前言
语言只是工具,不能决定你好不好找工作,决定你好不好找工作的是你的能力!!!!!
学历本科及以上就够用了!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
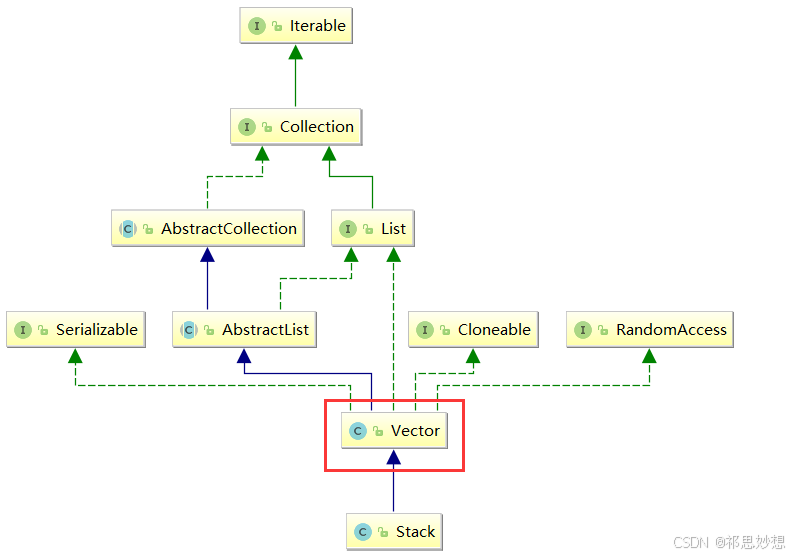
一、栈(stack)
1.1 栈的概念
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据在栈顶。

1.2 栈的使用
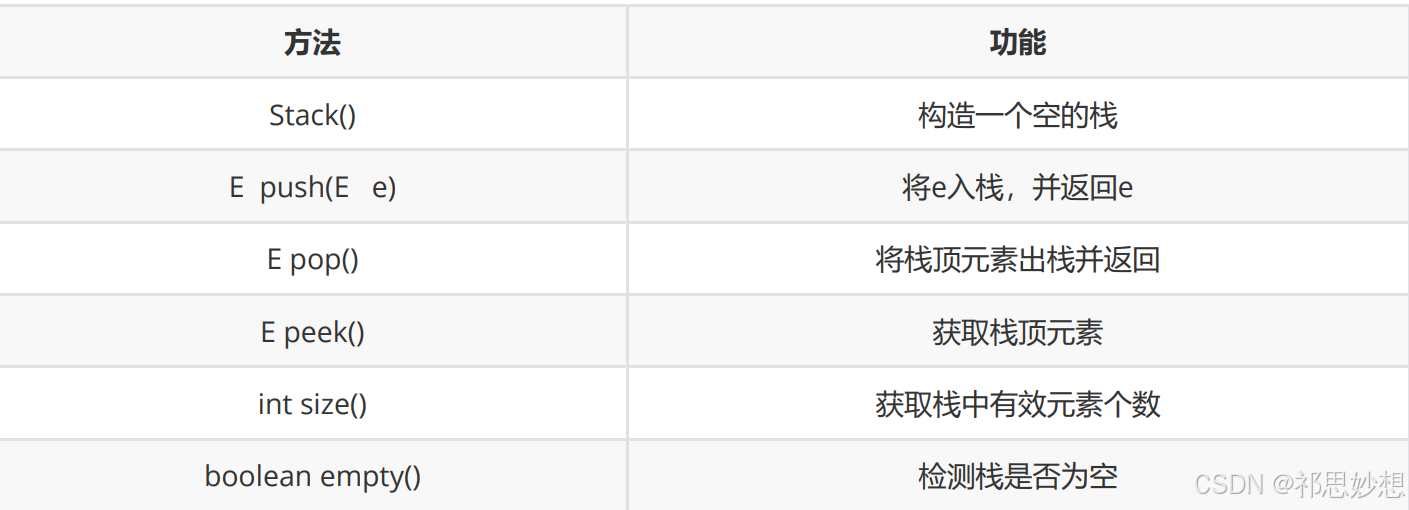
代码示例:
public static void main(string[] args) {
stack<integer> s = new stack();
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.push(4);
system.out.println(s.size()); // 获取栈中有效元素个数---> 4
system.out.println(s.peek()); // 获取栈顶元素---> 4
s.pop(); // 4出栈,栈中剩余1 2 3,栈顶元素为3
system.out.println(s.pop()); // 3出栈,栈中剩余1 2 栈顶元素为3
if(s.empty()){
system.out.println("栈空");
}else{
system.out.println(s.size());
}
}1.3 栈的模拟实现
private int[] elem;//定义一个数组来存储栈中元素
private int usesize;//记录栈中元素
private static final int default_capacity = 10;//定义一个静态常量 public int getusesize() {
return usesize;
} //构造一个容量为default_capacity的栈
public mystack(){
this.elem = new int[default_capacity];
} //检测栈是否满了
private boolean isfull(){
return this.usesize == this.elem.length;
} //将val放入栈
public void push(int val){
if (isfull()){
this.elem = arrays.copyof(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[usesize++] = val;
} //将栈顶元素取出并返回
public int pop(){
if (isempty()){
throw new emptyexception("stack为空!");
}
return elem[--usesize];
}
//获取栈顶元素
public int peek(){
if (isempty()){
throw new emptyexception("stack为空!");
