一、treeset比较常见形式
treeset可以对元素按照某种规则进行排序:
public class test {
public static void main(string[] args) {
set<integer> s1=new treeset<>();
s1.add(23);
s1.add(3);
s1.add(2);
s1.add(13);
s1.add(63);
s1.add(25);
s1.add(22);
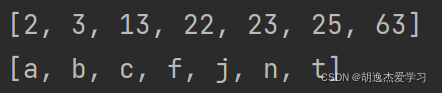
system.out.println(s1);
set<string> s2=new treeset<>();
s2.add("c");
s2.add("f");
s2.add("a");
s2.add("t");
s2.add("j");
s2.add("b");
s2.add("n");
system.out.println(s2);
}
}
如果添加的是对象(studen)时,如何排序呢?
class student{
private string name;
private int age;
public string getname() {
return name;
}
public void setname(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public student(string name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public student() {
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(string[] args) {
set<student> s1=new treeset<student>();
s1.add(new student("zhangsan",23));
s1.add(new student("lisi",22));
s1.add(new student("wangwu",32));
s1.add(new student("huyijie",19));
system.out.println("s1===================");
for(student s:s1){
system.out.println(s);
}
}
}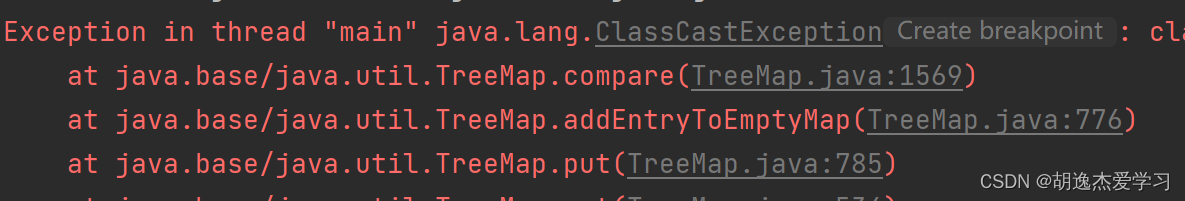
会发现无法排序。
二、解决方法
1 自然排序
- treeset存入数据后自动调用元素的compareto(object obj)方法,自动对数据进行排序,所以输出的数据是经过排序的数据
- 注:compareto方法返回值有:负数、零、整数,分别表示小于、等于、大于。
- 对于存入自定义的对象元素时,要重写元素的compareto(object obj)方法
- 元素定义时,需要实现comparable<t>接口
class student implements comparable<student>{
private string name;
private int age;
public string getname() {
return name;
}
public void setname(string name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public student(string name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public student() {
}
@override
public int compareto(student o) {
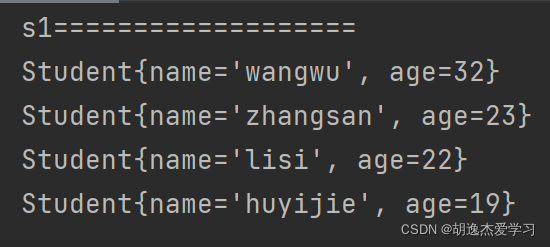
return o.age-this.age; //从大到小输出
}
@override
public string tostring() {
return "student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(string[] args) {
set<student> s1 = new treeset<student>((o1, o2) -> o1.getage() - o2.getage());
s1.add(new student("zhangsan", 23));
s1.add(new student("lisi", 22));
s1.add(new student("wangwu", 32));
s1.add(new student("huyijie", 19));
system.out.println("s1===================");
for (student s : s1) {
system.out.println(s);
}
}
}
2 自定义比较器排序
- 这种方法需要一个新的类实现comparator<t>接口,重写其中的compare方法
- treeset当元素不具备比较性,或者比较性不是所需要的时候,可以使treeset集合具有比较性,定义比较器,将比较器作为参数传给treeset集合,比较器需要实现comparator接口,当元素具备比较性和比较器同时出现时,以比较器为准。
class testcomparator implements comparator<student>{
@override
public int compare(student o1, student o2) {
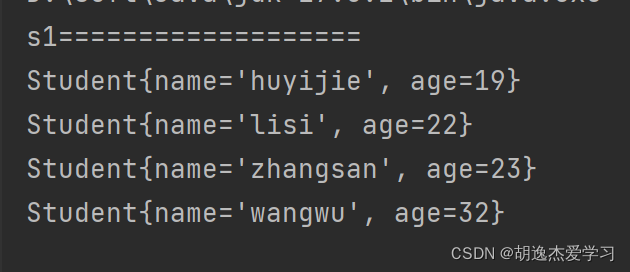
return o1.getage()-o2.getage();
}
}
//(o1, o2) -> o1.getage() - o2.getage()
public class test {
public static void main(string[] args) {
set<student> s1 = new treeset<student>(new testcomparator());
s1.add(new student("zhangsan", 23));
s1.add(new student("lisi", 22));
s1.add(new student("wangwu", 32));
