一、准备工作
# 创建数据表
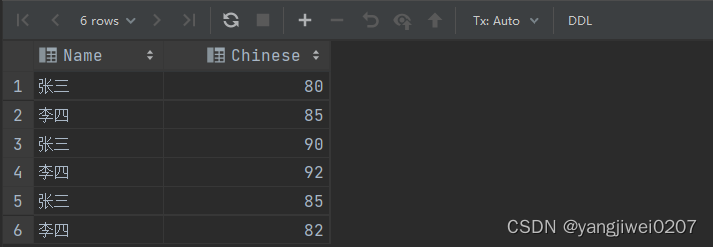
create table chengji
(
name varchar(32),
subject varchar(32),
result int(10)
);
# 插入数据
insert into chengji
values ('张三', '语文', 80),
('张三', '数学', 90),
('张三', '物理', 85),
('李四', '语文', 85),
('李四', '数学', 92),
('李四', '物理', 82);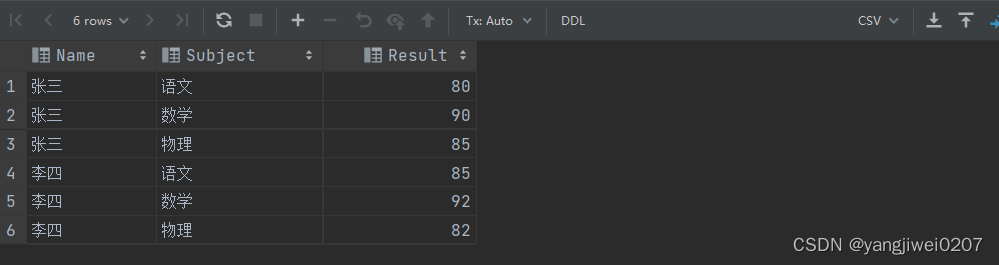
二、行转列
整体分两步走
1、先预处理数据,将数据进行初步的行转列,便于后续的分组处理
select name,
case
when subject = '语文' then result else 0
end as 'chinese',
case
when subject = '数学' then result else 0
end as 'math',
case
when subject = '物理' then result else 0
end as 'pha'
from chengji;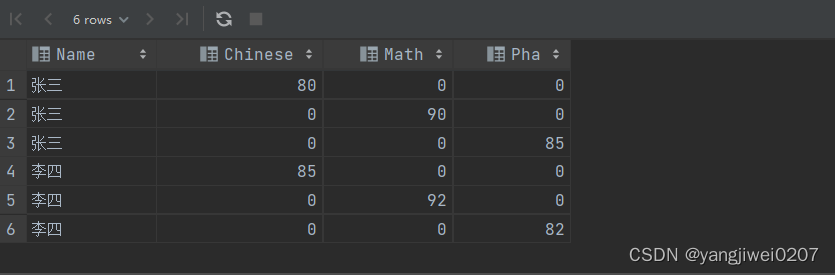
2、对预处理完毕的数据进行分组聚合,使多行数据汇聚到一个组内,达到数据集中的结果,这其中要注意的一点是:要明确按照哪个字段进行聚合操作。
with t1 as(select name,
case
when subject = '语文' then result else 0
end as 'chinese',
case
when subject = '数学' then result else 0
end as 'math',
case
when subject = '物理' then result else 0
end as 'pha'
from chengji)
select name,
sum(chinese) as 'chinese',
sum(math) as 'math',
sum(pha) as 'pha'
from t1
group by name;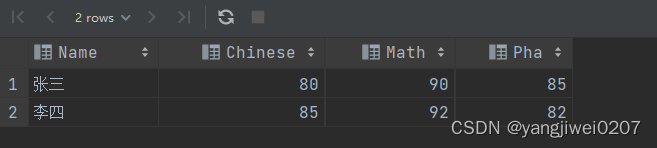
三、列转行
为便于理解,我们将刚才已经转置好的结果插入到一个结果表内
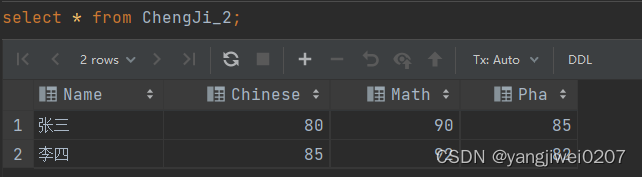
1、创建一个结果表
create table chengji_2(
name varchar(255),
chinese int,
math int,
pha int
);2、将行转列结果插入到结果表
insert into chengji_2
with t1 as(select name,
case
when subject = '语文' then result else 0
end as 'chinese',
case
when subject = '数学' then result else 0
end as 'math',
case
when subject = '物理' then result else 0
end as 'pha'
from chengji)
select name,
sum(chinese) as 'chinese',
sum(math) as 'math',
sum(pha) as 'pha'
from t1
group by name
;
3、对结果表进行列转行的操作,列转行相对于行转列较为简单,可直接使用 union all 进行操作。
select name,chinese from chengji_2 union all select name,math from chengji_2 union all select name,pha from chengji_2;
四、特殊的列转行/行转列
但是对于一些特殊的行列转置,以上方法就不再使用,通常情况下,我们的行列转置是有可以进行分组聚合操作可以完成的,而生产实践中也多数如此,但是有时有一些特殊的操作是以上方法无法完成的,这就需要一些特殊的行列转置来完成,对此,我给出了以下的方案。
1、准备工作,创建数据表并插入数据
create table 2003a
(
seat varchar(255) ,
status varchar(255) ,
rowid varchar(255)
)
;