}
return elem[usesize-1];
} //检测栈是否为空
private boolean isempty(){
return this.usesize == 0;
}1.4 栈的常见编程题
1.有效的括号
public boolean isvalid(string s) {
stack<character> stack = new stack<>();
//判断是否为有效的括号,具有先进后匹配的特点,因此我们用栈。首先创建一个栈
int len = s.length(); //首先得到字符串长度
if (len == 0) { //如果字符串为空,则返回true
return true;
}
if (len % 2 == 1) { //括号成双成对,因此如果字符串为奇数,那么直接返回false
return false;
} else { //如果为偶数,符合预期则,将字符串转字符数组。遍历这个字符数组
char[] chars = s.tochararray();
for (char ch : chars
) {
if (ch == '(' || ch == '[' || ch == '{') { //如果为左括号,则入栈。
stack.push(ch);
}
if (!stack.empty()) { //如果有左括号,到这里栈一定不为空。如果栈为空,则返回false,因为先得有左括号才会是有效括号
//接下来判断右括号,如果遍历到右括号,那么必有栈顶元素与之配对才会是有效括号,并出栈栈顶元素。否则返回false。
if (ch == '}') {
if (stack.pop() != '{') {
return false;
}
}
if (ch == ']') {
if (stack.pop() != '[') {
return false;
}
}
if (ch == ')') {
if (stack.pop() != '(') {
return false;
}
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
//最终判断栈是否为空,若全是左括号,那么就没有出栈。因此如果栈内有元素则为false。若匹配成功
//栈为空,返回true
return stack.empty();
}2.逆波兰表达式求值
import java.util.stack;
//运算方法是将数字入栈,如果碰到运算符号。则出栈将第一个出栈元素放在运算符右边,第二个出栈元素放入运算符左边
//计算这个结果,并将这个计算结果入栈。重复以上操作。即可计算出逆波兰表达式的值。
public class solution {
public int evalrpn(string[] tokens) {
stack<integer> stack = new stack<>();
int right;
int left;
for (string token:tokens
) {
switch (token){
case "+":
stack.push(stack.pop()+stack.pop());
