1. 什么是缓存
缓存(cache) 就是数据交换的缓冲区,是存贮数据的临时地方,一般读写性能较高。
缓存的作用:
- 降低后端负载
- 提高读写效率,降低响应时间
缓存的成本:
- 数据一致性成本
- 代码维护成本
- 运维成本
2. 添加 redis 缓存
2.1 缓存工作模型
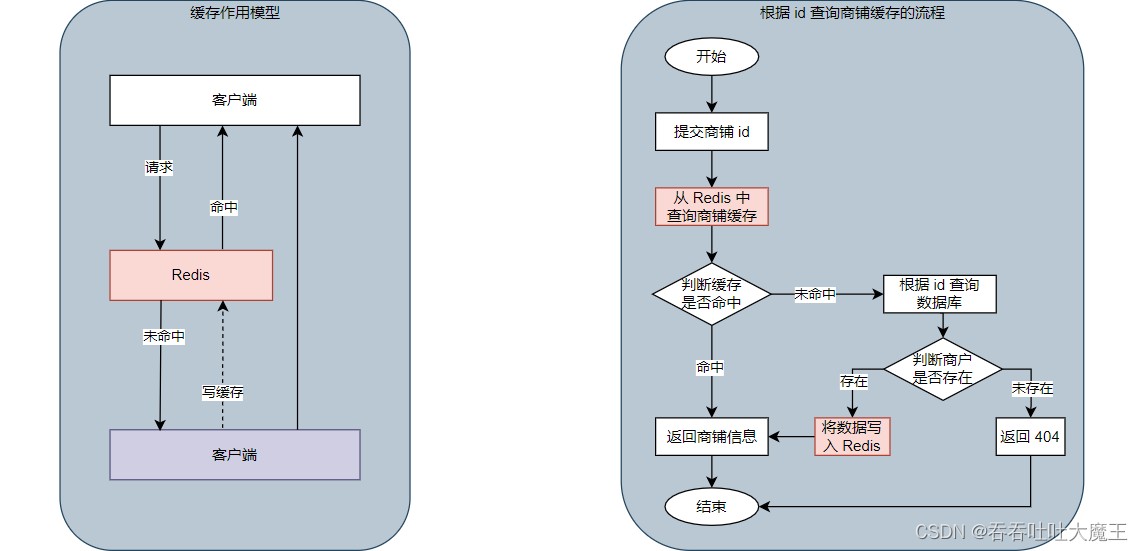
2.2 代码实现
前端请求说明:
| 说明 | |
|---|---|
| 请求方式 | post |
| 请求路径 | /shop/id |
| 请求参数 | id |
| 返回值 |
后端接口实现:
@service
public class shopserviceimpl extends serviceimpl<shopmapper, shop> implements ishopservice {
@resource
private stringredistemplate stringredistemplate;
@override
public result queryshopbyid(long id) {
string key = "cache:shop:" + id;
// 1. 从 redis 查询商铺缓存
string shopjson = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
// 2. 判断是否存在
if(!strutil.isblank(shopjson)) {
// 3. 存在,直接返回
shop shop = jsonutil.tobean(shopjson, shop.class);
return result.ok(shop);
}
// 4. 不存在,根据 id 查询数据库
shop shop = getbyid(id);
// 5. 不存在,返回错误
if(shop == null){
return result.fail("店铺不存在!");
}
// 6. 存在,写入 redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, jsonutil.tojsonstr(shop));
// 7. 返回
return result.ok(shop);
}
}
3. 缓存更新策略
3.1 缓存更新策略类型
| 缓存更新策略 | 内存淘汰 | 超时剔除 | 主动更新 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 不用自己维护,利用 redis 的内存淘汰机制,当内存不足时自动淘汰部分数据,下次查询时更新缓存。 | 给缓存数据添加 ttl 时间,到期后自动删除缓存。下次查询时更新缓存。 | 编写业务逻辑,在修改数据库的同时,更新缓存。 |
| 一致性 | 差 | 一般 | 好 |
| 维护成本 | 无 | 低 | 高 |
业务场景:
- 低一致性:使用内存淘汰机制。
- 高一致性:主动更新,并以超时剔除作为兜底方案。
3.2 主动更新策略
| 方式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| cache aside pattern | 由缓存的调用者,在更新数据库的同时更新缓存。 |
| read/write through pattern | 缓存与数据库整合为一个服务,由服务来维护一致性。调用者调用该服务,无需关心缓存一致性问题。 |
| write behind caching pattern | 调用者只操作缓存,由其它线程异步的将缓存持久化到数据库,保证最终一致性。 |
这里推荐使用 cache aside pattern,但操作缓存和数据库时有三个问题需要考虑:
删除缓存还是更新缓存?
