

目录
🌞一、实验目的
- 利用神经网络识别螺旋状数据集(python实现);
- 正确理解深度学习所需的数学知识。
🌞二、实验准备
- 根据gpu安装pytorch版本实现gpu运行实验代码;
- 配置环境用来运行 python、jupyter notebook和相关库等相关库。
🌞三、实验内容
资源获取:关注公众号【科创视野】回复 深度学习
🌼1. 生成螺旋状数据集
(1)利用numpy库生成螺旋状数据集,python源码如下:
# coding: utf-8
import numpy as np
def load_data(seed=2020264): #🍕🍕🍕生成数据集🍕🍕🍕
np.random.seed(seed) #设置随机数种子
n = 100 # 各类的样本数
dim = 2 # 数据的元素个数
cls_num = 3 # 类别数
x = np.zeros((n*cls_num, dim))
t = np.zeros((n*cls_num, cls_num), dtype=np.int)
for j in range(cls_num):
for i in range(n):#n*j, n*(j+1)):
rate = i / n
radius = 1.0*rate
theta = j*4.0 + 4.0*rate + np.random.randn()*0.2
ix = n*j + i
x[ix] = np.array([radius*np.sin(theta),
radius*np.cos(theta)]).flatten()
t[ix, j] = 1
return x, t解释:
🌼2. 打印数据集
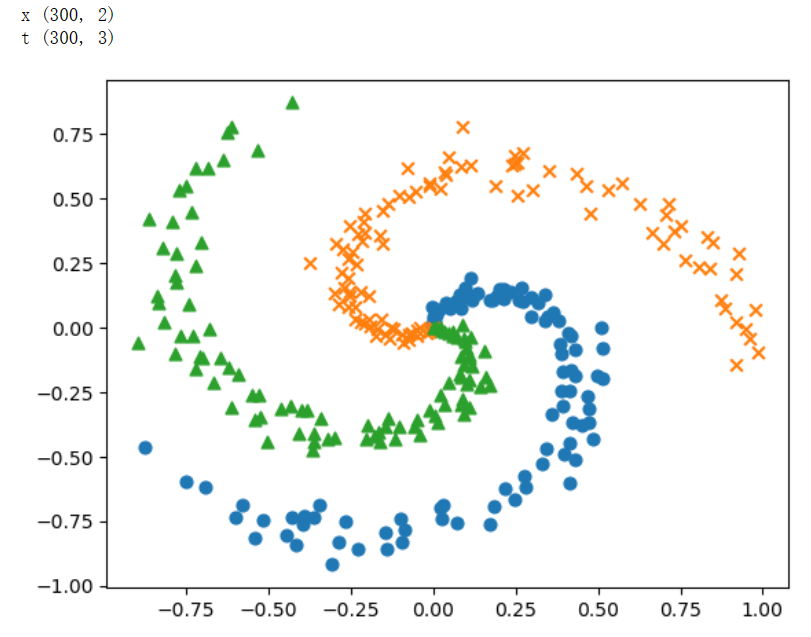
在加载完数据集后,利用plt将生成的数据集打印出来,python源码如下:
# coding: utf-8
import sys
sys.path.append('..') # 为了引入父目录的文件而进行的设定
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x, t = load_data()
print('x', x.shape) # (300, 2)
print('t', t.shape) # (300, 3)
# 绘制数据点
n = 100
cls_num = 3
markers = ['o', 'x', '^']
for i in range(cls_num):
plt.scatter(x[i*n:(i+1)*n, 0], x[i*n:(i+1)*n, 1], s=40, marker=markers[i])
plt.show()
解释:
结果图为:
🌼3. 编程实现
🌻仿射层-affine类
class affine:
def __init__(self,w,b):
self.params = [w,b]#保存参数
self.grads = [np.zeros_like(w),np.zeros_like(b)]#保存梯度
self.x = none
def forward(self,x):
w,b = self.params
out = np.dot(x,w) + b
self.x = x
return out
def backward(self,dout):
w,b = self.params
dx = np.dot(dout,w.t)
dw = np.dot(self.x.t,dout)
db = np.sum(dout,axis=0)
self.grads[0][...] = dw
self.grads[1][...] = db
return dx
解释:
🌻传播层-sigmoid类
class sigmoid:
def __init__(self):
self.params = []
self.grads = []
self.out = none
def forward(self,x):
out = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
self.out = out
return out