insert into 2003a
values ('2', '已预订', 'a');
insert into 2003a
values ('3', '未预订', 'a');
insert into 2003a
values ('4', '未预订', 'a');
insert into 2003a
values ('5', '未预订', 'a');
insert into 2003a
values ('6', '未预订', 'b');
insert into 2003a
values ('7', '未预订', 'b');
insert into 2003a
values ('8', '未预订', 'b');
insert into 2003a
values ('9', '未预订', 'b');
insert into 2003a
values ('10', '未预订', 'b');
insert into 2003a
values ('11', '未预订', 'c');
insert into 2003a
values ('12', '已预订', 'c');
insert into 2003a
values ('13', '已预订', 'c');
insert into 2003a
values ('14', '未预订', 'c');
insert into 2003a
values ('15', '未预订', 'c');
insert into 2003a
values ('16', '未预订', 'd');
insert into 2003a
values ('17', '未预订', 'd');
insert into 2003a
values ('18', '未预订', 'd');
insert into 2003a
values ('19', '未预订', 'd');
insert into 2003a
values ('20', '已预订', 'd');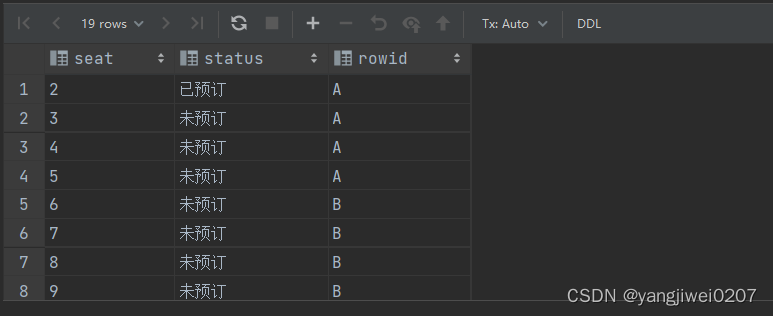
2、明确需求
原有表的结构:
2,已预订,a 3,未预订,a
需要完成的工作:
2,3 已预定,未预定 a,a
在这里我们可以很明显的看出,我们需要做的就是如何进行 行转列/列转行 的操作,在这里的行列转置是整行/整列进行转置,不再是依靠某个字段进行分组处理或者使用 union all 进行整体操作,因此,我是用以下方案来完成。
1、对原表字段进行 group_concat,指定 “,”为字段值之间的分隔符
select
group_concat(rowid order by rowid asc separator ', ') as rowid,
group_concat(status order by rowid asc separator ', ') as status,
group_concat(seat order by rowid asc separator ', ') as seat
from (
select rowid, status, seat from `2003a`
) as subquery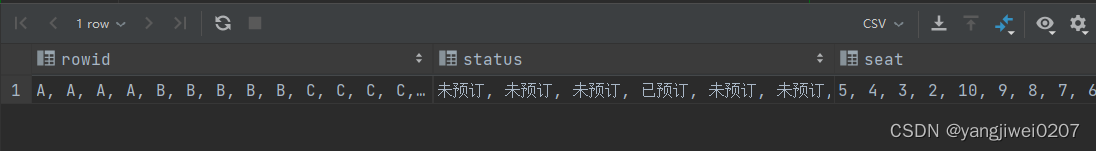
2、将所有的字段按照值聚合到一个数据表格内之后,我们可以使用 union all 来进行字段拆分
with t1 as (select
group_concat(rowid order by rowid asc separator ', ') as rowid,
group_concat(status order by rowid asc separator ', ') as status,
group_concat(seat order by rowid asc separator ', ') as seat
from (
select rowid, status, seat from `2003a`
) as subquery)
select seat from t1
union all
select status from t1
union all
select rowid from t1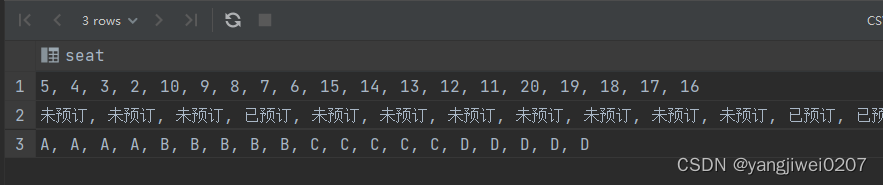
3、使用 substring_index来进行拆分,将所有的字段值拆分成单独的值
with t1 as (select
group_concat(rowid order by rowid asc separator ', ') as rowid,