- 更新缓存:每次更新数据库都更新缓存,无效写操作较多。
- 删除缓存(推荐):更新数据库时让缓存失效,查询时再更新缓存。
如何保证缓存与数据库的操作的同时成功或失败?
- 单体系统:将缓存与数据库操作放在一个事务。
- 分布式系统:利用 ttc 等分布式事务方案。
先操作缓存还是先操作数据库?
- 先删除缓存,再操作数据库。(问题:当一个线程进行修改操作时,先删除了缓存,然后另一个线程读取,读取不到缓存便读取数据库,然后更新缓存,更新的是旧的数据库的值,最后第一个线程又更新数据库,导致数据库和缓存不一致。这种问题出现的概率比较高。
- 先操作数据库,再删除缓存。(推荐。问题:当一个线程读取时正好缓存过期,那么将读取到数据库的数据,然后另一个线程进入进行修改操作,修改数据库后,将缓存删除。最后第一个线程将之前读取的数据写入缓存,就会造成数据库和缓存不一致。但读取缓存是微秒级的并又正好碰上缓存过期,因此该问题的概率很小。)
小结:
- 读操作:缓存命中直接返回;缓存未命中则查询数据库,并写入缓存,设定超时时间。
- 写操作:先写数据库,然后再删缓存。要确保数据库与缓存操作的原子性。
3.3 超时剔除和主动更新缓存实现
后端接口实现:
通过 id 查询店铺时,如果缓存未命中,则查询数据库,将数据库写入缓存,并设置超时时间。
@service
public class shopserviceimpl extends serviceimpl<shopmapper, shop> implements ishopservice {
@resource
private stringredistemplate stringredistemplate;
@override
public result queryshopbyid(long id) {
string key = "cache:shop:" + id;
// 1. 从 redis 查询商铺缓存
string shopjson = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
// 2. 判断是否存在
if(!strutil.isblank(shopjson)) {
// 3. 存在,直接返回
shop shop = jsonutil.tobean(shopjson, shop.class);
return result.ok(shop);
}
// 4. 不存在,根据 id 查询数据库
shop shop = getbyid(id);
// 5. 不存在,返回错误
if(shop == null){
return result.fail("店铺不存在!");
}
// 6. 存在,写入 redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, jsonutil.tojsonstr(shop));
stringredistemplate.expire(key, 30, timeunit.minutes);
// 7. 返回
return result.ok(shop);
}
}
通过 id 修改店铺时,先修改数据库,再删除缓存。
@service
public class shopserviceimpl extends serviceimpl<shopmapper, shop> implements ishopservice {
@resource
private stringredistemplate stringredistemplate;
@override
@transactional
public result updateshop(shop shop) {
long id = shop.getid();
if(id == null){
return result.fail("店铺 id 不能为空!");
}
// 1. 更新数据库