s1.add(new student("huyijie", 19));
system.out.println("s1===================");
for (student s : s1) {
system.out.println(s);
}
}
}
也可以通过匿名内部类简化,
public class test {
public static void main(string[] args) {
set<student> s1 = new treeset<student>(new comparator<student>() {
@override
public int compare(student o1, student o2) {
return o2.getage()-o1.getage();
}
});
s1.add(new student("zhangsan", 23));
s1.add(new student("lisi", 22));
s1.add(new student("wangwu", 32));
s1.add(new student("huyijie", 19));
system.out.println("s1===================");
for (student s : s1) {
system.out.println(s);
}
}
}可再通过lambda表达式简化,


三、treemap按值排序
首先说一下如果map对key进行从小到大默认排序是创建treemap对象。map<integer,integer> maps = new treemap<>();就行了。
那么如何实现按value排序呢? (把treemap的entryset转换成list,然后使用collections.sort排序)
这里使用的是java.util.collections类实现排序,将map转成list,再自定义比较器,代码如下:
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.collections;
import java.util.comparator;
import java.util.list;
import java.util.map;
import java.util.map.entry;
import java.util.treemap;
public class mapvalsort {
public static void main(string[] args) {
map<string, integer> maps = new treemap<string, integer>();
maps.put("zhangsan", 22);
maps.put("lisi", 24);
maps.put("wangwu", 18);
maps.put("zhaoliu", 22);
//自定义比较器
comparator<map.entry<string, integer>> valcmp = new comparator<map.entry<string,integer>>() {
@override
public int compare(entry<string, integer> o1, entry<string, integer> o2) {
// todo auto-generated method stub
return o2.getvalue()-o1.getvalue(); // 降序排序,如果想升序就反过来
}
};
//将map转成list,map的一组key,value对应list一个存储空间
list<map.entry<string, integer>> list = new arraylist<map.entry<string,integer>>(maps.entryset()); //传入maps实体
collections.sort(list,valcmp); // 注意此处collections 是java.util包下面的,传入list和自定义的valcmp比较器
//输出map
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) {
system.out.println(list.get(i).getkey() + " = " + list.get(i).getvalue());
}
}
}四、关于compareto方法
- ompareto() 方法用于将 number 对象与方法的参数进行比较。可用于比较 byte, long, integer等。
- compareto方法从第一位开始比较, 如果遇到不同的字符,则马上返回这两个字符的ascii值差值.返回值是int类型
返回参与比较的前后两个字符串的asc码的差值,如果两个字符串首字母不同,则该方法返回首字母的asc码的差值
string a1 = "a"; string a2 = "c"; system.out.println(a1.compareto(a2));//结果为-2
即参与比较的两个字符串如果首字符相同,则比较下一个字符,直到有不同的为止,返回该不同的字符的asc码差值
string a1 = "aa"; string a2 = "ad"; system.out.println(a1.compareto(a2));//结果为-3
如果两个字符串不一样长,可以参与比较的字符又完全一样,则返回两个字符串的长度差值
string a1 = "aa"; string a2 = "aa12345678"; system.out.println(a1.compareto(a2));//结果为-8
- 返回为正数表示a1>a2, 返回为负数表示a1<a2,返回0表示a1==a2。
数字类型不能用compareto,nt跟int的比较不能用compareto方法,直接用大于(>) 小于(<) 或者 等于(==) 不等于(!=)来比较即可
int型可以直接比较,所以没有用到compareto比较,如果声明的是date、string、integer、或者其他的,可以直接使用compareto比较,
integer n1 = 5; integer n2 = 6; system.out.println(n1.compareto(n2));//-1
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。





发表评论