一、数据集分析
该手写数据为sklearn内置数据集,导入数据集:
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits1.1 数据集规格
- 1797个样本,每个样本包括8*8像素的图像和一个[0, 9]整数的标签
- 数据集data中,每一个样本均有64个数据位float64型。
- 关于手写数字识别问题:通过训练一个8x8 的手写数字图片中每个像素点不同的灰度值,来判定数字,是一个分类问题.
内置文件来自作者的解说:
"""load and return the digits dataset (classification).
each datapoint is a 8x8 image of a digit.
================= ==============
classes 10
samples per class ~180
samples total 1797
dimensionality 64
features integers 0-16
================= ==============
this is a copy of the test set of the uci ml hand-written digits datasets
https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/optical+recognition+of+handwritten+digits
read more in the :ref:`user guide <digits_dataset>`.
parameters
----------
n_class : int, default=10
the number of classes to return. between 0 and 10.
return_x_y : bool, default=false
if true, returns ``(data, target)`` instead of a bunch object.
see below for more information about the `data` and `target` object.
.. versionadded:: 0.18
as_frame : bool, default=false
if true, the data is a pandas dataframe including columns with
appropriate dtypes (numeric). the target is
a pandas dataframe or series depending on the number of target columns.
if `return_x_y` is true, then (`data`, `target`) will be pandas
dataframes or series as described below.
.. versionadded:: 0.23
returns
-------
data : :class:`~sklearn.utils.bunch`
dictionary-like object, with the following attributes.
data : {ndarray, dataframe} of shape (1797, 64)
the flattened data matrix. if `as_frame=true`, `data` will be
a pandas dataframe.
target: {ndarray, series} of shape (1797,)
the classification target. if `as_frame=true`, `target` will be
a pandas series.
feature_names: list
the names of the dataset columns.
target_names: list
the names of target classes.
.. versionadded:: 0.20
frame: dataframe of shape (1797, 65)
only present when `as_frame=true`. dataframe with `data` and
`target`.
.. versionadded:: 0.23
images: {ndarray} of shape (1797, 8, 8)
the raw image data.
descr: str
the full description of the dataset.
(data, target) : tuple if ``return_x_y`` is true
a tuple of two ndarrays by default. the first contains a 2d ndarray of
shape (1797, 64) with each row representing one sample and each column
representing the features. the second ndarray of shape (1797) contains
the target samples. if `as_frame=true`, both arrays are pandas objects,
i.e. `x` a dataframe and `y` a series.
