方案核心思路
- 写入请求队列:使用
concurrentqueue接收来自任意线程的写入请求。 - 专用写入线程:由独立线程处理队列中的写入操作,确保顺序执行。
- 双信号机制:通过
manualreseteventslim控制读取线程的暂停与恢复。 - 线程安全确认:确保多个线程同时触发写入时,不会导致竞态条件。
完整代码实现
using system;
using system.collections.concurrent;
using system.threading;
public class crossthreadreadwritecontroller
{
// 控制读取线程暂停和恢复的信号
private readonly manualreseteventslim _pauserequest = new manualreseteventslim(false);
// 读取线程确认已暂停的信号
private readonly manualreseteventslim _pausedconfirmed = new manualreseteventslim(false);
// 写入请求队列(线程安全)
private readonly concurrentqueue<action> _writequeue = new concurrentqueue<action>();
// 停止标志
private volatile bool _stoprequested = false;
// 写入专用线程
private thread _writethread;
public crossthreadreadwritecontroller()
{
// 启动写入专用线程
_writethread = new thread(processwritequeue);
_writethread.start();
}
// 读取线程的循环任务
public void readloop()
{
while (!_stoprequested)
{
// 检查是否需要暂停
if (_pauserequest.isset)
{
// 确认已暂停,并等待恢复信号
_pausedconfirmed.set();
_pauserequest.wait();
_pausedconfirmed.reset();
}
// 模拟读取操作
console.writeline($"[read] {datetime.now:hh:mm:ss.fff} - reading data...");
thread.sleep(1000); // 模拟耗时操作
}
console.writeline("[read] thread stopped.");
}
// 处理写入队列的专用线程
private void processwritequeue()
{
while (!_stoprequested || !_writequeue.isempty)
{
if (_writequeue.trydequeue(out var writeaction))
{
// 触发暂停读取线程
requestpause();
// 执行写入操作
writeaction.invoke();
// 恢复读取线程
resumeread();
}
else
{
thread.sleep(50); // 队列为空时短暂休眠
}
}
console.writeline("[write] thread stopped.");
}
// 跨线程提交写入请求
public void submitwritecommand(action writeaction)
{
_writequeue.enqueue(writeaction);
}
// 请求暂停读取线程(线程安全)
private void requestpause()
{
_pauserequest.set();
_pausedconfirmed.wait(); // 等待读取线程确认暂停
}
// 恢复读取线程(线程安全)
private void resumeread()
{
_pauserequest.reset();
}
// 停止所有线程
public void stop()
{
_stoprequested = true;
_pauserequest.set(); // 确保读取线程退出等待
_writethread.join(); // 等待写入线程结束
}
}
// 使用示例
public class program
{
public static void main()
{
var controller = new crossthreadreadwritecontroller();
// 启动读取线程
var readthread = new thread(controller.readloop);
readthread.start();
// 模拟多个线程触发写入操作
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
var threadid = i;
new thread(() =>
{
controller.submitwritecommand(() =>
{
console.writeline($"[write-{threadid}] {datetime.now:hh:mm:ss.fff} - writing data...");
thread.sleep(500); // 模拟耗时操作
});
}).start();
}
thread.sleep(5000); // 等待所有写入完成
controller.stop();
readthread.join();
console.writeline("main thread exited.");
}
}关键改进解析
1.跨线程写入请求的提交
通过 submitwritecommand 方法,任何线程均可提交写入操作:
public void submitwritecommand(action writeaction)
{
_writequeue.enqueue(writeaction); // 线程安全入队
}2.专用写入线程处理队列
写入操作由独立线程顺序处理,避免多线程并发写入冲突:
private void processwritequeue()
{
while (!_stoprequested || !_writequeue.isempty)
{
if (_writequeue.trydequeue(out var writeaction))
{
requestpause(); // 暂停读取线程
writeaction(); // 执行写入
resumeread(); // 恢复读取线程
}
}
}3.双重信号确保原子性
通过 requestpause 和 resumeread 方法封装暂停与恢复逻辑:
private void requestpause()
{
_pauserequest.set(); // 发送暂停信号
_pausedconfirmed.wait(); // 阻塞等待读取线程确认暂停
}4.线程安全停止机制
通过 _stoprequested 标志和队列检查确保安全退出:
public void stop()
{
_stoprequested = true;
_writethread.join(); // 等待写入线程处理完队列
}运行效果
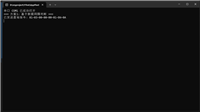
[read] 14:30:01.123 - reading data...
[read] 14:30:02.124 - reading data...
[write-0] 14:30:03.125 - writing data...
[read] 14:30:03.626 - reading data...
[write-1] 14:30:04.127 - writing data...
[read] 14:30:04.628 - reading data...
[write-2] 14:30:05.129 - writing data...
main thread exited.
方案优势
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 多线程安全 | 通过 concurrentqueue 和信号量,支持任意线程触发写入操作。 |
| 顺序执行 | 写入操作由专用线程顺序处理,避免并发冲突。 |
| 无锁读取 | 读取线程在非写入状态下完全无锁,最大化性能。 |
| 精准控制 | 通过双信号机制确保写入操作执行期间读取线程完全暂停。 |
适用场景
- 分布式任务调度:多个工作线程提交写入请求,由中心线程处理。
- 实时数据采集:采集线程持续读取数据,外部线程动态更新配置。
- 高并发服务:如网络服务器,处理来自不同客户端的并发更新操作。
注意事项
- 队列积压风险:若写入操作频率过高,需监控队列长度或添加背压机制。
- 异常处理:在写入操作中需捕获异常,避免导致写入线程崩溃。
- 性能调优:可根据场景调整
thread.sleep时间或使用无等待策略。
到此这篇关于c#中实现跨线程写入的示例代码的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c# 跨线程写入内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!






发表评论