目录
项目介绍:
本文是一个基于python和opencv的身份证号识别项目。它的主要目标是自动识别和提取身份证上的身份证号码。
下面是项目所用到的图片,大家可以自行下载:
- 待识别身份证照片:

- 用于数字模板匹配的图片:
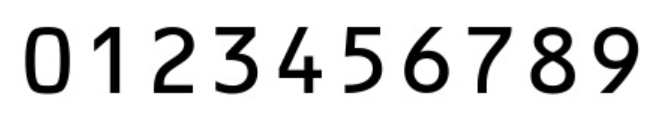
该项目的工作流程大致如下:
- 图像预处理:首先,需要对输入的身份证图像进行预处理,包括灰度化、二值化、去噪等操作,以便后续能更准确地进行文字识别。
- 文字定位和分割:接着,使用opencv中的图像处理技术,如边缘检测、形态学操作等,对预处理后的图像进行文字定位和分割,获取每个数字或字母的位置。
- 模板匹配:然后,利用模板匹配技术,对每个分割出来的数字或字母进行匹配。
- 信息整合:最后,将所有识别出的数字或字母按照它们在身份证上的位置进行排列,得到完整的身份证号码。
这个项目有很多实际的应用场景,比如在自动化办公、身份验证等场合,可以大大提高工作效率和准确性,话不多说,直接进入正题。
代码详解:
1.安装python和导入所需的库
import cv2
import numpy as np2.定义绘图函数,以便后续便于展示图片
#绘图展示
def cv_show(name,image):
cv2.imshow(name,image)
cv2.waitkey(0)3.定义排序函数,用于排序轮廓(contours)
def sort_contours(cnts,method='left-to-right'):
reverse=false
i=0
if method=="right-to-left" or method=='bottom-to-top':
reverse=true
if method=='top-to-bottom' or method=='bottom-to-top':
i=1
boundingboxes=[cv2.boundingrect(c) for c in cnts]
(cnts,boundingboxes)=zip(*sorted(zip(cnts,boundingboxes),
key=lambda b :b[1][i],
reverse=reverse))
#返回排序后的轮廓列表和相应的边界框列表。
return cnts,boundingboxes4.定义一个resize函数,用于调整图像大小。与cv2.resize不同的是,允许你基于指定的高度和/或宽度来调整图像的大小
def resize(image,width=none,height=none,inter=cv2.inter_area):
dim=none
(h,w)=image.shape[:2]
if width is none and height is none:
return image
if width is none:
r=height/float(h)
dim=(int(w*r),height)
else:
r=width/float(w)
dim=(width,int(h*r))
resize=cv2.resize(image,dim,interpolation=inter)
return resize5.模板图像中的数字定位处理
'''模板图像中的数字定位处理'''
img=cv2.imread("tp.png")
cv_show('img',img)
gray=cv2.imread("tp.png",0)
ref=cv2.threshold(gray,150,255,cv2.thresh_binary_inv)[1]
cv_show('ref',ref)
# 计算轮廓: cv2.findcontours()数接受的参数为二值图,即黑白的(不是灰度图)
# cv2.retr_external 只检测外轮廓,cv2.chain approx simple只保留终点坐标
refcnts,hierarchy=cv2.findcontours(ref.copy(),cv2.retr_external,cv2.chain_approx_simple)
cv2.drawcontours(img,refcnts,-1,(0,255,0),2)
cv_show('img',img)
refcnts=sort_contours(refcnts,method='left-to-right')[0]
# 保在模板中每个数字对应的像素值
digits={}
for (i,c) in enumerate(refcnts):
(x,y,w,h)=cv2.boundingrect(c)
roi=ref[y-2:y+h+2,x-2:x+w+2]
roi=cv2.resize(roi,(57,88))
roi=cv2.bitwise_not(roi)
# cv_show('roi',roi)
digits[i]=roi
cv2.destroyallwindows()图片处理结果展示:
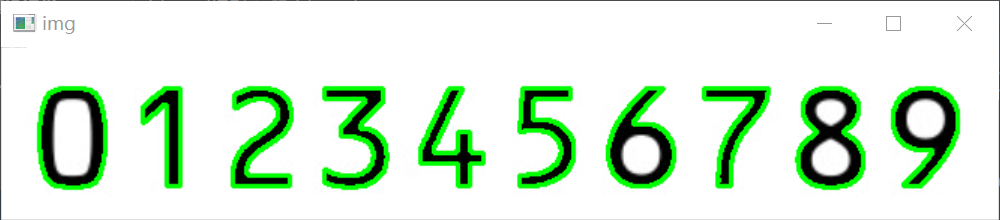
6.身份证图像处理
'''身份证号识别'''
img=cv2.imread('./card_id.jpg')
cv_show('img',img)
gray=cv2.imread('./card_id.jpg',0)
cv_show('gray',gray)
ref=cv2.threshold(gray,120,255,cv2.thresh_binary_inv)[1]
cv_show('ref',ref)
# 计算轮廓: cv2.findcontours()数接受的参数为二值图,即黑白的(不是灰度图)
# cv2.retr_external 只检测外轮廓,cv2.chain approx simple只保留终点坐标
refcnts,hierarchy=cv2.findcontours(ref.copy(),cv2.retr_external,cv2.chain_approx_simple)
cv2.drawcontours(img,refcnts,-1,(0,255,0),2)
cv_show('img',img)