group_concat(status order by rowid asc separator ', ') as status,
group_concat(seat order by rowid asc separator ', ') as seat
from (
select rowid, status, seat from `2003a`
) as subquery)
,t2 as (select seat from t1
union all
select status from t1
union all
select rowid from t1)
select substring_index(seat,',',1) as p1,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',2),',',-1) as p2,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',3),',',-1) as p3,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',4),',',-1) as p4,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',5),',',-1) as p5,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',6),',',-1) as p6,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',7),',',-1) as p7,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',8),',',-1) as p8,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',9),',',-1) as p9,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',10),',',-1) as p10,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',11),',',-1) as p11,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',12),',',-1) as p12,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',13),',',-1) as p13,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',14),',',-1) as p14,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',15),',',-1) as p15,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',16),',',-1) as p16,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',17),',',-1) as p17,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',18),',',-1) as p18,
substring_index(substring_index(seat,',',19),',',-1) as p19
from t2在这里需要注意的是:第一个substring_index我们取的是源数据的第一个值,第二个substring_index以及之后的,我们取得是源数据的倒数第一个值,因此这里需要注意一下我们给到的是“-1”
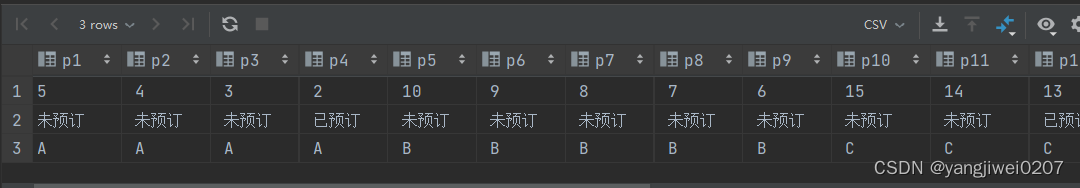
至此,我们使用group_concat()以及substring_index()来达到了特殊的行列转置操作。
总结
到此这篇关于sql行列转置以及非常规的行列转置的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关sql行列转置内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!





发表评论