前言
本文分析@feignclient注解如何别扫描并注入到spring容器中,重点分析 @enablefeignclients工作原理。由于通过源码分析涉及内容比较多建议根据文章中流程debug调试进行学习。
文章涉及 容器刷新模板方法,configurationclasspostprocessor(bean工厂后置处理器),@import注解等工作原理分析
@enablefeignclients分析
在分析前先提出几个问题:
- @enablefeignclients通过什么原理可以把自己加到spring启动的生命周期中完成feign的bean扫描?
- sprintboot run方法如何能扫描 bean definition并放入spring容器中的?
- springboot启动阶段设置了哪些beanfactorypostprocessor到容器中?
本文在分析的过程中会将上述问题逐一讲解。在@enablefeignclients注解中可以看到该注解主要功能:
- 扫描声@feignclient 注解声明的类
- @feignclient注解的类注入后可通过@autowire @component方式进行使用。类似@configuration。
真正实现这些功能其实通过@import注解+feignclientsregistrar类实现。
@import 注解在spring启动生命周期中通过组合 importselector实现类或者 importbeandefinitionregistrar实现类完成bean definition 加载
@enablefeignclients就是用过这种机制完成@feignclient的扫描
在springboot中@import 注解加载bean definition是通过spring的后置处理器 beanfactorypostprocessor完成。
