栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出lifo(last in first out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
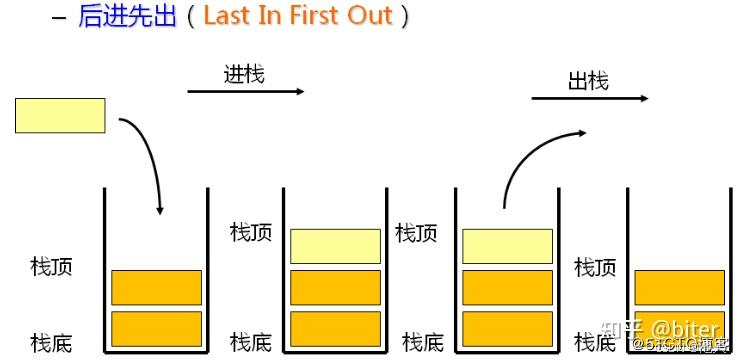
栈的定义
typedef int stdatatype;
typedef struct stack
{
stdatatype* _a;//数组
int _top; // 栈顶,类似顺序表中的_size
int _capacity; // 容量
}stack;对栈的操作
栈初始化
_top可以初始化为0,此时栈顶元素是_top-1的位置
_top也可以初始化为1,此时栈顶元素就是_top的位置
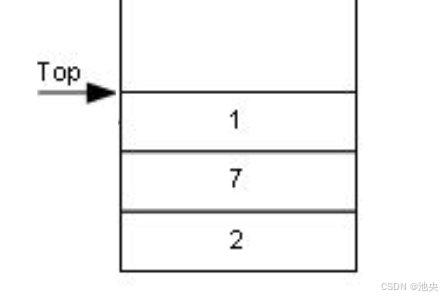
初始化为0
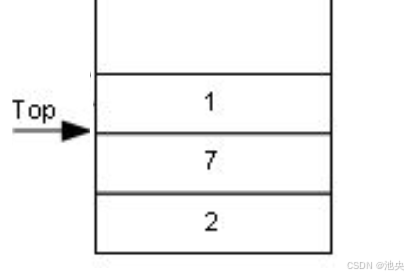
初始化为1
// 初始化栈
void stackinit(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_a = null;
ps->_capacity = 0;
ps->_top = 0;
}压栈(入栈)
// 入栈
void stackpush(stack* ps, stdatatype data)
{
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->_capacity == ps->_top)
{
int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * (ps->_capacity);
stdatatype* tmp = (stdatatype*)realloc(ps->_a, newcapacity * sizeof(stdatatype));
if (tmp == null)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->_a = tmp;
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->_a[ps->_top++] = data;
}出栈
void stackpop(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!stackempty(ps));
ps->_top--;
}取栈顶元素
stdatatype stacktop(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_a[ps->_top-1];
}判断栈是否为空
bool stackempty(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top == 0;
}栈的长度
_top初始化为0,此时的_top的大小刚好就是栈的长度
int stacksize(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top;
}栈销毁
void stackdestroy(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_capacity = ps->_top = 0;
free(ps->_a);
ps->_a = null;
}完整总代码
头文件
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef int stdatatype;
typedef struct stack
{
stdatatype* _a;//数组
int _top; // 栈顶,类似顺序表中的_size
int _capacity; // 容量
}stack;
// 初始化栈
void stackinit(stack* ps);
// 入栈
void stackpush(stack* ps, stdatatype data);
// 出栈
void stackpop(stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
stdatatype stacktop(stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int stacksize(stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool stackempty(stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void stackdestroy(stack* ps);函数定义
#include"stack.h"
// 初始化栈
void stackinit(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_a = null;
ps->_capacity = 0;
ps->_top = 0;
}
// 入栈
void stackpush(stack* ps, stdatatype data)
{
assert(ps);
//扩容
if (ps->_capacity == ps->_top)
{
int newcapacity = ps->_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * (ps->_capacity);
stdatatype* tmp = (stdatatype*)realloc(ps->_a, newcapacity * sizeof(stdatatype));
if (tmp == null)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->_a = tmp;
ps->_capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->_a[ps->_top++] = data;
}
// 出栈
void stackpop(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!stackempty(ps));
ps->_top--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
stdatatype stacktop(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_a[ps->_top-1];
}
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int stacksize(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top;
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool stackempty(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->_top == 0;
}
// 销毁栈
void stackdestroy(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->_capacity = ps->_top = 0;
free(ps->_a);
ps->_a = null;
}测试
#include"stack.h"
void test()
{
stack s;
stackinit(&s);
stackpush(&s, 1);
stackpush(&s, 2);
stackpush(&s, 3);
stackpush(&s, 4);
while (stacksize(&s)>0)
{
printf("%d ", stacktop(&s));
stackpop(&s);
}
stackdestroy(&s);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}到此这篇关于c语言实现数组栈的代码示例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c语言数组栈内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论