break;
case "-":
right = stack.pop();
left = stack.pop();
stack.push(left-right);
break;
case "*":
stack.push(stack.pop()*stack.pop());
break;
case "/":
right = stack.pop();
left = stack.pop();
stack.push(left/right);
break;
default:stack.push(integer.parseint(token)); //注意这里放入栈的时候要将字符串转整型类型
}
}
return stack.peek();
}
}3.栈的压入、弹出序列
import java.util.stack;
public class solution {
public boolean ispoporder(int [] pusha,int [] popa) {
int n = pusha.length;
//辅助栈
stack<integer> s = new stack<>();
//遍历入栈的下标
int j = 0;
//遍历出栈的数组
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
//入栈:栈为空或者栈顶不等于出栈数组
while(j < n && (s.isempty() || s.peek() != popa[i])){
s.push(pusha[j]);
j++;
}
//栈顶等于出栈数组
if(s.peek() == popa[i])
s.pop();
//不匹配序列
else
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
4.最小栈
class minstack {
deque<integer> xstack;
deque<integer> minstack;
public minstack() {
xstack = new linkedlist<integer>();
minstack = new linkedlist<integer>();
minstack.push(integer.max_value);
}
public void push(int x) {
xstack.push(x);
minstack.push(math.min(minstack.peek(), x));
}
public void pop() {
xstack.pop();
minstack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return xstack.peek();
}
public int getmin() {
return minstack.peek();
}
}
1.5栈的应用场景
将递归转化为循环
比如:逆序打印链表
// 递归方式
void printlist(node head){
if(null != head){
printlist(head.next);