源码调用分析
下面结合springboot整体启动的流程分析下@enablefeignclients如何被加载的,主要分析关键逻辑具体细节不在此处展开。
- 首先springapplication run 方法启动
- 执行refresh方法 该方法为 abstractapplicationcontext 模板方法
- 执行 invokebeanfactorypostprocessors方法 该方法会将实现了beandefinitionregistrypostprocessor类的后置处理进行实例化并调用
- 执行 configurationclasspostprocessor 后置处理处理@componentscan @import @importresources @propertysource等注解
- 调用feignclientsregistrar类的解析bean definition方法
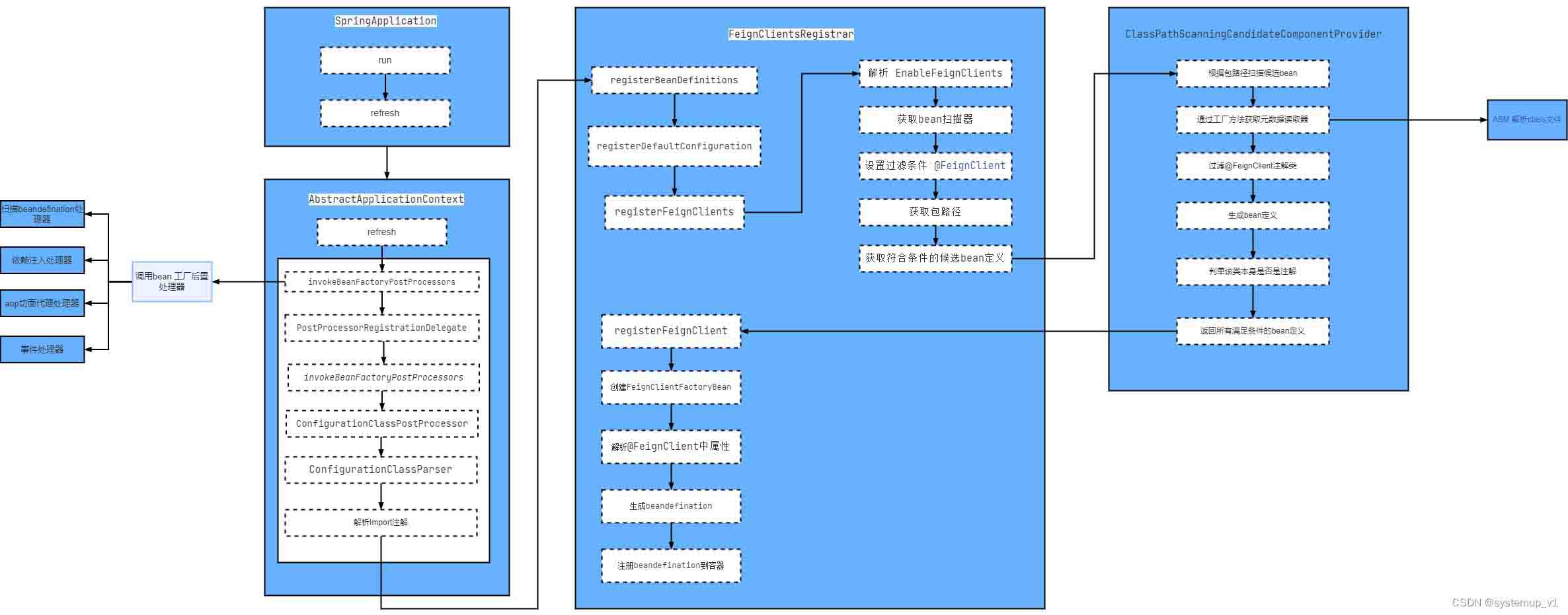
接下来分析abstractapplicationcontext 的refresh方法中invokebeanfactorypostprocessors调用逻辑。
此方法主要实例化 beanfactorypostprocessor并调用 postprocessbeanfactory方法。
特别提示所有beanfactorypostprocessor实例化一定要在所有bean初始化前。
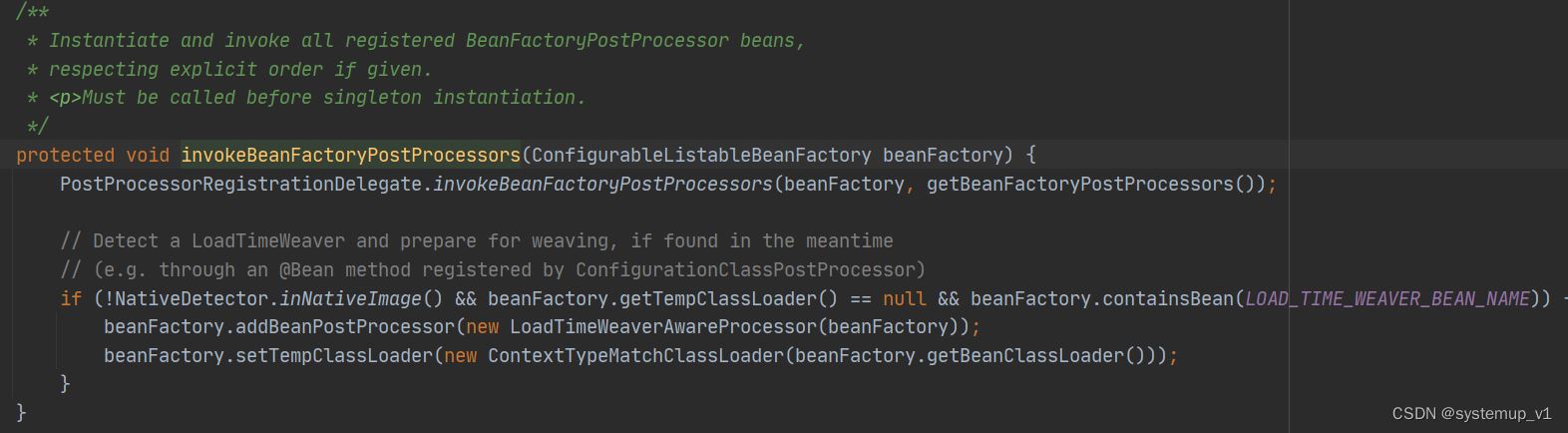
重点分析invokebeanfactorypostprocessors方法及bean后置处理器调用逻辑
