背景:搜索引擎elasticsearch8.x+springboo3.x的用途如下
-
实时搜索功能:elasticsearch是一个开源的实时分布式搜索和分析引擎,它能够实现高效的实时搜索功能。学习elasticsearch可以帮助我们构建强大的搜索功能,提升用户体验和搜索效率,多数互联网公司里面用的技术,构建业务搜索/日志存储分析/可视化大屏
-
数据分析能力:elasticsearch不仅仅可以用于搜索功能,还可以用于数据分析和数据可视化。学习elasticsearch可以帮助我们深入了解数据分析的原理和方法,提升我们的数据分析能力。
-
分布式系统:elasticsearch是一个分布式系统,可以在多个节点上分布数据和处理请求。学习elasticsearch可以帮助我们了解分布式系统的设计和实现原理,提升我们的分布式系统开发能力。
-
spring boot和elasticsearch的结合:spring boot是一个快速开发框架,可以帮助我们快速构建企业级应用程序。学习spring boot和elasticsearch的结合可以帮助我们构建强大的搜索引擎应用程序,提升我们的开发效率。
-
有谁在用,进一线大厂(国内大厂多数都有用 ),国内:阿里、字节、腾讯 、微信、网易、虎牙、青云、新浪等;国外:谷歌、facebook、亚马逊、苹果等;产品:维基百科、github、stackoverflow都是使用elasticsearch存储数据
学完我们这个文章后的能力
-
elasticstack8.x核心架构和应用场景,实战云服务器选购+linux服务器源码安装
-
源码安装kibana8.x+es8.x常用命令操作,多案例实战index和document核心操作
-
es8.x映射mapping定义和ik中文分词配置query dsl多案例 match/match_all/filter/
-
match高级用法多字段匹配和短语搜索案例,单词纠错fuzzy模糊查询和搜索高亮语法实战
-
agg指标metric聚合搜索sum/avg/max/trem/range/date histogram多案例实战
-
新版springboot3.x+elasticsearch8.x整合多案例实战
什么是elastic stack?
学习elasticsearch之前,需要知道下什么是elastic stack?是一个开源的数据分析和可视化平台,由elasticsearch、logstash、kibana和beats组成。
很多同学听说过elk,实际上elk是三款软件的简称,分别是elasticsearch、 logstash、kibana组成,在发展的过程中有新成员beats的加入,所以就形成了elastic stack,elk是旧的称呼,elastic stack是新的名字
elasticsearch:一个分布式实时搜索和分析引擎,高性能和可伸缩性闻名,能够快速地存储、搜索和分析大量结构化和非结构化数据,基于java开发,它是elastic stack的核心组件,提供分布式数据存储和搜索能力。
logstash:是一个用于数据收集、转换和传输的数据处理引擎,支持从各种来源(如文件、日志、数据库等)收集数据;基于java开发,并对数据进行结构化、过滤和转换,然后将数据发送到elasticsearch等目标存储或分析系统。
kibana:基于node.js开发,数据可视化和仪表盘工具,连接到elasticsearch,通过简单易用的用户界面创建各种图表、图形和仪表盘;帮助用户快速探索和理解数据,并进行强大的数据分析和可视化
elasticsearch8.x核心概念
在新版elasticsearch中,文档document就是一行记录(json),而这些记录存在于索引库(index)中, 索引名称必须是小写,下面对比关系性数据库mysql,好轻松理解相关概念
| mysql数据库 | elastic search |
|---|---|
| database | 7.x版本前有type,对比数据库中的表,新版取消了 |
| table | index |
| row | document |
| column | field |
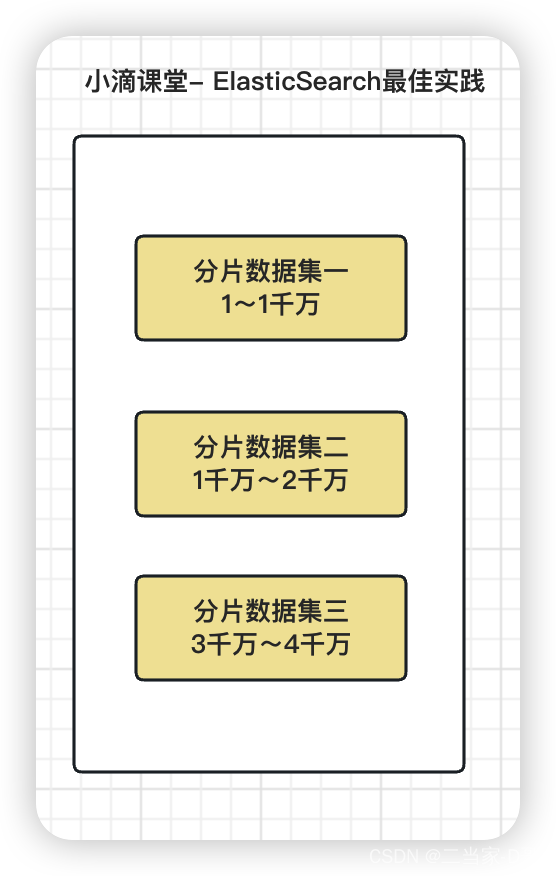
分片shards:数据量特大,没有足够大的硬盘空间来一次性存储,且一次性搜索那么多的数据,响应跟不上,2es提供把数据进行分片存储,这样方便进行拓展和提高吞吐
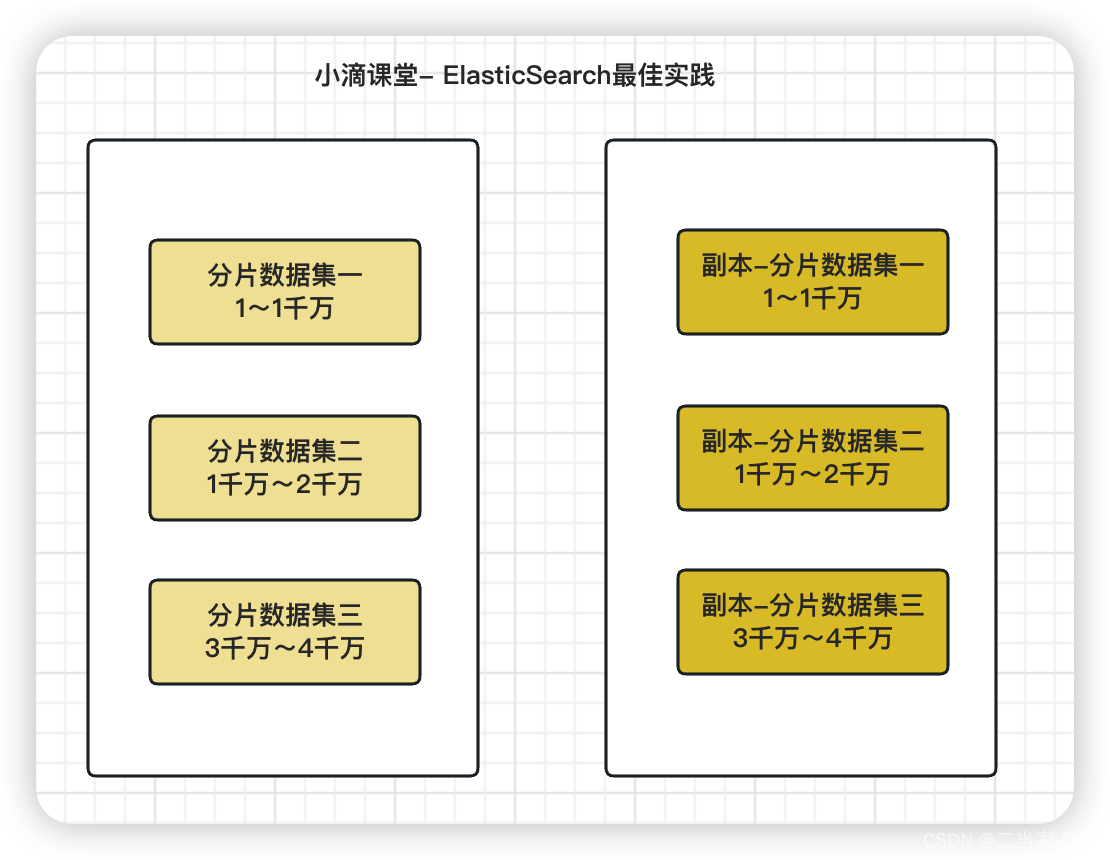
副本replicas:分片的拷贝,当主分片不可用的时候,副本就充当主分片进行使用,索引分片的备份,shard和replica一般存储在不同的节点上,用来提高可靠性
元数据:elasticsearch中以 “ _” 开头的属性都成为元数据,都有自己特定的意思