def backward(self,dout):
dx = dout * (1.0 - self.out) * self.out
return dx
解释:
🌻损失函数相关类
def softmax(x):
if x.ndim == 1:
x = x - np.max(x)
x = np.exp(x)/np.sum(np.exp(x))
elif x.ndim == 2:
x = x - x.max(axis = 1,keepdims = true)
x = np.exp(x)
x /= x.sum(axis=1, keepdims=true)
return x
def cross_entropy_error(y,t):
if y.ndim == 1:
t = t.reshape(1,t.size)
y = y.reshape(1,y.size)
#因为监督标签是one-hot-vector形式,所以这里要取下标
if t.size == y.size:
t = t.argmax(dim=1)
batch_size = y.shape[0]
#没看懂为啥
return -np.sum(np.log(y[np.arange(batch_size), t] + 1e-7)) / batch_size
class softmaxwithloss:
def __init__(self):
self.params = []
self.grads = []
self.y = none #softmx的输出
self.t = none #监督标签
def forward(self,x,t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
if self.t.size == self.y.size:
self.t = self.t.argmax(axis=1)
loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y,self.t)
return loss
def backward(self,dout =1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
dx = self.y.copy()
dx[np.arange(batch_size),self.t] -= 1
dx *= dout
dx = dx/batch_size
return dx
解释:
🌻三层神经网络类-threelayernet
class threelayernet:
def __init__(self,input_size,hidden_size1,hidden_size2,output_size):
i,h1,h2,o = input_size,hidden_size1,hidden_size2,output_size
#初始化权重和偏置
w1 = 0.01 * np.random.randn(i,h1) #形状:i*h
b1 = np.zeros(h1)
w2 = 0.01 * np.random.randn(h1,h2)
b2 = np.zeros(h2)
w3 = 0.01 * np.random.randn(h2,o)
b3 = np.zeros(o)
#生成层
self.layers = [
affine(w1,b1),
sigmoid(),
affine(w2,b2),
sigmoid(),
affine(w3,b3)
]
#softmax with loss层和其他层的处理方式不同
#所以不将它放在layers列表中,而是单独存储在变量loss_layer中
self.loss_layer = softmaxwithloss()
self.params,self.grads = [],[]
for layer in self.layers:
self.params += layer.params
self.grads += layer.grads
def predict(self,x):
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
