文章目录

前言
一、简介
1.1 操作日志在企业应用中的重要性
操作日志在企业应用中扮演着至关重要的角色。它不仅能够记录用户的操作行为,还能帮助开发和运维人员快速定位和解决问题,提升系统的稳定性和安全性。通过记录操作日志,企业可以:
- 监控用户行为:了解用户在系统中的操作轨迹,分析用户行为,改进用户体验。
- 故障排查:发生问题时,通过日志快速找到问题的根源,缩短问题排查时间。
- 审计与合规:记录关键操作,满足法律法规和行业标准的要求,防止恶意操作和数据泄露。
- 性能分析:分析操作日志,可以发现系统性能瓶颈,指导性能优化。
1.2 使用aop和注解实现操作日志记录的好处
在springboot项目中,通过aop(面向切面编程)和自定义注解来实现操作日志记录具有诸多好处:
- 分离关注点:将日志记录逻辑从业务代码中分离出来,保持代码的清洁和可维护性。
- 减少重复代码:避免在每个业务方法中手动添加日志记录代码,提升开发效率。
- 灵活性与可配置性:通过注解配置不同的日志记录需求,灵活应对各种场景。
- 统一管理与维护:集中管理日志记录逻辑,方便后续的功能扩展和维护。
二、开发环境
- jdk版本:jdk 17
- spring boot版本:spring boot 3.2.2
- mysql版本:8.0.37
- redis版本:5.0.14.1
- 构建工具:maven
三、准备工作
3.1 创建操作日志记录表
create table `sys_oper_log` (
`id` bigint(20) not null auto_increment comment '日志主键',
`title` varchar(50) default '' comment '模块标题',
`business_type` varchar(20) default '0' comment '业务类型(0其它 1新增 2修改 3删除)',
`method` varchar(100) default '' comment '方法名称',
`request_method` varchar(10) default '' comment '请求方式',
`oper_name` varchar(50) default '' comment '操作人员',
`oper_url` varchar(255) default '' comment '请求url',
`oper_ip` varchar(128) default '' comment '主机地址',
`oper_param` varchar(2000) default '' comment '请求参数',
`json_result` varchar(2000) default '' comment '返回参数',
`status` int(1) default '0' comment '操作状态(1正常 0异常)',
`error_msg` varchar(2000) default '' comment '错误消息',
`oper_time` datetime default null comment '操作时间',
`execute_time` bigint(20) not null default '0' comment '执行时长(毫秒)',
primary key (`id`)
) engine=innodb auto_increment=64 default charset=utf8 comment='操作日志记录';
3.2 创建系统日志实体类
/**
* 操作日志记录
*
* @date 2024/07/14
*/
@data
@schema(description = "操作日志记录")
@tablename(value = "sys_oper_log")
public class sysoperlog implements serializable {
@tablefield(exist = false)
private static final long serialversionuid = 1l;
@tableid(type = idtype.auto)
@schema(description = "日志主键")
private long id;
@schema(description = "模块标题")
private string title;
@schema(description = "业务类型(0其它 1新增 2修改 3删除)")
private string businesstype;
@schema(description = "方法名称")
private string method;
@schema(description = "请求方式")
private string requestmethod;
@schema(description = "操作类别(0其它 1后台用户 2手机端用户)")
private string operatortype;