es默认为一个索引创建1个主分片和1个副本,在创建索引的时候使用settings属性指定,每个分片必须有零到多个副本
注意:索引一旦创建成功,主分片primary shard数量不可以变(只能重建索引),副本数量可以改变
linux服务器源码安装jdk17+elasticsearch8.x实战(结尾有安装包)
第一步:上传jdk17+elasticsearch8.x相关安装包
第二步:安装jdk17
vim /etc/profile
#增加下面内容
java_home=/usr/local/software/elk_test/jdk17
classpath=$java_home/lib/
path=$path:$java_home/bin
export path java_home classpath
环境变量立刻生效
source /etc/profile第三步:安装elasticsearc8.x和配置相关
#上传安装包和解压
tar -zxvf elasticsearch-8.4.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
#新建一个用户,安全考虑,elasticsearch默认不允许以root账号运行
创建用户:useradd es_user
设置密码:passwd es_user
#修改目录权限
# chmod是更改文件的权限
# chown是改改文件的属主与属组
# chgrp只是更改文件的属组。
chgrp -r es_user /usr/local/software/elk_test/elasticsearch-8.4.1
chown -r es_user /usr/local/software/elk_test/elasticsearch-8.4.1
chmod -r 777 /usr/local/software/elk_test/elasticsearch-8.4.1
# 修改文件和进程最大打开数,需要root用户,如果系统本身有这个文件最大打开数和进程最大打开数配置,则不用
在文件内容最后添加后面两行(切记*不能省略)
vim /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 65536
#修改虚拟内存空间,默认太小
在配置文件中改配置 最后一行上加上,执行 sysctl -p(立即生效)
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
vm.max_map_count=262144
#修改elasticsearch的jvm内存,机器内存不足,常规线上推荐16到24g内存
vim config/jvm.options
-xms1g
-xmx1g
# 修改 elasticsearch相关配置
vim config/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: my-application
node.name: node-1
path.data: /usr/local/software/elk_test/elasticsearch-8.4.1/data
path.logs: /usr/local/software/elk_test/elasticsearch-8.4.1/logs
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
xpack.security.enabled: false
xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: false
ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false配置说明
cluster.name: 指定elasticsearch集群的名称。所有具有相同集群名称的节点将组成一个集群。
node.name: 指定节点的名称。每个节点在集群中应该具有唯一的名称。
path.data: 指定用于存储elasticsearch索引数据的路径。
path.logs: 指定elasticsearch日志文件的存储路径。
network.host: 指定节点监听的网络接口地址。0.0.0.0表示监听所有可用的网络接口,开启远程访问连接
http.port: 指定节点上的http服务监听的端口号。默认情况下,elasticsearch的http端口是9200。
cluster.initial_master_nodes: 指定在启动集群时作为初始主节点的节点名称。
xpack.security.enabled: 指定是否启用elasticsearch的安全特性。在这里它被禁用(false),意味着不使用安全功能。
xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: 指定是否启用elasticsearch的安全认证和密钥管理特性。在这里它被禁用(false)。
ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: 指定是否启用geoip数据库下载功能。在这里它被禁用(false)启动elasticsearch
切换到es_user用户启动, 进入bin目录下启动, &为后台启动,再次提示es消息时 ctrl + c 跳出
./elasticsearch &
#安装命令,可以检查端口占用情况
yum install lsof -y常见命令,可以用postman访问(网络安全组记得开发端口)
#查看集群健康情况
http://120.78.85.91:9200/_cluster/health
#查看分片情况
http://120.78.85.91:9200/_cat/shards?v=true&pretty
#查看节点分布情况
http://120.78.85.91:9200/_cat/nodes?v=true&pretty
#查看索引列表
http://120.78.85.91:9200/_cat/indices?v=true&pretty常见问题
磁盘空间需要85%以下,不然es状态会不正常
不要用root用户安装
linux内存不够
linux文件句柄
没开启远程访问 或者 网络安全组没看开放端口
有9300 tcp端口,和http 9200端口,要区分
没权限访问,重新执行目录权限分配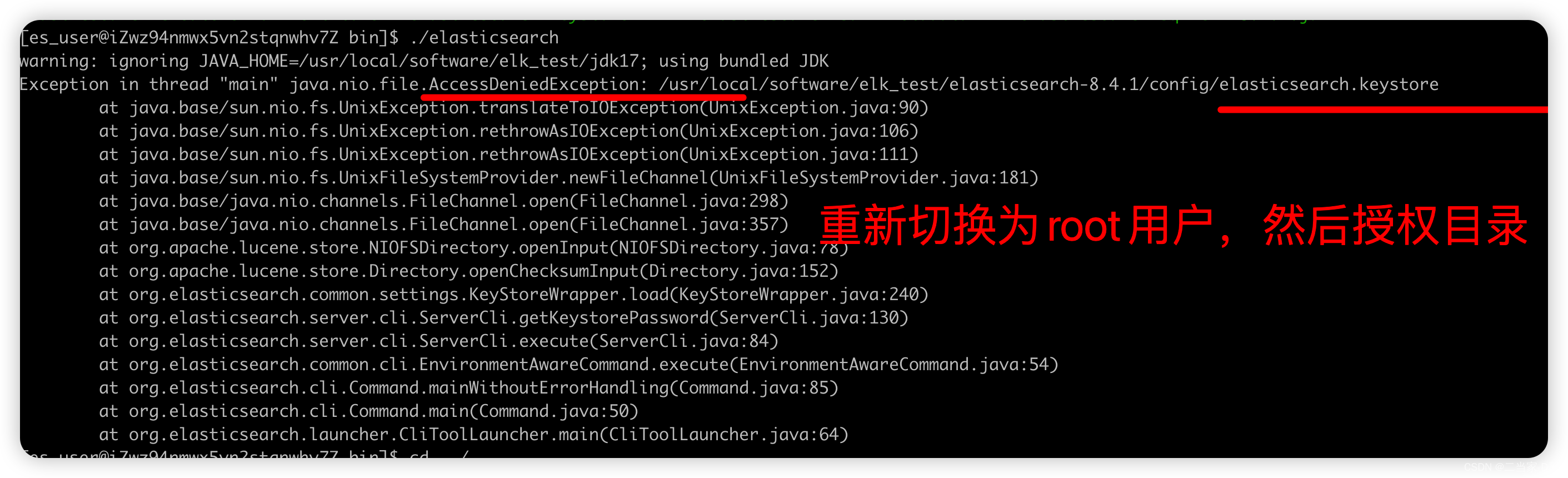
新版springboot3.x整合elasticsearch8.x
环境说明:本地 jdk17安装(springboot3.x要求jdk17),没相关环境的可以去oracle官网安装下jdk17,项目开发,快速创建 https://start.spring.io/
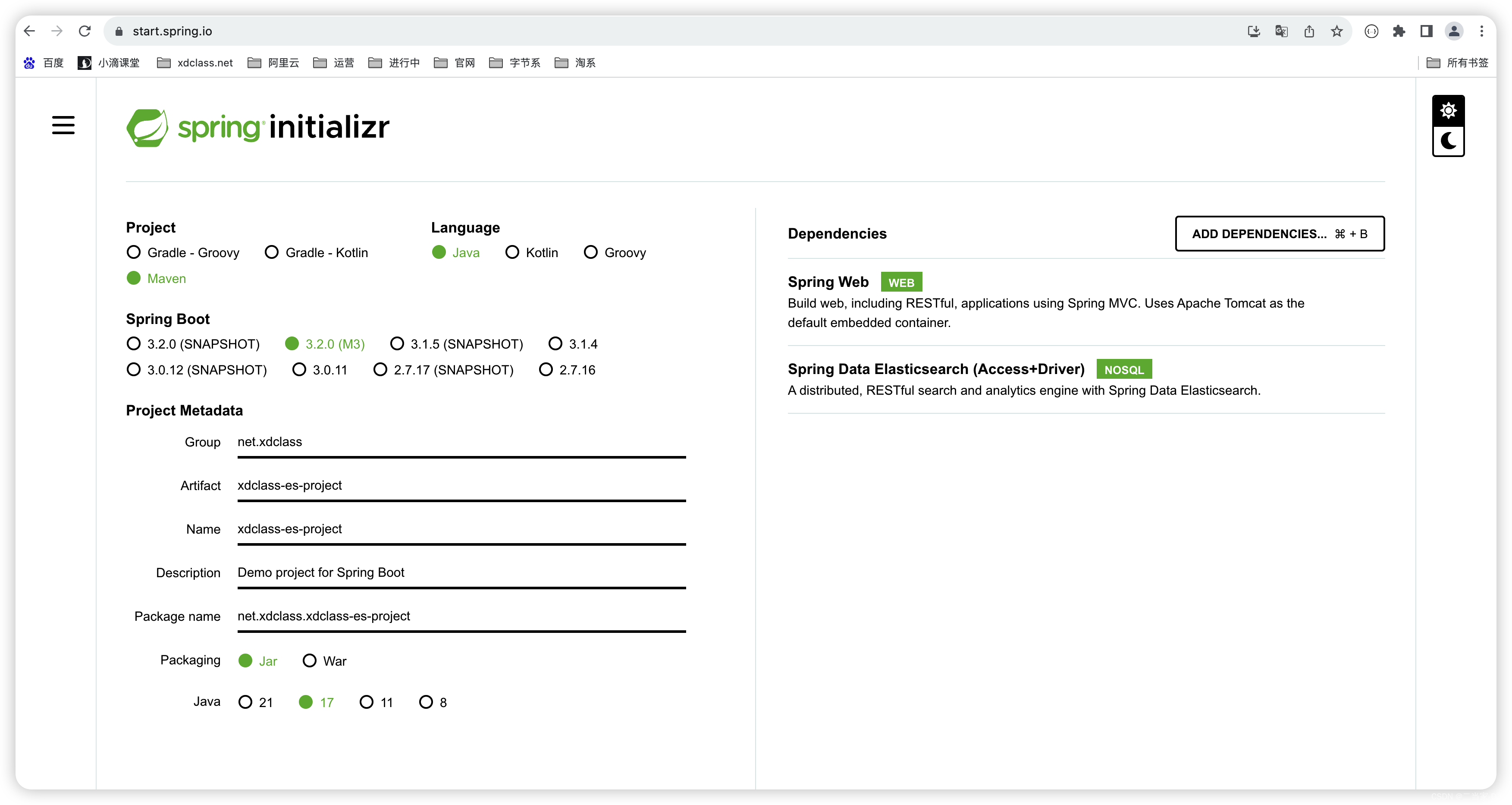
依赖包引入
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactid>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>es官方针对java推出多个客户端进行接入es,也分两种
-
更旧版的es会用transportclient(7.0版本标记过期)
-
java low level rest client(有继续迭代维护)
-
基于低级别的 rest 客户端,通过发送原始 http 请求与 elasticsearch 进行通信。
-
自己拼接好的字符串,并且自己解析返回的结果;兼容所有的elasticsearch版本
-
-
java high level rest client(7.1版本标记过期)
-
基于低级别 rest 客户端,提供了更高级别的抽象,简化了与 elasticsearch 的交互。
-
提供了更易用的 api,封装了底层的请求和响应处理逻辑,提供了更友好和可读性更高的代码。
-
自动处理序列化和反序列化 json 数据,适用于大多数常见的操作,如索引、搜索、聚合等。
-
对于较复杂的高级功能和自定义操作,可能需要使用低级别 rest 客户端或原生的 elasticsearch rest api
-
-
java api client(8.x版本开始推荐使用)
-
elasticsearch在7.1版本之前使用的java客户端是java rest client
-
从7.1版本开始elastic官方将java rest client标记为弃用(deprecated),推荐使用新版java客户端java api client
-
新版的java api client是一个用于与elasticsearch服务器进行通信的java客户端库
-
封装了底层的transport通信,并提供了同步和异步调用、流式和函数式调用等方法
-
springboot3.x如何整合elastic search
方案一:使用 elasticsearch 官方提供的高级客户端库 - elasticsearch api client
<dependency>
<groupid>co.elastic.clients</groupid>
<artifactid>elasticsearch-java</artifactid>
<version>8.5.3</version>
</dependency>方案二:使用 spring data elasticsearch
<!--这个starter里面就是依赖 spring-data-elasticsearch-->
<dependency>
<groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid>