postprocessorregistrationdelegate.invokebeanfactorypostprocessors(beanfactory, getbeanfactorypostprocessors());
方法逻辑比较长但很好理解下图中红色框逻辑完全一样都是从当前bean定义中找到 beandefinitionregistrypostprocessor实现类然筛选出优先级注解类 priorityordered跟排序注解类ordered并调用完成所有bean的扫描并注册到容器中扫描来源分为:注解&xml。
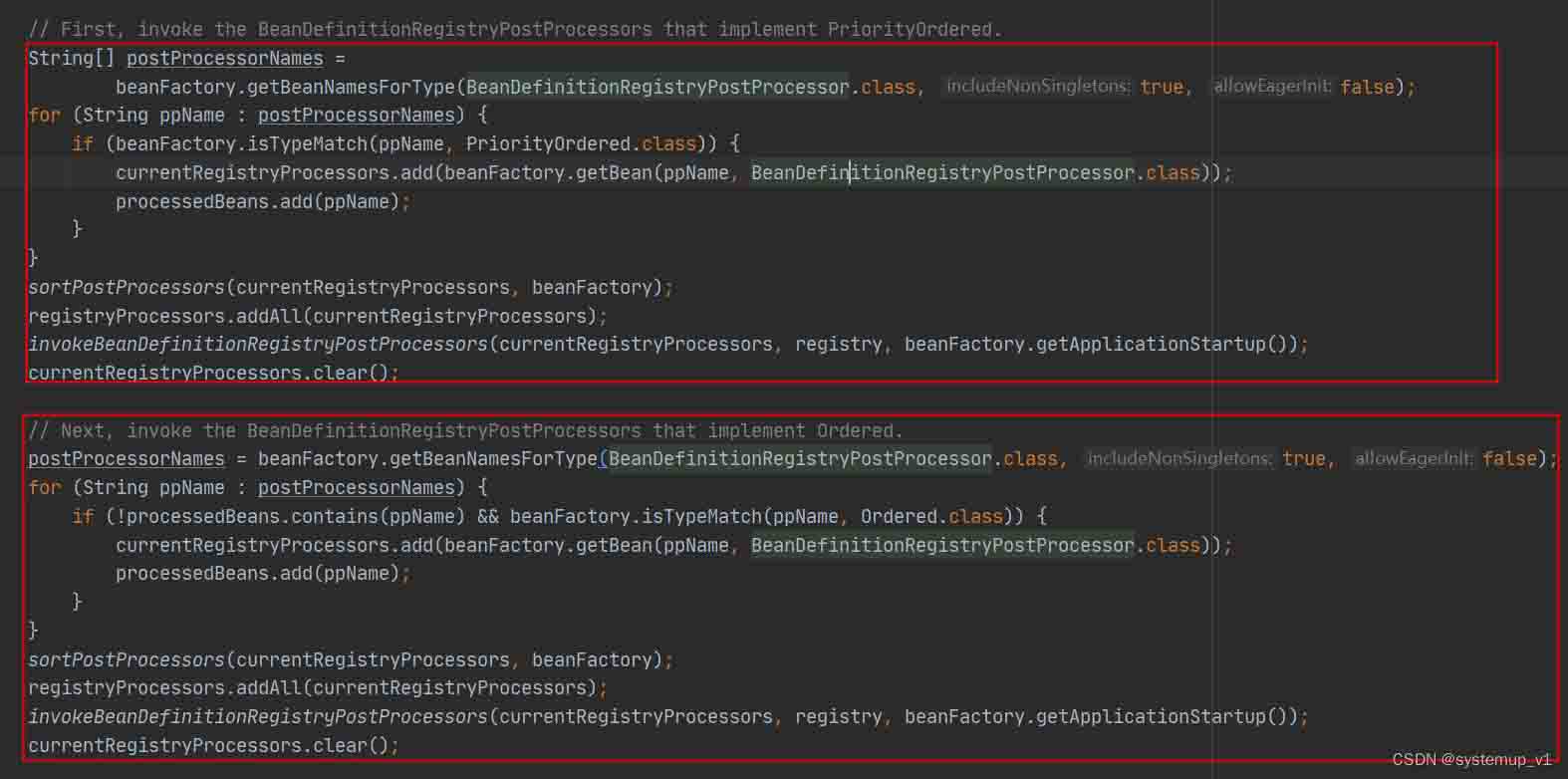
完成所有bean定义扫描类的后置处理器为 configurationclasspostprocessor
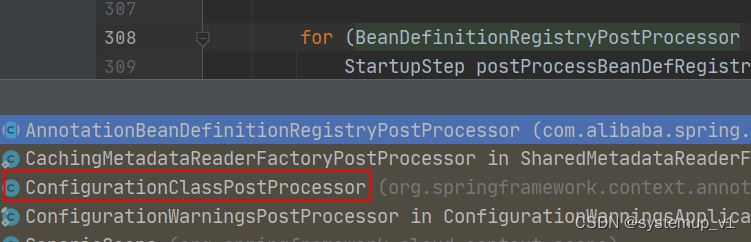
configurationclasspostprocessor 的 postprocessbeandefinitionregistry方法开始解析bean 定义。
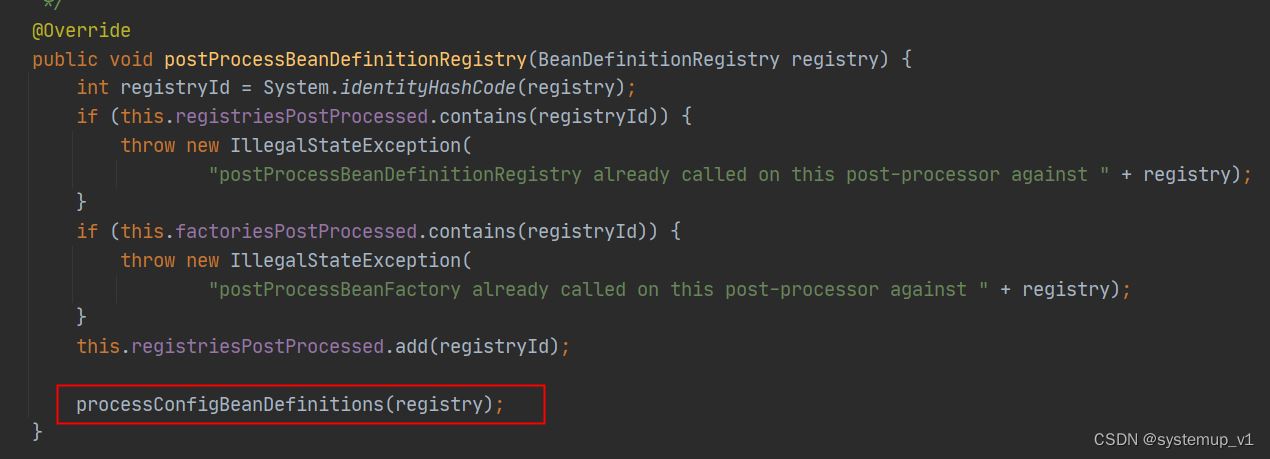
postprocessbeandefinitionregistry中核心逻辑是通过配置类解析器进行解析,配置类一般为springboot中@springbootapplication注解修饰类。
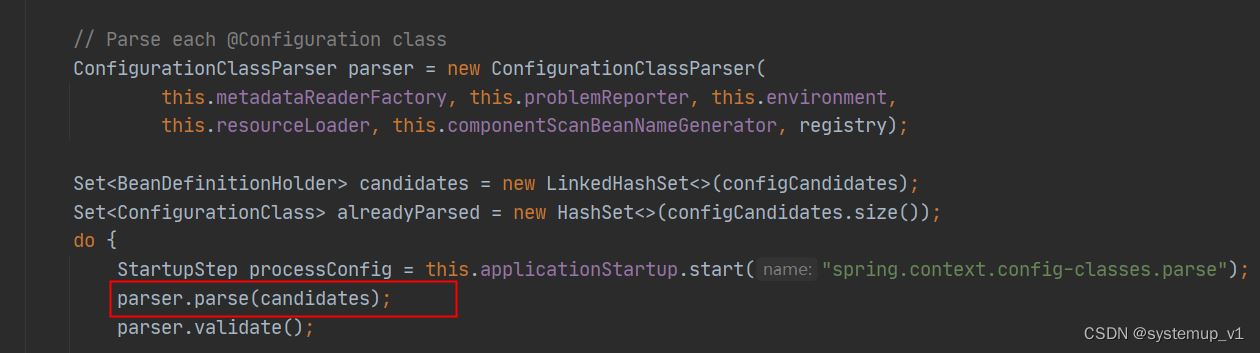
此处为springboot启动时解析入口 ,通过配置类分析
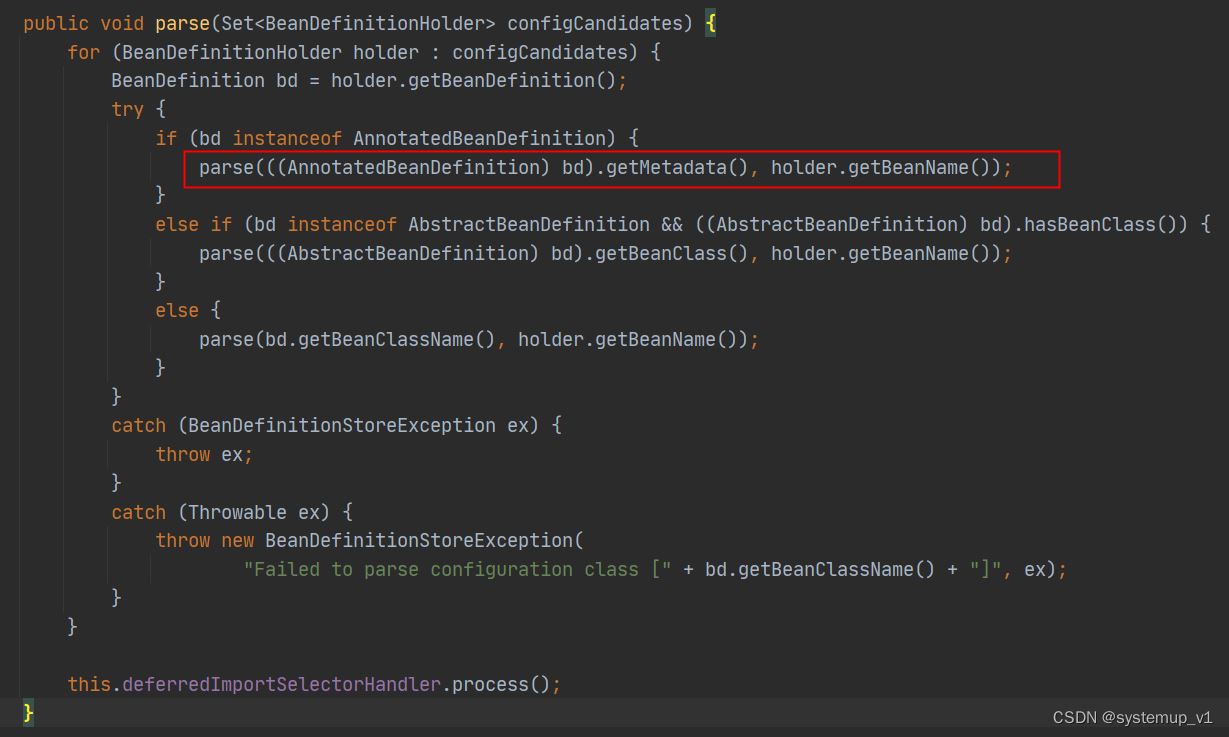
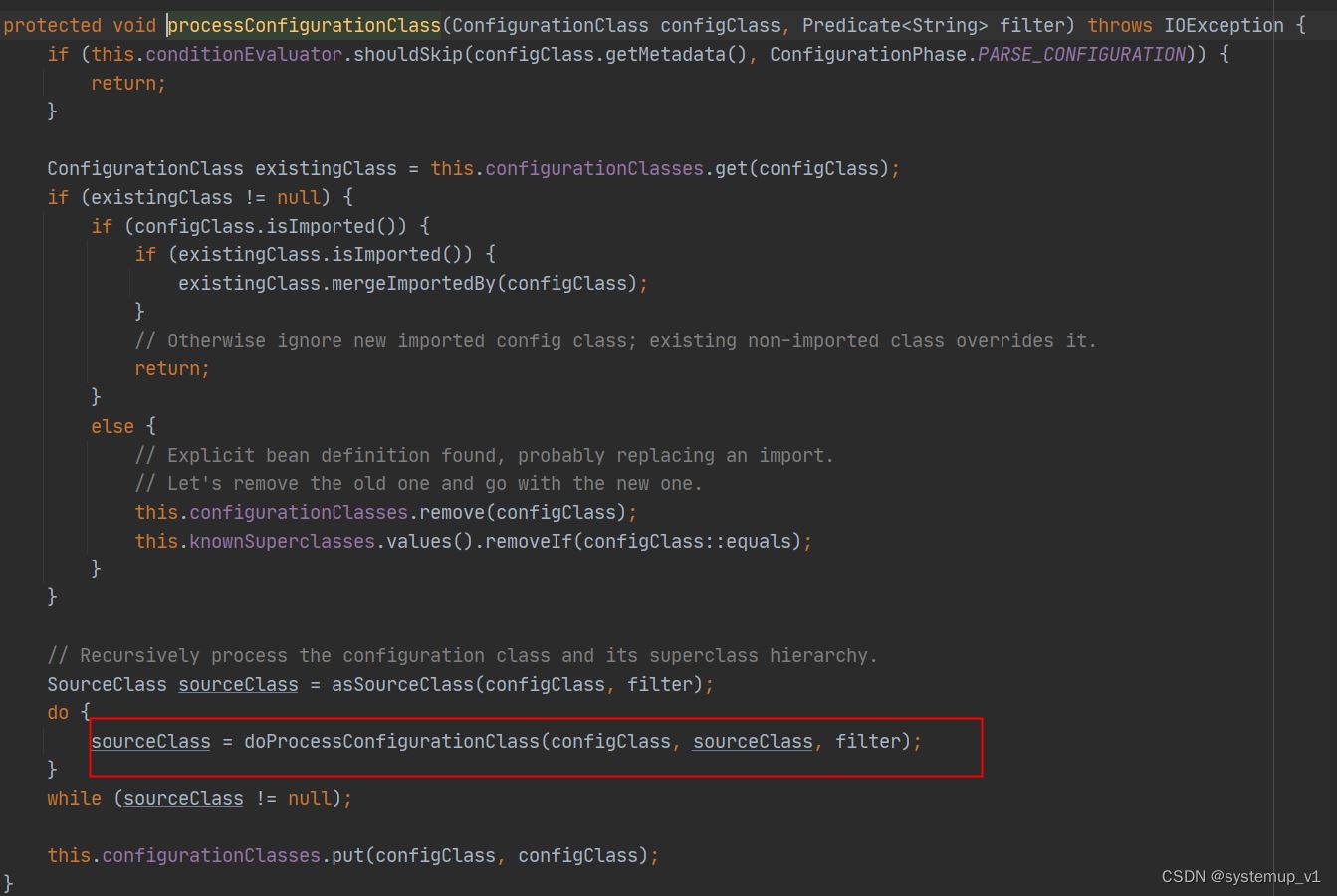
doprocessconfigurationclass方法开始解析各种常用注解如:@component @import等