@schema(description = "操作人员")
private string opername;
@schema(description = "请求url")
private string operurl;
@schema(description = "主机地址")
private string operip;
@schema(description = "请求参数")
private string operparam;
@schema(description = "返回参数")
private string jsonresult;
@schema(description = "操作状态(1正常 0异常)")
private integer status;
@schema(description = "错误消息")
private string errormsg;
@schema(description = "操作时间")
private date opertime;
@schema(description = "执行时长")
private long executetime;
}
四、代码实现
4.1 创建业务枚举类
/**
* 业务操作类型
*
*/
public enum businesstype {
/**
* 其他类型
*/
other,
/**
* 新增
*/
insert,
/**
* 修改
*/
update,
/**
* 删除
*/
delete,
/**
* 更新状态
*/
status,
/**
* 授权
*/
assign
}
4.2 创建日志注解
/**
* 自定义操作日志记录注解
*
*/
@target({elementtype.parameter, elementtype.method})
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@documented
public @interface log {
/**
* 模块名称
*/
string title() default "";
/**
* 业务操作类型
*/
businesstype businesstype() default businesstype.other;
/**
* 是否保存请求参数
*/
boolean issaverequestdata() default true;
/**
* 是否保存响应数据
*/
boolean issaveresponsedata() default true;
/**
* 排除指定的请求参数
*/
public string[] excludeparamnames() default {};
}
4.3 创建操作状态枚举类
/**
* 操作状态
*
*/
public enum businessstatus
{
/**
* 成功
*/
success,
/**
* 失败
*/
fail,
}
4.4 创建ip工具类
/**
* ip工具类
*/
public class iputil {
/**
* 获取ip
* @param request 请求
* @return {@link string }
*/
public static string getipaddress(httpservletrequest request) {
string ipaddress = null;
try {
ipaddress = request.getheader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = request.getheader("proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = request.getheader("wl-proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ipaddress == null || ipaddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ipaddress)) {
ipaddress = request.getremoteaddr();
if (ipaddress.equals("127.0.0.1")) {
// 根据网卡取本机配置的ip
inetaddress inet = null;
try {
inet = inetaddress.getlocalhost();
} catch (unknownhostexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
ipaddress = inet.gethostaddress();
}
}
// 对于通过多个代理的情况,第一个ip为客户端真实ip,多个ip按照','分割