<artifactid>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactid>
</dependency>
增加配置
spring.elasticsearch.uris=http://112.74.167.42:9200springboot3.x+elasticsearchtemplate索引库操作
elasticsearchtemplate,是 spring data elasticsearch 提供的一个核心类,是 elasticsearchclient 的一个具体实现,用于在 spring boot 中操作 elasticsearch 进行数据的存取和查询,提供了一组方法来执行各种操作,如保存、更新、删除和查询文档,执行聚合操作等;
elasticsearchtemplate 的一些常用方法
- `save(object)`: 保存一个对象到 elasticsearch 中。
- `index(indexquery)`: 使用 indexquery 对象执行索引操作。
- `delete(string, string)`: 删除指定索引和类型的文档。
- `get(string, string)`: 获取指定索引和类型的文档。
- `update(updatequery)`: 使用 updatequery 对象执行更新操作。
- `search(searchquery, class)`: 执行搜索查询,并将结果映射为指定类型的对象。
- `count(searchquery, class)`: 执行搜索查询,并返回结果的计数elasticsearchtemplate 常见注解配置(都是属于spring data elasticsearch)
@id 指定主键
@document指定实体类和索引对应关系,indexname:索引名称
@field指定普通属性
type 对应elasticsearch中属性类型,使用filedtype枚举快速获取。
text 类型能被分词
keywords 不能被分词
index 是否创建索引,作为搜索条件时index必须为true
analyzer 指定分词器类型。案例实战
//创建dto
@document(indexname = "video")
public class videodto {
@id
@field(type = fieldtype.text, index = false)
private long id;
@field(type = fieldtype.text)
private string title;
@field(type = fieldtype.text)
private string description;
@field(type = fieldtype.keyword)
private string category;
@field(type = fieldtype.integer)
private integer duration;
@field(type = fieldtype.date, format = dateformat.date_hour_minute_second)
private localdatetime createtime;
public videodto(){}
public videodto(long id, string title, string description, integer duration,string category) {
this.id = id;
this.title = title;
this.description = description;
this.duration = duration;
this.createtime = localdatetime.now();
this.category = category;
}
//省略set get方法
}//创建测试方法
@springboottest
class xdclassesprojectapplicationtests {
@autowired
private elasticsearchtemplate resttemplate;
/**
* 判断索引是否存在索引
*/
@test
void existsindex() {
indexoperations indexoperations = resttemplate.indexops(videodto.class);
boolean exists = indexoperations.exists();
system.out.println(exists);
}
/**
* 创建索引
*/
@test
void createindex() {
// spring data es所有索引操作都在这个接口