.. versionadded:: 0.18
examples
--------
to load the data and visualize the images::
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
>>> digits = load_digits()
>>> print(digits.data.shape)
(1797, 64)
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> plt.gray()
>>> plt.matshow(digits.images[0])
<...>
>>> plt.show()
"""翻译(翻译的一言难尽,将就一下吧![]() ):
):
1.2 加载数据
# 获取数据集数据和标签
datas = load_digits()
x_data = datas.data
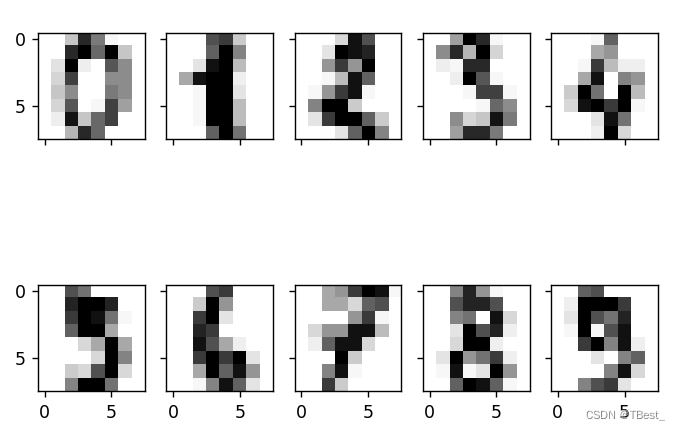
y_data = datas.target1.3 展示数据集中前十个数据
代码:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 展示前十个数据的图像
fig, ax = plt.subplots(
nrows=2,
ncols=5,
sharex=true,
sharey=true, )
ax = ax.flatten()
for i in range(10):
ax[i].imshow(datas.data[i].reshape((8, 8)), cmap='greys', interpolation='nearest')
plt.show()图像:
二、数据处理
2.1 划分数据集
# 划分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_data, y_data, test_size=0.3)三、建立模型
3.1 逻辑回归
3.1.1 logisticregression()主要参数
3.2 建立逻辑回归模型
# 建立逻辑回归模型
model = logisticregression(max_iter=10000, random_state=42, multi_class='multinomial')
# 训练模型
model.fit(x_train, y_train)四、模型评估
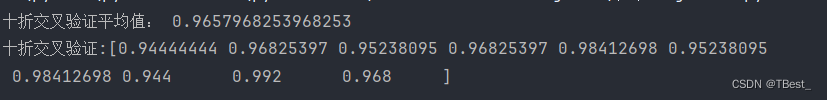
4.1 十折交叉验证
scores = cross_val_score(model, x_train, y_train, cv=10) # 十折交叉验证
k = 0
for i in scores:
k += i
print("十折交叉验证平均值:", k / 10)
print(f"十折交叉验证:{scores}\n")结果:
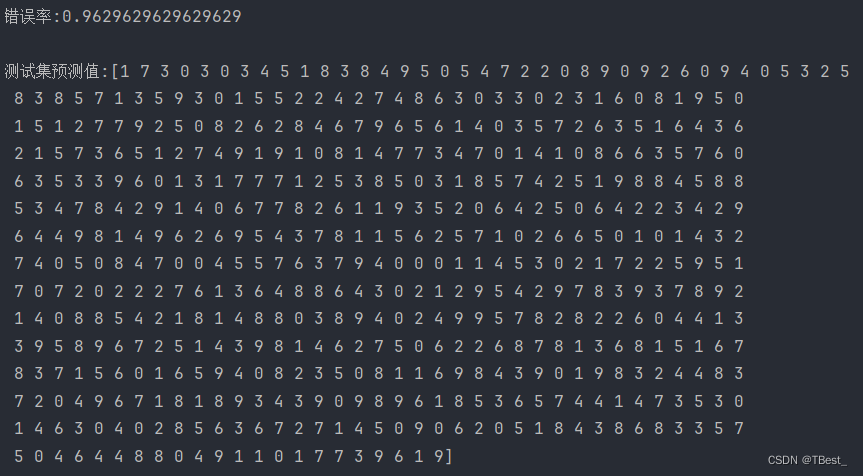
4.2 错误率
y_pred = model.predict(x_test)
error_rate = model.score(x_test, y_test)
print(f"错误率:{error_rate}\n")
print(f"测试集预测值:{y_pred}\n")结果:
五、源码
from sklearn.linear_model import logisticregression
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, train_test_split
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 获取数据集数据和标签
datas = load_digits()
x_data = datas.data
y_data = datas.target
# 展示前十个数据的图像
fig, ax = plt.subplots(
nrows=2,
ncols=5,
sharex=true,
sharey=true, )
ax = ax.flatten()
for i in range(10):
ax[i].imshow(datas.data[i].reshape((8, 8)), cmap='greys', interpolation='nearest')
plt.show()
# 划分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_data, y_data, test_size=0.3)
# 建立逻辑回归模型
model = logisticregression(max_iter=10000, random_state=42, multi_class='multinomial')
scores = cross_val_score(model, x_train, y_train, cv=10) # 十折交叉验证
k = 0
for i in scores:
k += i
print("十折交叉验证平均值:", k / 10)
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(x_test)
error_rate = model.score(x_test, y_test)
print(f"十折交叉验证:{scores}\n")
print(f"错误率:{error_rate}\n")
print(f"测试集预测值:{y_pred}\n")




发表评论