if (ipaddress != null && ipaddress.length() > 15) { // "***.***.***.***".length()
// = 15
if (ipaddress.indexof(",") > 0) {
ipaddress = ipaddress.substring(0, ipaddress.indexof(","));
}
}
} catch (exception e) {
ipaddress="";
}
// ipaddress = this.getrequest().getremoteaddr();
return ipaddress;
}
/**
* 获取网关ip
* @param request 请求
* @return {@link string }
*/
public static string getgatwayipaddress(serverhttprequest request) {
httpheaders headers = request.getheaders();
string ip = headers.getfirst("x-forwarded-for");
if (ip != null && ip.length() != 0 && !"unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
// 多次反向代理后会有多个ip值,第一个ip才是真实ip
if (ip.indexof(",") != -1) {
ip = ip.split(",")[0];
}
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = headers.getfirst("proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = headers.getfirst("wl-proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = headers.getfirst("http_client_ip");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = headers.getfirst("http_x_forwarded_for");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = headers.getfirst("x-real-ip");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getremoteaddress().getaddress().gethostaddress();
}
return ip;
}
}
4.5 创建切面类
import cn.hutool.core.thread.threadlocal.namedthreadlocal;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.json;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.jsonobject;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.propertyprefilters;
import com.voyager.annotation.log;
import com.voyager.domain.entity.sysoperlog;
import com.voyager.domain.enums.businessstatus;
import com.voyager.entity.user;
import com.voyager.service.sysoperlogservice;
import com.voyager.utils.iputil;
import com.voyager.utils.userholder;
import jakarta.servlet.http.httpservletrequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.httpservletresponse;
import lombok.requiredargsconstructor;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.arrayutils;
import org.aspectj.lang.joinpoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.afterreturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.afterthrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.component;
