一、简单去重
public class distincttest {
/**
* 没有重写 equals 方法
*/
@setter
@getter
@tostring
@allargsconstructor
@noargsconstructor
public static class user {
private string name;
private integer age;
}
/**
* lombok(@data) 重写了 equals 方法 和 hashcode 方法
*/
@data
@allargsconstructor
@noargsconstructor
public static class user2 {
private string name;
private integer age;
}
@test
public void easytest() {
list<integer> integers = arrays.aslist(1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 77, 77);
system.out.println("======== 数字去重 =========");
system.out.print("原数字列表:");
integers.foreach(x -> system.out.print(x + " "));
system.out.println();
system.out.print("去重后数字列表:");
integers.stream().distinct().collect(collectors.tolist()).foreach(x -> system.out.print(x + " "));
system.out.println();
system.out.println();
list<user> list = lists.newarraylist();
user three = new user("张三", 18);
user three2 = new user("张三", 18);
user three3 = new user("张三", 24);
user four = new user("李四", 18);
list.add(three);
list.add(three);
list.add(three2);
list.add(three3);
list.add(four);
system.out.println("======== 没有重写equals方法的话,只能对相同对象(如:three)进行去重,不能做到元素相同就可以去重) =========");
// 没有重写 equals 方法时,使用的是超类 object 的 equals 方法
// 等价于两个对象 == 的比较,只能筛选同一个对象
system.out.println("初始对象列表:");
list.foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println("简单去重后初始对象列表:");
list.stream().distinct().collect(collectors.tolist()).foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println();
system.out.println();
list<user2> list2 = lists.newarraylist();
user2 five = new user2("王五", 18);
user2 five2 = new user2("王五", 18);
user2 five3 = new user2("王五", 24);
user2 two = new user2("二蛋", 18);
list2.add(five);
list2.add(five);
list2.add(five2);
list2.add(five3);
list2.add(two);
system.out.println("======== 重写了equals方法的话,可以做到元素相同就可以去重) =========");
// 所以如果只需要写好 equals 方法 和 hashcode 方法 也能做到指定属性的去重
system.out.println("初始对象列表:");
list2.foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println("简单去重后初始对象列表:");
list2.stream().distinct().collect(collectors.tolist()).foreach(system.out::println);
}
}二、根据对象某个属性去重
0、user对象
/**
* 没有重写 equals 方法
*/
@setter
@getter
@tostring
@allargsconstructor
@noargsconstructor
public static class user {
private string name;
private integer age;
}1、使用filter进行去重
@test
public void objecttest() {
list<user> list = arrays.aslist(
new user(null, 18),
new user("张三", null),
null,
new user("张三", 24),
new user("张三5", 24),
new user("李四", 18)
);
system.out.println("初始对象列表:");
list.foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println();
system.out.println("======== 使用 filter ,根据特定属性进行过滤(重不重写equals方法都不重要) =========");
system.out.println("根据名字过滤后的对象列表:");
// 第一个 filter 是用于过滤 第二个 filter 是用于去重
list<user> collect = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null)
.filter(distinctpredicate(user::getname)).collect(collectors.tolist());
collect.foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println("根据年龄过滤后的对象列表:");
list<user> collect1 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getage() != null)
.filter(distinctpredicate(user::getage)).collect(collectors.tolist());
collect1.foreach(system.out::println);
}
/**
* 列表对象去重
*/
public <k, t> predicate<k> distinctpredicate(function<k, t> function) {
// 因为stream流是多线程操作所以需要使用线程安全的concurrenthashmap
concurrenthashmap<t, boolean> map = new concurrenthashmap<>();
return t -> null == map.putifabsent(function.apply(t), true);
}测试

①、疑惑
- 既然 filter 里面调用的是 distinctpredicate 方法,而该方法每次都 new 一个新的 map 对象,那么 map 就是新的,怎么能做到可以过滤呢