indexoperations indexoperations = resttemplate.indexops(videodto.class);
// 是否存在,存在则删除
if(indexoperations.exists()){
indexoperations.delete();
}
// 创建索引
indexoperations.create();
//设置映射: 在正式开发中,几乎不会使用框架创建索引或设置映射,这是架构或者管理员的工作,不适合使用代码实现
resttemplate.indexops(videodto.class).putmapping();
}
/**
* 删除索引
*/
@test
void deleteindex() {
indexoperations indexoperations = resttemplate.indexops(videodto.class);
boolean delete = indexoperations.delete();
system.out.println(delete);
}
}springboot3.x操作es8.x文档document案例实战
案例一 新增文档
@test
void insert(){
videodto videodto = new videodto();
videodto.setid(1l);
videodto.settitle("小滴课堂架构大课和spring cloud");
videodto.setcreatetime(localdatetime.now());
videodto.setduration(100);
videodto.setcategory("后端");
videodto.setdescription("这个是综合大型课程,包括了jvm,redis,新版spring boot3.x,架构,监控,性能优化,算法,高并发等多方面内容");
videodto saved = resttemplate.save(videodto);
system.out.println(saved);
}案例二 更新文档
@test
void update(){
videodto videodto = new videodto();
videodto.setid(1l);
videodto.settitle("小滴课堂架构大课和spring cloud v2");
videodto.setcreatetime(localdatetime.now());
videodto.setduration(102);
videodto.setcategory("后端");
videodto.setdescription("这个是综合大型课程,包括了jvm,redis,新版spring boot3.x,架构,监控,性能优化,算法,高并发等多方面内容");
videodto saved = resttemplate.save(videodto);
system.out.println(saved);
}案例三 批量插入
@test
void batchinsert() {
list<videodto> list = new arraylist<>();
list.add(new videodto(2l, "老王录制的按摩课程", "主要按摩和会所推荐", 123, "后端"));
list.add(new videodto(3l, "冰冰的前端性能优化", "前端高手系列", 100042, "前端"));
list.add(new videodto(4l, "海量数据项目大课", "d哥的后端+大数据综合课程", 5432345, "后端"));
list.add(new videodto(5l, "小滴课堂永久会员", "可以看海量专题课程,it技术持续充电平台", 6542, "后端"));
list.add(new videodto(6l, "大钊-前端低代码平台", "高效开发底层基础平台,效能平台案例", 53422, "前端"));
list.add(new videodto(7l, "自动化测试平台大课", "微服务架构下的spring cloud架构大课,包括jvm,效能平台", 6542, "后端"));
iterable<videodto> result = resttemplate.save(list);
system.out.println(result);
}案例四 根据主键查询
@test
void searchbyid(){
videodto videodto = resttemplate.get("3", videodto.class);
assert videodto != null;
system.out.println(videodto);
}案例五 根据id删除
@test
void deletebyid() {
string delete = resttemplate.delete("2", videodto.class);