updatebyid(shop);
// 2. 删除缓存
stringredistemplate.delete("cache:shop:" + id);
return result.ok();
}
}
4. 缓存穿透
4.1 基本介绍
缓存穿透 是指客户端请求的数据在缓存中和数据库中都不存在,这样缓存永远不生效,这些请求都会打到数据库。(如果不断发起这样的请求,会给数据库带来巨大压力)
常见解决方案:
| 方案 | 描述 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 缓存空对象 | 如果请求的数据缓存不存在,并且数据库也不存在,数据库将给缓存更新个空对象。 | 实现简单,维护方便。 | 额外的内存消耗,可能造成短期的不一致。 |
| 布隆过滤器 | 内存占用较少,没有多余 key | 实现复杂,存在误判可能 | |
| 增强 id 的复杂度,避免被猜测 id 规律 | |||
| 做好数据的基础格式校验 | |||
| 做好热点参数的限流 |
4.2 通过缓存空对象解决缓存穿透问题
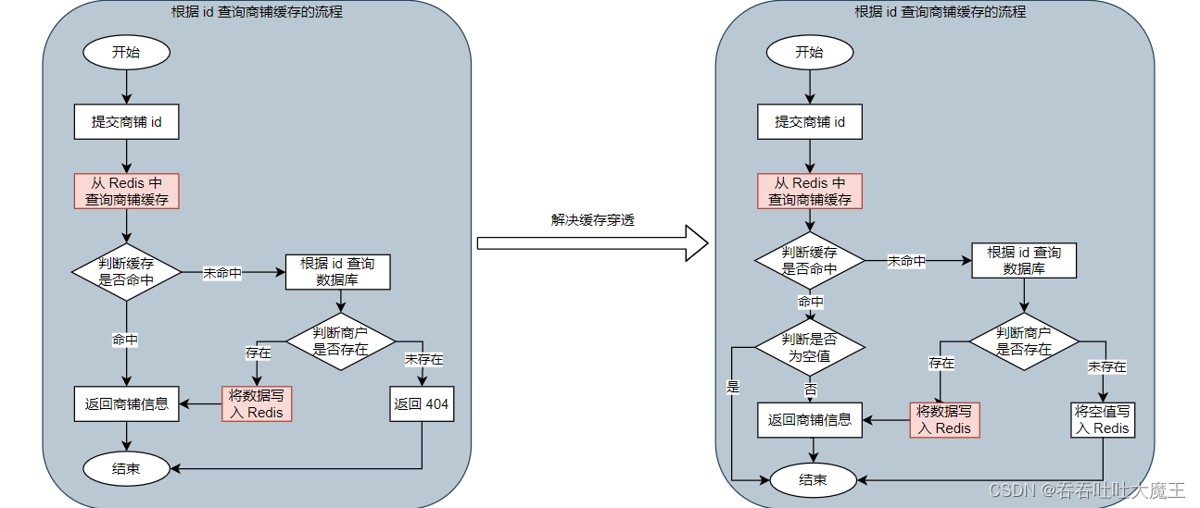
代码实现:
public shop querywithpassthrough(long id) {
string key = "cache:shop:" + id;
// 1. 从 redis 查询商铺缓存
string shopjson = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
// 2. 判断是否存在
if (!strutil.isblank(shopjson)) {
// 3. 存在,直接返回
return jsonutil.tobean(shopjson, shop.class);
}
// 判断命中的是否为空值
if (shopjson != null) {
return null;
}
// 4. 不存在,根据 id 查询数据库
shop shop = getbyid(id);
// 5. 不存在,返回错误
if (shop == null) {
// 将空值写入 redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, "", 2, timeunit.minutes);
// 返回错误信息
return null;
}
// 6. 存在,写入 redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, jsonutil.tojsonstr(shop));
stringredistemplate.expire(key, 30, timeunit.minutes);
// 7. 返回
return shop;
}
5. 缓存雪崩
缓存雪崩 是指在同一时段大量的缓存 key 同时失效或者 redis 服务宕机,导致大量请求到达数据库,带来巨大压力。
解决方案:
- 给不同的 key 的 ttl 添加随机值
- 利用 redis 集群提高服务的可用性
- 给缓存业务添加降级限流策略
- 给业务添加多级缓存
6. 缓存击穿
6.1 基本介绍
缓存击穿 问题也叫热点 key 问题,就是一个被高并发访问并且缓存重建业务较复杂的 key 突然失效了,无数的请求访问会在瞬间给数据库带来巨大的冲击。
常见解决方案:
| 解决方案 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 互斥锁 | 没有额外的内存消耗;保证一致性;实现简单 | 线程需要等待,性能受影响;可能有死锁风险 |
| 逻辑过期 | 线程无需等待,性能较好 | 不保证一致性;有额外内存消耗;实现复杂 |
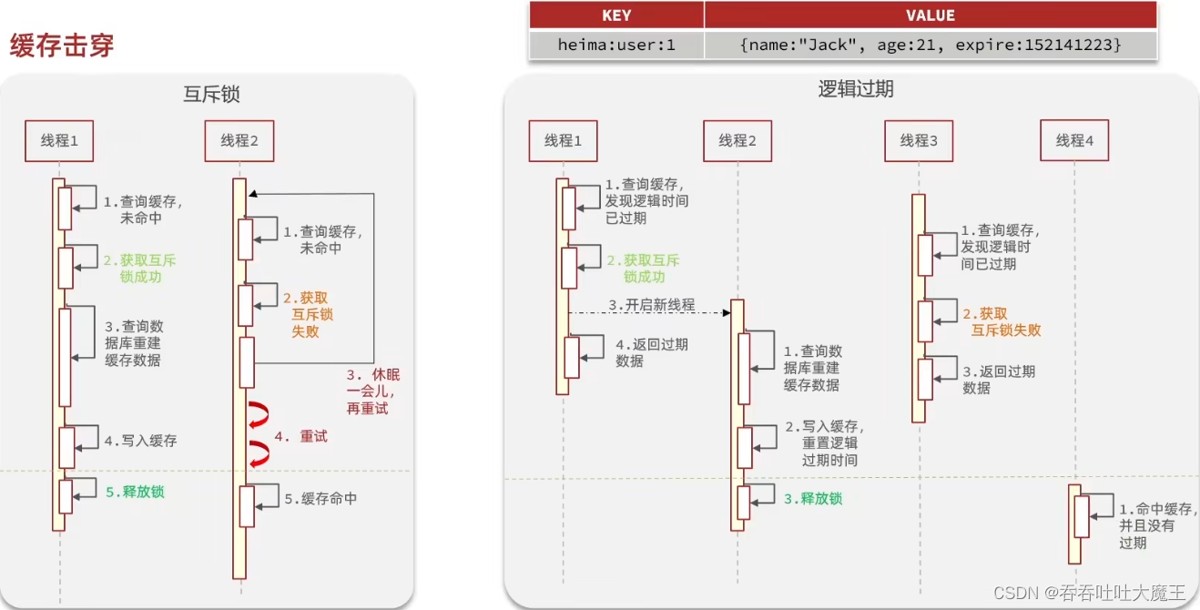
6.2 基于互斥锁方式解决缓存击穿问题