②、解惑
- 先看一下 filter 的部分实现逻辑,他使用了函数式接口 predicate ,每次调用filter时,会使用 predicate 对象的 test 方法,这个对象的test 方法就是 null == map.putifabsent(function.apply(t), true)
- 而 distinctpredicate 方法作用就是生成了一个线程安全的 map 集合,和一个 predicate 对象,且该对象的 test 方法为 null == map.putifabsent(function.apply(t), true)
- 之后 stream 流的 filter 方法每次都只会使用 predicate 对象的 test 方法,而该 test 方法中的 map 对象在该流中是唯一的,并不会重新初始化
@override
public final stream<p_out> filter(predicate<? super p_out> predicate) {
objects.requirenonnull(predicate);
return new statelessop<p_out, p_out>(this, streamshape.reference,
streamopflag.not_sized) {
@override
sink<p_out> opwrapsink(int flags, sink<p_out> sink) {
return new sink.chainedreference<p_out, p_out>(sink) {
@override
public void begin(long size) {
downstream.begin(-1);
}
@override
public void accept(p_out u) {
if (predicate.test(u))
downstream.accept(u);
}
};
}
};
}2、使用collectors.tomap() 实现根据某一属性去重(这个可以实现保留前一个还是后一个)
要注意 collectors.tomap(key,value) 中 value 不能为空,会报错,key 可以为 null,但会被转换为字符串的 “null”
@test
public void objecttest() {
list<user> list = arrays.aslist(
new user(null, 18),
new user("张三", null),
null,
new user("张三", 24),
new user("张三5", 24),
new user("李四", 18)
);
system.out.println("初始对象列表:");
list.foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println();
system.out.println("======== 使用 collectors.tomap() 实现根据某一属性去重 =========");
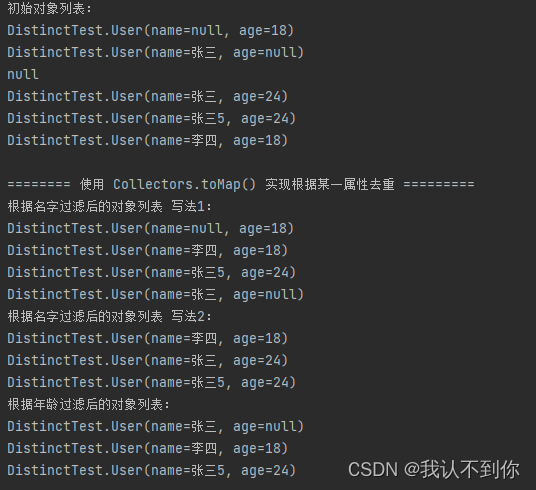
system.out.println("根据名字过滤后的对象列表 写法1:");
// (v1, v2) -> v1 的意思 两个名字一样的话(key一样),存前一个 value 值
map<string, user> collect = list.stream().filter(objects::nonnull).collect(collectors.tomap(user::getname, o -> o, (v1, v2) -> v1));
// o -> o 也可以写为 function.identity() ,两个是一样的,但后者可能比较优雅,但阅读性不高,如下
// map<string, user> collect = list.stream().filter(objects::nonnull).collect(collectors.tomap(user::getname, function.identity(), (v1, v2) -> v1));
list<user> list2 = new arraylist<>(collect.values());
list2.foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println("根据名字过滤后的对象列表 写法2:");
map<string, user> map2 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null)
.collect(hashmap::new, (m, o) -> m.put(o.getname(), o), hashmap::putall);
list2 = new arraylist<>(map2.values());
list2.foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println("根据年龄过滤后的对象列表:");
// (v1, k2) -> v2 的意思 两个年龄一样的话(key一样),存后一个 value 值
map<integer, user> collect2 = list.stream().filter(objects::nonnull).collect(collectors.tomap(user::getage, o -> o, (v1, v2) -> v2));
list2 = new arraylist<>(collect2.values());
list2.foreach(system.out::println);
}测试
3、collectors.tomap() 的变种 使用 collectors.collectingandthen()
collectors.collectingandthen() 函数 它可接受两个参数,第一个参数用于 reduce操作,而第二参数用于 map操作。
也就是,先把流中的所有元素传递给第一个参数,然后把生成的集合传递给第二个参数来处理。
@test
public void objecttest() {
list<user> list = arrays.aslist(
new user(null, 18),
new user("张三", null),
null,
new user("张三", 24),
new user("张三5", 24),
new user("李四", 18)
);
system.out.println("初始对象列表:");
list.foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println();
system.out.println("======== 使用 collectors.tomap() 实现根据某一属性去重 =========");
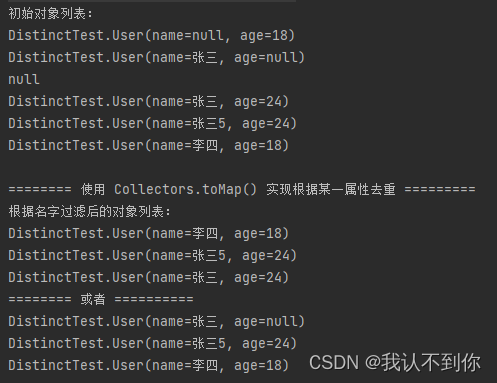
system.out.println("根据名字过滤后的对象列表:");
arraylist<user> collect1 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null).collect(
collectors.collectingandthen(collectors.tomap(user::getname, o -> o, (k1, k2) -> k2), x-> new arraylist<>(x.values())));
collect1.foreach(system.out::println);
system.out.println("======== 或者 ==========");
list<user> collect = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null).collect(
