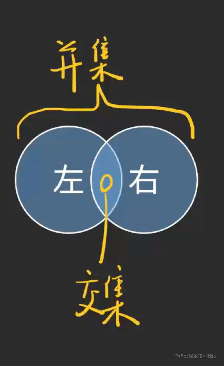
一. ts类型系统中的交叉类型(交集)
type a = string & number; // never, 一般我们都不会把交集用在基本类型,而是用在对象上
type 有右手的人 = {
right: string;
};
type c = 有左手的人 | 有右手的人;
type d = 有左手的人 & 有右手的人;
const d: d = {
left: 'yes', // 会报错,缺少right
};
二. 有左手的人能否有右手
// 场景一. 直接初始化赋值
type 有左手的人 = {
left: string;
};
const a: 有左手的人 = {
left: '一米八',
right: '一米五', // 这么写会报错
};
// 场景二. 先声明好对象,再赋值
type 有左手的人 = {
left: string;
};
const b = {
left: '一米八',
right: '一米五',
};
const a: 有左手的人 = b; // 这么写不报错小结
场景一中的直接对象字面量声明会触发属性匹配验证,而场景二中的先声明变量再赋值的方式会绕过这种验证,因此不会报错。
三. 接口也能求交集
interface colorful {
color: string;
}
interface circle {
radius: number;
}
type colorfulcircle = colorful & circle;
const cc: colorfulcircle = {
color: 'red',
radius: 11,
};四. 使用&模拟继承
type person = {
name: string;
age: number;
};
type user = person & {
id: number;
email: string;
};
const u: user = {
name: 'jack',
age: 18,
id: 1,
email: 'jack@alibaba.com',
};五. 使用&时属性冲突的场景
会求交集
// 场景一
type person = {
name: string;
age: number;
id: string;
};
type user = person & {
id: number;
email: string;
};
const u: user = {
name: 'jack',
age: 18,
id: 1 as never, // 这个变成了never,且必须存在
email: 'jack@alibaba.com',
};
// 场景二 user是never, 这是一种特殊的场景
type person = {
id: 'a';
name: string;
age: number;
};
type user = person & {
id: 'b';
email: string;
};六. interface遇到冲突会如何
interface person {
id: string;
name: string;
}
// 会报错 接口“user”错误扩展接口“person”。属性“id”的类型不兼容。不能将类型“number”分配给类型“string”。
interface user extends person {
id: number;
email: string;
}这里也可以看出,当我们去写一些可扩展的类型的时候interface会更好,如果写的不合逻辑,在写类型的瞬间就会报错,如果用type只会给你搞出一个never,当你用到的时候才会发现有问题
七. 对函数类型的取交集
两个函数类型求交集,最终会得到参数取并集,这个之后会详细讲,这里先看一下结论
type a = {
method: (a: number) => void;
};
type b = {
method: (a: string) => void;
} & a;
const b: b = {
method(a) {
a; // number | string
},
};总结
交叉类型常用于有交集的类型a,b。如果a,b无交集可能会得到never,也有可能是属性为never。
以上就是typescript 交叉类型使用方法示例总结的详细内容,更多关于typescript 交叉类型的资料请关注代码网其它相关文章!







发表评论