这里通过 redis 中的 setnx 命令去自定义一个互斥锁,通过 del 命令去删除这个 key 来解锁。
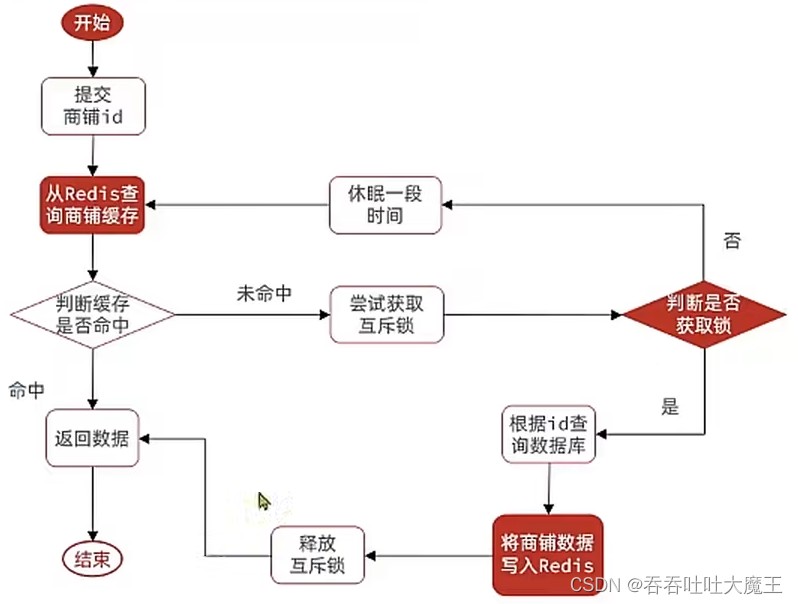
自定义尝试获取锁和释放锁实现
// 尝试获取锁
private boolean trylock(string key){
boolean flag = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().setifabsent(key, "1", 10, timeunit.seconds);
// 拆箱过程可能有空值
return booleanutil.istrue(flag);
}
// 释放锁
private void unlock(string key){
stringredistemplate.delete(key);
}
业务逻辑实现:
@override
public result queryshopbyid(long id) {
// 互斥锁缓存击穿
shop shop = querywithmutex(id);
if(shop == null){
result.fail("店铺不存在!");
}
// 7. 返回
return result.ok(shop);
}
// 互斥锁存击穿
public shop querywithmutex(long id){
string key = "cache:shop:" + id;
// 1. 从 redis 查询商铺缓存
string shopjson = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
// 2. 判断是否存在
if(!strutil.isblank(shopjson)) {
// 3. 存在,直接返回
return jsonutil.tobean(shopjson, shop.class);
}
// 判断命中的是否为空值
if(shopjson != null ){
return null;
}
// 4. 实现缓存重建
// 4.1 获取互斥锁
string lockkey = "lock:shop:" + id;
shop shop = null;
try {
boolean islock = trylock(lockkey);
// 4.2 判断是否获取成功
if(!islock) {
// 4.3 失败,则休眠并重试
thread.sleep(50);
return querywithmutex(id);
}
// 4.4 成功,则根据 id 查询数据库
shop = getbyid(id);
// 5. 不存在,返回错误
if(shop == null){
// 将空值写入 redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, "", 2, timeunit.minutes);
// 返回错误信息
return null;
}
// 6. 存在,写入 redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, jsonutil.tojsonstr(shop));
stringredistemplate.expire(key, 30, timeunit.minutes);
// 7. 释放互斥锁
unlock(lockkey);
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
}
// 8. 返回
return shop;
}
6.3 基于逻辑过期方式解决缓存击穿问题
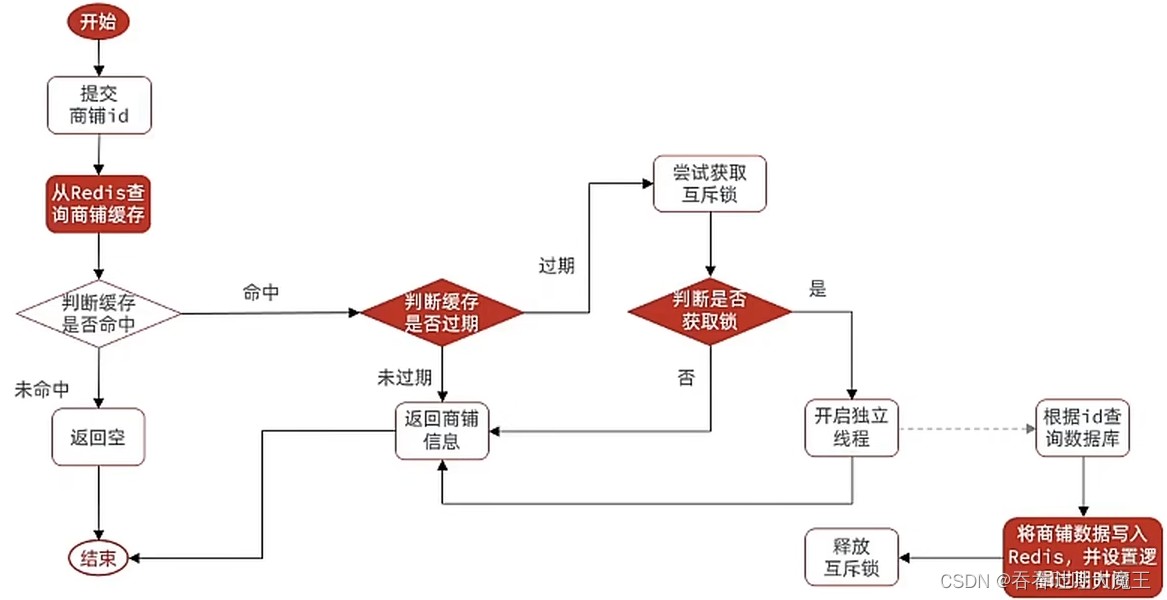
在不修改原有实体类的情况下,可以新定义一个类用来保存原有的数据并添加逻辑过期时间
@data
