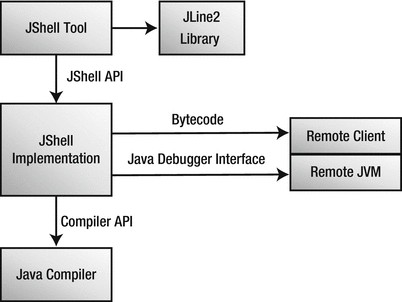
repl,全称read eval print loop,中文是交互式解释器,其实,就是一种代码所见即所得的即时编译器。
java 9引入了repl,并将其命令为jshell,这真是我们java开发的福音,以后演示代码的时候再也不用搬着一个ide到处跑了。
对于我们java开发者来说,应该是java 9带来的最大的个性吧。我们终于可以像python、ruby和node.js那样在shell可见即可得的运行一些范例代码了。
也就是说,使用repl,我们可以编写和测试基于java的逻辑,无需使用javac进行编译,直接查看计算结果。
jshell的主要特性
- 交互式编程:jshell提供了一个交互式环境,允许用户输入和执行java代码片段。用户可以在jshell会话中输入代码,并立即看到结果。
- 代码片段执行:与完整的java应用程序不同,jshell允许你执行单个代码片段,例如表达式、方法定义或类定义。这些代码片段不必包含在main方法中,也不必创建一个完整的类结构。
- 自动导入:jshell会自动导入常用的java类库,如java.lang和java.util。此外,它还支持通过/import命令手动导入其他包和类。
- 变量和方法保留:在jshell会话中定义的变量和方法会保留在会话中,可以在后续的输入中引用它们。
- 方法定义和调用:你可以在jshell中定义方法,并在后续的输入中调用这些方法。
- 命令和语法高亮:jshell支持一些特定的命令,如
/help(显示帮助信息)和/exit(退出jshell会话)。它还支持语法高亮,以提高代码的可读性。 - 错误处理和异常:如果代码片段包含错误或抛出异常,jshell会显示相应的错误消息和异常堆栈跟踪。
jshell的使用
要使用jshell,只需在命令行中输入jshell并按回车键。然后,你就可以开始输入java代码片段并查看结果了。
$ jshell feb 26, 2024 2:30:09 pm java.util.prefs.filesystempreferences$1 run info: created user preferences directory. | welcome to jshell -- version 18.0.1.1 | for an introduction type: /help intro
查询帮助
正如提示那样,我们可以输入/help来获得一些帮助:
jshell> /help | type a java language expression, statement, or declaration. | or type one of the following commands: | /list [<name or id>|-all|-start] | list the source you have typed | /edit <name or id> | edit a source entry | /drop <name or id> | delete a source entry | /save [-all|-history|-start] <file> | save snippet source to a file | /open <file> | open a file as source input | /vars [<name or id>|-all|-start] | list the declared variables and their values | /methods [<name or id>|-all|-start] | list the declared methods and their signatures | /types [<name or id>|-all|-start] | list the type declarations | /imports | list the imported items | /exit [<integer-expression-snippet>] | exit the jshell tool | /env [-class-path <path>] [-module-path <path>] [-add-modules <modules>] ... | view or change the evaluation context | /reset [-class-path <path>] [-module-path <path>] [-add-modules <modules>]... | reset the jshell tool | /reload [-restore] [-quiet] [-class-path <path>] [-module-path <path>]... | reset and replay relevant history -- current or previous (-restore) | /history [-all] | history of what you have typed | /help [<command>|<subject>] | get information about using the jshell tool | /set editor|start|feedback|mode|prompt|truncation|format ... | set configuration information | /? [<command>|<subject>] | get information about using the jshell tool | /! | rerun last snippet -- see /help rerun | /<id> | rerun snippets by id or id range -- see /help rerun | /-<n> | rerun n-th previous snippet -- see /help rerun | | for more information type '/help' followed by the name of a | command or a subject. | for example '/help /list' or '/help intro'. | | subjects: | | intro | an introduction to the jshell tool | keys | a description of readline-like input editing | id | a description of snippet ids and how use them | shortcuts | a description of keystrokes for snippet and command completion, | information access, and automatic code generation | context | a description of the evaluation context options for /env /reload and /reset | rerun | a description of ways to re-evaluate previously entered snippets