def forward(self,x,t):
score = self.predict(x)
loss = self.loss_layer.forward(score,t)
return loss
def backward(self,dout = 1):
dout = self.loss_layer.backward(dout)
for layer in reversed(self.layers):
dout = layer.backward(dout)
return dout
解释:
🌻随机梯度下降法的类-sgd
class sgd:
'''
随机梯度下降法(stochastic gradient descent)
'''
def __init__(self, lr=0.01):
self.lr = lr
def update(self, params, grads):
for i in range(len(params)):
params[i] -= self.lr * grads[i]
解释:
🌻训练过程
#1.设定超参数
max_epoch = 300
batch_size = 30
hidden_size = 10
learning_rate =3.5
#2.读入数据,生成模型和优化器
x,t = load_data()
model = threelayernet(input_size=2,hidden_size1=hidden_size,hidden_size2=hidden_size,output_size=3)
optimizer = sgd(lr=learning_rate)
#学习用的变量
data_size = len(x)
max_iters = data_size // batch_size
total_loss = 0
loss_count = 0
loss_list = []
for epoch in range(max_epoch):
#3.打乱数据
idx = np.random.permutation(data_size)
x = x[idx]
t = t[idx]
for iters in range(max_iters):
batch_x = x[iters*batch_size:(iters+1)*batch_size]
batch_t = t[iters*batch_size:(iters+1)*batch_size]
#4.计算梯度,更新参数
loss = model.forward(batch_x,batch_t)
model.backward()
optimizer.update(model.params,model.grads)
total_loss += loss
loss_count += 1
#5.定期输出学习过程
if (iters+1)%10 == 0:
avg_loss = total_loss / loss_count
print('| epoch %d | iterations %d / %d | loss %0.2f'% (epoch+1,iters + 1,max_iters,avg_loss))
loss_list.append(avg_loss)
total_loss,loss_count = 0,0
解释:
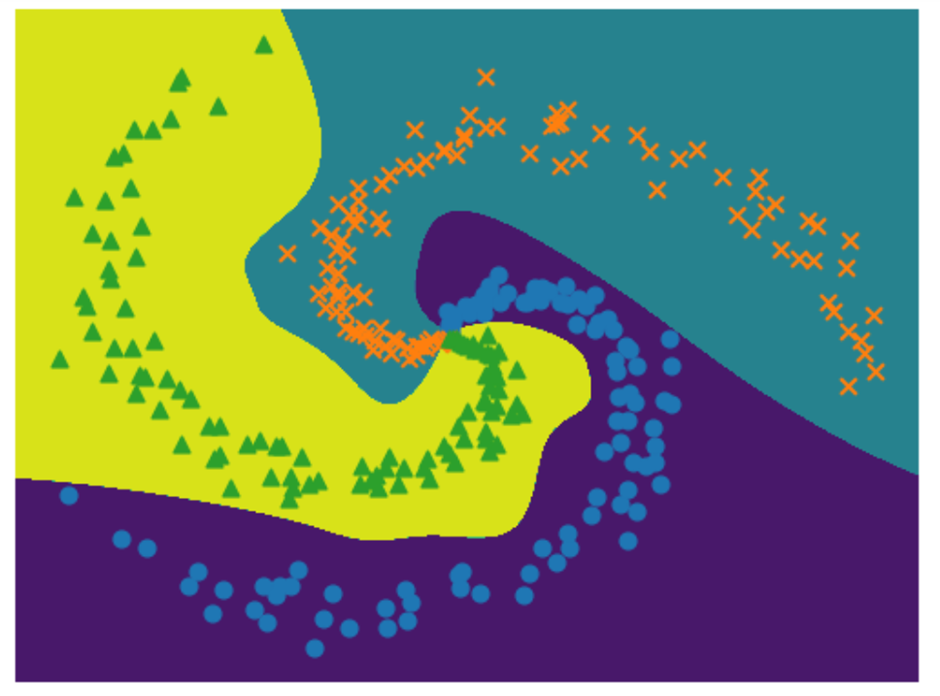
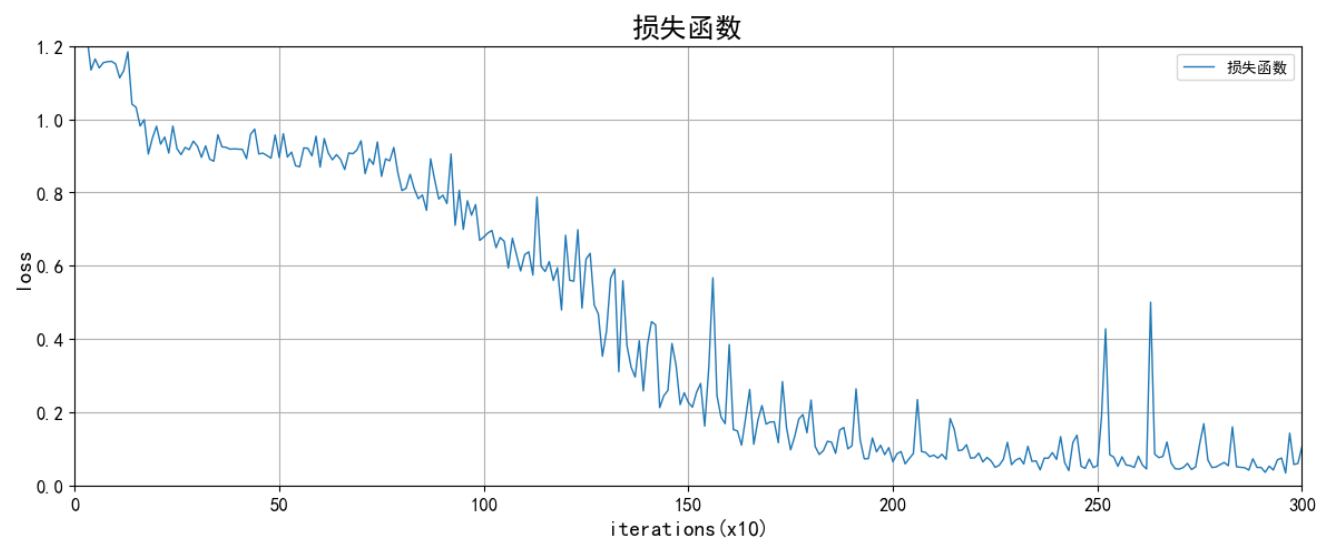
运行迭代300次的结果图如下:


x, t = load_data()
# 绘制数据点
n = 100
cls_num = 3
markers = ['o', 'x', '^']
# 绘制决策边界
h = 0.001
x_min, x_max = x[:, 0].min() - .1, x[:, 0].max() + .1
y_min, y_max = x[:, 1].min() - .1, x[:, 1].max() + .1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
x = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
