js判断文件类型详解
通过file的type属性判断
<input type="file" onchange="onchangecb(this)" />
<script>
function onchangecb(e) {
const file = e.files[0];
console.log(file.type);
}
</script>
像html中input标签,就是根据选择文件的后缀来生成一个file对象。
像下面的几种文件:
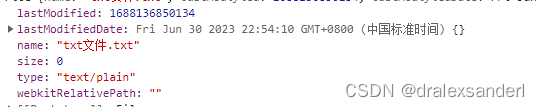
txt文件:
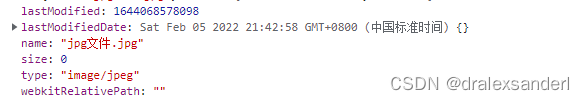
jpg文件:
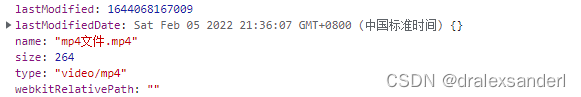
mp4文件:
使用文件后缀来判断
function onchangecb(e) {
const file = e.files[0];
//获取最后一个.的位置
const index= file.name.lastindexof(".");
//获取后缀
const ext = file.name.substr(index+1);
console.log(ext);
}
在得到文件后缀名后,根据后缀即可判断文件的类型(文件格式)。比如需要判断一个文件是否是图片格式,首先定义一个判断函数:
function isimage(ext) {
return [
'png', 'jpg', 'jpeg', 'bmp', 'gif', 'webp', 'psd', 'svg', 'tiff'].
indexof(ext.tolowercase()) !== -1;
}
虽然可以直接通过对象的type属性或者文件后缀来获取文件类型,但是如果强行修改文件后缀,同样可以将其他类型的文件上传至服务器,或者文件压根就没有后缀,那又要怎么判断呢?因此前端需要使用一个更加合理的方式。
根据二进制流及文件头来判断
虽然文件后缀可以手动改,因此可以直接通过读取文件的二进制来判断。
通常来说固定类型的文件头都是相同的,比如说jpeg的文件头是ff d8 ff e0。
这里提供一些常用的文件头:
const filemap = {
jpeg: "ff d8 ff e0",
jpg: "ff d8 ff e1",
png: "89 50 4e 47",
gif: "47 49 46 38",
tiff: "49 49 2a 00",
bmp: "42 4d",
dwg: "41 43 31 30",
psd: "38 42 50 53",
rtf: "7b 5c 72 74 66",
xml: "3c 3f 78 6d 6c",
html: "68 74 6d 6c 3e",
eml: "44 65 6c 69 76 65 72 79 2d 64 61 74 65 3a",
dbx: "cf ad 12 fe c5 fd 74 6f",
pst: "21 42 44 4e",
xls: "d0 cf 11 e0",
doc: "d0 cf 11 e0",
mdb: "53 74 61 6e 64 61 72 64 20 4a",
wpd: "ff 57 50 43",
pdf: "25 50 44 46 2d 31 2e",
qdf: "ac 9e bd 8f",
pwl: "e3 82 85 96",
zip: "50 4b 03 04",
rar: "52 61 72 21",
wav: "57 41 56 45",
avi: "41 56 49 20",
ram: "2e 72 61 fd",
rm: "2e 52 4d 46",
mpg: "00 00 01 ba",
mpg: "00 00 01 b3",
mov: "6d 6f 6f 76",
asf: "30 26 b2 75 8e 66 cf 11",
mid: "4d 54 68 64",
mp3: "49 44 33",
};
通过onchange方法获取到选择的文件后,使用filereader读取文件的二进制,之后判断二进制的前几位是否跟符合相应类型文件的文件头。
以下是一些使用文件头来判断文件类型的简单代码
// 判断文件后缀与该文件内容是否相同类型
async function issamefiletype(file) {
const suffix = getfilesuffix(file.name).touppercase();
const fileblobstring = await blobtostring(file.slice(0, 14));
// 如果文件类型中没有该类型,默认为false
if (!(suffix in filemap)) {
return false;
}
return fileblobstring.includes(filemap[suffix]);
}
async function blobtostring(blob) {
return new promise((resolve) => {
const reader = new filereader();
reader.onload = function () {
const ret = reader.result
.split("") // 分隔开
.map((v) => v.charcodeat()) // 循环返回指定位置的字符的 unicode 编码
.map((v) => v.tostring(16).touppercase()) // 返回十六进制格式
.map((v) => v.padstart(2, "0")) // 给空的那个填充 00 ,防止空缺
.join(" "); // 每个子节之间空格隔开
resolve(ret);
};
reader.readasbinarystring(blob); // 调用之后触发onload事件
});
// 二进制=》ascii码=》转成16进制字符串
}