system.out.println(delete);
}进阶springboot3.x+es8.x多案例搜索实战
新版的elasticsearch的query接口,query是spring data elasticsearch的接口,有多种具体实现,新版官方文档缺少,这边看源码给案例实战
criteriaquery:创建criteria来搜索数据,而无需了解 elasticsearch 查询的语法或基础知识,允许用户通过简单地连接和组合,指定搜索文档必须满足的对象来构建查询
stringquery:将elasticsearch查询作为json字符串,更适合对elasticsearch查询的语法比较了解的人,也更方便使用kibana或postman等客户端工具行进调试
nativequery:复杂查询或无法使用criteriaapi 表达的查询时使用的类,例如在构建查询和使用聚合的场景
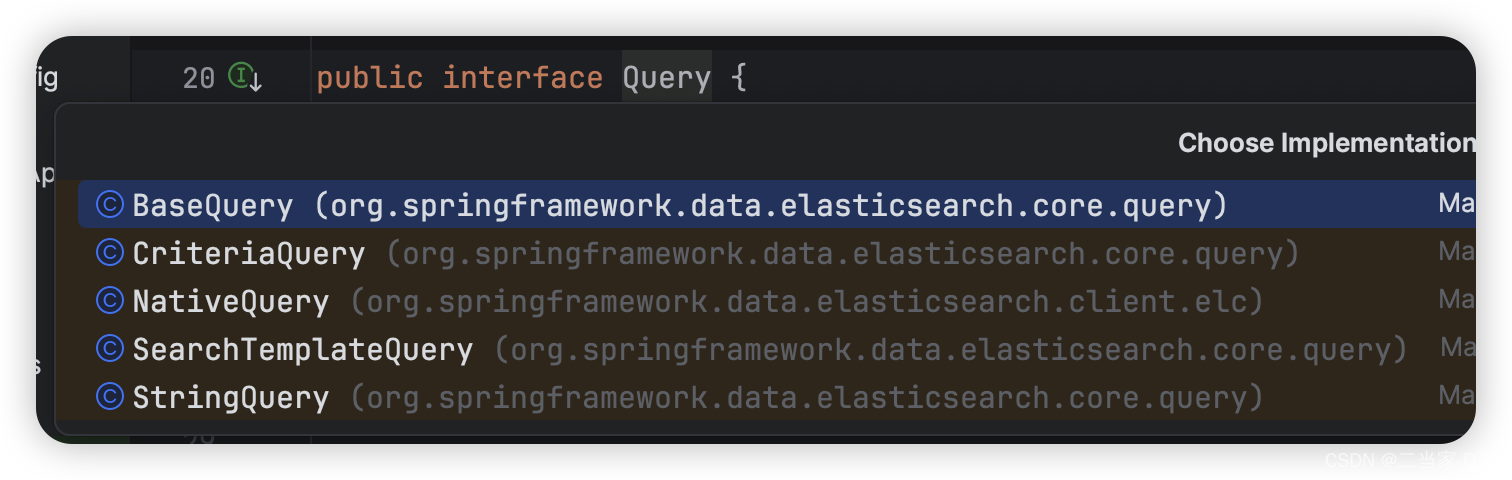
新版的搜索语法案例,查询采用新版的lambda表达式语法,更简洁
案例一:搜索全部
/**
* 查询所有
*/
@test
void searchall(){
searchhits<videodto> search = resttemplate.search(query.findall(), videodto.class);
list<searchhit<videodto>> searchhits = search.getsearchhits();
// 获得searchhits,进行遍历得到content
list<videodto> videodtos = new arraylist<>();
searchhits.foreach(hit -> {
videodtos.add(hit.getcontent());
});
system.out.println(videodtos);
}案例二:匹配搜索
/**
* match查询
*/
@test
void matchquery(){
query query = nativequery.builder().withquery(q -> q
.match(m -> m
.field("description") //字段
.query("spring") //值
)).build();
searchhits<videodto> searchhits = resttemplate.search(query, videodto.class);
// 获得searchhits,进行遍历得到content
list<videodto> videodtos = new arraylist<>();
searchhits.foreach(hit -> {
videodtos.add(hit.getcontent());
});
system.out.println(videodtos);
}案例三:分页搜索
/**
* 分页查询
*/
@test
void pagesearch() {
query query = nativequery.builder().withquery(query.findall())
.withpageable(pageable.ofsize(3).withpage(0)).build();
searchhits<videodto> searchhits = resttemplate.search(query, videodto.class);
// 获得searchhits,进行遍历得到content
list<videodto> videodtos = new arraylist<>();
searchhits.foreach(hit -> {
videodtos.add(hit.getcontent());
});
system.out.println(videodtos);
}案例四:搜索排序,withsort() 需要传入 sort 对象,.by代表根据一个字段进行排序
/**
* 排序查询,根据时长降序排列
*/
@test
void sortsearch() {
query query = nativequery.builder().withquery(query.findall())
.withpageable(pageable.ofsize(10).withpage(0))
.withsort(sort.by("duration").descending()).build();
searchhits<videodto> searchhits = resttemplate.search(query, videodto.class);
// 获得searchhits,进行遍历得到content
list<videodto> videodtos = new arraylist<>();