import org.springframework.util.stringutils;
import org.springframework.validation.bindingresult;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.requestattributes;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.requestcontextholder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.servletrequestattributes;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.multipartfile;
import java.util.collection;
import java.util.date;
import java.util.map;
/**
* 日志切面
*/
@aspect
@component
@requiredargsconstructor
public class logaspect {
/**
* 定义需要排除在日志记录之外的属性名称数组
*/
private static final string[] exclude_properties = {"password", "oldpassword", "newpassword", "confirmpassword"};
private final sysoperlogservice sysoperlogservice;
/**
* 使用threadlocal维护一个线程局部变量,用于记录操作的耗时
*/
private static final threadlocal<long> time_threadlocal = new namedthreadlocal<long>("cost time");
/**
* 返回通知
*
* @param joinpoint 切点
*/
@afterreturning(pointcut = "@annotation(controllerlog)", returning = "jsonresult")
public void doafterreturning(joinpoint joinpoint, log controllerlog, object jsonresult) {
//调用处理日志的方法
handlelog(joinpoint, controllerlog, null, jsonresult);
}
/**
* 异常通知
*
* @param joinpoint 切点
* @param e 异常
*/
@afterthrowing(pointcut = "@annotation(controllerlog)", throwing = "e")
public void doafterthrowing(joinpoint joinpoint, log controllerlog, exception e) {
handlelog(joinpoint, controllerlog, e, null);
}
/**
* 处理请求前执行,此方法旨在记录方法的开始时间。
*
* @param joinpoint 切点
* @param controllerlog 一个注解对象,表示目标方法上标注的注解。这里用于判断方法是否应该被此切面处理。
*/
@before(value = "@annotation(controllerlog)")
public void bobefore(joinpoint joinpoint, log controllerlog) {
time_threadlocal.set(system.currenttimemillis());
}
/**
* 处理操作日志的逻辑。
* 当方法执行完毕或发生异常时,此方法用于封装和记录操作日志。
*
* @param joinpoint 切点,用于获取目标方法的信息。
* @param controllerlog 控制器上的日志注解,用于获取方法描述等信息。
* @param e 异常对象,如果方法执行过程中抛出异常。
* @param jsonresult 方法返回的对象,用于日志记录,此参数可能为null。
*/
private void handlelog(joinpoint joinpoint, log controllerlog, exception e, object jsonresult) {
try {
// 获取当前请求的属性,包括httpservletrequest对象。
requestattributes requestattributes = requestcontextholder.getrequestattributes();