system.out.print(head.val + " ");
}
}// 循环方式
void printlist(node head){
if(null == head){
return;
}
stack<node> s = new stack<>();
// 将链表中的结点保存在栈中
node cur = head;
while(null != cur){
s.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 将栈中的元素出栈
while(!s.empty()){
system.out.print(s.pop().val + " ");
}
}二、队列
2.1队列的概念
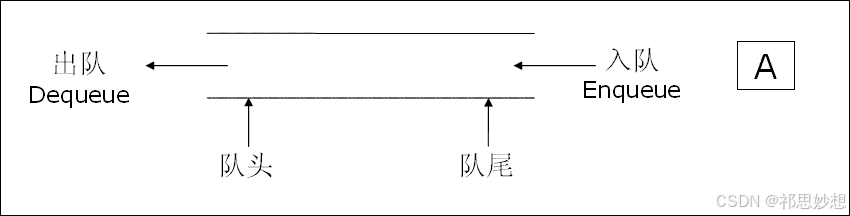
2.2 队列的使用
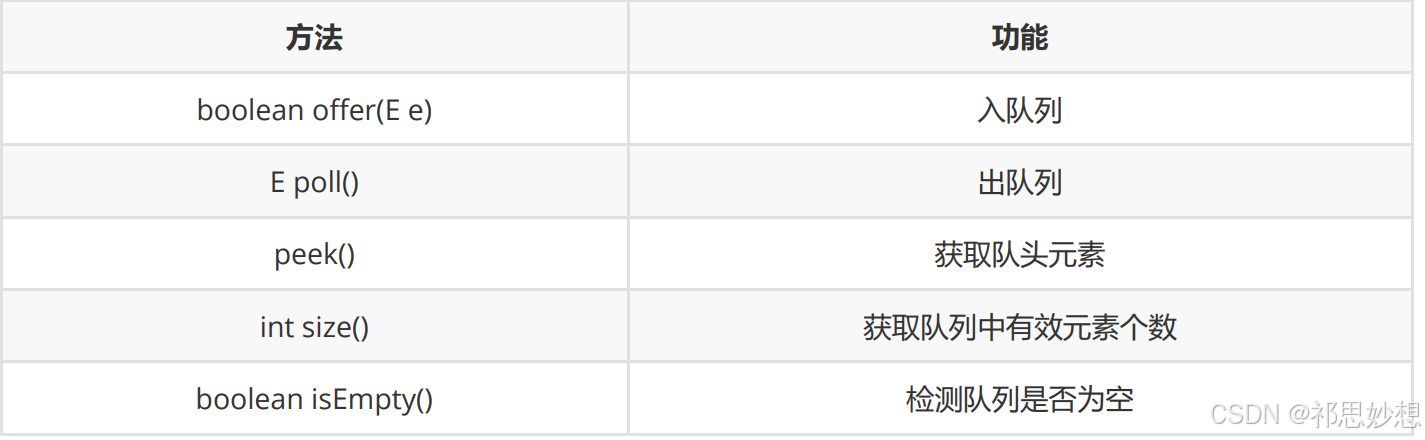
public static void main(string[] args) {
queue<integer> q = new linkedlist<>();
q.offer(1);
q.offer(2);
q.offer(3);
q.offer(4);
q.offer(5); // 从队尾入队列
system.out.println(q.size());
system.out.println(q.peek()); // 获取队头元素
q.poll();
system.out.println(q.poll()); // 从队头出队列,并将删除的元素返回
if(q.isempty()){
system.out.println("队列空");
}else{
system.out.println(q.size());
}
}2.3 队列模拟实现
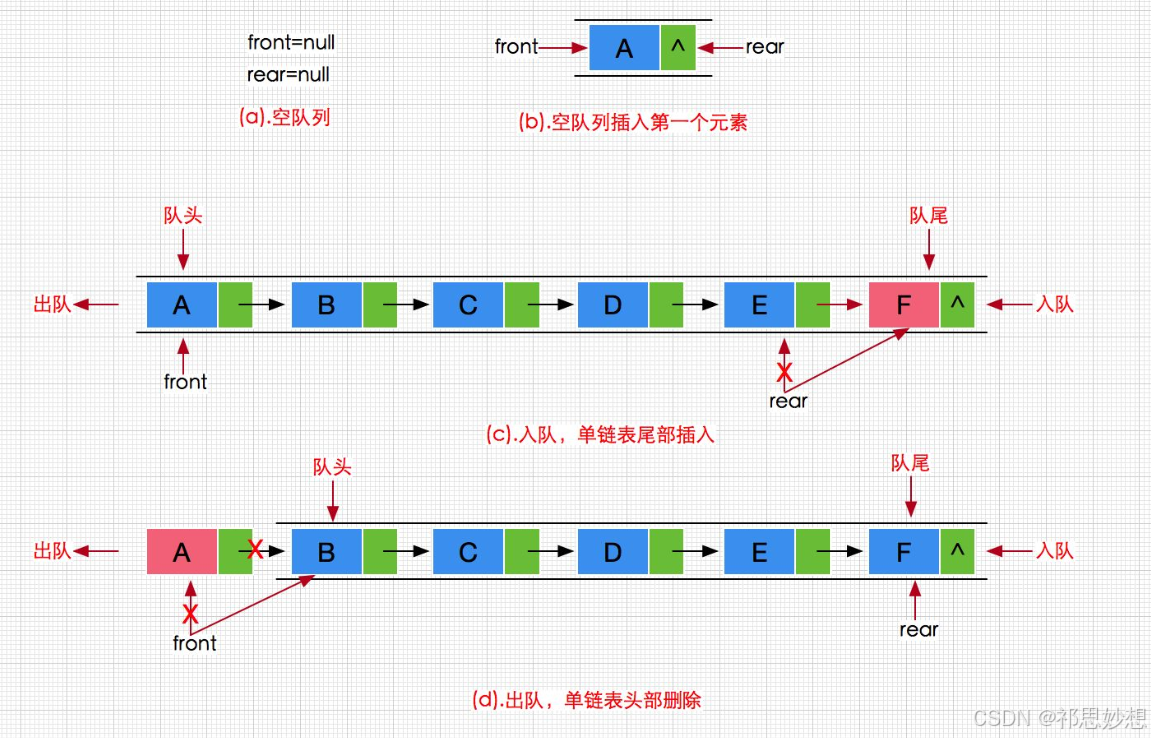
static class listnode{
private int val;
private listnode prev;
private listnode next;
public listnode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
private listnode front;//队头
private listnode rear;//队尾
private int usesize;//队员数
} public int getusesize() {
return usesize;
} //入队操作,相当于头插法
public void offer(int x){
listnode node = new listnode(x);
if(front == null){
front = rear = node;
}else {
node.next = front;
front.prev = node;
front = node;
}
usesize++;
} //出队操作,相当于删除尾节点
public int poll(){
if(rear == null){