public class redisdata {
// 逻辑过期时间
private localdatetime expiretime;
// 要存储到 redis 中的数据
private object data;
}
将店铺数据和逻辑过期时间封装并保存到 redis 中
public void saveshop2redis(long id, long expireseconds){
// 1. 查询店铺数据
shop shop = getbyid(id);
// 2. 封装逻辑过期时间
redisdata redisdata = new redisdata();
redisdata.setdata(shop);
redisdata.setexpiretime(localdatetime.now().plusseconds(expireseconds));
// 3. 写入 redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set("cache:shop:" + id, jsonutil.tojsonstr(redisdata));
}
业务实现:
// 定义线程池
private static final executorservice cache_rebuild_executor = executors.newfixedthreadpool(10);
// 基于逻辑过期缓存穿透
public shop querywithlogicalexpire(long id) {
string key = "cache:shop:" + id;
// 1. 从 redis 查询商铺缓存
string shopjson = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
// 2. 判断是否存在
if (strutil.isblank(shopjson)) {
// 3. 不存在,直接返回
return null;
}
// 4. 命中,需要吧 json 反序列化为对象
redisdata redisdata = jsonutil.tobean(shopjson, redisdata.class);
localdatetime expiretime = redisdata.getexpiretime();
// 因为 data 类型为 object,并不知道为 shop,这里会转成 jsonobject
jsonobject data = (jsonobject) redisdata.getdata();
shop shop = jsonutil.tobean(data, shop.class);
// 5. 判断是否过期
if (expiretime.isafter(localdatetime.now())) {
// 5.1 未过期,直接返回店铺信息
return shop;
}
// 5.2 已过期,需要缓存重建
// 6. 缓存重建
// 6.1 获取互斥锁
string lockkey = "lock:shop:" + id;
boolean islock = trylock(lockkey);
// 6.2 判断是否获取锁成功
if (islock) {
// 6.3 成功,开启独立线程,实现缓存重建
cache_rebuild_executor.submit(() -> {
// 重建缓存
this.saveshop2redis(id, 1800l);
// 释放锁
unlock(lockkey);
});
}
// 6.4 返回过期的店铺信息
return shop;
}
7. 缓存工具封装
接下来将对以下四个方法进行封装:
- 将任意 java 对象序列化为 json 并存储在 string 类型的 key 中,并可以设置 ttl 过期时间