protected final sourceclass doprocessconfigurationclass(
configurationclass configclass, sourceclass sourceclass, predicate<string> filter)
throws ioexception {
if (configclass.getmetadata().isannotated(component.class.getname())) {
// recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processmemberclasses(configclass, sourceclass, filter);
}
// process any @propertysource annotations
for (annotationattributes propertysource : annotationconfigutils.attributesforrepeatable(
sourceclass.getmetadata(), propertysources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.propertysource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof configurableenvironment) {
processpropertysource(propertysource);
}
else {
logger.info("ignoring @propertysource annotation on [" + sourceclass.getmetadata().getclassname() +
"]. reason: environment must implement configurableenvironment");
}
}
// process any @componentscan annotations
set<annotationattributes> componentscans = annotationconfigutils.attributesforrepeatable(
sourceclass.getmetadata(), componentscans.class, componentscan.class);
if (!componentscans.isempty() &&
!this.conditionevaluator.shouldskip(sourceclass.getmetadata(), configurationphase.register_bean)) {
for (annotationattributes componentscan : componentscans) {
// the config class is annotated with @componentscan -> perform the scan immediately
set<beandefinitionholder> scannedbeandefinitions =
this.componentscanparser.parse(componentscan, sourceclass.getmetadata().getclassname());