// 如果请求属性为空,则直接返回,不处理日志。
if (requestattributes == null) {
return;
}
// 将请求属性转换为servletrequestattributes,以便获取httpservletrequest对象。
servletrequestattributes servletrequestattributes = (servletrequestattributes) requestattributes;
// 获取httpservletrequest对象。
httpservletrequest request = servletrequestattributes.getrequest();
// 重新获取请求属性,目的是为了后续获取请求方法等信息。
requestattributes attributes = requestcontextholder.getrequestattributes();
servletrequestattributes http = (servletrequestattributes) attributes;
// 再次获取httpservletrequest对象。
httpservletrequest httpservletrequest = http.getrequest();
// 创建sysoperlog对象,用于存储操作日志的信息。
sysoperlog sysoperlog = new sysoperlog();
// 默认设置操作状态为正常。
sysoperlog.setstatus(businessstatus.success.ordinal());
// 如果方法执行过程中抛出异常,则将操作状态设置为异常。
if (e != null) {
// 设置状态为异常
sysoperlog.setstatus(businessstatus.fail.ordinal());
// 设置异常信息。
sysoperlog.seterrormsg(e.getmessage());
}
// 获取ip地址
string ipaddress = iputil.getipaddress(request);
// 设置ip地址
sysoperlog.setoperip(ipaddress);
// 设置请求地址
sysoperlog.setoperurl(request.getrequesturi());
// 获取当前登录的用户信息。
user user = userholder.getuser();
// 获取用户名
string username = userholder.getuser().getusername();
// 设置操作者名称。
// 设置操作人员
sysoperlog.setopername(username);
// 获取并设置请求方法,例如get、post等。
sysoperlog.setrequestmethod(request.getmethod());
// 获取目标对象的类名。
string classname = joinpoint.gettarget().getclass().getname();
// 获取方法名
string methodname = joinpoint.getsignature().getname();
// 设置方法名称
sysoperlog.setmethod(classname + "." + methodname + "()");
// 获取注解中对方法的描述信息
getcontrollermethoddescription(joinpoint, controllerlog, jsonresult, sysoperlog);
// 计算执行时长(毫秒)
long executetime = system.currenttimemillis() - time_threadlocal.get();
sysoperlog.setexecutetime(executetime);
// 设置操作时间。
sysoperlog.setopertime(new date());
// 保存操作日志
sysoperlogservice.save(sysoperlog);
} catch (exception ex) {
// 记录处理日志过程中发生的异常。
ex.printstacktrace();
}
}
/**
* 从注解中获取控制器方法的描述信息,并填充到操作日志对象中。
*
* @param joinpoint 切点对象,用于获取方法名和参数信息。
* @param controllerlog 控制器日志注解对象,包含标题、业务类型等配置信息。
* @param jsonresult 方法的返回结果,用于判断是否需要记录响应数据。
* @param sysoperlog 系统操作日志对象,此处将从controllerlog中获取的信息填充到该对象中。
*/