注意:千万不要省略开头的反斜杠
/。
如果要查看某个具体的命令的帮助信息,可以输入/help [command]来获得。
比如/help intro获取工具简介:
jshell> /help intro | | intro | ===== | | the jshell tool allows you to execute java code, getting immediate results. | you can enter a java definition (variable, method, class, etc), like: int x = 8 | or a java expression, like: x + x | or a java statement or import. | these little chunks of java code are called 'snippets'. | | there are also the jshell tool commands that allow you to understand and | control what you are doing, like: /list | | for a list of commands: /help
比如/help /list查询/list命令的使用:
jshell> /help /list | | /list | ===== | | show the snippets, prefaced with their snippet ids. | | /list | list the currently active snippets of code that you typed or read with /open | | /list -start | list the evaluated startup snippets | | /list -all | list all snippets including failed, overwritten, dropped, and startup | | /list <name> | list snippets with the specified name (preference for active snippets) | | /list <id> | list the snippet with the specified snippet id. | one or more ids or id ranges may used, see '/help id'
查看jshell默认导入哪些包
我们可以使用/imports命令查看jshell默认导入了哪些包:
jshell> /imports | import java.io.* | import java.math.* | import java.net.* | import java.nio.file.* | import java.util.* | import java.util.concurrent.* | import java.util.function.* | import java.util.prefs.* | import java.util.regex.* | import java.util.stream.*
使用jshell import命令导入某个包或文件
我们可以使用import命令导入某个类或包,就像我们代码中使用的那样:
jshell> import java.time.* jshell> /import | import java.io.* | import java.math.* | import java.net.* | import java.nio.file.* | import java.util.* | import java.util.concurrent.* | import java.util.function.* | import java.util.prefs.* | import java.util.regex.* | import java.util.stream.* | import java.time.*
导入外部jar
我们可以使用/env命令将第三方的jar添加到class-path中,这样就可以使用import命令导入第三方的类了:
jshell> /env -class-path /root/hutool-all-5.8.12.jar
| setting new options and restoring state.
jshell> import cn.hutool.core.util.*
jshell> strutil.isblankifstr("abc")
$2 ==> false使用jshell进行一些简单的数学运算
jshell默认支持一些简单的数学运算符,例如:
jshell> 5 * 6 $2 ==> 30 jshell> $2 $2 ==> 30 jshell> 10 * $2 $4 ==> 300 jshell> int a = $4 a ==> 300 jshell> a a ==> 300
可以看到,jshell会将每一此执行的结果保存到一个以$开始的变量中,而后面,我们就可以对这些变量进行引用。
jshell中默认的上下文
可以在jshell中使用我们平时在java中使用的类和方法来获取当前的运行上下文。
获取当前的执行线程:
jshell> thread.currentthread() $7 ==> thread[main,5,main]
在jshell中定义一些方法
因为内部方法和内部类的关系,我们还可以在jshell中定义一个方法。
在一行内定义:
jshell> int add(int a, int b) { return a + b;}
| created method add(int,int)
jshell> add(3,4)
$10 ==> 7在多行定义:
jshell> int sub(int a, int b) {
...> return a - b;
...> }
| created method sub(int,int)
jshell> sub(10, 5)
$12 ==> 5退出jshell
如果要退出jshell,只能输入/exit命令:
jshell> /exit | goodbye
输入exit或按下ctrl+c键是没有任何效果的:
jshell> exit | error: | cannot find symbol | symbol: variable exit | exit | ^--^
到此这篇关于java9新特性之命令行交互式解释器jshell的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关java解释器jshell内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论