public class cloudserversideapplication {
public static void main(string[] args) {
springapplication.run(cloudserversideapplication.class, args);
}
}
- 提供grpc服务的类grpcserverservice,和local-server模块中的一样:
package com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials;
import com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials.lib.helloreply;
import com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials.lib.simplegrpc;
import net.devh.boot.grpc.server.service.grpcservice;
import java.util.date;
@grpcservice
public class grpcserverservice extends simplegrpc.simpleimplbase {
@override
public void sayhello(com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials.lib.hellorequest request,
io.grpc.stub.streamobserver responseobserver) {
helloreply reply = helloreply.newbuilder().setmessage("1. hello " + request.getname() + ", " + new date()).build();
responseobserver.onnext(reply);
responseobserver.oncompleted();
}
}
- 以上就是服务端代码了,可见除了将grpc端口设置为0,以及常规使用eureka的配置,其他部分和local-server模块是一样的;
[](
)grpc客户端开发
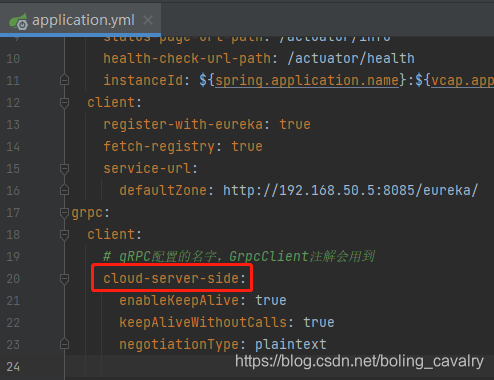
- 依赖eureka的grpc客户端,其重点在于:第一,配置使用eureka,第二,配置中的grpc配置项的名字要等于grpc服务端在eureka注册的名字,如下图红框所示:
- 在父工程grpc-turtorials下面新建名为cloud-client-side的模块,其build.gradle内容如下,注意要引入grpc客户端相关的starter:
// 使用springboot插件
plugins {
id ‘org.springframework.boot’
}
dependencies {
implementation ‘org.projectlombok:lombok’
implementation ‘org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web’
implementation ‘org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter’
// 作为grpc服务使用方,需要用到此库
implementation ‘net.devh:grpc-client-spring-boot-starter’
// 作为eureka的client
implementation ‘org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client’
// 状态暴露需要的依赖
implementation ‘org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator’
// 依赖自动生成源码的工程
implementation project(‘:grpc-lib’)
// annotationprocessor不会传递,使用了lombok生成代码的模块,需要自己声明annotationprocessor
annotationprocessor ‘org.projectlombok:lombok’
}
- 配置文件application.yml,设置自己的web端口号,另外值得注意的是grpc配置项cloud-server-side的名字要等于grpc服务端在eureka注册的名字,并且不需要address配置项:
server:
port: 8086
spring:
application:
name: cloud-client-side
eureka:
instance:
prefer-ip-address: true
status-page-url-path: /actuator/info
health-check-url-path: /actuator/health
instanceid: s p r i n g . a p p l i c a t i o n . n a m e : {spring.application.name}: spring.application.name:{vcap.application.instance_id:katex parse error: expected '}', got 'eof' at end of input: …on.instance_id:{random.value}}}
client:
register-with-eureka: true
fetch-registry: true
service-url:
defaultzone: http://192.168.50.5:8085/eureka/
grpc:
client:
grpc配置的名字,grpcclient注解会用到