searchhits.foreach(hit -> {
videodtos.add(hit.getcontent());
});
system.out.println(videodtos);
}进阶springboot3.x+es8.x原始stringquery搜索
stringquery,将elasticsearch查询作为json字符串,更适合对elasticsearch查询的语法比较了解的人,也更方便使用kibana或postman等客户端工具行进调试
案例一:布尔must查询,搜索标题有 架构 关键词,描述有 spring关键字,时长范围是 10~6000之间的
//原始dsl查询
get /video/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [{
"match": {
"title": "架构"
}
}, {
"match": {
"description": "spring"
}
}, {
"range": {
"duration": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 6000
}
}
}]
}
}
}
//springboot+springdata查询
@test
void stringquery() {
//搜索标题有 架构 关键词,描述有 spring关键字,时长范围是 10~6000之间的
string dsl = """
{"bool":{"must":[{"match":{"title":"架构"}},{"match":{"description":"spring"}},{"range":{"duration":{"gte":10,"lte":6000}}}]}}
""";
query query = new stringquery(dsl);
list<searchhit<videodto>> searchhitlist = resttemplate.search(query, videodto.class).getsearchhits();
// 获得searchhits,进行遍历得到content
list<videodto> videodtos = new arraylist<>();
searchhitlist.foreach(hit -> {
videodtos.add(hit.getcontent());
});
system.out.println(videodtos);
}案例二:统计不同分类下的视频数量
/**
* 聚合查询
*/
@test
void aggquery() {
query query = nativequery.builder()
.withaggregation("category_group", aggregation.of(a -> a
.terms(ta -> ta.field("category").size(2))))
.build();
searchhits<videodto> searchhits = resttemplate.search(query, videodto.class);
//获取聚合数据
elasticsearchaggregations aggregationscontainer = (elasticsearchaggregations) searchhits.getaggregations();
map<string, elasticsearchaggregation> aggregations = objects.requirenonnull(aggregationscontainer).aggregationsasmap();
//获取对应名称的聚合
elasticsearchaggregation aggregation = aggregations.get("category_group");
buckets<stringtermsbucket> buckets = aggregation.aggregation().getaggregate().sterms().buckets();
//打印聚合信息
buckets.array().foreach(bucket -> {
system.out.println("组名:"+bucket.key().stringvalue() + ", 值" + bucket.doccount());
});
// 获得searchhits,进行遍历得到content
list<videodto> videodtos = new arraylist<>();
searchhits.foreach(hit -> {
videodtos.add(hit.getcontent());
});
system.out.println(videodtos);