cv2.destroyallwindows()
# 遍历轮廓,找到数字部分像素区城
locs = []
for (i, c) in enumerate(refcnts):
(x,y,w,h) = cv2.boundingrect(c) # 计外接知形
# 选择合适的区域,根据实际任务来
if (y > 330 and y< 360) and x>220: #符的留下来
locs.append((x,y,w,h))
locs = sorted(locs, key=lambda x:x[0])处理结果展示:

7.模板匹配并添加文本
output = [] # 用于存储最终结果
for (i, (gx,gy,gw, gh)) in enumerate(locs):
groupoutput = []
group = gray[gy - 2:gy + gh + 2,gx - 2:gx + gw + 2]# 适当加一点边界cv_show('group',group)
#预处理
group = cv2.threshold(group,0,255,cv2.thresh_binary | cv2.thresh_otsu)[1]
# cv_show('group',group)
# 计算每一组的轮廓
digitcnts,hierarchy = cv2.findcontours(group.copy(),cv2.retr_external ,cv2.chain_approx_simple)
digitcnts = sort_contours(digitcnts,method='left-to-right')[0]
# 计算每一组中的每一个数值
for c in digitcnts:
#找到当前数值的轮廓,resize成合适的的大小
(x,y,w,h) = cv2.boundingrect(c)
roi = group[y:y + h,x:x + w]
roi = cv2.resize(roi,(57,88))
# cv_show('roi',roi)
'''-------使用模板匹配,计算匹配得分-----------'''
scores = []
# 在模板中计算每一个得分
for (digit, digitroi) in digits.items():
# 模板匹配
result = cv2.matchtemplate(roi, digitroi, cv2.tm_ccoeff)
(_, score, _, _) = cv2.minmaxloc(result)
scores.append(score)
# 得到最合适的数字
groupoutput.append(str(np.argmax(scores)))
# 画出来
cv2.rectangle(img, (gx - 5, gy - 5), (gx + gw + 5, gy + gh + 5), (0, 0, 255), 1)
# cv2.puttext()是opencv库中的一个函数,用于在图像上添加文本。
cv2.puttext(img, "".join(groupoutput), (gx, gy - 15), cv2.font_hershey_simplex, 0.65, (0, 0, 255), 2)
output.extend(groupoutput) # 得到结果模板匹配后的识别结果:

8.打印结果
# 打印结果
print("id card #: {}".format("".join(output)))
cv2.imshow("image", img)
cv2.waitkey(0)
cv2.destroyallwindows() ![]()
完整代码展示:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @time : 2023/10/18 9:32
# @author :muzi
# @file : id_card.py
# @software: pycharm
import cv2
#绘图展示
def cv_show(name,image):
cv2.imshow(name,image)
cv2.waitkey(0)
def sort_contours(cnts,method='left-to-right'):
reverse=false
i=0
if method=="right-to-left" or method=='bottom-to-top':
reverse=true
if method=='top-to-bottom' or method=='bottom-to-top':
i=1
boundingboxes=[cv2.boundingrect(c) for c in cnts]
(cnts,boundingboxes)=zip(*sorted(zip(cnts,boundingboxes),
key=lambda b :b[1][i],
reverse=reverse))
return cnts,boundingboxes
def resize(image,width=none,height=none,inter=cv2.inter_area):
dim=none
(h,w)=image.shape[:2]
if width is none and height is none:
return image
if width is none:
r=height/float(h)
dim=(int(w*r),height)
else:
r=width/float(w)
dim=(width,int(h*r))
resize=cv2.resize(image,dim,interpolation=inter)
return resize
'''模板图像中的数字定位处理'''
img=cv2.imread("tp.png")
cv_show('img',img)
gray=cv2.imread("tp.png",0)
ref=cv2.threshold(gray,150,255,cv2.thresh_binary_inv)[1]
cv_show('ref',ref)