private void getcontrollermethoddescription(joinpoint joinpoint, log controllerlog, object jsonresult, sysoperlog sysoperlog) {
//设置操作模块
sysoperlog.settitle(controllerlog.title());
//设置业务类型
sysoperlog.setbusinesstype(controllerlog.businesstype().name());
// 判断是否需要保存请求数据,如果需要,则调用setrequestvalue方法进行处理
if (controllerlog.issaverequestdata()) {
//调用设置请求数据的方法
setrequestvalue(joinpoint, sysoperlog, controllerlog.excludeparamnames());
}
// 判断是否需要保存响应数据且返回结果不为空,如果满足条件,则将返回结果转为json字符串并保存到操作日志中
if (controllerlog.issaveresponsedata() && !stringutils.isempty(jsonresult)) {
//设置响应数据
sysoperlog.setjsonresult(json.tojsonstring(jsonresult));
}
}
/**
* 设置操作日志的请求参数信息。
*
* @param joinpoint 切点,用于获取方法参数。
* @param operlog 操作日志对象,用于设置请求参数信息。
* @param excludeparamnames 需要排除的参数名数组,这些参数不会被记录在日志中。
*/
private void setrequestvalue(joinpoint joinpoint, sysoperlog operlog, string[] excludeparamnames) {
// 获取当前请求的属性
map<string, string[]> parametermap = getparametermap();
// 如果参数不为空且不为空集合
if (parametermap != null && !parametermap.isempty()) {
// 将参数转换为json字符串,通过excludepropertyprefilter过滤掉不需要记录的参数
string params = jsonobject.tojsonstring(parametermap, excludepropertyprefilter(excludeparamnames));
// 设置操作日志的请求参数,截取前2000个字符以防止过长
operlog.setoperparam(org.apache.commons.lang3.stringutils.substring(params, 0, 2000));
} else {
// 如果请求参数为空,尝试从方法参数中获取信息
object args = joinpoint.getargs();
// 如果方法参数不为空
if (args != null) {
// 将方法参数转换为字符串,同样支持排除某些参数名
string params = argsarraytostring(joinpoint.getargs(), excludeparamnames);
// 设置操作日志的请求参数,同样截取前2000个字符
operlog.setoperparam(org.apache.commons.lang3.stringutils.substring(params, 0, 2000));
}
}
}
/**
* 获取当前http请求的参数
*
* @return 一个map,映射参数名称到参数值数组。这允许处理多值参数。
*/
private static map<string, string[]> getparametermap() {
// 从spring的requestcontextholder中获取当前请求的属性
requestattributes requestattributes = requestcontextholder.getrequestattributes();
// 将requestattributes强制转换为servletrequestattributes,以便访问http请求特定的属性
servletrequestattributes servletrequestattributes = (servletrequestattributes) requestattributes;
// 从servletrequestattributes中获取当前http请求对象
httpservletrequest request = (httpservletrequest) servletrequestattributes.getrequest();
