一、使用gettickcount()函数
gettickcount()是一个函数,可以把它理解为打点计时器。gettickcount()是通过计算从函数开始运行计时,直到函数运行结束所求出函数的运行时间。它返回从操作系统启动所经过的毫秒数,
返回值:dword
头文件:winbase.h
函数原型:dword gettickcount(void)
此处需要注意的是,这个函数所求的的运行时间并非准确运行时间,不过相对来说比较准确,它的精度和cpu有关,一般精度在16ms左右,由于gettickcount()返回值以32位的双字类型dword存储,所以它的存储最大值是(2^32-1) ms约为49.71天,一旦一个程序运行时间超过这个值,这个数字就会归为0。
测试代码:
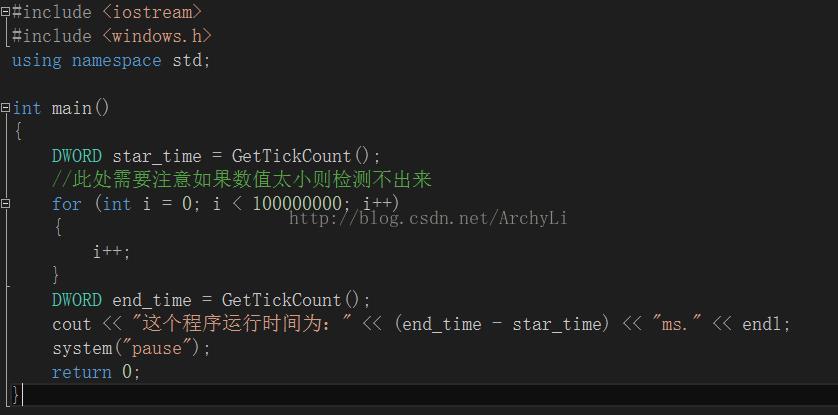
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
dword star_time = gettickcount();
//此处需要注意如果数值太小则检测不出来
for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++)
{
i++;
}
dword end_time = gettickcount();
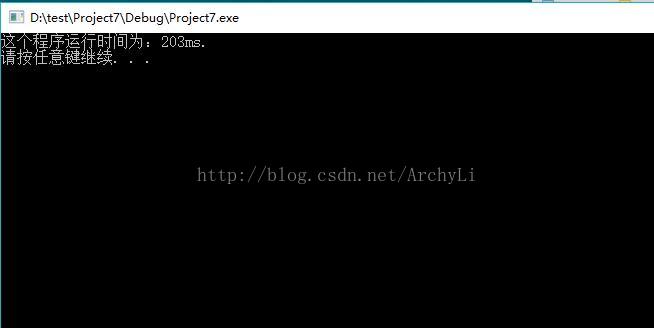
cout << "这个程序运行时间为:" << (end_time - star_time) << "ms." << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
二、调用clock
在头文件ctime里面提供了一个函数
clock_t clock();//# define long clock_t
该函数返回的是从程序开始运行到调用clock函数时所打的点数,即clock tick(时钟打点);有一个常数clk_tck,是机器时钟每秒所走的时钟打点数,是这样定义 的,
//#define clk_tck clocks_per_sec
//# define clocks_per_sec 1000
所以,定义两个clock的变量begin,end;然后在要测试的函数前后分别调用clock函数就可以得出时钟打点数,再除以clk_tck就得到时间了,代码如下:
# include<iostream>
# include<ctime>
using namespace std;
clock_t begin, end;
double duration;
//typedef long clock_t
# define n 10000
void fun1(int);
void fun2(int);
int main()
{
begin = clock();//开始计时
//====================这里写要测试的代码===================
fun1(100);
//=========================================================
end = clock();//结束计时
duration = double(end - begin) / clk_tck;//duration就是运行函数所打的
//点数,clk_tck是每秒所打点数
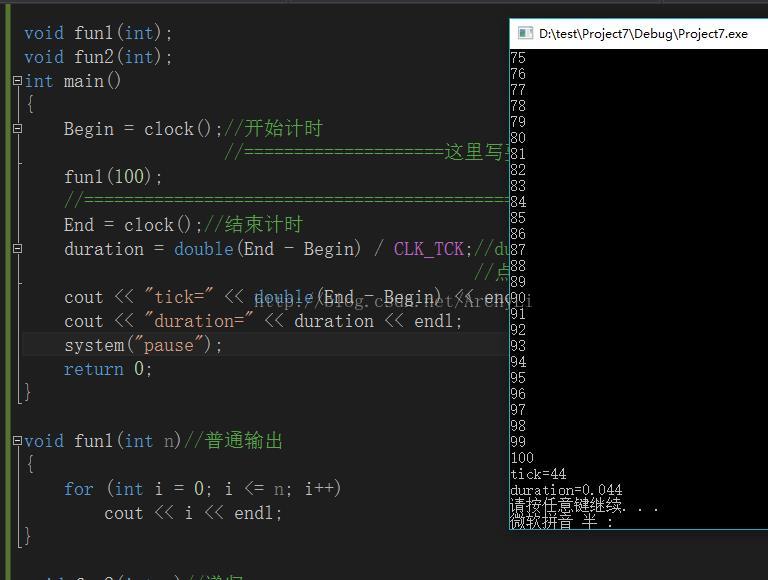
cout << "tick=" << double(end - begin) << endl;
cout << "duration=" << duration << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void fun1(int n)//普通输出
{
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
cout << i << endl;
}
void fun2(int n)//递归
{
if (n)
{
fun2(n - 1);
cout << n << endl;
}
else cout << 0 << endl;
}
clock()函数计算运行时间,表示范围一定大于gettickcount()函数,所以,建议使用clock()函数。
三、使用boost库中的timer
timer类可以测量时间是小型计时器,提供度量时间和进度显示功能。供程序员手工控制使用,就像是个方便的秒表。
位于名字空间boost,为了使用timer组件,需要包含头文件<boost/timer.hpp>
使用方法:
#include <boost/timer.hpp>
using namespace boost;
int main()
{
timer t;
cout << t.elapsed_max() / 3600 << "h" << endl;
cout << t.elapsed_min() << "s" <<endl;
cout << t.elapsed()<< "s" << endl;
}四、高精度时控函数queryperformancefrequency,queryperformancecounter
原理:cpu上也有一个计数器,以机器的clock为单位,可以通过rdtsc读取,而不用中断,因此其精度与系统时间相当。
精度:计算机获取硬件支持,精度比较高,可以通过它判断其他时间函数的精度范围。
使用方法:
#include<windows.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double time = 0;
double counts = 0;
large_integer nfreq;
large_integer nbegintime;
large_integer nendtime;
queryperformancefrequency(&nfreq);
queryperformancecounter(&nbegintime);//开始计时
for (int i = 0; i<99999; i++)
{
counts++;
}
queryperformancecounter(&nendtime);//停止计时
time = (double)(nendtime.quadpart - nbegintime.quadpart) / (double)nfreq.quadpart;//计算程序执行时间单位为s
cout << "程序执行时间:" << time * 1000 << "ms" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
总结
到此这篇关于c++中测试程序运行时间的几种方法总结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c++测试程序运行时间内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论