java实现n叉树数据结构
package maximumdepthnarytreenew;
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.linkedlist;
import java.util.queue;
// class representing node of n-ary tree
class node {
int val;
arraylist<node> children;
public node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.children = new arraylist<>();
}
}
class numberofsiblingsofagivennodeinnarytree {
public static int maxdepth(node root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
int max = 0;
for (node n : root.children) {
max = math.max(max, maxdepth(n));
}
return max + 1;
}
private static int siblings(node root, int target) {
// if the given node is equals to the root or root is null, return 0
if (root == null || root.val == target) {
return 0;
}
// create a queue of nodes
queue<node> queue = new linkedlist<>();
// push the root to queue
queue.add(root);
// do a bfs of the tree
while (!queue.isempty()) {
// remove one element from the queue
node curr = queue.poll();
// traverse its children
for (int i = 0; i < curr.children.size(); i++) {
// current child
node currchild = curr.children.get(i);
// if current child is the target, return (parent's children count - 1)
if (currchild.val == target) {
return (curr.children.size() - 1);
}
// add the child to the queue
queue.add(currchild);
}
}
// if there is no match, return -1
return -1;
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
// example n-ary tree
node root = new node(51);
// children of 51
root.children.add(new node(10));
root.children.add(new node(41));
root.children.add(new node(6));
root.children.add(new node(32));
// children of 10
root.children.get(0).children.add(new node(53));
// children of 41
root.children.get(1).children.add(new node(95));
// children of 6
root.children.get(2).children.add(new node(28));
// children of 32
root.children.get(3).children.add(new node(9));
root.children.get(3).children.add(new node(11));
// children of 53
root.children.get(0).children.get(0).children.add(new node(5));
root.children.get(0).children.get(0).children.add(new node(7));
// children of 11
root.children.get(3).children.get(1).children.add(new node(3));
root.children.get(3).children.get(1).children.add(new node(8));
system.out.println(siblings(root, 10));
system.out.println(siblings(root, 11));
system.out.println(maxdepth(root));
}
}n叉树的结点定义
n叉树
public class treenode{
public int data;
public treenode firstchild;
public treenode secondchild;
public treenode thirdchild;
...
...
}
由于并不是在所有的情况下都需要使用所有的指针,所以将导致大量的内存浪费,此外,另外一个问题是事先不知道节点个数
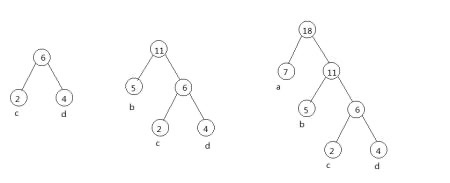
n叉树的表示
因为需要遍历树中的所有节点,所以一种可能的解决方法是:
1.同一个双亲节点(兄弟)孩子节点从左至右排列
2.双亲节点只能指向第一个孩子节点,删除从双亲节点到其他孩子节点的指针链接,
上述的具体含义是,如果孩子节点之间有一条链路相连,那么双亲节点就不需要额外的指针指向所有的孩子节点。这是因为从双亲节点的第一个孩子节点开始就能够遍历所有节点,因此,只要双亲节点用一个指针指向其第一个孩子节点,且同一个双亲节点的所有孩子之间都有链路,就可以解决上述问题
代码定义表示
public class treenode{
public int data;
public treenode firstchild;
public treenode nextsibling;
public int getdata(){
return data;
}
public void setdata(int data){
this.data = data;
}
public binarytreenode getfirstchild(){
return firstchild;
}
public void setfirstchild(binarytreenode firstchild){
this.firstchild = firstchild;
}
public binarytreenode getnextsibling(){
return nextsibling;
}
public void setnextsibling(binarytreenode nextsib ling){
this.nextsibling = nextsibling;
}
}
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。







发表评论