// 获取请求的所有参数
map<string, string[]> parametermap = request.getparametermap();
return parametermap;
}
/**
* 忽略敏感属性
*
* @param excludeparamnames 需要排除的参数名数组
* @return {@link propertyprefilters.mysimplepropertyprefilter }
*/
public propertyprefilters.mysimplepropertyprefilter excludepropertyprefilter(string[] excludeparamnames) {
return new propertyprefilters().addfilter().addexcludes(arrayutils.addall(exclude_properties, excludeparamnames));
}
/**
* 将对象数组转换为字符串,排除指定的参数名(敏感参数)。
*
* @param paramsarray 参数数组,可以包含任意类型的对象。
* @param excludeparamnames 需要排除的参数名数组,这些参数不会被转换为字符串。
* @return 返回转换后的参数字符串,各参数间以空格分隔。
*/
private string argsarraytostring(object[] paramsarray, string[] excludeparamnames) {
// 使用stringbuilder来构建最终的参数字符串
stringbuilder params = new stringbuilder();
// 检查参数数组是否为空或长度为0,避免不必要的处理
if (paramsarray != null) {
// 遍历参数数组中的每个对象
for (object o : paramsarray) {
// 检查对象是否为空且不属于被过滤的类型
if (o != null && !isfilterobject(o)) {
try {
// 将对象转换为json字符串,排除指定的属性
object jsonobj = jsonobject.tojsonstring(o, excludepropertyprefilter(excludeparamnames));
// 将转换后的json字符串追加到参数字符串中,并以空格分隔各个参数
params.append(jsonobj).append(" ");
} catch (exception ignored) {
// 忽略转换过程中的异常,确保方法的健壮性
}
}
}
}
return params.tostring().trim();
}
/**
* 判断传入的对象是否需要被过滤。
* 这个方法主要用于处理上传文件时,判断接收的参数是否为文件类型或其他特定类型。
*
* @param o 待检查的对象
* @return 如果对象需要被过滤(即对象为multipartfile或其他特定类型),则返回true;否则返回false。
*/
@suppresswarnings("rawtypes")
public boolean isfilterobject(final object o) {
// 获取对象的类类型
class<?> clazz = o.getclass();
// 检查对象是否为数组类型
if (clazz.isarray()) {
// 如果数组的组件类型可以被multipartfile类转换,则返回true
return clazz.getcomponenttype().isassignablefrom(multipartfile.class);
} else if (collection.class.isassignablefrom(clazz)) {
// 如果对象是集合类型,将其转换为collection接口实例
collection collection = (collection) o;
// 遍历集合中的每个元素,如果任意元素是multipartfile实例,则返回true
for (object value : collection) {
return value instanceof multipartfile;
}
} else if (map.class.isassignablefrom(clazz)) {
// 如果对象是map类型,将其转换为map接口实例
map map = (map) o;
// 遍历map中的每个条目,如果任意条目的值是multipartfile实例,则返回true
for (object value : map.entryset()) {
map.entry entry = (map.entry) value;
return entry.getvalue() instanceof multipartfile;