return -1;
}
int ret = rear.val;
if(front == rear){
front = null;
rear = null;
return ret;
}
rear = rear.prev;
rear.next = null;
usesize--;
return ret;
} //获取队头元素
public int peek(){
if(front == null){
return -1;
}
return front.val;
} //检测队列是否为空
public boolean isempty(){
return this.usesize == 0;
}2.4 循环队列
数组下标循环的小技巧
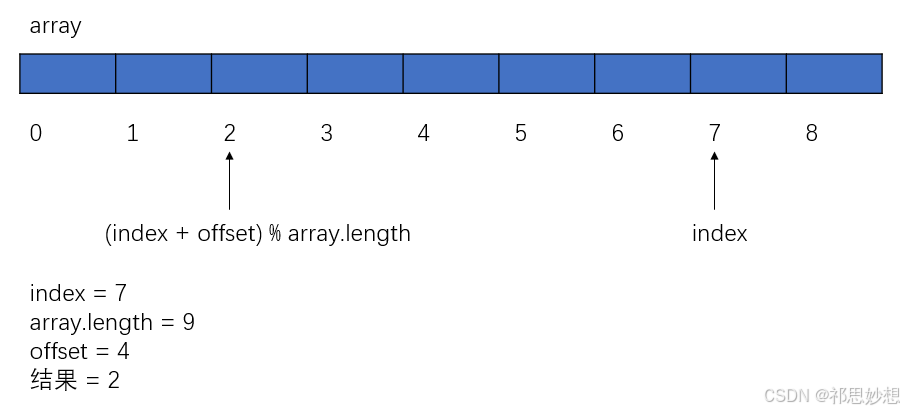
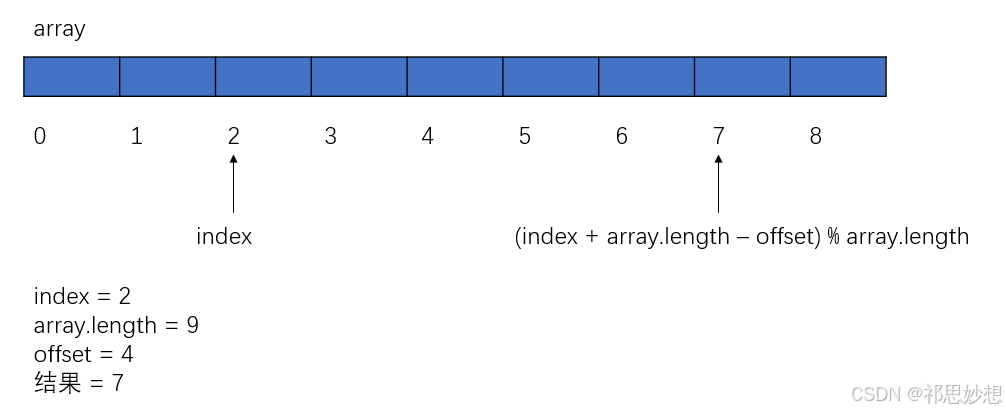
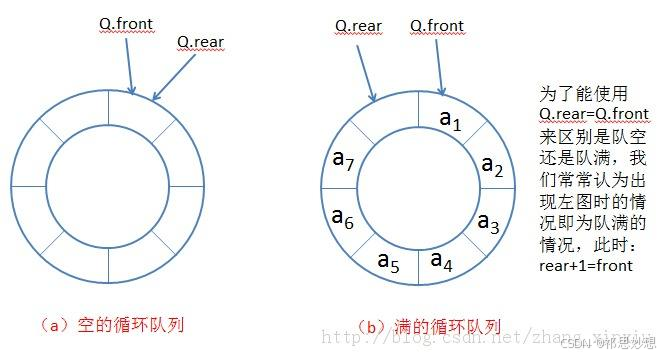
三、双端队列 (deque)
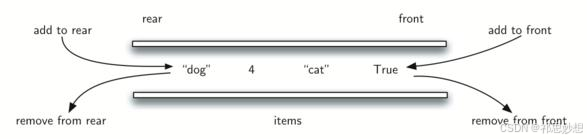
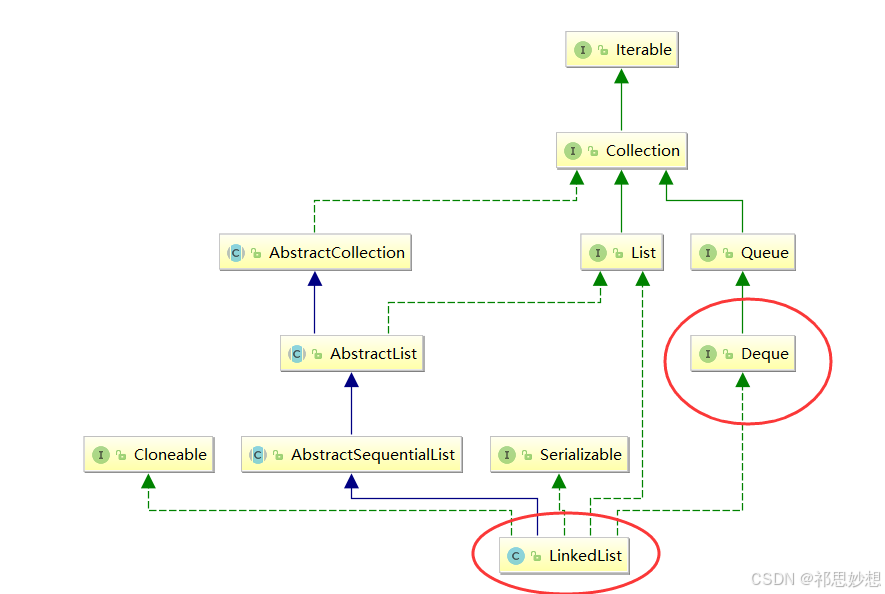
deque<integer> stack = new arraydeque<>();//双端队列的线性实现
deque<integer> queue = new linkedlist<>();//双端队列的链式实现2.5设计循环队列
class mycircularqueue {
private int front;
private int rear;
private int capacity;
private int[] elements;
public mycircularqueue(int k) {
capacity = k + 1;
elements = new int[capacity];
rear = front = 0;
}
public boolean enqueue(int value) {
if (isfull()) {
return false;
}
elements[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
public boolean dequeue() {
if (isempty()) {
return false;
}
front = (front + 1) % capacity;
return true;
}
public int front() {
if (isempty()) {
return -1;
}
return elements[front];
}
public int rear() {
if (isempty()) {
return -1;
}
return elements[(rear - 1 + capacity) % capacity];
}
public boolean isempty() {
return rear == front;
}
public boolean isfull() {
return ((rear + 1) % capacity) == front;
}
}
四、面试题
1.用队列实现栈
class mystack {
queue<integer> queue1;
queue<integer> queue2;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public mystack() {
queue1 = new linkedlist<integer>();
queue2 = new linkedlist<integer>();
}
/** push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
queue2.offer(x);
while (!queue1.isempty()) {
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
queue<integer> temp = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = temp;
}
/** removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll();
}
/** get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
/** returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isempty();
}
}
2.用栈实现队列
class myqueue {
deque<integer> instack;
deque<integer> outstack;
public myqueue() {
instack = new arraydeque<integer>();
outstack = new arraydeque<integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
instack.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (outstack.isempty()) {
in2out();
}
return outstack.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (outstack.isempty()) {
in2out();
}
return outstack.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return instack.isempty() && outstack.isempty();
}
private void in2out() {
while (!instack.isempty()) {
outstack.push(instack.pop());
}
}
}




发表评论