cloud-server-side:
enablekeepalive: true
keepalivewithoutcalls: true
negotiationtype: plaintext
- 启动类cloudclientsideapplication.java,使用了eureka相关的注解:
package com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials;
import org.springframework.boot.springapplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.springbootapplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.enablediscoveryclient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.enableeurekaclient;
@enableeurekaclient
@enablediscoveryclient
@springbootapplication
public class cloudclientsideapplication {
public static void main(string[] args) {
springapplication.run(cloudclientsideapplication.class, args);
}
}
- 封装grpc调用的服务类grpcserverservice,和local-server模块中的一样,grpcclient注解对应配置中的grpc配置项:
package com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials;
import com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials.lib.helloreply;
import com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials.lib.hellorequest;
import com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials.lib.simplegrpc;
import io.grpc.statusruntimeexception;
import net.devh.boot.grpc.client.inject.grpcclient;
import org.springframework.stereotype.service;
@service
public class grpcclientservice {
@grpcclient(“cloud-server-side”)
private simplegrpc.simpleblockingstub simplestub;
public string sendmessage(final string name) {
try {
final helloreply response = this.simplestub.sayhello(hellorequest.newbuilder().setname(name).build());
return response.getmessage();
} catch (final statusruntimeexception e) {
return "failed with " + e.getstatus().getcode().name();
}
}
}
- 再做一个web接口类,这样我们就能通过web调用验证grpc服务了:
package com.bolingcavalry.grpctutorials;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestparam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller;
@restcontroller
public class grpcclientcontroller {
@autowired
private grpcclientservice grpcclientservice;
@requestmapping(“/”)
public string printmessage(@requestparam(defaultvalue = “will”) string name) {
return grpcclientservice.sendmessage(name);
}
}
- 客户端开发完毕,接下来可以验证了;
[](
)验证
- 启动cloud-eureka:
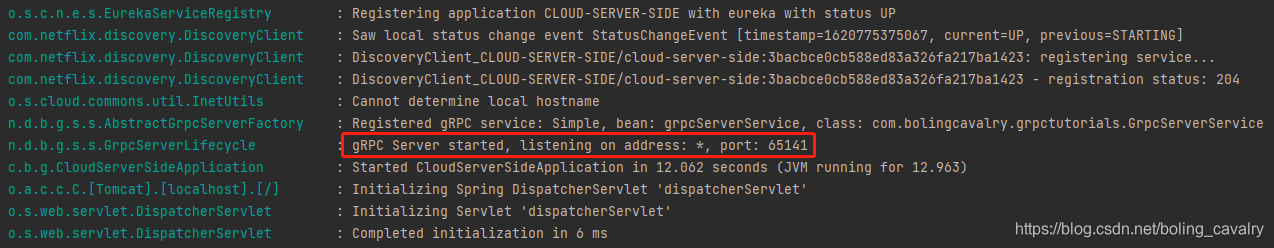
- 启动cloud-server-side,可见grpc服务端口自动分配了65141,不过我们无需关心这个值,因为客户端可以从eureka获取到:
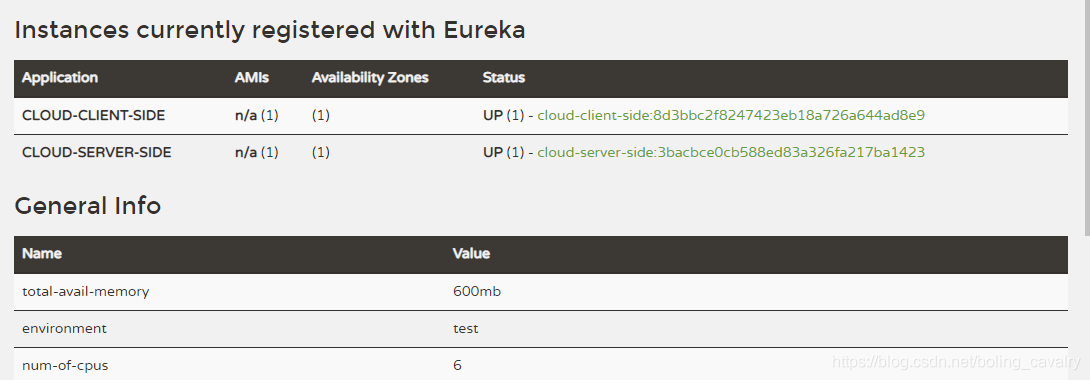
- 接下来启动cloud-client-side,启动成功后eureka上可见两个服务的注册信息:
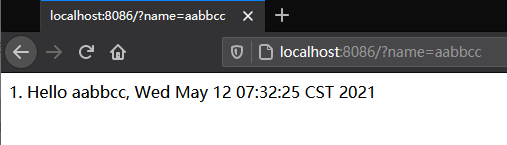
- 浏览器访问cloud-client-side提供的web接口,响应如下,可见cloud-client-side成功调用了cloud-server-side的grpc服务:
[](
)一点疑惑
-
如果您对eureka有所了解,可能会产生一点疑惑:cloud-client-side从eureka取得的cloud-server-side信息,应该是http服务的地址和端口,不应该有grpc的端口号,因为eureka的注册发现服务并不包含grpc有关的!
