动态热点缓存内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!



发表评论