std::condition_variable
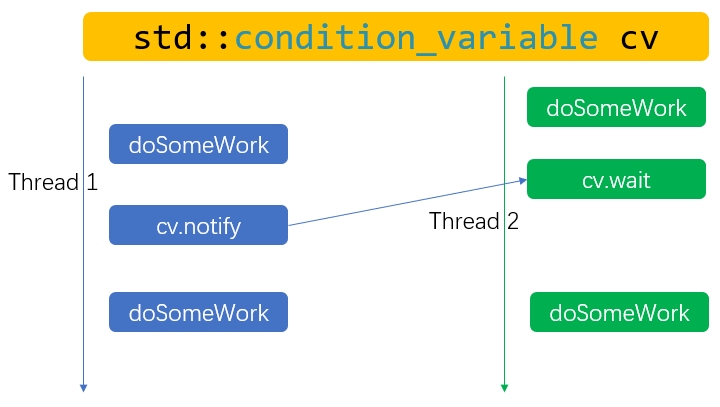
条件变量std::condition_variable有wait和notify接口用于线程间的同步。如下图所示,thread 2阻塞在wait接口,thread 1通过notify接口通知thread 2继续执行。
具体参见示例代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<mutex>
#include<thread>
#include<queue>
std::mutex mt;
std::queue<int> data;
std::condition_variable cv;
auto start=std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
void logcurrenttime()
{
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto elapsed = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start).count();
std::cout << elapsed << ":";
}
void prepare_data()
{
logcurrenttime();
std::cout << "this is " << __function__ << " thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
data.push(i);
logcurrenttime();
std::cout << "data ok:" << i << std::endl;
}
//start to notify consume_data thread data is ok!
cv.notify_one();
}
void consume_data()
{
logcurrenttime();
std::cout << "this is: " << __function__ << " thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lk(mt);
//wait first for notification
cv.wait(lk); //it must accept a unique_lock parameter to wait
while (!data.empty())
{
logcurrenttime();
std::cout << "data consumed: " << data.front() << std::endl;
data.pop();
}
}
int main()
{
std::thread t2(consume_data);
//wait for a while to wait first then prepare data,otherwise stuck on wait
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));
std::thread t1(prepare_data);
t1.join();
t2.join();
return 0;
}
分析
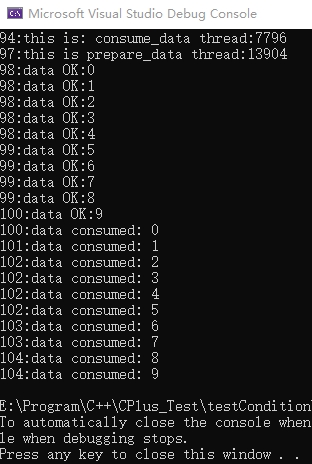
主线程中另启两个线程,分别执行consume_data和prepare_data,其中consume_data要先执行,以保证先等待再通知,否则若先通知再等待就死锁了。首先consume_data线程在从wait 处阻塞等待。后prepare_data线程中依次向队列写入0-10,写完之后通过notify_one 通知consume_data线程解除阻塞,依次读取0-10。
std::future
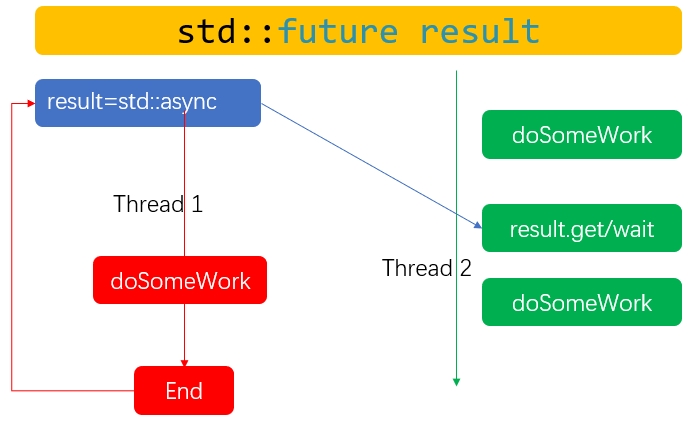
std::future与std::async配合异步执行代码,再通过wait或get接口阻塞当前线程等待结果。如下图所示,thread 2中future接口的get或wait接口会阻塞当前线程,std::async异步开启的新线程thread1执行结束后,将结果存于std::future后通知thread 1获取结果后继续执行.
具体参见如下代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <future>
#include<thread>
int test()
{
std::cout << "this is " << __function__ << " thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(1000));
return 10;
}
int main()
{
std::cout << "this is " <<__function__<<" thread:" << std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;;
//this will lanuch on another thread
std::future<int> result = std::async(test);
std::cout << "after lanuch a thread: "<< std::this_thread::get_id() << std::endl;
//block the thread and wait for the result
std::cout << "result is: " <<result.get()<< std::endl;
std::cout << "after get result "<< std::endl;
return 0;
}输出结果
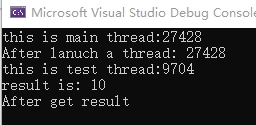
分析主程序中调用std::async异步调用test函数,可以看到main函数的线程id 27428与test函数执行的线程id 9704并不一样,说明std::async另起了一个新的线程。在test线程中,先sleep 1000ms,所以可以看到"after lanuch a thread:"先输出,说明主线程异步执行,不受子线程影响。而"after get result "最后输出,说明get()方法会阻塞主线程,直到获取结果。
作者:robot2017
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/stephen2023/p/18416810
版权:本文版权归作者和博客园共有
转载:欢迎转载,但未经作者同意,必须保留此段声明;必须在文章中给出原文连接;否则必究法律责任
到此这篇关于c++11 线程同步接口std::condition_variable和std::future的简单使用示例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c++11 线程同步接口std::condition_variable和std::future内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论