score = model.predict(x)
predict_cls = np.argmax(score, axis=1)
z = predict_cls.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, z)
for i in range(cls_num):
plt.scatter(x[i*n:(i+1)*n, 0], x[i*n:(i+1)*n, 1], s=40, marker=markers[i])
plt.axis('off') # 是否关闭坐标轴
plt.show()解释:
由此产生的图像可以看到相较于两层神经网络的效果更好,三层神经网络的结果如下所示:

🌻绘制迭代效果图
# loss_list----记录300次迭代次数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#正确显示中文和负号
plt.rcparams['font.sans-serif']=['simhei']
plt.rcparams['axes.unicode_minus']=false
# 数据准备
x3=range(1,301)
y3=loss_list
# 设置画布大小
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
# plot 画x与y和x与z的关系图
plt.plot(x3,y3,label='损失函数',color='#1f77b4', linewidth=1,marker='',markersize=3)
# 设置x轴标签、坐标轴范围,坐标轴刻度,坐标轴刻度旋转角度
plt.xlabel('iterations(x10)',size=14)
plt.xlim(0,300)
plt.xticks([0,50,100,150,200,250,300],rotation=0,size=12) #
# 设置y轴标签、坐标轴范围,坐标轴刻度,坐标轴刻度旋转角度
plt.ylabel('loss',size=14)
plt.ylim(0,1.2)
plt.yticks([0,0.2,0.4,0.6,0.8,1.0,1.2],rotation=0,size=12)
#标题
plt.title('损失函数',size=18)
# 紧凑布局:自动调整图形、坐标轴、标签之间的距离,对于多个子图时尤其有用。
plt.tight_layout()
# 设置显示图例,要在plt.plot 时设置 label='xxx'才能显示图例
plt.legend()
#加网格线
plt.grid(true)
# 保存图像,可以是任意后缀名,dpi设置图像清晰度
#plt.savefig('./fig1.pdf', dpi=600) #要放在plt.show()之前,否作保存的图像为空白
# 显示图像
plt.show()解释:
实验结果如下:
🌞四、实验心得
通过这次实验,我成功创建了一个用于识别螺旋状的数据集三层神经网络,并对深度学习所需的数学知识有了更深入的理解。
一开始,我选择了relu激活函数,但是在调整学习率时无法找到合适的参数。因此改用sigmoid作为激活函数。通过建立三层神经网络,我发现之前适用于两层神经网络的学习率并不适用于三层神经网络,需要重新寻找适合的学习率,而学习率设置得太小会导致学习的收敛速度变慢。
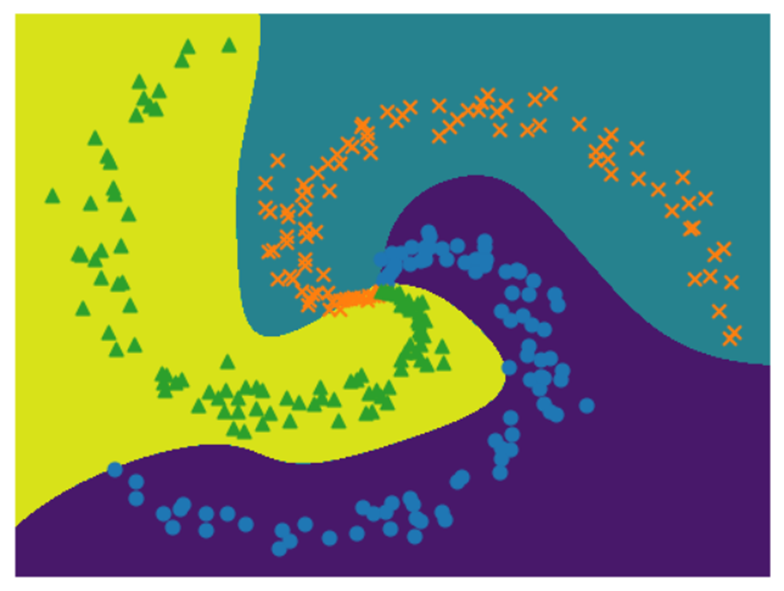
通过对比两层和三层神经网络的训练结果,我发现它们之间存在明显的差异,特别是在中心点区域。这说明增加网络的层数可以更好地拟合复杂的数据集,但也需要仔细调整参数以确保网络的有效训练。
两层神经网络结果:
三层神经网络结果:


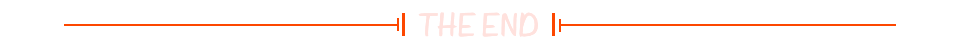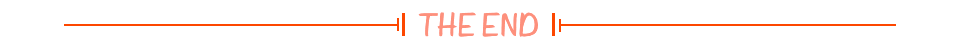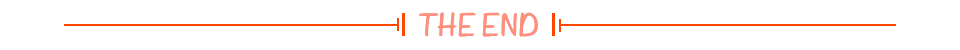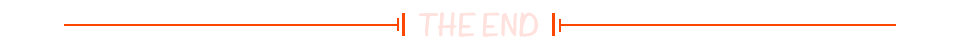


发表评论