}
elastic search8.x常见性能优化最佳实践
官方数据elastic search最高的性能可以达到,pb级别数据秒内相应,但是很多同学公司的elastic search集群,里面存储了几百万或者几千万数据,但是es查询就很慢了,记住,es数量常规是亿级别为起点,之所以达不到官方的数据,多数是团队现有技术水平不够和业务场景不一样
elastic search8.x常见性能优化最佳实践
- 硬件资源优化:
- 内存分配
- 将足够的堆内存分配给elasticsearch进程,以减少垃圾回收的频率
- elasticsearch推荐的最大jvm堆空间是30~32g, 所以分片最大容量推荐限制为30gb
- 30g heap 大概能处理的数据量 10 t,如果内存很大如128g,可在一台机器上运行多个es节点
- 比如业务的数据能达到200gb, 推荐最多分配7到8个分片
- 存储器选择
- 使用高性能的存储器,如ssd,以提高索引和检索速度
- ssd的读写速度更快,适合高吞吐量的应用场景。
- cpu和网络资源
- 根据预期的负载需求,配置合适的cpu和网络资源,以确保能够处理高并发和大数据量的请求。
- 分片和副本优化:
- 合理设置分片数量
- 过多的分片会增加cpu和内存的开销,因此要根据数据量、节点数量和性能需求来确定分片的数量。
- 一般建议每个节点上不超过20个分片
- 考虑副本数量
- 根据可用资源、数据可靠性和负载均衡等因素,设置合适的副本数量
- 至少应设置一个副本,以提高数据的冗余和可用性。
- 不是副本越多,检索性能越高,增加副本数量会消耗额外的存储空间和计算资源,
- 索引和搜索优化
- 映射和数据类型
- 根据实际需求,选择合适的数据类型和映射设置
- 避免不必要的字段索引,尽可能减少数据在硬盘上的存储空间。
- 分词和分析器
- 根据实际需求,选择合适的分词器和分析器,以优化搜索结果。
- 了解不同分析器的性能特点,根据业务需求进行选择
- 查询和过滤器
- 使用合适的查询类型和过滤器,以减少不必要的计算和数据传输
- 尽量避免全文搜索和正则表达式等开销较大的查询操作。
- 缓存和缓冲区优化:
- 缓存大小
- 在elasticsearch的jvm堆内存中配置合适的缓存大小,以加速热数据的访问
- 可以根据节点的角色和负载需求来调整缓存设置。
- 索引排序字段
- 选择合适的索引排序字段,以提高排序操作的性能
- 对于经常需要排序的字段,可以为其创建索引,或者选择合适的字段数据类型。
- 监控和日志优化
- 监控集群性能
- 使用elasticsearch提供的监控工具如elastic stack的elasticsearch监控、x-pack或其他第三方监控工具
- 实时监控集群的健康状态、吞吐量、查询延迟和磁盘使用情况等关键指标。
- 集群规划和部署:
- 多节点集群
- 使用多个节点组成集群,以提高数据的冗余和可用性。多节点集群还可以分布负载和增加横向扩展的能力。
- 节点类型和角色
- 根据节点的硬件配置和功能需求,将节点设置为合适的类型和角色
- 如数据节点、主节点、协调节点等,以实现负载均衡和高可用性。
- 性能测试和优化:
- 压力测试
- 使用性能测试工具模拟真实的负载,评估集群的性能极限和瓶颈
- 根据测试结果,优化硬件资源、配置参数和查询操作等。
- 日常性能调优
- 通过监控指标和日志分析,定期评估集群的性能表现,及时调整和优化配置,以满足不断变化的需求。
- 升级和版本管理:
- 计划升级
- 定期考虑升级elasticsearch版本,以获取新功能、性能改进和安全修复。
- 在升级过程中,确保备份数据并进行合理的测试。
- 版本管理
- 跟踪elasticsearch的发行说明和文档,了解新版本的特性和已知问题,并根据实际需求选择合适的版本。今天文章就先写到这里,还有很多内容下次继续,大家有任何疑惑也可以评论区留言
- springboot3.x整合elastic search8.x集群
-
elastic search集群进行升级,不同大版本如何升级,索引读写不兼容,比如elasticsearch5.x或6.x升级为8.x
-
业务一开始规划的索引分片、类型mapping分配不合理,原有数据量太大、分片数太少 ;原有数据量太小、分片数太多;es索引分片,一旦创建,原索引是不能修改分片数量
-
elasticsearch中搜索文档排序里面有个评分,表示相关性,按score得分从高到底排好序的结果集,机制上怎样的?
-
海量数据存储,但是有些数据很少方法,也占据比较高的存储资源,如何做冷热数据归档?
-
es被称为可以实时的搜索nrt,es索引分片写入原理是怎样的,为什么新加一条数据在下一秒就可以被搜索?
如果使用新版springboot3.x+elasticsearch8.x有任何疑惑,可以互相交流下
如果需要完整文章代码和安装包,直接获取即可


发表评论