- 将任意 java 对象序列化为 json 并存储在 string 类型的 key 中,并可以设置逻辑过期时间,用于处理缓存击穿问题
- 根据指定的 key 查询缓存,并反序列化为指定类型,利用缓存空值的方式解决缓存穿透问题
- 根据指定的 key 查询缓存,并反序列化为指定类型,利用逻辑过期解决缓存击穿问题
@slf4j
@component
public class cacheclient {
private final stringredistemplate stringredistemplate;
public cacheclient(stringredistemplate stringredistemplate) {
this.stringredistemplate = stringredistemplate;
}
// 将任意 java 对象序列化为 json 并存储在 string 类型的 key 中,并可以设置 ttl 过期时间
public void set(string key, object value, long time, timeunit unit) {
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, jsonutil.tojsonstr(value), time, unit);
}
// 将任意 java 对象序列化为 json 并存储在 string 类型的 key 中,并可以设置逻辑过期时间,用于处理缓存击穿问题
public void setwithlogicalexpire(string key, object value, long time, timeunit unit) {
// 设置逻辑过期
redisdata redisdata = new redisdata();
redisdata.setdata(value);
redisdata.setexpiretime(localdatetime.now().plusseconds(unit.toseconds(time)));
// 写入 redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, jsonutil.tojsonstr(redisdata));
}
// 根据指定的 key 查询缓存,并反序列化为指定类型,利用缓存空值的方式解决缓存穿透问题
public <r, id> r querywithpassthrough(
string keyprefix, id id, class<r> type, function<id, r> dbfallback, long time, timeunit unit) {
string key = keyprefix + id;
// 1. 从 redis 查询商铺缓存
string json = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
// 2. 判断是否存在
if (!strutil.isblank(json)) {
// 3. 存在,直接返回
return jsonutil.tobean(json, type);
}
// 判断命中的是否为空值
if (json != null) {
return null;
}
// 4. 不存在,根据 id 查询数据库
r r = dbfallback.apply(id);
// 5. 不存在,返回错误
if (r == null) {
// 将空值写入 redis
stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().set(key, "", 2, timeunit.minutes);
// 返回错误信息
return null;
}
// 6. 存在,写入 redis
this.set(key, r, time, unit);