// check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (beandefinitionholder holder : scannedbeandefinitions) {
beandefinition bdcand = holder.getbeandefinition().getoriginatingbeandefinition();
if (bdcand == null) {
bdcand = holder.getbeandefinition();
}
if (configurationclassutils.checkconfigurationclasscandidate(bdcand, this.metadatareaderfactory)) {
parse(bdcand.getbeanclassname(), holder.getbeanname());
}
}
}
}
// process any @import annotations
processimports(configclass, sourceclass, getimports(sourceclass), filter, true);
// process any @importresource annotations
annotationattributes importresource =
annotationconfigutils.attributesfor(sourceclass.getmetadata(), importresource.class);
if (importresource != null) {
string[] resources = importresource.getstringarray("locations");
class<? extends beandefinitionreader> readerclass = importresource.getclass("reader");
for (string resource : resources) {
string resolvedresource = this.environment.resolverequiredplaceholders(resource);
configclass.addimportedresource(resolvedresource, readerclass);
}
}
// process individual @bean methods
set<methodmetadata> beanmethods = retrievebeanmethodmetadata(sourceclass);
for (methodmetadata methodmetadata : beanmethods) {
configclass.addbeanmethod(new beanmethod(methodmetadata, configclass));
}
// process default methods on interfaces
processinterfaces(configclass, sourceclass);
// process superclass, if any
if (sourceclass.getmetadata().hassuperclass()) {
string superclass = sourceclass.getmetadata().getsuperclassname();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startswith("java") &&