}
}
// 如果对象不是数组、集合或map类型,检查它是否为multipartfile、httpservletrequest、httpservletresponse或bindingresult实例
return o instanceof multipartfile || o instanceof httpservletrequest || o instanceof httpservletresponse
|| o instanceof bindingresult;
}
}
4.6 操作日志注解使用
/**
* 获取用户信息
*
* @param id 用户id
* @return {@link result }<{@link userinfo }>
*/
@log(title = "获取用户信息", businesstype = businesstype.other)
@operation(description = "获取用户信息")
@getmapping("/{id}")
public result<userinfo> getuser(@pathvariable long id) {
return result.success(userinfoservice.getbyid(id));
}
/**
* 插入用户信息
*
* @param userinfo 用户信息
* @return {@link result }<{@link string }>
*/
@log(title = "插入用户信息", businesstype = businesstype.insert)
@operation(description = "插入用户信息")
@postmapping
public result<string> insertuser(@requestbody userinfo userinfo) {
boolean saved = userinfoservice.save(userinfo);
if (!saved) {
return result.error("插入失败");
}
return result.success();
}
/**
* 更新用户信息
*
* @param userinfo 用户信息
* @return {@link result }<{@link string }>
*/
@log(title = "更新用户信息", businesstype = businesstype.update)
@operation(description = "更新用户信息")
@putmapping
public result<string> updateuser(@requestbody userinfo userinfo) {
boolean updated = userinfoservice.updatebyid(userinfo);
if (!updated) {
return result.error("更新失败");
}
return result.success();
}
/**
* 删除用户信息
* @param id i用户id
* @return {@link result }<{@link string }>
*/
@log(title = "删除用户信息", businesstype = businesstype.delete)
@operation(description = "删除用户信息")
@deletemapping("/{id}")
public result<string> deleteuser(@pathvariable long id) {
boolean deleted = userinfoservice.removebyid(id);
if (!deleted) {
return result.error("删除失败");
}
return result.success();
}
五、测试
- 分别执行请求四个接口:
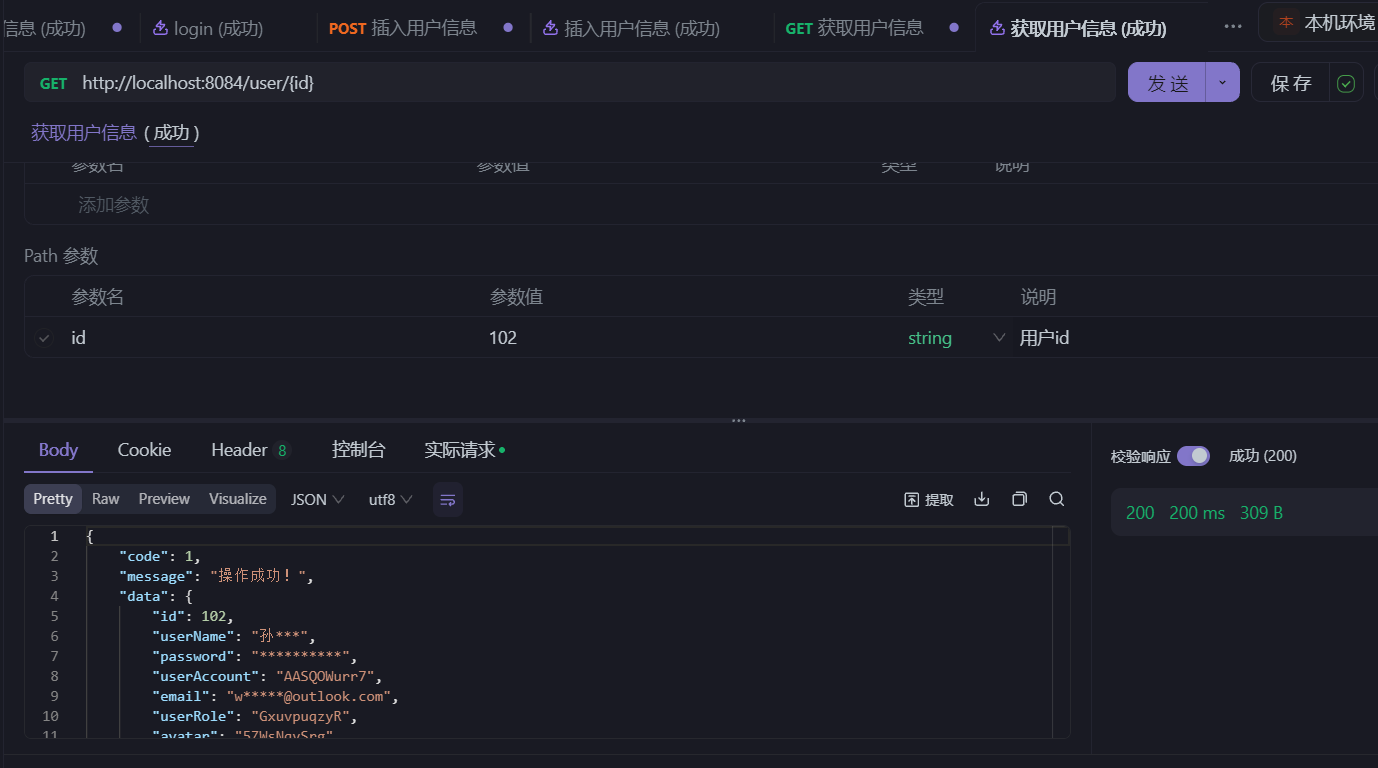
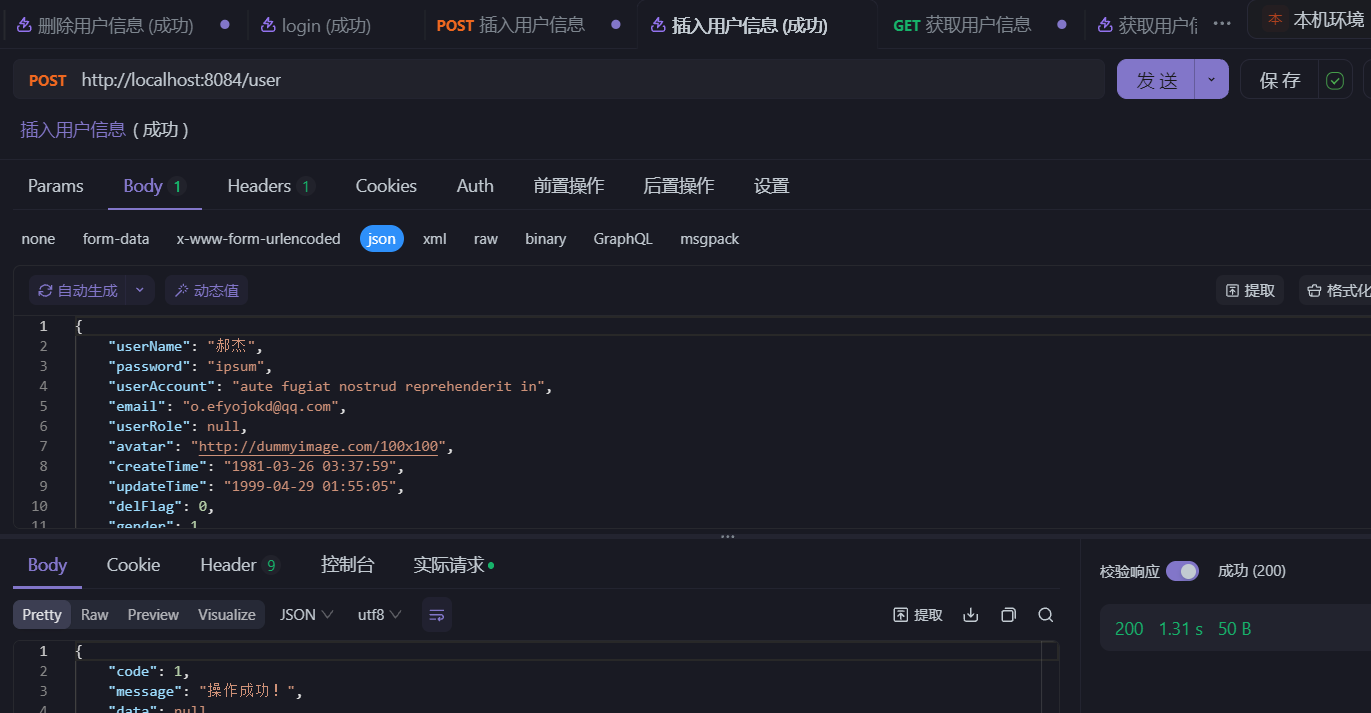
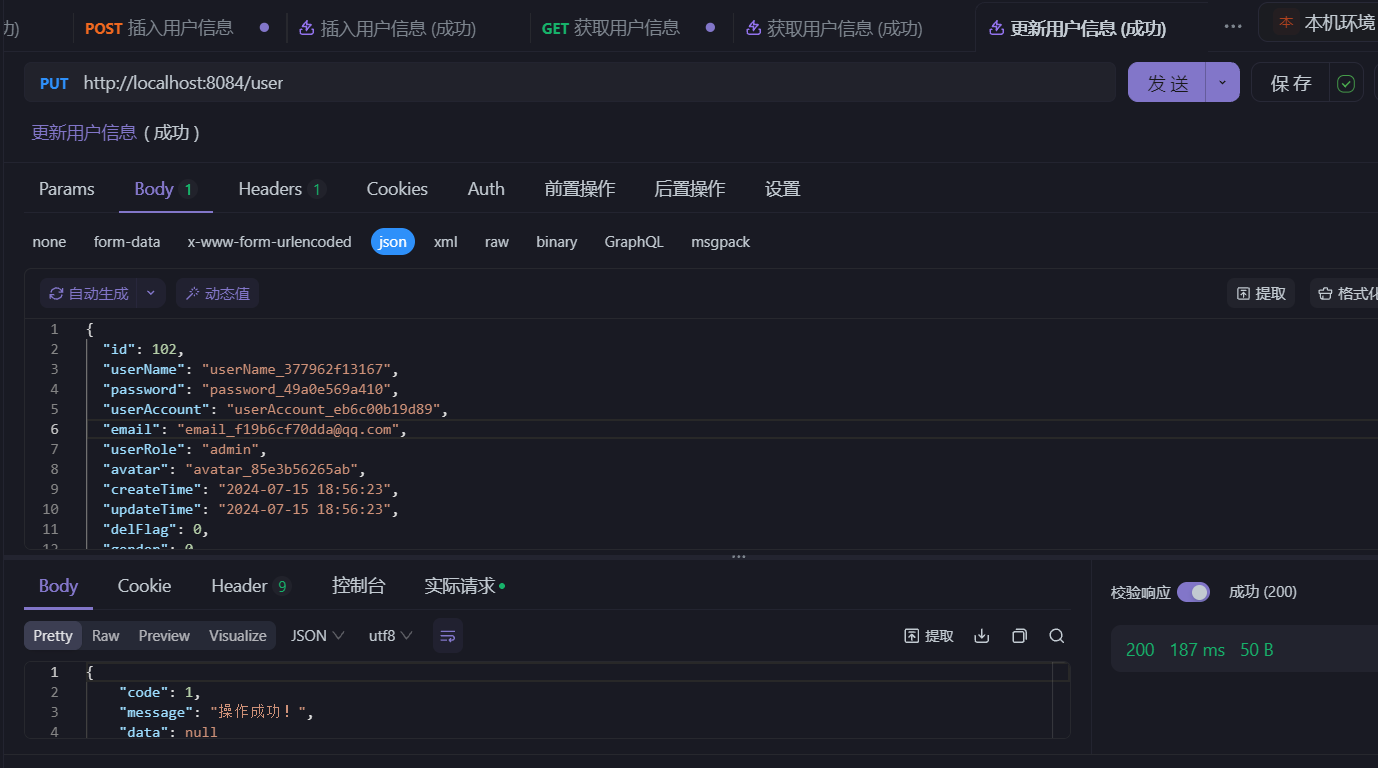
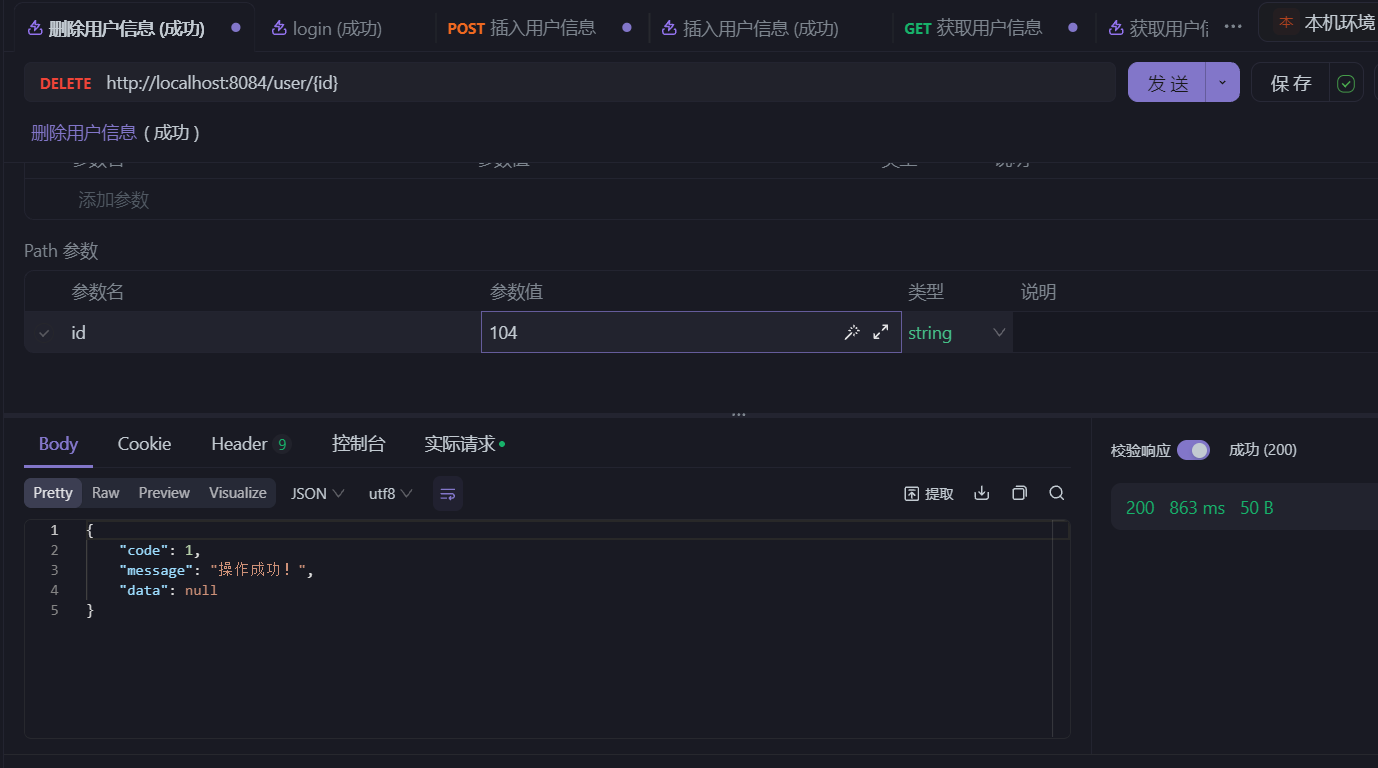
- 查看数据库
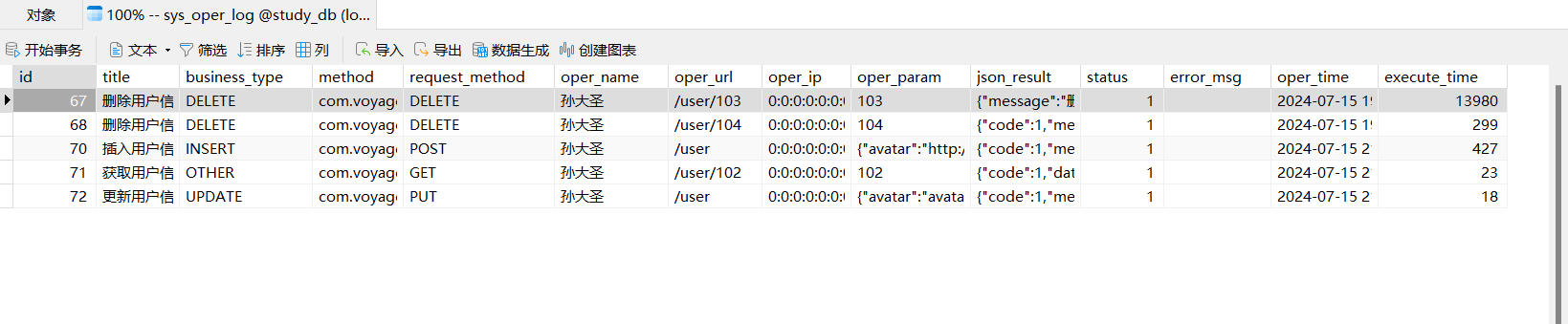
六、总结
本文主要参考了若依框架的操作日志记录功能的实现,记录了操作日志记录功能的实现和其中遇到的一些问题(比如:getresponse()返回值的问题)。在文章的开始,我们探讨了在springboot应用程序中实现日志操作日志记录的重要性,随后采用基于aop+注解的解决方案,以将日志数据存储到数据库中。通过这个方案,我们能够有效地记录用户的操作行为,从而方便后续的审计和分析,希望对大家有所帮助😊。
附录:





发表评论