collectors.collectingandthen(collectors.tocollection(
() -> new treeset<>(comparator.comparing(user::getname))), arraylist<user>::new));
collect.foreach(system.out::println);
}测试
三、测试哪个方法比较快
@test
public void objecttest() {
list<user> list = new arraylist<>(arrays.aslist(
new user(null, 18),
new user("张三", null),
null,
new user("张三", 24),
new user("张三5", 24),
new user("李四", 18)
));
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
list.add(new user((math.random() * 10) + "", (int) (math.random() * 10)));
}
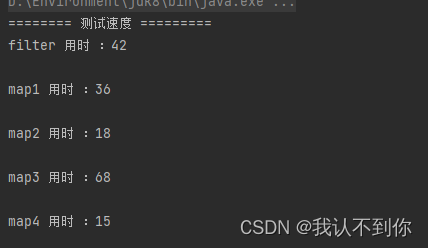
system.out.println("======== 测试速度 =========");
long starttime = system.currenttimemillis();
list<user> list1 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null)
.filter(distinctpredicate(user::getname)).collect(collectors.tolist());
long endtime = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("filter 用时 :" + (endtime - starttime));
system.out.println();
starttime = system.currenttimemillis();
map<string, user> map1 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null)
.collect(collectors.tomap(user::getname, o -> o, (v1, v2) -> v1));
list<user> list2 = new arraylist<>(map1.values());
endtime = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("map1 用时 :" + (endtime - starttime));
system.out.println();
starttime = system.currenttimemillis();
arraylist<user> list3 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null).collect(
collectors.collectingandthen(collectors.tomap(user::getname, o -> o, (k1, k2) -> k2), x -> new arraylist<>(x.values())));
endtime = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("map2 用时 :" + (endtime - starttime));
system.out.println();
starttime = system.currenttimemillis();
list<user> list4 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null).collect(
collectors.collectingandthen(collectors.tocollection(
() -> new treeset<>(comparator.comparing(user::getname))), arraylist<user>::new));
endtime = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("map3 用时 :" + (endtime - starttime));
system.out.println();
starttime = system.currenttimemillis();
map<string, user> map2 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null)
.collect(hashmap::new, (m, o) -> m.put(o.getname(), o), hashmap::putall);
list<user> list5 = new arraylist<>(map2.values());
endtime = system.currenttimemillis();
system.out.println("map4 用时 :" + (endtime - starttime));
}测试:
总结
1、去重最快
arraylist<user> list3 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null).collect(
collectors.collectingandthen(collectors.tomap(user::getname, o -> o, (k1, k2) -> k2), x -> new arraylist<>(x.values())));
// 或者
map<string, user> map2 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null)
.collect(hashmap::new, (m, o) -> m.put(o.getname(), o), hashmap::putall);
list<user> list5 = new arraylist<>(map2.values());2、其次
map<string, user> map1 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null)
.collect(collectors.tomap(user::getname, o -> o, (v1, v2) -> v1));
list<user> list2 = new arraylist<>(map1.values());
// distinctpredicate 是一个方法 本文中有 ,可以 ctrl + f 查找
list<user> list1 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null)
.filter(distinctpredicate(user::getname)).collect(collectors.tolist());3、最慢
list<user> list4 = list.stream().filter(o -> o != null && o.getname() != null).collect(
collectors.collectingandthen(collectors.tocollection(
() -> new treeset<>(comparator.comparing(user::getname))), arraylist<user>::new));以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。







发表评论