!this.knownsuperclasses.containskey(superclass)) {
this.knownsuperclasses.put(superclass, configclass);
// superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceclass.getsuperclass();
}
}
// no superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}本文分析@import注解调用逻辑

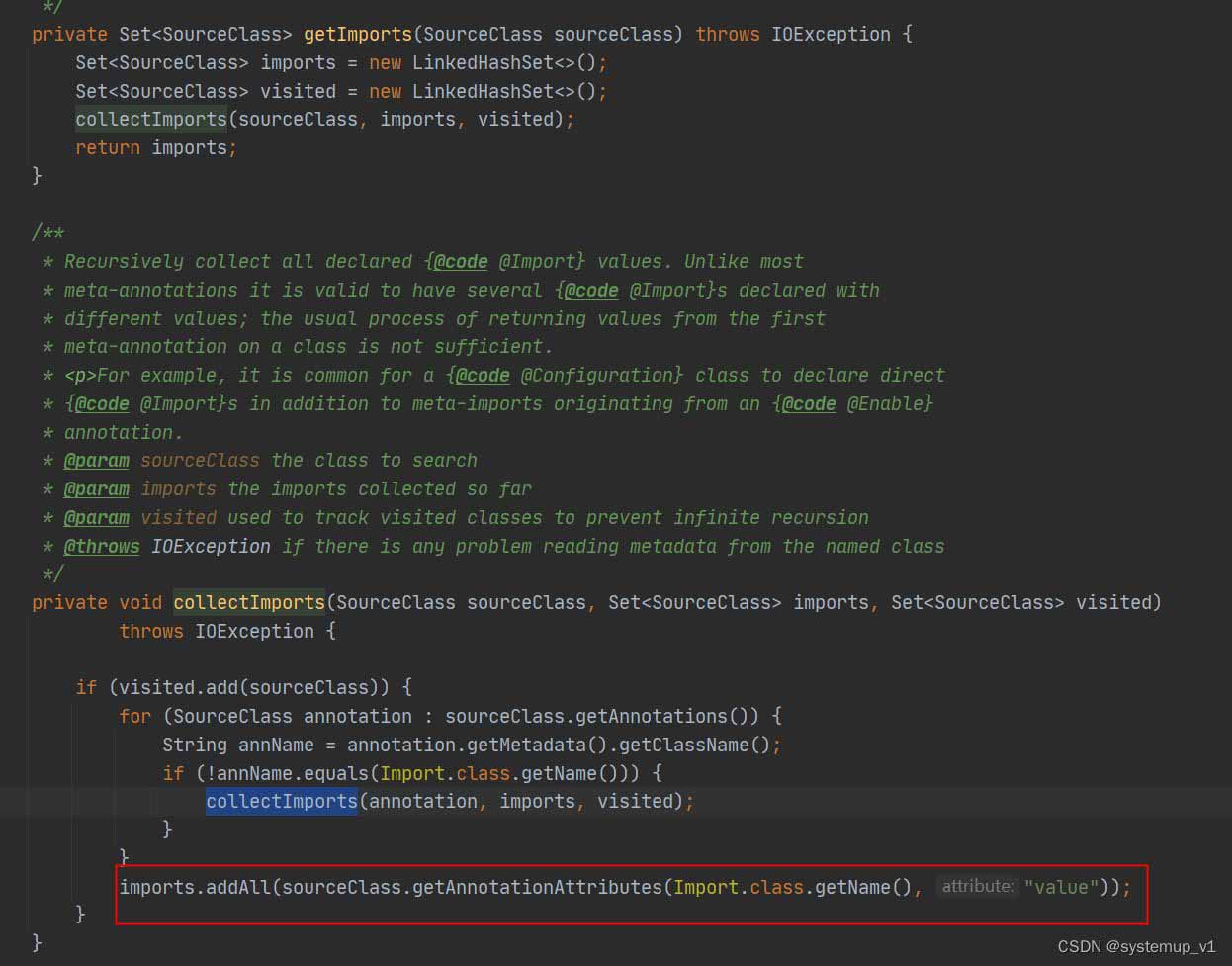
解析import注解中value并返回所有类
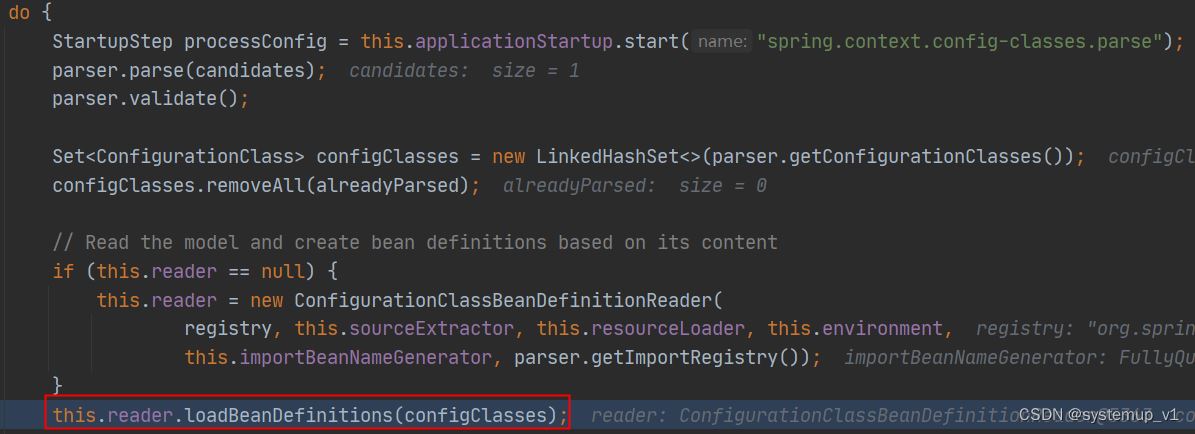
开始加载bean定义
loadbeandefinitionsforconfigurationclass 方法开始加载import注解中配置类。
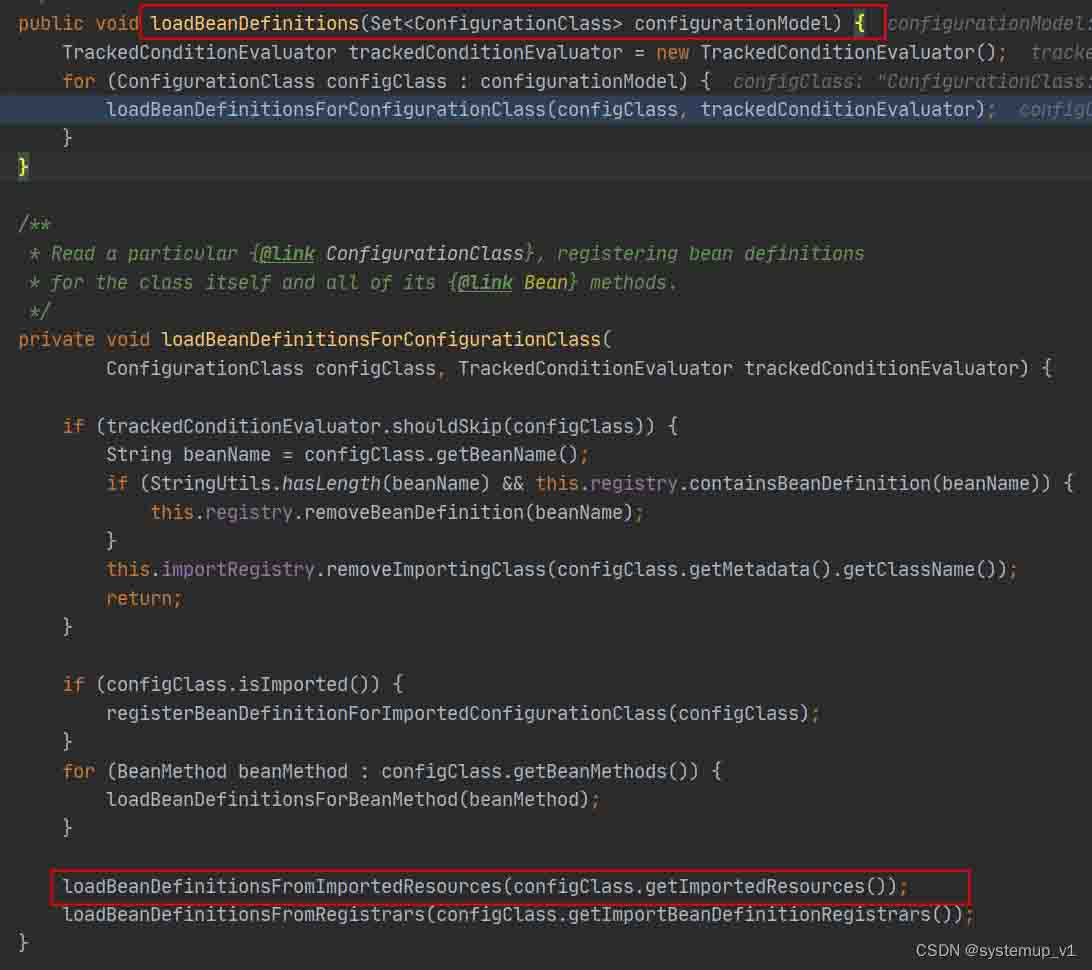
通过调用栈信息最终找到执行feignclientregistrar接口
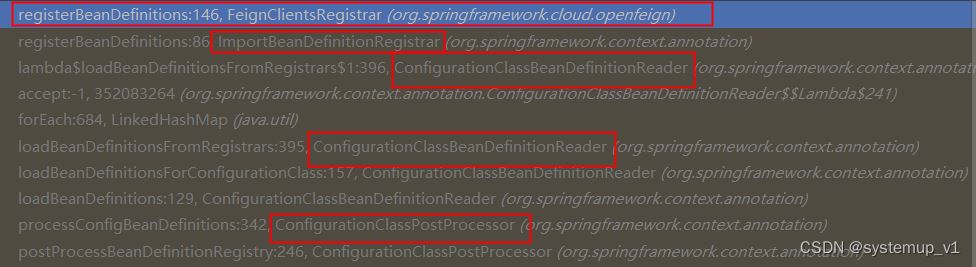
springboot 注解加载流程逻辑
为了对springboot中各个注解是在spring生命周期每个阶段时如何执行的可以参考下图,具体流程可以单步debug进行分析
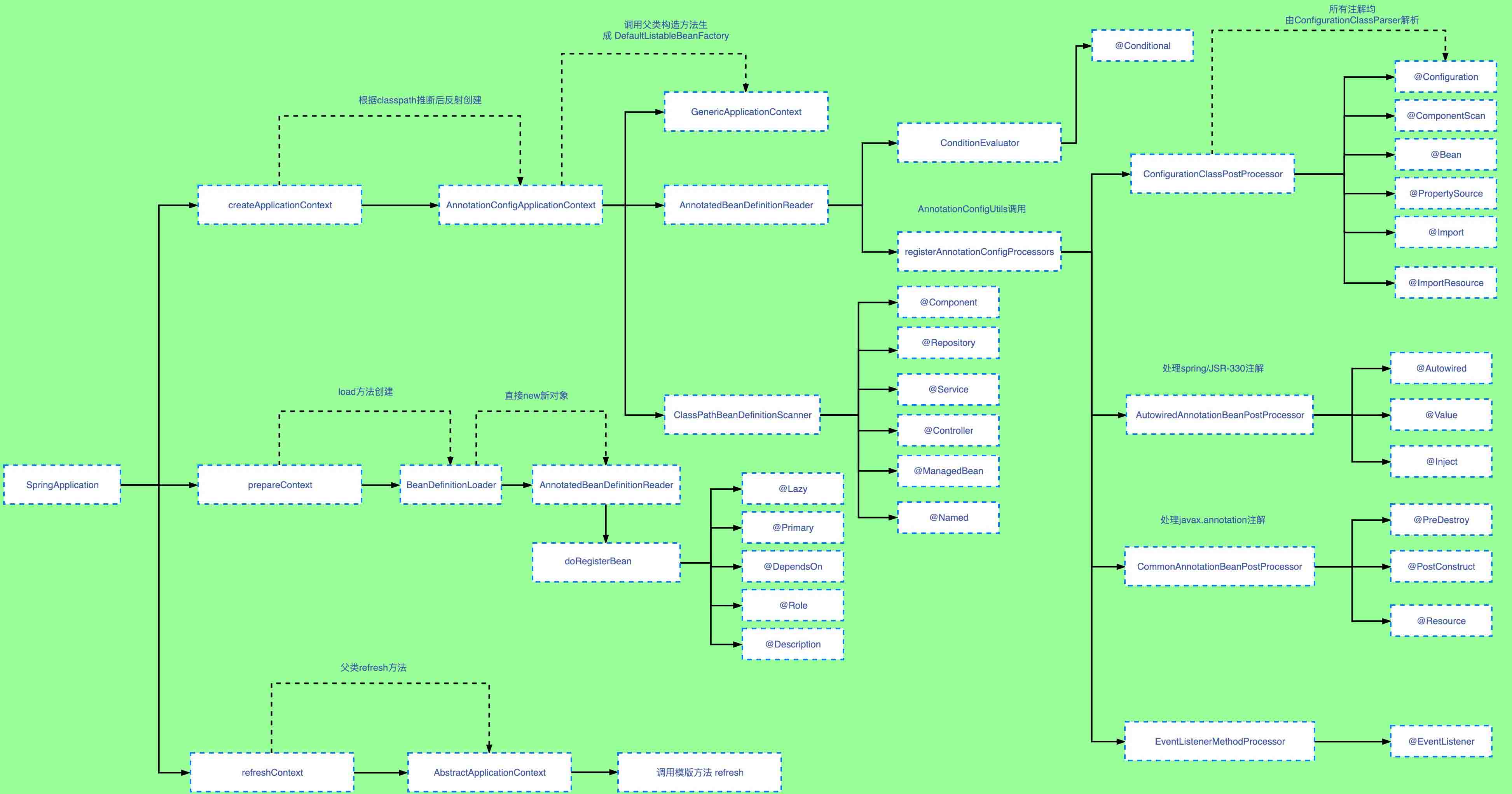
总结
本文简单分析了springboot加载bean definition与feignclient加载流程,由于细节逻辑太多本文不在展开分析。







发表评论