前言
在spring boot中定义和读取自定义配置是日常开发中常见的需求,它允许我们以灵活的方式管理应用的配置信息,无论是通过外部配置文件(如application.properties或application.yml)还是通过环境变量。
作为高级程序员,我们需要掌握这一技能,以确保应用的可配置性和可维护性。以下是一个详细的步骤说明,包括示例代码,展示如何在spring boot中定义和读取自定义配置。
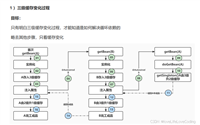
在spring boot中,你可以通过以下步骤定义和读取自定义配置:
在
application.properties或application.yml中定义自定义配置项。
例如,在application.yml中添加:
app:
custom:
my-property: value创建一个配置类来绑定这些属性。
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.configurationproperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;
@configuration
@configurationproperties(prefix = "app.custom")
public class customproperties {
private string myproperty;
public string getmyproperty() {
return myproperty;
}
public void setmyproperty(string myproperty) {
this.myproperty = myproperty;
}
}在spring bean中注入
customproperties类来使用配置值。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.component;
@component
public class mycomponent {
private final customproperties customproperties;
@autowired
public mycomponent(customproperties customproperties) {
this.customproperties = customproperties;
}
public void printcustomproperty() {
system.out.println(customproperties.getmyproperty());
}
}确保@configurationproperties注解的prefix属性与你在配置文件中定义的前缀相匹配。spring boot会自动将配置属性绑定到customproperties类的字段上。然后你可以在应用程序的任何部分通过自动装配的方式来使用这些配置值。
或者:
定义自定义配置属性
# application.properties myapp.name=spring boot application myapp.description=this is a demo application for custom configuration myapp.server.port=8081
创建配置类
接下来,我们需要创建一个配置类来绑定这些自定义属性。在spring boot中,这通常通过@configurationproperties注解实现,它允许我们将配置文件中的属性绑定到javabean上。
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.configurationproperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;
@configuration
@configurationproperties(prefix = "myapp")
public class myappconfig {
private string name;
private string description;
private int serverport;
// 标准的getter和setter方法
public string getname() {
return name;
}
public void setname(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
public string getdescription() {
return description;
}
public void setdescription(string description) {
this.description = description;
}
public int getserverport() {
return serverport;
}
public void setserverport(int serverport) {
this.serverport = serverport;
}
}注意,@configurationproperties(prefix = "myapp")注解指定了配置属性的前缀为myapp,这样spring boot就能自动将application.properties中所有以myapp开头的属性绑定到myappconfig类的相应字段上。
读取配置
我们可以在应用的任何地方通过依赖注入的方式读取这些配置。例如,在一个controller中
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.getmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller;
@restcontroller
public class myappconfigcontroller {
private final myappconfig myappconfig;
@autowired
public myappconfigcontroller(myappconfig myappconfig) {
this.myappconfig = myappconfig;
}
@getmapping("/config")
public string getconfig() {
return "name: " + myappconfig.getname() + ", description: " + myappconfig.getdescription() + ", server port: " + myappconfig.getserverport();
}
}总结
通过上述步骤,我们成功地在spring boot中定义了自定义配置属性,并通过@configurationproperties注解将它们绑定到了javabean上。最后,我们通过依赖注入的方式在应用中读取这些配置。这种方式不仅提高了代码的可读性和可维护性,还使得配置管理变得更加灵活和方便。在实际开发中,合理利用spring boot的配置管理功能,可以大大提升应用的灵活性和可扩展性。
以上就是在springboot中定义和读取自定义配置的方法步骤的详细内容,更多关于springboot定义和读取配置的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!

发表评论