# 计算轮廓: cv2.findcontours()数接受的参数为二值图,即黑白的(不是灰度图)
# cv2.retr_external 只检测外轮廓,cv2.chain approx simple只保留终点坐标
refcnts,hierarchy=cv2.findcontours(ref.copy(),cv2.retr_external,cv2.chain_approx_simple)
cv2.drawcontours(img,refcnts,-1,(0,255,0),2)
cv_show('img',img)
refcnts=sort_contours(refcnts,method='left-to-right')[0]
# 保在模板中每个数字对应的像素值
digits={}
for (i,c) in enumerate(refcnts):
(x,y,w,h)=cv2.boundingrect(c)
roi=ref[y-2:y+h+2,x-2:x+w+2]
roi=cv2.resize(roi,(57,88))
roi=cv2.bitwise_not(roi)
# cv_show('roi',roi)
digits[i]=roi
cv2.destroyallwindows()
'''身份证号识别'''
img=cv2.imread('./card_id.jpg')
cv_show('img',img)
gray=cv2.imread('./card_id.jpg',0)
cv_show('gray',gray)
ref=cv2.threshold(gray,120,255,cv2.thresh_binary_inv)[1]
cv_show('ref',ref)
# 计算轮廓: cv2.findcontours()数接受的参数为二值图,即黑白的(不是灰度图)
# cv2.retr_external 只检测外轮廓,cv2.chain approx simple只保留终点坐标
refcnts,hierarchy=cv2.findcontours(ref.copy(),cv2.retr_external,cv2.chain_approx_simple)
cv2.drawcontours(img,refcnts,-1,(0,255,0),2)
cv_show('img',img)
cv2.destroyallwindows()
# 遍历轮廓,找到数字部分像素区城
locs = []
for (i, c) in enumerate(refcnts):
(x,y,w,h) = cv2.boundingrect(c) # 计外接知形
ar = w / float(h)
# 选择合适的区域,根据实际任务来
if (y > 330 and y< 360) and x>220: #符的留下来
locs.append((x,y,w,h))
cnt = refcnts[20]
(x, y), r = cv2.minenclosingcircle(cnt) # 计算轮廓的外接圆
locs = sorted(locs, key=lambda x:x[0])
import numpy as np
output = []
for (i, (gx,gy,gw, gh)) in enumerate(locs):
groupoutput = []
group = gray[gy - 2:gy + gh + 2,gx - 2:gx + gw + 2]# 适当加一点边界cv_show('group',group)
#预处理
group = cv2.threshold(group,0,255,cv2.thresh_binary | cv2.thresh_otsu)[1]
# cv_show('group',group)
# 计算每一组的轮廓
digitcnts,hierarchy = cv2.findcontours(group.copy(),cv2.retr_external ,cv2.chain_approx_simple)
digitcnts = sort_contours(digitcnts,method='left-to-right')[0]
# 计算每一组中的每一个数值
for c in digitcnts:
#找到当前数值的轮廓,resize成合适的的大小
(x,y,w,h) = cv2.boundingrect(c)
roi = group[y:y + h,x:x + w]
roi = cv2.resize(roi,(57,88))
# cv_show('roi',roi)
'''-------使用模板匹配,计算匹配得分-----------'''
scores = []
# 在模板中计算每一个得分
for (digit, digitroi) in digits.items():
# 模板匹配
result = cv2.matchtemplate(roi, digitroi, cv2.tm_ccoeff)
(_, score, _, _) = cv2.minmaxloc(result)
scores.append(score)
# 得到最合适的数字
groupoutput.append(str(np.argmax(scores)))
# 画出来
cv2.rectangle(img, (gx - 5, gy - 5), (gx + gw + 5, gy + gh + 5), (0, 0, 255), 1)
# cv2.puttext()是opencv库中的一个函数,用于在图像上添加文本。
cv2.puttext(img, "".join(groupoutput), (gx, gy - 15), cv2.font_hershey_simplex, 0.65, (0, 0, 255), 2)
output.extend(groupoutput) # 得到结果
# 打印结果
print("card id #: {}".format("".join(output)))
cv2.imshow("image", img)
cv2.waitkey(0)
cv2.destroyallwindows()




发表评论