// 获取文件后缀
function getfilesuffix(filename) {
return filename.substring(filename.lastindexof(".") + 1, filename.length);
}
判断是否是png类型:
async function ispng(file) {
// 同理
const ret = await blobtostring(file.slice(0, 4));
const ispng = ret === filemap.png;
return ispng;
}
当然也可以针对图片高宽进行限制:
在png二进制中,第18-20位是图片的宽,22-24是高。
获取图片宽高:
function getrectbyoffset(file, widthoffset, heightoffset, reverse) {
let width = await blobtostring(file.slice(...widthoffset));
let height = await blobtostring(file.slice(...heightoffset));
const w = parseint(width.replace(" ", ""), 16);
const h = parseint(height.replace(" ", ""), 16);
return { w, h };
}
修改一下之前判断ispng的方法,加上高宽限制
const img_width_limit = 1000;
const img_height_limit = 800
function ispng(file) {
// 同理
const ret = await this.blobtostring(file.slice(0, 4));
const ispng = ret === filemap.png;
if (ispng) {
const { w, h } = await this.getrectbyoffset(file, [18, 20], [22, 24]);
console.log(`png 宽高 ${w},${h}`);
if (w > img_width_limit || h > img_height_limit) {
this.$message.error(
"png图片宽高不得超过 " + img_width_limit + "和" + img_height_limit
);
return false;
}
}
return ispng;
}附:js已知文件路径,通用获取文件名、后缀、类型
代码参考
// 选择文件后返回 { resultdata: '/storage/emulated/0/dcim/camera/img_20170703_133717.jpg' }
var path ='/storage/emulated/0/dcim/camera/img_20170703_133717.jpg' ;
var filename = common.getfilenamebypath(path); // .jpg
console.log("文件名="+filename);
var filetype=common.getfiletypebypath(path); // jpg
console.log("文件类型="+filetype);
var fileextension=common.getfileextensionbypath(path); // .jpg
console.log("文件后缀="+fileextension);
核心代码
/**
* 作者: 丸子
* 描述: 自定义工具
*/
'use strict';
window.common = window.common || (function(exports) {
/*
* 已知文件路径,获取文件名xxx.doc
*/
exports.getfilenamebypath = function(path) {
var index = path.lastindexof("/"); // lastindexof("/") 找到最后一个 / 的位置
var filename = path.substr(index + 1); // substr() 截取剩余的字符,即得文件名xxx.doc
return filename;
};
/*
* 已知文件路径,获取文件类型doc
*/
exports.getfiletypebypath = function(path) {
var index = path.lastindexof("."); // lastindexof("/") 找到最后一个 / 的位置
var filetype = path.substr(index + 1); // substr() 截取剩余的字符,即文件名doc
return filetype;
};
/*
* 已知文件路径,获取文件后缀.doc
*/
exports.getfileextensionbypath = function(path) {
var index1 = path.lastindexof("."); // lastindexof("/") 找到最后一个 / 的位置
var index2 = path.length;
var fileextension = path.substr(index1, index2); // substr() 截取剩余的字符,即文件名.doc
return fileextension;
};
return exports;
})({});
总结
到此这篇关于javascript判断文件类型三种方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关js判断文件类型内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论