-
篇幅所限,这里不适合将上述问题展开分析,咱们来关注最核心的地方,相信聪明的您看上一眼就会豁然开朗;
-
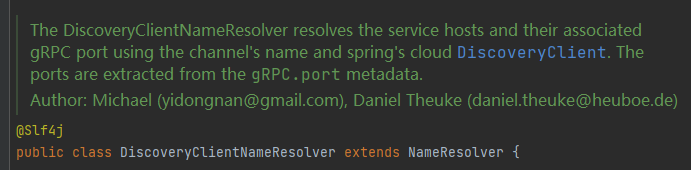
discoveryclientnameresolver来自grpc-client-spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar,用来保存从eureka取得的服务端信息,该类的注释已经说得很清楚了,从metadata的grpc.port配置项中取得grpc端口号:
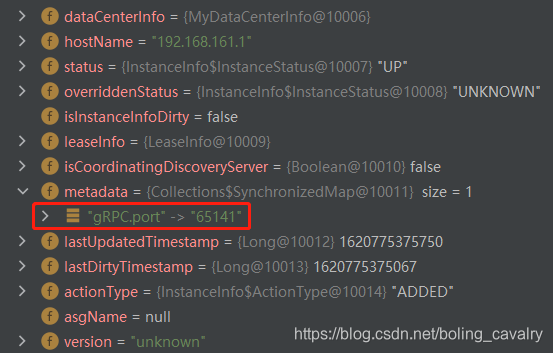
- 在discoveryclientnameresolver的代码中打上断点,查看成员变量instancelist,可见metadata中确实有grpc端口的信息:
- 至于cloud-server-side如何将端口号提交到eureka,以及cloud-client-side为何会使用discoveryclientnameresolver来处理eureka的服务列表信息,就不在本文中讨论了,您要是有兴趣深入研究eureka,可以参考《程序员欣宸文章汇总(spring篇)》中的eureka源码分析专题,如下图:

- 至此,基于eureka的grpc服务注册发现的开发和验证就完成了,希望本文可以给您带来一些参考,让您的服务在注册中心的加持下更加灵活和可靠;
[](
)你不孤单,欣宸原创一路相伴
最后
光给面试题不给答案不是我的风格。这里面的面试题也只是凤毛麟角,还有答案的话会极大的增加文章的篇幅,减少文章的可读性
java面试宝典2021版


最常见java面试题解析(2021最新版)

2021企业java面试题精选
[](
)你不孤单,欣宸原创一路相伴
最后
光给面试题不给答案不是我的风格。这里面的面试题也只是凤毛麟角,还有答案的话会极大的增加文章的篇幅,减少文章的可读性
java面试宝典2021版
[外链图片转存中…(img-3mtjslbu-1710356772137)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-6hiqyjlw-1710356772137)]
最常见java面试题解析(2021最新版)
[外链图片转存中…(img-uqibjj6c-1710356772138)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-8dllplyy-1710356772138)]
2021企业java面试题精选
[外链图片转存中…(img-nvdh0w9m-1710356772139)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-ojlg45dt-1710356772139)]



发表评论