// 7. 返回
return r;
}
// 根据指定的 key 查询缓存,并反序列化为指定类型,利用逻辑过期解决缓存击穿问题
// 定义线程池
private static final executorservice cache_rebuild_executor = executors.newfixedthreadpool(10);
// 尝试获取锁
private boolean trylock(string key) {
boolean flag = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().setifabsent(key, "1", 10, timeunit.seconds);
// 拆箱过程可能有空值
return booleanutil.istrue(flag);
}
// 释放锁
private void unlock(string key) {
stringredistemplate.delete(key);
}
// 基于逻辑过期缓存穿透
public <r, id> r querywithlogicalexpire(
string keyprefix1, string keyprefix2, id id, class<r> type, function<id, r> dbfallback, long time, timeunit unit) {
string key = keyprefix1 + id;
// 1. 从 redis 查询商铺缓存
string json = stringredistemplate.opsforvalue().get(key);
// 2. 判断是否存在
if (strutil.isblank(json)) {
// 3. 不存在,直接返回
return null;
}
// 4. 命中,需要吧 json 反序列化为对象
redisdata redisdata = jsonutil.tobean(json, redisdata.class);
localdatetime expiretime = redisdata.getexpiretime();
// 因为 data 类型为 object,并不知道为 shop,这里会转成 jsonobject
jsonobject data = (jsonobject) redisdata.getdata();
r r = jsonutil.tobean(data, type);
// 5. 判断是否过期
if (expiretime.isafter(localdatetime.now())) {
// 5.1 未过期,直接返回店铺信息
return r;
}
// 5.2 已过期,需要缓存重建
// 6. 缓存重建
// 6.1 获取互斥锁
string lockkey = keyprefix2 + id;
boolean islock = trylock(lockkey);
// 6.2 判断是否获取锁成功
if (islock) {
// 6.3 成功,开启独立线程,实现缓存重建
cache_rebuild_executor.submit(() -> {
try {
// 重建缓存
// 查询数据库
r r1 = dbfallback.apply(id);
// 写入 redis
this.setwithlogicalexpire(key, r1, time, unit);
} catch (exception e) {
throw new runtimeexception(e);
} finally {
// 释放锁
unlock(lockkey);
}
});
}
// 6.4 返回过期的店铺信息
return r;
}
}
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持代码网。






发表评论